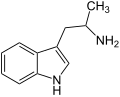
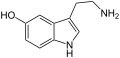
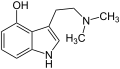
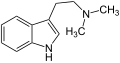
Tryptamine
(Weitergeleitet von5-MeO-NMT)
Tryptaminesindchemische Verbindungen,die vom2-(Indol-3-yl)ethylaminabgeleitet sind. Sie sindStoffwechselproduktezahlreicher Lebewesen (vor allem Pflanzen) und zählen zu denIndolalkaloiden.ProminenteDerivatemit Tryptamin-Struktur sind dieNeurotransmitterSerotoninundMelatonin,dieAminosäureTryptophanund diepsychedelischwirksamenHalluzinogeneDimethyltryptaminundPsilocybinsowiePsilocin.
Die wesentlichen Strukturmerkmale von Tryptaminen undPhenylethylaminenfinden sich in denLysergsäureamidenvereint.[1]
Tabellarische Übersicht
[Bearbeiten|Quelltext bearbeiten]
| |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | R4 | R5 | Rα | RN1 | RN2 | chemischer Name | Herkunft |
| Tryptamin | H | H | H | H | H | 2-(Indol-3-yl)ethylamin | natürlich |
| N-Methyltryptamin (NMT) | H | H | H | H | CH3 | N-Methyltryptamin | natürlich |
| 5-Methoxy-N-methyltryptamin (5-MeO-NMT) | H | OCH3 | H | H | CH3 | 5-Methoxy-N-methyltryptamin | natürlich |
| Dimethyltryptamin | H | H | H | CH3 | CH3 | N,N-Dimethyltryptamin | natürlich |
| O-Methylbufotenin (5-MeO-DMT) | H | OCH3 | H | CH3 | CH3 | 5-Methoxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamin | natürlich |
| 5-Brom-N,N-dimethyltryptamin (5-Brom-DMT) | H | Br | H | CH3 | CH3 | 5-Brom-N,N-dimethyltryptamin | natürlich |
| Bufotenin | H | OH | H | CH3 | CH3 | 5-Hydroxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamin | natürlich |
| N-Methylserotonin | H | OH | H | CH3 | H | 5-Hydroxy-N-methyltryptamin | natürlich |
| Serotonin | H | OH | H | H | H | 5-Hydroxytryptamin | natürlich |
| Psilocin | OH | H | H | CH3 | CH3 | 4-Hydroxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamin | natürlich |
| Psilocybin | OPO3H2 | H | H | CH3 | CH3 | 4-Phosphoryloxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamin | natürlich |
| Baeocystin | OPO3H2 | H | H | CH3 | H | 4-Phosphoryloxy-N-methyltryptamin | natürlich |
| Norbaeocystin | OPO3H2 | H | H | H | H | 4-Phosphoryloxytryptamin | natürlich |
| Melatonin | H | OCH3 | H | O=C-CH3 | H | 5-Methoxy-N-acetyltryptamin | natürlich |
| Tryptophan | H | H | COOH | H | H | α-Carboxytryptamin | natürlich |

| |||||||
| Name | R4 | R5 | Rα | RN1 | RN2 | chemischer Name | Herkunft |
| Alpha-Methyltryptamin (AMT) | H | H | CH3 | H | H | α-Methyltryptamin | synthetisch |
| 5-Methoxy-α-methyltryptamin (5-MeO-AMT) | H | OCH3 | CH3 | H | H | 5-Methoxy-α-methyltryptamin | synthetisch |
| α-Ethyltryptamin (AET) | H | H | CH2CH3 | H | H | α-Ethyltryptamin | synthetisch |
| N-Ethyltryptamin (NET) | H | H | H | H | CH2CH3 | N-Ethyltryptamin | synthetisch |
| Diethyltryptamin(DET) | H | H | H | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | N,N-Diethyltryptamin | synthetisch |
| Diisopropyltryptamin(DiPT) | H | H | H | CH(CH3)2 | CH(CH3)2 | N,N-Diisopropyltryptamin | synthetisch |
| Dipropyltryptamin(DPT) | H | H | H | CH2CH2CH3 | CH2CH2CH3 | N,N-Dipropyltryptamin | synthetisch |
