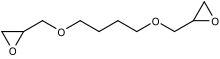
1,4-Butanediol diglycidyl ether(B14DODGE) is an organic chemical in theglycidyletherfamily. It is aliphatic and a colorless liquid. It has twoepoxide(oxirane) groups per molecule.[1]Its main use is in modifyingepoxyresins especiallyviscosityreduction.[2]
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-[4-(Oxiran-2-ylmethoxy)butoxymethyl]oxirane
| |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.017.611 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChemCID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard(EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H18O4 | |
| Molar mass | 202.250g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in theirstandard state(at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
It isREACHregistered.[3]The IUPAC name is 2-[4-(oxiran-2-ylmethoxy)butoxymethyl]oxirane.
Synthesis
edit1,4-Butanediolandepichlorohydrinare reacted in the presence of aLewis acidascatalystto form ahalohydrin:eachhydroxyl groupof the diol reacts with an epoxide on epichlorohydrin. This process is followed by washing withsodium hydroxideto re-form the epoxide rings indehydrochlorinationreaction.[4]One of the quality control tests would involve measuring theEpoxy valueby determination of the epoxy equivalent weight.
Uses
editA key use is modifying the viscosity and properties of epoxy resins[5]which may then be formulated into CASE applications:Coatings,[6]Adhesives,Sealants,Elastomers,composite materials,fillers, putties, plasters, modelling clay and semiconductors. It also has a number of medical applications.[7][8][9]The molecule is also used to synthesize other molecules.[10][11]As anEpoxymodifier it is classed as an epoxyreactive diluent.The use of the diluent does effect mechanical properties and microstructure of epoxy resins.[12][13]
Toxicity
editThe toxicity is fairly well known and understood and is rated as a severe skin and eye irritant. Contactdermatitisis also possible.[14][15][16]
References
edit- ^PubChem."1,4-Butanediol diglycidyl ether".pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.Retrieved2022-04-02.
- ^Jagtap, Ameya Rajendra; More, Aarti (2022-08-01)."Developments in reactive diluents: a review".Polymer Bulletin.79(8): 5667–5708.doi:10.1007/s00289-021-03808-5.ISSN1436-2449.S2CID235678040.
- ^"Substance Information - ECHA".echa.europa.eu.Retrieved2022-04-02.
- ^Crivello, James V. (2006)."Design and synthesis of multifunctional glycidyl ethers that undergo frontal polymerization".Journal of Polymer Science Part A: Polymer Chemistry.44(21): 6435–6448.Bibcode:2006JPoSA..44.6435C.doi:10.1002/pola.21761.ISSN0887-624X.
- ^Monte, Salvatore J. (1998), Pritchard, Geoffrey (ed.),"Diluents and viscosity modifiers for epoxy resins",Plastics Additives: An A-Z reference,Polymer Science and Technology Series, vol. 1, Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands, pp. 211–216,doi:10.1007/978-94-011-5862-6_24,ISBN978-94-011-5862-6,retrieved2022-03-29
- ^Howarth G.A "Synthesis of a legislation compliant corrosion protection coating system based on urethane, oxazolidine and waterborne epoxy technology" page 23 Master of Science Thesis April 1997 Imperial College London
- ^Ji, Gyu Yeul; Oh, Chang Hyun; Moon, Byung Gwan; Yi, Seong; Han, In Bo; Heo, Dong Hwa; Kim, Ki-Tack; Shin, Dong Ah; Kim, Keung Nyun (June 2015)."Efficacy and Safety of Sodium Hyaluronate with 1,4-Butanediol Diglycidyl Ether Compared to Sodium Carboxymethylcellulose in Preventing Adhesion Formation after Lumbar Discectomy".Korean Journal of Spine.12(2): 41–47.doi:10.14245/kjs.2015.12.2.41.ISSN1738-2262.PMC4513167.PMID26217381.
- ^Nicoletti, A.; Fiorini, M.; Paolillo, J.; Dolcini, L.; Sandri, M.; Pressato, D. (2013-01-01)."Effects of different crosslinking conditions on the chemical–physical properties of a novel bio-inspired composite scaffold stabilised with 1,4-butanediol diglycidyl ether (BDDGE)".Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine.24(1): 17–35.doi:10.1007/s10856-012-4782-4.ISSN1573-4838.PMID23053811.S2CID22093094.
