Ascending cholangitis,also known asacute cholangitisor simplycholangitis,isinflammationof thebile duct,usually caused bybacteriaascending fromits junctionwith theduodenum(first part of thesmall intestine). It tends to occur if the bile duct is already partially obstructed bygallstones.[1][2]
| Ascending cholangitis | |
|---|---|
| Other names | acute cholangitis, cholangitis |
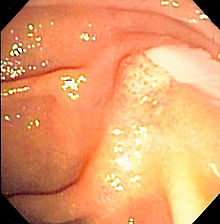 | |
| Duodenoscopy image of pus extruding from theampulla of Vater,indicative of cholangitis | |
| Specialty | Gastroenterology General surgery |
| Symptoms | jaundice,feverandabdominal pain |
Cholangitis can be life-threatening, and is regarded as amedical emergency.[1]Characteristic symptoms includeyellow discoloration of the skin or whites of the eyes,fever,abdominal pain,and in severe cases,low blood pressureandconfusion.Initial treatment is withintravenous fluidsandantibiotics,but there is often an underlying problem (such as gallstones ornarrowingin the bile duct) for which further tests and treatments may be necessary, usually in the form ofendoscopyto relieve obstruction of the bile duct.[1][3]The word is from Greekchol-, bile +ang-, vessel + -itis,inflammation.
Signs and symptoms
editA person with cholangitis may complain ofabdominal pain(particularly in theright upper quadrantof theabdomen),fever,rigors(uncontrollable shaking) and a feeling of uneasiness (malaise). Some may reportjaundice(yellow discoloration of the skin and the whites of the eyes).[1]
Physical examinationfindings typically include jaundice and right upper quadrant tenderness.[1]Charcot's triadis a set of three common findings in cholangitis: abdominal pain, jaundice, and fever.[4]This was assumed in the past to be present in 50–70% of cases, although more recently the frequency has been reported as 15–20%.[1]Reynolds' pentadincludes the findings of Charcot's triad with the presence ofseptic shockandmental confusion.[5]This combination of symptoms indicates worsening of the condition and the development ofsepsis,and is seen less commonly still.[1][2]
In the elderly, the presentation may be atypical; they may directly collapse due to sepsis without first showing typical features.[2]Those with an indwelling stent in the bile duct (see below) may not develop jaundice.[2]
Causes
editBile duct obstruction, which is usually present in acute cholangitis, is generally due togallstones.10–30% of cases, however, are due to other causes such asbenignstricturing (narrowing of the bile duct without an underlying tumor), postoperative damage or an altered structure of the bile ducts such as narrowing at the site of ananastomosis(surgical connection), various tumors (cancer of the bile duct,gallbladder cancer,cancer of theampulla of Vater,pancreatic cancer,cancer of the duodenum),anaerobic organismssuch asClostridiumandBacteroides(especially in the elderly and those who have undergone previous surgery of thebiliary system).[1]
Parasites which may infect the liver and bile ducts may cause cholangitis; these include theroundwormAscaris lumbricoidesand theliver flukesClonorchis sinensis,Opisthorchis viverriniandOpisthorchis felineus.[6]In people withAIDS,a large number of opportunistic organisms has been known to causeAIDS cholangiopathy,but the risk has rapidly diminished since the introduction ofeffective AIDS treatment.[1][7]Cholangitis may also complicate medical procedures involving the bile duct, especially ERCP. To prevent this, it is recommended that those undergoing ERCP for any indication receive prophylactic (preventative) antibiotics.[3][8]
The presence of a permanent biliary stent (e.g. in pancreatic cancer) slightly increases the risk of cholangitis, but stents of this type are often needed to keep the bile duct patent under outside pressure.[1]
Pathogenesis
editBile is produced by the liver, and serves to eliminatecholesterolandbilirubinfrom the body, as well asemulsifyingoffatsto make them more soluble in water and aid in their digestion. Bile is formed in the liver byhepatocytes(liver cells) and excreted into thecommon hepatic duct.Part of the bile is stored in thegall bladderbecause of back pressure (exerted by thesphincter of Oddi), and may be released at the time of digestion. The gallbladder also concentrates the bile by absorbing water and dissolved salts from it. All bile reaches theduodenum(first part of the small intestine) through thecommon bile ductand theampulla of Vater.The sphincter of Oddi, located at the junction of the ampulla of Vater and the duodenum, is a circular muscle that controls the release of both bile andpancreaticsecretionsinto the digestive tract.[1]
The biliary tree is normally relatively free of bacteria because of certain protective mechanisms. The sphincter of Oddi acts as a mechanical barrier. The biliary system normally has low pressure (8 to 12cmH2O)[9]and allows bile to flow freely through. The continuous forward flow of the bile in the duct flushes bacteria, if present, into the duodenum, and does not allow the establishment of an infection. The constitution of bile—bile salts[1]andimmunoglobulin[2]secreted by theepitheliumof the bile duct also has a protective role.
