Get started with CMake Tools on Linux
CMake is an open-source, cross-platform tool that uses compiler and platform independent configuration files to generate native build tool files specific to your compiler and platform.
The CMake Tools extension integrates Visual Studio Code and CMake to make it easy to configure, build, and debug your C++ project.
In this tutorial, you'll use the CMake Tools extension for Visual Studio Code to configure, build, and debug a simple C++ CMake project on Linux. Aside from installing CMake, your compiler, debugger, and build tools, the steps in this tutorial apply generally to how you'd use CMake on other platforms, like Windows.
If you have any trouble, please file an issue for this tutorial in theVS Code documentation repository.Also, for more information about CMake Tools in general, seeCMake Tools for Visual Studio Code documentation
Prerequisites
To complete this tutorial on Ubuntu, install the following:
-
C++ extension for VS Code.Install the C/C++ extension by searching for 'c++' in theExtensionsview (⇧⌘X(Windows, LinuxCtrl+Shift+X)).

-
CMake Tools extension for VS Code.Install the CMake Tools extension by searching for 'CMake tools' in theExtensionsview (⇧⌘X(Windows, LinuxCtrl+Shift+X)).
-
You'll also need to install CMake, a compiler, a debugger, and build tools.
Video: What is a build system? How do you add CMake to your project?
Watch this video to understand when a build system will help you and how to set up CMake for your project, or follow the steps in the following sections.
Ensure that CMake is installed
The VS Code CMake Tools extension does its work by using CMake installed on your system. For best results, use CMake version 3.27 or greater.
See if CMake is already installed on your system. Open a Terminal window and enter the following command:
cmake --version
To install CMake, or to get a later version if you don't at least have version 3.27, see the instructions for your platform atKitware APT Repository.Install version 3.27 or greater.
Ensure that development tools are installed
Although you'll use VS Code to edit your source code, you'll compile and debug the source code using the compiler, debugger, and build tools (such asmake) installed on your system.
For this tutorial on Ubuntu, we'll use the GCC compiler, GDB to debug, andmaketo build the project. These tools are not installed by default on Ubuntu, so you need to install them. Fortunately, that's easy.
Check if GCC is installed
To see if GCC is already installed on your system, open a Terminal window and enter the following command:
gcc -v
If GCC isn't installed, run the following command from the Terminal window to update the Ubuntu package lists. An out-of-date Linux distribution can interfere with getting the latest packages.
sudo apt-get update
Next, install the GNU compiler,make,and the GDB debugger with this command:
sudo apt-get install build-essential gdb
Create a CMake project
If you do not have an existing CMake project, follow the steps inCreate a CMake project.
If you already have an existing CMake project that has aCMakeLists.txtfile in the root directory, continue toConfigure Hello Worldto configure your project.
Configure Hello World
Before you can use the CMake Tools extension to build a project, you need to configure it to know about the compilers on your system. There are two ways to configure CMake in VS Code:
- Use CMake Presets (recommended)
- Use CMake Kits/Variants
Configure using CMake Presets
We recommend using CMake Presets for managing your CMake configurations. CMake Presets enable you to specify a common JSON file, where you store all the configurations for your project. You can then share this file with others, across different IDEs, and across different operating systems.
If you created a project by following the step inCreate a CMake project,your project is configured to use CMake Presets.
If your project has aCMakePresets.jsonfile, you can use the Configure and Build presets for specifying how to build your project on your machine.
You can view the active configuration of presets in the Project Status in the CMake Tools view under theConfigureandBuildnode. You can select these nodes at any time to set or change your Configure and Build presets.
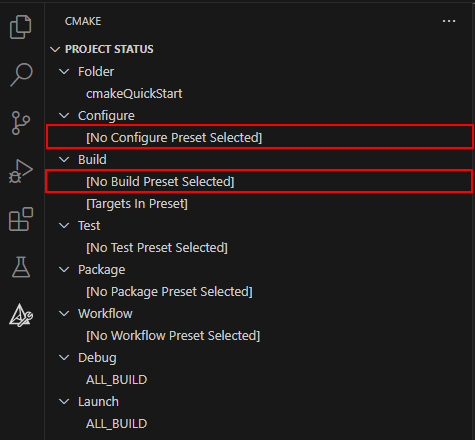
You can also set any of your presets by running theCMake: Select Configure PresetorCMake: Select Build Presetcommands in the Command Palette (⇧⌘P(Windows, LinuxCtrl+Shift+P)).

