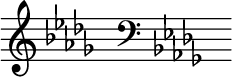B-flat minoris aminor scalebased onB♭,consisting of the pitches B♭,C,D♭,E♭,F,G♭,andA♭.Itskey signaturehas fiveflats.Itsrelative majorisD-flat majorand itsparallel majorisB-flat major.Itsenharmonicequivalent,A-sharp minor,which would contain seven sharps, is not normally used.
| Relative key | D-flat major |
|---|---|
| Parallel key | B-flat major |
| Dominant key | F minor |
| Subdominant | E-flat minor |
| Enharmonic | A-sharp minor |
| Component pitches | |
| B♭,C, D♭,E♭,F, G♭,A♭ | |
The B-flatnatural minor scaleis:
Changes needed for the melodic and harmonic versions of the scale are written in with accidentals as necessary. The B-flatharmonic minorandmelodic minor scalesare:
Scale degree chords
editThescale degreechords of B-flat minor are:
Characteristics
editB-flat minor is traditionally a 'dark' key.[1]
The oldvalvelesshornwas barely capable of playing in B-flat minor: the only example found in 18th-century music is a modulation that occurs in the first minuet ofFranz Krommer's Concertino inD major,Op. 80.[2]
Notable classical compositions
edit- Charles-Valentin Alkan
- Prelude Op. 31,No. 12 (Le temps qui n'est plus)
- Symphony for Solo Piano, 3rd movement: Menuet
- Samuel Barber
- Frédéric Chopin
- Franz Liszt
- Transcendental Étude No. 12(Chasse-neige) fromTranscendental Études
- Sergei Rachmaninoff
- Piano Sonata No. 2,Op. 36
- Dmitri Shostakovich
- Symphony No. 13,Op. 113 ( "Babi Yar" )
- String Quartet No. 13,Op. 138
- Richard Strauss
- An Alpine Symphonybegins and ends in B-flat minor.
- Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky
- William Walton
References
edit- ^Wilfrid Mellers,"Round and About in Górecki's Symphony No. 3"Tempo1683 (1989): 23
- ^J. Murray Barbour,Trumpets, Horns, and Music(1964), p. 163
- ^Piano Sonata No. 2, Op. 35 (Chopin):Scores at theInternational Music Score Library Project
- ^Nocturnes, Op. 9 (Chopin):Scores at theInternational Music Score Library Project
- ^Scherzo No. 2, Op. 31 (Chopin):Scores at theInternational Music Score Library Project
- ^Preludes, Op.28 (Chopin):Scores at theInternational Music Score Library Project
- ^Piano Concerto No. 1, Op. 23 (Tchaikovsky):Scores at theInternational Music Score Library Project
External links
edit- Media related toB-flat minorat Wikimedia Commons