Bacterial contamination alone in absence of obstruction does not usually result in cholangitis.[2]However increased pressure within the biliary system (above 20 cmH2O)[10]resulting from obstruction in the bile duct widens spaces between the cells lining the duct, bringing bacterially contaminated bile in contact with the blood stream. It also adversely affects the function ofKupffer cells,which are specializedmacrophagecells that assist in preventing bacteria from entering the biliary system. Finally, increased biliary pressure decreases production ofIgAimmunoglobulins in the bile.[11]This results inbacteremia(bacteria in the blood stream) and gives rise to thesystemic inflammatory response syndrome(SIRS) comprising fever (often withrigors),tachycardia,increasedrespiratory rateand increased white blood cell count; SIRS in the presence of suspected or confirmed infection is calledsepsis.[1]Biliary obstruction itself disadvantages theimmune systemand impairs its capability to fight infection, by impairing the function of certain immune system cells (neutrophil granulocytes) and modifying the levels of immune hormones (cytokines).[1]
In ascending cholangitis, it is assumed that organisms migrate backwards up the bile duct as a result of partial obstruction and decreased function of the sphincter of Oddi.[1]Other theories about the origin of the bacteria, such as through theportal veinor transmigration from thecolon,are considered less likely.[1]
Diagnosis
editBlood tests
editRoutineblood testsshow features of acute inflammation (raisedwhite blood cellcount and elevatedC-reactive proteinlevel), and usually abnormalliver function tests(LFTs). In most cases the LFTs will be consistent with obstruction: raisedbilirubin,alkaline phosphataseandγ-glutamyl transpeptidase.In the early stages, however, pressure on the liver cells may be the main feature and the tests will resemble those inhepatitis,with elevations inalanine transaminaseandaspartate transaminase.[1]
Blood culturesare often performed in people with fever and evidence of acute infection. These yield the bacteria causing the infection in 36% of cases,[12]usually after 24–48 hours of incubation. Bile, too, may be sent for culture during ERCP (see below). The most common bacteria linked to ascending cholangitis aregram-negativebacilli:Escherichia coli(25–50%),Klebsiella(15–20%) andEnterobacter(5–10%). Of thegram-positivecocci,Enterococcuscauses 10–20%.[13]
Medical imaging
editGiven that ascending cholangitis usually occurs in the setting of bile duct obstruction, various forms ofmedical imagingmay be employed to identify the site and nature of this obstruction. The first investigation is usuallyultrasound,as this is the most easily available.[1]Ultrasound may show dilation of the bile duct and identifies 38% of bile duct stones; it is relatively poor at identifying stones farther down the bile duct. Ultrasound can help distinguish between cholangitis andcholecystitis(inflammation of the gallbladder), which has similar symptoms to cholangitis but appears differently on ultrasound.[14]A better test ismagnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography(MRCP), which usesmagnetic resonance imaging(MRI); this has a comparable sensitivity to ERCP.[14]Smaller stones, however, can still be missed on MRCP depending on the quality of the hospital's facilities.[1]
Thegold standardtest for biliary obstruction is stillendoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography(ERCP). This involves the use ofendoscopy(passing a tube through the mouth into theesophagus,stomachand thence to theduodenum) to pass a small cannula into the bile duct. At that point,radiocontrastis injected to opacify the duct, andX-raysare taken to get a visual impression of the biliary system. On the endoscopic image of the ampulla, one can sometimes see a protuberant ampulla from an impacted gallstone in the common bile duct or the frank extrusion of pus from the common bile duct orifice. On the X-ray images (known ascholangiograms), gallstones are visible as non-opacified areas in the contour of the duct. For diagnostic purposes, ERCP has now generally been replaced by MRCP. ERCP is only used first-line in critically ill patients in whom delay for diagnostic tests is not acceptable; however, if the index of suspicion for cholangitis is high, an ERCP is typically done to achieve drainage of the obstructed common bile duct.[1]
