Each running virtual device provides a console that lets you query and control the emulated device environment. For example, you can use the console to manage port redirection, network characteristics, and telephony events while your app is running on the emulator.
The following commands require that you already have an emulator running. For more information about running an emulator, see Run apps on the Android Emulatorand Start the emulator from the command line.
Start and stop a console session
To access the console and enter commands from a terminal window, usetelnetto
connect to the console port and provide your authentication token. Each time the console displays
OK,it's ready to accept commands. There isn't a typical prompt.
To connect to the console of a running virtual device:
- Open a terminal window and enter the following command:
- After the console displays
OK,enter theauth auth_tokencommand. - After you're connected to the console, enterconsole commands.
- To exit the console session, enter
quitorexit.
telnet localhostconsole-port
The emulator window title lists the console port number when running in a separate window but
not when running in a tool window. For example, the window title for an emulator using console port 5554
could bePixel8_API_34:5554.Also, theadb devicescommand prints a
list of running virtual devices and their console port numbers. For more information, see
Query for devices.
Note:The emulator listens for connections on ports 5554 to 5585
and accepts connections fromlocalhostonly.
Before you can enterconsole commands,the emulator console
requires authentication.auth_tokenmust
match the contents of the.emulator_console_auth_tokenfile in your home directory.
If that file doesn't exist, thetelnet localhostconsole-port
command creates the file, which contains a randomly generated authentication token. To disable
authentication, delete the token from the
.emulator_console_auth_tokenfile or create an empty file if it doesn't exist.
Enterhelp,helpcommand,orhelp-verbose
to see a list of console commands and learn about specific
commands.
Here's an example session:
$telnet localhost 5554 Trying::1... telnet: connect to address::1: Connection refused Trying 127.0.0.1... Connected to localhost. Escape character is '^]'. Android Console: Authentication required Android Console: type 'auth <auth_token>' to authenticate Android Console: you can find your <auth_token> in '/Users/me/.emulator_console_auth_token' OK auth 123456789ABCdefZ Android Console: type 'help' for a list of commands OK help-verbose Android console command help: help|h|? Prints a list of commands help-verbose Prints a list of commands with descriptions ping Checks if the emulator is alive automation Manages emulator automation event Simulates hardware events geo Geo-location commands gsm GSM related commands cdma CDMA related commands crash Crashes the emulator instance crash-on-exit Simulates crash on exit for the emulator instance kill Terminates the emulator instance restart Restarts the emulator instance network Manages network settings power Power related commands quit|exit Quits control session redir Manages port redirections sms SMS related commands avd Controls virtual device execution qemu QEMU-specific commands sensor Manages emulator sensors physics Manages physical model finger Manages emulator finger print debug Controls the emulator debug output tags rotate Rotates the screen clockwise by 90 degrees screenrecord Records the emulator's display fold Folds the device unfold Unfolds the device multidisplay Configures the multi-display nodraw turn on/off NoDraw mode. (experimental) resize-display resize the display resolution to the preset size virtualscene-image customize virtualscene image for virtulscene camera proxy manage network proxy server settings phonenumber set phone number for the device try 'help <command>' for command-specific help OK exit Connection closed by foreign host.
Emulator command reference
The following table describes the emulator console commands with their parameters and values:
Table 1.Emulator console commands
| General commands | Description |
|---|---|
avd {stop|start|status|name}
|
Queries, controls, and manages the virtual device, as follows:
|
avd snapshot {list|savename|loadname|delete
name}
|
Saves and restores the device state in snapshots, as follows:
The following example saves a snapshot with the name
avd snapshot save firstactivitysnapshot |
fold
|
Folds the device to display its smaller screen configuration, if the device is foldable and currently unfolded. |
unfold
|
Unfolds the device to display its larger screen configuration, if the device is foldable and currently folded. |
kill
|
Terminates the virtual device. |
ping
|
Checks whether the virtual device is running. |
rotate
|
Rotates the AVD counterclockwise in 45 degree increments. |
| Crash the emulator | Description |
crash
|
Crashes the emulator during app execution. |
crash-on-exit |
Crashes the emulator when the app exits. |
| Debug tags | Description |
debugtags...
|
Enables or disables debug messages from specific parts of the emulator.
Thetagsparameter must be a value from the list of debug tags that appears when
you execute
The following example enables the debug radio |
| Port redirection | Description |
redir list
|
Lists the current port redirection. |
redir addprotocol:host-port:guest-port
|
Adds a new port redirection, as follows:
|
redir delprotocol:host-port
|
Deletes a port redirection.
|
| Geographic location | Description |
|
Sets the geographic location reported to the apps running inside an emulator by sending a GPS fix to the emulator. You can issue one of the following |
|
geo fixlongitude latitude [altitude] [satellites] [velocity]
|
Sends a simple GPS fix to the emulator.