| Dibutyltryptamin(DBT) | H | H | H | CH2CH2CH2CH3 | CH2CH2CH2CH3 | N,N-Dibutyltryptamin | synthetisch |
| 4-Hydroxy-N-methyl-N-ethyltryptamin (4-HO-MET) | OH | H | H | CH3 | CH2CH3 | 4-Hydroxy-N-methyl-N-ethyltryptamin | synthetisch |
| 4-Hydroxy-N,N-diethyltryptamin (4-HO-DET) | OH | H | H | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | 4-Hydroxy-N,N-diethyltryptamin | synthetisch |
| 4-Phosphoryloxy-N,N-diethyltryptamin (4-PO-DET) | OPO3H2 | H | H | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | 4-Phosphoryloxy-N,N-diethyltryptamin | synthetisch |
| 4-Hydroxy-N,N-diisopropyltryptamin (4-HO-DIPT) | OH | H | H | CH(CH3)2 | CH(CH3)2 | 4-Hydroxy-N,N-diisopropyltryptamin | synthetisch |
| 4-Hydroxy-N-isopropyl-N-methyltryptamin (4-HO-MiPT) | OH | H | H | CH(CH3)2 | CH3 | 4-Hydroxy-N-isopropyl-N-methyltryptamin | synthetisch |
| 5-Methoxy-N,N-diallyltryptamin (5-MeO-DALT) | H | OCH3 | H | H2C=CH-CH2 | H2C=CH-CH2 | 5-Methoxy-N,N-diallyltryptamin | synthetisch |
| 5-Methoxy-N,N-diisopropyltryptamin (5-MeO-DiPT) | H | OCH3 | H | CH(CH3)2 | CH(CH3)2 | 5-Methoxy-N,N-diisopropyltryptamin | synthetisch |
| 5-Methoxy-N,N-methylisopropyltryptamin (5-MeO-MiPT) | H | OCH3 | H | CH3 | CH(CH3)2 | 5-Methoxy-N,N-methylisopropyltryptamin | synthetisch |
| Sumatriptan | H | CH2SO2NHCH3 | H | CH3 | CH3 | 5-Methylaminosulfonyl-N,N-dimethyltryptamin | synthetisch |
Synthese
[Bearbeiten|Quelltext bearbeiten]Tryptamin kann durch das Abramovitch-Shapiro-Syntheseverfahren hergestellt werden.[2]

Grafische Übersicht
[Bearbeiten|Quelltext bearbeiten]Übersicht über eine kleine Auswahl an endogenen, natürlichen und synthetischen Tryptaminen.
Körpereigene, pflanzliche und synthetische Tryptamine
[Bearbeiten|Quelltext bearbeiten]-
α-Methyltryptamin
-
α-Ethyltryptamin
-
Serotonin (5-Hydroxytryptamin)
-
N-Methyltryptamin
-
N-Ethyltryptamin
-
Psilocin
-
Dimethyltryptamin (N,N-Dimethyltryptamin)
-
Diethyltryptamin (N,N-Diethyltryptamin)
-
L-Tryptophan (natürliche Aminosäure)
-
Melatonin
-
MiPT
-
DiPT
Literatur
[Bearbeiten|Quelltext bearbeiten]- Alexander Shulgin,Ann Shulgin:TiHKAL:The Continuation.Transform Press, Berkeley 1997,ISBN 0-9630096-9-9.
- Keeper of the Trout & Friends:Some Simple Tryptamines (Second Edition).Mydriatic Productions, 2007,ISBN 978-0-9770876-5-5.
- Ana Margarida Araújo, Félix Carvalho u. a.:The hallucinogenic world of tryptamines: an updated review.In:Archives of Toxicology.89, 2015, S. 1151,doi:10.1007/s00204-015-1513-x.
Einzelnachweise
[Bearbeiten|Quelltext bearbeiten]- ↑Fabrizio Schifano, Laura Orsolini, Duccio Papanti, John Corkery:NPS: Medical Consequences Associated with Their Intake.In: Michael H. Baumann, Richard A. Glennon, Jenny L. Wiley:Neuropharmacology of New Psychoactive Substances (NPS).Springer, E-Book 2016,ISBN 978-3-319-52444-3,S. 364.
- ↑R. A. Abramovitch, D. Shapiro:880. Tryptamines, carbolines, and related compounds. Part II. A convenient synthesis of tryptamines and β-carbolines.In:Journal of the Chemical Society (Resumed).1956, S. 4589,doi:10.1039/JR9560004589.