Dental alveoli(singularalveolus) are sockets in thejawsin which the roots ofteethare held in thealveolar processwith theperiodontal ligament.The lay term for dental alveoli istooth sockets.Ajointthat connects the roots of the teeth and the alveolus is called agomphosis(pluralgomphoses). Alveolar bone is the bone that surrounds the roots of the teeth forming bone sockets.
| Dental alveolus | |
|---|---|
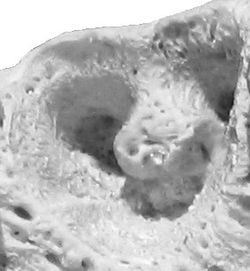 Alveola of the second premolar tooth in a bovine maxillary bone | |
| Details | |
| Artery | Anterior superior alveolar arteries,posterior superior alveolar artery,inferior alveolar artery |
| Nerve | Anterior superior alveolar nerve,posterior superior alveolar nerve,inferior alveolar nerve |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | alveolus dentalis |
| MeSH | D020390 |
| TA98 | A03.1.03.008 |
| FMA | 57490 |
| Anatomical terminology | |

Inmammals,tooth sockets are found in themaxilla,thepremaxilla,and themandible.
Etymology
edit1706, "a hollow", especially "the socket of a tooth", from Latin alveolus "a tray, trough, basin; bed of a small river; small hollow or cavity", diminutive of alvus "belly, stomach, paunch, bowels; hold of a ship", from PIE root *aulo- "hole, cavity" (source also of Greek aulos "flute, tube, pipe"; Serbo-Croatian, Polish, Russian ulica "street", originally "narrow opening"; Old Church Slavonic uliji, Lithuanian aulys "beehive" (hollow trunk), Armenian yli "pregnant" ). The word was extended in 19c. anatomy to other small pits, sockets, or cells.
Socket preservation
editSocket preservationor alveolar ridge preservation (ARP)[1]is a procedure to reduce bone loss aftertooth extractionto preserve the dental alveolus (tooth socket) in thealveolar bone.Aplatelet-rich fibrin(PRF)[2]membrane containing bone growth enhancing elements can be stitched over the wound or a graft material or scaffold is placed in the socket of an extracted tooth.[3][4]The socket is then directly closed with stitches or covered with a non-resorbable or resorbable membrane andsutured.[5]
Pathology
editThe swelling of the dental alveoli can result inalveolitis,causing pain and discomfort to the mouth.
See also
editReferences
edit- ^Peck, Mogammad Thabit; Marnewick, Johan; Stephen, Lawrence (2011)."Alveolar Ridge Preservation Using Leukocyte and Platelet-Rich Fibrin: A Report of a Case".Case Reports in Dentistry.2011:1–5.doi:10.1155/2011/345048.ISSN2090-6447.PMC3335652.PMID22567435.
- ^Khiste, Sujeet Vinayak; Naik Tari, Ritam (2013)."Platelet-Rich Fibrin as a Biofuel for Tissue Regeneration".ISRN Biomaterials.2013:1–6.doi:10.5402/2013/627367.ISSN2314-4025.
- ^Tassos Irinakis, Rationale for Socket Preservation after Extraction of a Single-Rooted Tooth when Planning for Future Implant Placement, Journal of Canadian Dental Association 2006; 72(10):917–922
- ^Fickl, Stefan; Zuhr, Otto; Wachtel, Hannes; Stappert, Christian F. J.; Stein, Jamal M.; Hürzeler, Markus B. (2008). "Dimensional changes of the alveolar ridge contour after different socket preservation techniques".Journal of Clinical Periodontology.35(10): 906–913.doi:10.1111/j.1600-051X.2008.01305.x.ISSN0303-6979.PMID18713258.
- ^"Extraction socket preservation: The time is now"(PDF).Archived fromthe original(PDF)on 2014-07-14.Retrieved2014-06-18.
External links
edit- National Institute of Health,CRISP Database