Specifylongitudeandlatitude
in decimal degrees. Use a number from 1 to 12 to specify the number of
satellitesto use to determine the position,
and specifyaltitudein meters and
velocityin knots.
|
geo nmeasentence
|
Sends an NMEA 0183 sentence to the emulated device as if it were sent from an emulated
GPS modem. Startsentencewith '$GP'.
Only '$GPGGA' and '$GPRCM' sentences are currently supported. The following example
is a GPGGA (Global Positioning System Fix Data) sentence that gets the
time, position, and fix data for a GPS receiver:
geo nmea $GPGGA,hhmmss.ss,llll.ll,a,yyyyy.yy,a,x,xx,x.x,x.x,M,x.x,M,x.x,xxxx |
| Fake hardware events | Description |
event types
|
Lists all fake event types. For events that have codes, the number of codes is listed in
parentheses on the right.
event types event <type> can be an integer or one of the following aliases: EV_SYN EV_KEY (405 code aliases) EV_REL (2 code aliases) EV_ABS (27 code aliases) EV_MSC EV_SW (4 code aliases) EV_LED EV_SND EV_REP EV_FF EV_PWR EV_FF_STATUS EV_MAX OK |
event sendtypes [types...]
|
Sends one or more fake event types. |
event codestype
|
Lists the event codes for the specified fake event type. |
event sendtype[:code]:[value] [...]
|
Sends one or more fake events with optional codes and code values.
To discover exactly which event to send, you can use the These are the events generated when you press the power button: adb shell getevent -lt /dev/input/event12: EV_KEY KEY_POWER DOWN /dev/input/event12: EV_SYN SYN_REPORT 00000000 /dev/input/event12: EV_KEY KEY_POWER UP /dev/input/event12: EV_SYN SYN_REPORT 00000000For example, to simulate a long press of the power button, send two EV_KEYevents for keydown and keyup:
event send EV_KEY:KEY_POWER:0 OK event send EV_KEY:KEY_POWER:1 OK |
event textmessage
|
Sends a string of characters that simulate keypresses. The message must be a UTF-8 string. Unicode posts are reverse-mapped according to the current device keyboard, and unsupported characters are discarded silently. |
| Power state controls | Description |
power display
|
Displays battery and charger state. |
power ac {on|off}
|
Sets AC charging state toonoroff.
|
power status {unknown|charging|discharging|not-charging|full}
|
Changes battery status as specified. |
power present {true|false}
|
Sets battery presence state. |
power health {unknown|good|overheat|dead|overvoltage|failure}
|
Sets battery health state. |
power capacitypercent
|
Sets remaining battery capacity state as a percent from 0 to 100. |
| Network connection status | Description |
network status
|
Checks the network status and current delay and speed characteristics. |
network delaylatency
|
Changes the emulated network latency. The emulator lets you simulate various network latency levels so that you can test your app in an environment more typical of actual running conditions. You can set a latency level or range at emulator startup, or you can use the console to change the latency while the app is running in the emulator. The format of networklatencyis one of the following (numbers are milliseconds): Network latency format:
To set latency at emulator startup, use the emulator -netdelay gprs emulator -netdelay 40,100 To make changes to network delay while the emulator is running, connect to the console and use
the network delay gprs network delay 40 100 |
network speedspeed |
The emulator lets you simulate various network transfer rates.
You can set a transfer rate or range at emulator startup, or you can use the console to change the rate while the app is running in the emulator. The format of network Network speed format:
To set the network speed at emulator startup, use the emulator -netspeed gsm @Pixel_API_26 emulator -netspeed 14.4,80 @Pixel_API_26 To make changes to network speed while the emulator is running, connect to the console
and use the network speed 14.4 80 |
network capture {start|stop}file |
Sends packets to a file. The following list describes the parameters and
parameter values:
|
| Telephony emulation | Description |
| The Android emulator includes its own GSM and CDMA emulated modems that let you simulate telephony functions in the emulator. For example, with GSM you can simulate inbound phone calls and establish and terminate data connections. With CDMA, you provide a subscription source and the preferred roaming list. The Android system handles simulated calls exactly as it would actual calls. The emulator doesn't support call audio. | |
gsm {call|accept|cancel|busy}phonenumber
|
Thegsmparameters are the following:
|
gsm {data|voice}state
|
Thedatastatecommand changes the state of the GPRS data connection,
and thedata voicestatecommand changes the state of the GPRS voice
connection, as follows:
|
gsm hold
|
Changes the state of a call tohold.You can change a
call state toholdonly when its current state isactiveor
waiting.
|
gsm list
|
Lists all inbound and outbound calls and their states. |
gsm status
|
Reports the current GSM voice/data state. Values are those
described for thevoiceanddatacommands.
|
gsm signal {rssi|ber}
|
Changes the reported signal strength (rssi) and bit error rate (ber) on the next 15
seconds of update. The following list describes the parameters and their values:
|
gsm signal-profilenum
|
Sets the signal strength profile.
numis a number from 0 through 4.