- ^Fiorani, Andrea; Gualandi, Chiara; Panseri, Silvia; Montesi, Monica; Marcacci, Maurilio; Focarete, Maria Letizia; Bigi, Adriana (2014-10-01)."Comparative performance of collagen nanofibers electrospun from different solvents and stabilized by different crosslinkers".Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine.25(10): 2313–2321.doi:10.1007/s10856-014-5196-2.ISSN1573-4838.PMID24664673.S2CID5270837.
- ^Wu, Chi; Zuo, Ju; Chu, Benjamin (February 1989)."Molecular weight distribution of a branched epoxy polymer: 1,4-butanediol diglycidyl ether with cis-1,2-cyclohexanedicarboxylic anhydride".Macromolecules.22(2): 633–639.Bibcode:1989MaMol..22..633W.doi:10.1021/ma00192a021.ISSN0024-9297.
- ^Xue, Yu; Chen, Hongyue; Xu, Chao; Yu, Dinghua; Xu, Huajin; Hu, Yi (2020)."Synthesis of hyaluronic acid hydrogels by crosslinking the mixture of high-molecular-weight hyaluronic acid and low-molecular-weight hyaluronic acid with 1,4-butanediol diglycidyl ether".RSC Advances.10(12): 7206–7213.Bibcode:2020RSCAd..10.7206X.doi:10.1039/C9RA09271D.PMC9049836.PMID35493875.S2CID214083413.
- ^Khalina, Morteza; Beheshty, Mohammad Hosain; Salimi, Ali (2019-08-01)."The effect of reactive diluent on mechanical properties and microstructure of epoxy resins".Polymer Bulletin.76(8): 3905–3927.doi:10.1007/s00289-018-2577-6.ISSN1436-2449.S2CID105389177.
- ^Pastarnokienė, Liepa; Jonikaitė-Švėgždienė, Jūratė; Lapinskaitė, Neringa; Kulbokaitė, Rūta; Bočkuvienė, Alma; Kochanė, Tatjana; Makuška, Ričardas (2023-07-01)."The effect of reactive diluents on curing of epoxy resins and properties of the cured epoxy coatings".Journal of Coatings Technology and Research.20(4): 1207–1221.doi:10.1007/s11998-022-00737-4.ISSN1935-3804.S2CID256749849.
- ^"1,4-Butanediol diglycidyl ether - Hazardous Agents | Haz-Map".haz-map.com.Retrieved2022-04-02.
- ^Jolanki, Riitta; Estlander, Tuula; Kanerva, Lasse (February 1987)."Contact allergy to an epoxy reactive diluent: 1,4-butanediol diglycidyl ether".Contact Dermatitis.16(2): 87–92.doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1987.tb01385.x.PMID2952443.S2CID36846087– via Wiley online.
- ^Berdasco, Nancy Anne M.; Waechter, John M. (2012-08-17), Bingham, Eula; Cohrssen, Barbara; Powell, Charles H. (eds.),"Epoxy Compounds: Aromatic Diglycidyl Ethers, Polyglycidyl Ethers, Glycidyl Esters, and Miscellaneous Epoxy Compounds",Patty's Toxicology,Hoboken, NJ, USA: John Wiley & Sons, Inc., pp. 491–528,doi:10.1002/0471435139.tox083.pub2,ISBN978-0-471-12547-1,retrieved2022-07-28
Further reading
edit- Epoxy resin technology.Paul F. Bruins, Polytechnic Institute of Brooklyn. New York: Interscience Publishers. 1968.ISBN0-470-11390-1.OCLC182890.
{{cite book}}:CS1 maint: others (link) - Flick, Ernest W. (1993).Epoxy resins, curing agents, compounds, and modifiers: an industrial guide.Park Ridge, NJ.ISBN978-0-8155-1708-5.OCLC915134542.
{{cite book}}:CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Lee, Henry (1967).Handbook of epoxy resins.Kris Neville ([2nd, expanded work] ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill.ISBN0-07-036997-6.OCLC311631322.
- "Dow Epoxy Resins"(PDF).