If other causes rather than gallstones are suspected (such as atumor),computed tomographyandendoscopic ultrasound(EUS) may be performed to identify the nature of the obstruction. EUS may be used to obtainbiopsy(tissue sample) of suspicious masses.[1]EUS may also replace diagnostic ERCP for stone disease, although this depends on local availability.[3]
Treatment
editFluids and antibiotics
editCholangitis requires admission to hospital.Intravenous fluidsare administered, especially if the blood pressure is low, andantibioticsare commenced.Empirical treatmentwithbroad-spectrum antibioticsis usually necessary until it is known for certain which pathogen is causing the infection, and to which antibiotics it is sensitive. Combinations ofpenicillinsandaminoglycosidesare widely used, althoughciprofloxacinhas been shown to be effective in most cases, and may be preferred to aminoglycosides because of fewer side effects.Metronidazoleis often added to specifically treat the anaerobic pathogens, especially in those who are very ill or at risk of anaerobic infections. Antibiotics are continued for 7–10 days.[1]Drugs that increase the blood pressure (vasopressors) may also be required to counter the low blood pressure.[2]
Endoscopy
editThe definitive treatment for cholangitis is relief of the underlying biliary obstruction.[1]This is usually deferred until 24–48 hours after admission, when the patient is stable and has shown some improvement with antibiotics, but may need to happen as an emergency in case of ongoing deterioration despite adequate treatment,[1]or if antibiotics are not effective in reducing the signs of infection (which happens in 15% of cases).[2][3]
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography(ERCP) is the most common approach in unblocking the bile duct. This involves endoscopy (passing afiberoptictube through the stomach into the duodenum), identification of the ampulla of Vater and insertion of a small tube into the bile duct. A sphincterotomy (making a cut in the sphincter of Oddi) is typically done to ease the flow of bile from the duct and to allow insertion of instruments to extract gallstones that are obstructing thecommon bile duct;alternatively or additionally, the common bile duct orifice can be dilated with a balloon.[15]Stones may be removed either by direct suction or by using various instruments, including balloons and baskets to trawl the bile duct in order to pull stones into the duodenum. Obstructions that are caused by larger stones may require the use of an instrument known as a mechanicallithotriptorin order to crush the stone prior to removal.[16]Obstructing stones that are too large to be removed or broken mechanically by ERCP may be managed byextracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy.This technique uses acoustic shock waves administered outside the body to break down the stones.[17]An alternative technique to remove very large obstructing stones is electrohydraulic lithotripsy, where a small endoscope known as a cholangioscope is inserted by ERCP to directly visualize the stone. A probe uses electricity to generate shock waves that break down the obstructing stone.[18]Rarely, surgical exploration of the common bile duct (termed choledochotomy), which can be performed withlaparoscopy,is required to remove the stone.[19]
Narrowed areas may be bridged by astent,a hollow tube that keeps the duct open. Removable plastic stents are used in uncomplicated gallstone disease, while permanentself-expanding metal stentswith a longer lifespan are used if the obstruction is due to pressure from a tumor such aspancreatic cancer.A nasobiliary drain may be left behind; this is a plastic tube that passes from the bile duct through the stomach and the nose and allows continuous drainage of bile into a receptible. It is similar to anasogastric tube,but passes into the common bile duct directly, and allows for serial x-ray cholangiograms to be done to identify the improvement of the obstruction. The decision on which of the aforementioned treatments to apply is generally based on the severity of the obstruction, findings on other imaging studies, and whether the patient has improved with antibiotic treatment.[1]Certain treatments may be unsafe ifblood clottingis impaired, as the risk of bleeding (especially from sphincterotomy) is increased in the use of medication such asclopidogrel(which inhibitsplateletaggregation) or if theprothrombin timeis significantly prolonged. For a prolonged prothrombin time,vitamin Korfresh frozen plasmamay be administered to reduce bleeding risk.[1]
Percutaneous biliary drainage