Configure using CMake Kits
If your project does not have aCMakePresets.jsonfile, you need to use kits. A kit represents a toolchain, which is the compiler, linker, and other tools used to build your project.
To scan for kits:
-
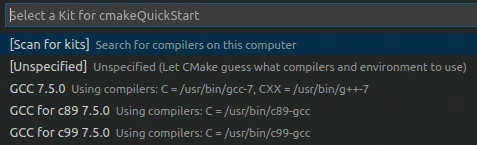
Open the Command Palette (⇧⌘P(Windows, LinuxCtrl+Shift+P)) and runCMake: Select a Kit.The extension automatically scans for kits on your computer and creates a list of compilers found on your system.
-
Select the compiler you want to use. For example, depending on the compilers you have installed, you might see something like:
The kit you selected previously is now shown in theProject Statussection in the CMake Tools view.
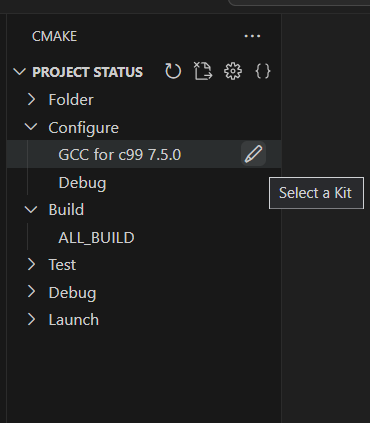
To change the kit, you can select the kit in theProject Statussection in the CMake Tools view, or run theCMake: Select a Kitcommand again from the Command Palette. If you don't see the compiler you're looking for, you can edit thecmake-tools-kits.jsonfile in your project. To edit the file, open the Command Palette (⇧⌘P(Windows, LinuxCtrl+Shift+P)) and run theCMake: Edit User-Local CMake Kitscommand.
Then, you'll need to select a variant.
A variant contains instructions for how to build your project. By default, the CMake Tools extension provides four variants, each corresponding to a default build type:Debug,Release,MinRelSize,andRelWithDebInfo.These options do the following:
Debug:disables optimizations and includes debug info.
Release:Includes optimizations but no debug info.
MinRelSize:Optimizes for size. No debug info.
RelWithDebInfo:Optimizes for speed and includes debug info.
To select a variant, open the Command Palette (⇧⌘P(Windows, LinuxCtrl+Shift+P)) run theCMake: Select Variantcommand.
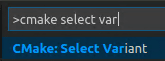
SelectDebugto include debug information with your build.
The selected variant will appear in the Status bar next to the active kit.
CMake: Configure
Now that you've selected your configuration settings via presets or kits/variants, open the Command Palette (⇧⌘P(Windows, LinuxCtrl+Shift+P)) and run theCMake: Configurecommand to configure your project. This generates build files in the project's build folder using the configurations you selected.
Build hello world
After configuring your project, you're ready to build. Open the Command Palette (⇧⌘P(Windows, LinuxCtrl+Shift+P)) and run theCMake: Buildcommand, or select theBuildbutton from the status bar.
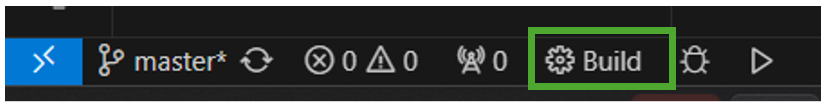
You can select which targets you'd like to build by selectingCMake: Set Build Targetfrom the Command Palette. By default, CMake Tools builds all targets. The selected target will appear in theProject Statusview in the CMake Tools sidebar underneath theBuildnode and can be set from there as well.

Debug hello world
To run and debug your project, openmain.cppand put a breakpoint on thestd::coutline.
Then open the Command Palette (⇧⌘P(Windows, LinuxCtrl+Shift+P)) and runCMake: Debug.The debugger will stop on thestd::coutline:
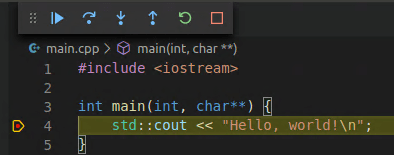
Go ahead and pressF5to continue.
You've now used the VS Code CMake Tools extension to use CMake to build and debug a C++ app on Ubuntu. The steps are the same for other platforms; the difference being how you install CMake and the compiler/debugger for the platform of your choice. For instructions on setting up compilers/debuggers for other platforms, see the following:
Next steps
- Explore theCMake Toolsdocumentation
- Review theOverview of the C++ extension