|
cdma ssourcesource
|
Sets the current CDMA subscription source, where
sourceis a network-based allowlist that contains the
CDMA carrier's subscribers and their values, as follows:
|
cdma prl_versionversion
|
Dumps the current preferred roaming list (PRL) version. The version number is for the PRL database that contains information used during the system selection and acquisition process. |
| Manage sensors on the emulator | Description |
These commands relate to
which sensors are available in the AVD. Besides using thesensorcommand, you
can see and adjust the settings in the emulator in theVirtual sensorsscreen in
theAccelerometerandAdditional sensorstabs.
|
|
sensor status |
Lists all sensors and their status. The following is example output for the
sensor statuscommand:
|
sensor getsensor-name
|
Gets the settings forsensor-name.The following example gets the
value for the acceleration sensor:
sensor get acceleration acceleration = 2.23517e-07:9.77631:0.812348
The |
sensor setsensor-namevalue-x:value-y:value-z
|
Sets the values forsensor-name.The following example sets the
acceleration sensor to the x, y, and z values
separated by colons.
sensor set acceleration 2.23517e-07:9.77631:0.812348 |
| SMS emulation | Description |
sms sendsender-phone-numbertextmessage
|
Generates an emulated incoming SMS. The following list describes the parameters and
their values:
The following example sends the message "hi there" to the 4085555555 phone number: sms send 4085555555 hi there The console forwards the SMS message to the Android framework, which passes it to an app on the emulator that handles SMS, such as the Messages app. If you pass 10 numbers, the app formats it as a phone number. Longer or shorter numeric strings display the way you sent them.
|
| Fingerprint simulation | Description |
finger touchfingerprint-id
|
Simulates a finger touching the sensor. |
finger remove
|
Simulates finger removal.
For instructions about how to use these commands, see the following section about fingerprint simulation and validation. |
Fingerprint simulation and validation
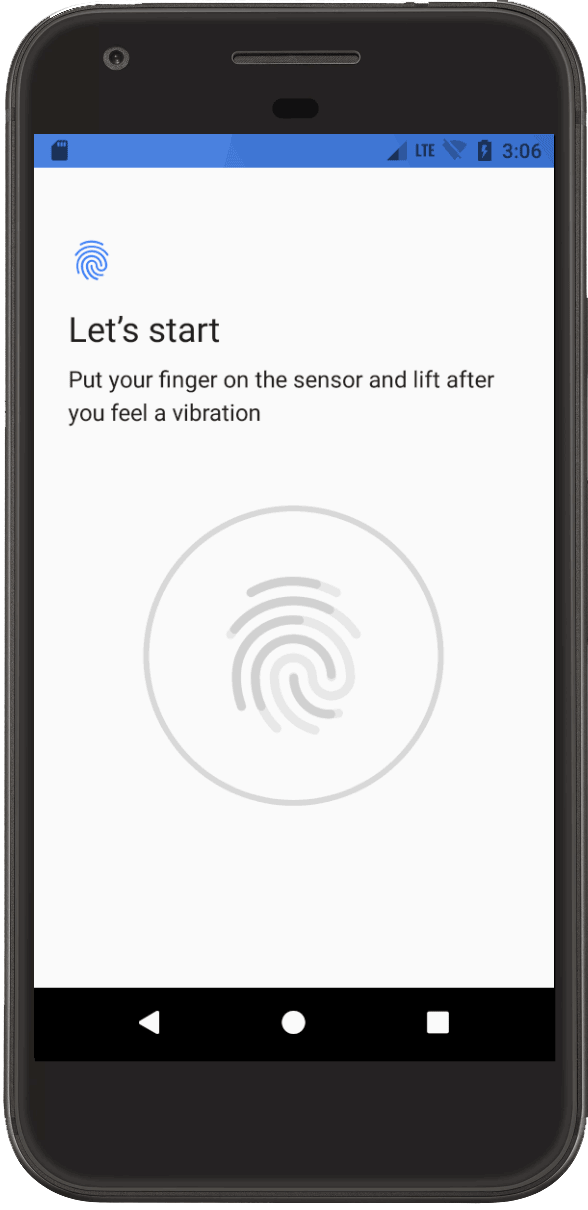
Figure 1.Fingerprint authentication screen.
Use thefingercommand to simulate and validate fingerprint authentication for your
app. You need SDK Tools 24.3 or higher and Android 6.0 (API level 23) or higher.
To simulate and validate fingerprint authentication, follow these steps:
- If you don't yet have a fingerprint ID, enroll a new fingerprint in the emulator by selectingSettings>Security>Fingerprintand following the enrollment instructions.
- Set up your app to accept fingerprint authentication.After you perform this setup, your device displays the fingerprint authentication screen.
- While your app displays the fingerprint authentication screen, go to the console and
enter the
finger touchcommand and the fingerprint ID you created. This simulates a finger touch. - Then, enter the
finger removecommand to simulate finger removal.Your app should respond as if a user touched and then removed their finger from the fingerprint sensor.