editIn cases where a person is too ill to tolerate endoscopy or when a retrograde endoscopic approach fails to access the obstruction, apercutaneous transhepatic cholangiogram(PTC) may be performed to evaluate the biliary system for placement of a percutaneous biliary drain (PBD).[20][3]This is often necessary in the case of a proximal stricture or a bilioentericanastomosis(a surgical connection between the bile duct and small bowel, such as theduodenumorjejunum).[2]Once access across the stricture is obtained, balloon dilation can be performed and stones can be swept forward into the duodenum.[20]Due to potential complications of percutaneous biliary drain placement and the necessity of regular drain maintenance,[2]a retrograde approach via ERCP remains first-line therapy.[1]
Cholecystectomy
editNot all gallstones implicated in ascending cholangitis actually originate from the gallbladder, butcholecystectomy(surgical removal of the gallbladder) is generally recommended in people who have been treated for cholangitis due to gallstone disease. This is typically delayed until all symptoms have resolved and ERCP or MRCP have confirmed that the bile duct is clear of gallstones.[1][2][3]Those who do not undergo cholecystectomy have an increased risk of recurrent biliary pain, jaundice, further episodes of cholangitis, and need for further ERCP or cholecystostomy; the risk of death is also significantly increased.[21]
Prognosis
editAcute cholangitis carries a significant risk of death, the leading cause being irreversibleshockwithmultiple organ failure(a possible complication of severe infections).[7]Improvements in diagnosis and treatment have led to a reduction in mortality: before 1980, the mortality rate was greater than 50%, but after 1980 it was 10–30%.[7]Patients with signs of multiple organ failure are likely to die unless they undergo early biliary drainage and treatment with systemic antibiotics. Other causes of death following severe cholangitis includeheart failureandpneumonia.[22]
Risk factors indicating an increased risk of death include older age, female gender, a history ofliver cirrhosis,biliary narrowing due tocancer,acute kidney injuryand the presence ofliver abscesses.[23]Complications following severe cholangitis include kidney failure,respiratory failure(inability of the respiratory system to oxygenate blood and/or eliminate carbon dioxide),abnormal heart rhythms,wound infection,pneumonia,gastrointestinal bleedingandmyocardial ischemia(lack of blood flow to the heart, leading toheart attacks).[22]
Epidemiology
editIn the Western world, about 15% of all people have gallstones in their gallbladder but the majority are unaware of this and have no symptoms. Over ten years, 15–26% will have one or more episodes ofbiliary colic(abdominal pain due to the passage of gallstones through the bile duct into the digestive tract), and 2–3% will develop complications of obstruction:acute pancreatitis,cholecystitisor acute cholangitis.[3]Prevalence of gallstone disease increases with age andbody mass index(a marker ofobesity). However, the risk is also increased in those who lose weight rapidly (e.g. afterweight loss surgery) due to alterations in the composition of the bile that makes it prone to form stones. Gallstones are slightly more common in women than in men, and pregnancy increases the risk further.[24]
History
editDrJean-Martin Charcot,working at theSalpêtrière Hospitalin Paris, France, is credited with early reports of cholangitis, as well as his eponymous triad, in 1877.[4]He referred to the condition as "hepatic fever" (fièvre hépatique).[4][7]Dr Benedict M. Reynolds, an American surgeon, reignited interest in the condition in his 1959 report with colleague Dr Everett L. Dargan, and formulatedthe pentadthat carries his name.[5]It remained a condition generally treated by surgeons, with exploration of the bile duct and excision of gallstones, until the ascendancy of ERCP in 1968.[25]ERCP is generally performed by internal medicine or gastroenterology specialists. In 1992 it was shown that ERCP was generally safer than surgical intervention in ascending cholangitis.[26]
See also
edit- Primary sclerosing cholangitis(anautoimmune diseaseleading to narrowing of the bile ducts)
- Gallstone-related pancreatitis
References
edit- ^abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzaaabKinney TP (April 2007). "Management of ascending cholangitis".Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am.17(2):289–306.doi:10.1016/j.giec.2007.03.006.PMID17556149.
- ^abcdefghijkOddsdóttir M, Hunter JG (2005). "Gallbladder and the extrahepatic biliary system (chapter 31)". In Brunicardi FC, Anderson DK, Billiar TR, Dunn DL, Hunter JG, Pollock RE (eds.).Schwartz's Principles of Surgery(Eighth ed.). McGraw-Hill. p. 1203.ISBN978-0-07-141090-8.
- ^abcdefgWilliams EJ, Green J, Beckingham I, Parks R, Martin D, Lombard M (2008)."Guidelines on the management of common bile duct stones".Gut.57(7):1004–1021.doi:10.1136/gut.2007.121657.PMID18321943.S2CID206945855.
- ^abcCharcot JM (2004) [1877].Leçons sur les maladies du foie, des voies biliaires et des reins faites à la Faculté de médecine de Paris: Recueillies et publiées par Bourneville et Sevestre.Paris: Bureaux du Progrés Médical & Adrien Delahaye.ISBN978-1-4212-1387-3.
- ^abReynolds BM, Dargan EL (August 1959)."Acute obstructive cholangitis; a distinct clinical syndrome".Ann Surg.150(2):299–303.doi:10.1097/00000658-195908000-00013.PMC1613362.PMID13670595.
- ^Lim JH (2011)."Liver flukes: the malady neglected".Korean J Radiol.12(3):269–79.doi:10.3348/kjr.2011.12.3.269.PMC3088844.PMID21603286.
- ^abcdKimura Y, Takada T, Kawarada Y, et al. (2007)."Definitions, pathophysiology, and epidemiology of acute cholangitis and cholecystitis: Tokyo Guidelines".J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg.14(1):15–26.doi:10.1007/s00534-006-1152-y.PMC2784509.PMID17252293.
- ^Brand, M; Bizos, D; O'Farrell P, Jr (6 October 2010). "Antibiotic prophylaxis for patients undergoing elective endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography".The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews(10): CD007345.doi:10.1002/14651858.CD007345.pub2.PMID20927758.
- ^Dooley JS (1999).Oxford textbook of clinical hepatology.Oxford University Press. p. 1650.ISBN978-0-19-262515-1.
- ^Huang T, Bass JA, Williams RD (May 1969). "The significance of biliary pressure in cholangitis".Arch Surg.98(5):629–632.doi:10.1001/archsurg.1969.01340110121014.PMID4888283.
- ^Sung JY, Costerton JW, Shaffer EA (May 1992). "Defense system in the biliary tract against bacterial infection".Dig Dis Sci.37(5):689–96.doi:10.1007/BF01296423.PMID1563308.S2CID21258760.
- ^Sung JJ, Lyon DJ, Suen R, Chung SC, Co AL, Cheng AF, Leung JW, Li AK (June 1995). "Intravenous ciprofloxacin as treatment for patients with acute suppurative cholangitis: a randomized, controlled clinical trial".J Antimicrob Chemother.35(6):855–864.doi:10.1093/jac/35.6.855.PMID7559196.
- ^Chetana Vaishnavi (2013).Infections of the Gastrointestinal System.JP Medical Ltd. p. 511.ISBN9789350903520.
- ^abVarghese JC, Liddell RP, Farrell MA, Murray FE, Osborne DH, Lee MJ (January 2000). "Diagnostic accuracy of magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography and ultrasound compared with direct cholangiography in the detection of choledocholithiasis".Clin Radiol.55(1):25–35.doi:10.1053/crad.1999.0319.PMID10650107.
- ^Heo JH, Kang DH, Jung HJ, et al. (October 2007). "Endoscopic sphincterotomy plus large-balloon dilation versus endoscopic sphincterotomy for removal of bile-duct stones".Gastrointest Endosc.66(4):720–6, quiz 768, 771.doi:10.1016/j.gie.2007.02.033.PMID17905013.
- ^Caddy GR, Tham TC (2006). "Gallstone disease: Symptoms, diagnosis and endoscopic management of common bile duct stones".Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol.20(6):1085–101.doi:10.1016/j.bpg.2006.03.002.PMID17127190.
- ^Hochberger J, Tex S, Maiss J, Hahn EG (October 2003). "Management of difficult common bile duct stones".Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am.13(4):623–34.doi:10.1016/S1052-5157(03)00102-8.PMID14986790.
- ^Arya N, Nelles SE, Haber GB, Kim YI, Kortan PK (December 2004). "Electrohydraulic lithotripsy in 111 patients: a safe and effective therapy for difficult bile duct stones".Am J Gastroenterol.99(12):2330–4.doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.2004.40251.x.PMID15571578.S2CID6147693.
- ^Karaliotas C, Sgourakis G, Goumas C, Papaioannou N, Lilis C, Leandros E (December 2007). "Laparoscopic common bile duct exploration after failed endoscopic stone extraction".Surg Endosc.22(8):1826–31.doi:10.1007/s00464-007-9708-8.PMID18071799.S2CID2347888.
- ^abGarcía-García, Lorenzo; Lanciego, Carlos (2004-03-01). "Percutaneous Treatment of Biliary Stones: Sphincteroplasty and Occlusion Balloon for the Clearance of Bile Duct Calculi".American Journal of Roentgenology.182(3):663–670.doi:10.2214/ajr.182.3.1820663.ISSN0361-803X.PMID14975967.
- ^McAlister VC, Davenport E, Renouf E (2007). McAlister V (ed.)."Cholecystectomy deferral in patients with endoscopic sphincterotomy".Cochrane Database Syst Rev.2010(4): CD006233.doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006233.pub2.PMC8923260.PMID17943900.
- ^abLai EC, Tam PC, Paterson IA, Ng MM, Fan ST, Choi TK, Wong J (January 1990)."Emergency surgery for severe acute cholangitis. The high-risk patients".Ann Surg.211(1):55–9.doi:10.1097/00000658-199001000-00009.PMC1357893.PMID2294844.
- ^Gigot JF, Leese T, Coutinho J, Castaing D, Bismuth H (April 1989)."Acute cholangitis. Multivariate analysis of risk factors".Ann Surg.209(4):435–8.doi:10.1097/00000658-198904000-00008.PMC1493983.PMID2930289.
- ^Bateson MC (June 1999)."Fortnightly review: gallbladder disease".BMJ.318(7200):1745–8.doi:10.1136/bmj.318.7200.1745.PMC1116086.PMID10381713.
- ^McCune WS, Shorb PE, Moscovitz H (May 1968)."Endoscopic cannulation of the ampulla of vater: a preliminary report".Ann Surg.167(5):752–6.doi:10.1097/00000658-196805000-00013.PMC1387128.PMID5646296.
- ^Lai EC, Mok FP, Tan ES, et al. (June 1992). "Endoscopic biliary drainage for severe acute cholangitis".N Engl J Med.326(24):1582–6.doi:10.1056/NEJM199206113262401.hdl:10722/45379.PMID1584258.