Detroit Metropolitan Airport
Detroit Metropolitan Wayne County Airport(IATA:DTW,ICAO:KDTW,FAALID:DTW) is the primaryinternational airportservingDetroitand itssurrounding metropolitan areainMichigan,United States.It is located inRomulus,a Detroit suburb. It is by far Michigan's busiest airport, with ten times as many enplanements and deplanements as the next-busiest,Gerald R. Ford International AirportinGrand Rapidsand more than all other airports in the state combined.
Detroit Metropolitan Wayne County Airport | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Summary | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Airport type | Public | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Owner/Operator | Wayne County Airport Authority | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serves | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Location | Romulus,Michigan,U.S. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Opened | September 4, 1930 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hubfor | Delta Air Lines | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating base for | Spirit Airlines | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Time zone | EST(UTC−05:00) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Summer (DST) | EDT (UTC−04:00) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ElevationAMSL | 197 m / 645 ft | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Coordinates | 42°12′45″N083°21′12″W/ 42.21250°N 83.35333°W | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Website | metroairport | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Maps | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
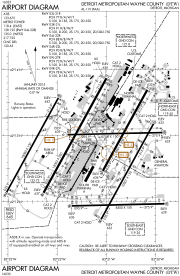 FAA airport diagram | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Runways | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Statistics (2024) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Source: Detroit Metropolitan Airport[1] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
TheFederal Aviation Administration(FAA)National Plan of Integrated Airport Systemsfor 2017–2021categorizedit as a large hub primary commercial service facility.[2]The airport covers 4,850 acres (1,960 ha) of land.[2][3]
The airport is a major hub forDelta Air Linesand is also a base forSpirit Airlines.[4][5]Detroit serves as Delta's main gateway to Asia for the Eastern United States. The airport has service to 30 international destinations and service to 39 states across the United States. Operated by theWayne County Airport Authority,the airport has six runways, two terminals, and 129 in-service gates.[6]Detroit Metropolitan Airport has maintenance facilities capable of servicing and repairing aircraft as large as theBoeing 747-400.[7]
Metro Airport serves theMetropolitan Detroitarea; theToledo, Ohio,area about 40 miles (64 km) south; theAnn Arborarea to the west;Windsor, Ontario;andSouthwestern Ontarioin Canada.[8]The airport serves over 140 destinations[6]and was named the best large U.S. airport in customer satisfaction byJ.D. Power & Associatesin 2010, 2019, and 2022.[9][10][11]
History
editWayne County began to plan an airport in the western townships of the county as early as 1927. The following year, the county board of commissioners issued a $2 million bond to fund the purchase of one square mile (2.6 km2) of land at the corner of Middlebelt and Wick roads, the northeastern boundary of today's airport. Construction was completed in 1929, and the first landing was on February 22, 1930; Wayne County Airport was dedicated on September 4, 1930.[12]That year, Thompson Aeronautical Corporation, a forerunner ofAmerican Airlines,began service from the airport. From 1931 until 1945, the airport hostedMichigan Air National Guardoperations gained by theUnited States Army Air Forces.It was namedRomulus Fieldduring the war; it was then all east of Merriman Road and north of Goddard Road. The intersection of the two runways is still visible at42°13′58″N83°20′08″W/ 42.23266°N 83.33564°W.
Wayne County expanded the airport to become Detroit's primary airport. It renamed it Detroit-Wayne Major Airport in 1947, and in the next three years expanded threefold as three more runways were built. In 1949 the airport added runways 3L/21R and 9L/27R, followed by runway 4R/22L in 1950. In 1946-47 most airline traffic moved from the crampedDetroit City Airport(now Coleman A. Young International Airport) northeast of downtown Detroit toWillow Run Airportover 20 miles (32 km) west of the city, and 10 miles (16 km) west of Wayne County Airport.
Pan-Am(1954) andBOAC(1956) were the first passenger airlines at Detroit-Wayne Major. In the April 1957 Official Airline Guide they were the only passenger airlines: three Pan AmDC-7Cseach weekFRA–LHR–SNN–DTW–ORDand back, and one BOAC DC-7C each week LHR–PIK–YUL–DTW–ORD and back (skipping YUL on the return flight).
Aerial photographs of DTW from 1949 and 1956 show the airport's expansion.[13]In 1958 the Civil Aviation Administration—now the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA)—announced the inclusion of Detroit-Wayne in the first group of American airports to receive new long-range radar equipment, enabling the airport to become the first inland airport in the United States certified for jet airliners. Also, in 1958, airport management completed the Leroy C. Smith (South) Terminal and gave the airport its present name.[14]
American Airlines moved from Willow Run to Detroit-Wayne in October 1958, followed byNorthwest,Allegheny, and Delta in the next few months; the other airlines stayed at Willow Run until 1966.
Northwest's flights to Minneapolis were DTW's only nonstops west beyond Chicago and Milwaukee until 1966. The first scheduled jets were Delta DC-8s to Miami in late 1959. The North Terminal (later renamed the James M. Davey Terminal) opened in 1966, which was located on the current site of the Evans Terminal. A third terminal, the Michael Berry International Terminal, opened in 1974. The last of its original three parallel runways (3R/21L) was completed in 1976; a new parallel crosswind runway (9R/27L) opened in 1993.
Republic Airlinesbegan hub operations in 1984,[15]and its merger withNorthwest Airlinesin 1986 expanded the hub. The Northwest hub operated out of the Davey Terminal throughout the 1980s and 1990s.[16]Transpacific flights began in 1987, with Northwest providing nonstop service toTokyo–Narita.[17]The last of Metro's six runways (4L/22R) was completed in December 2001 in preparation for the opening of the mile-long, 122-gate, $1.2 billion McNamara Terminal in the airport midfield in 2002.[14]The airport remained a hub for Northwest Airlines until it merged with Delta Air Lines.[18]
The present Runway 3L/21R has had four identifiers. When it opened in 1949, it was Runway 3/21. With the opening of the new west side Runway 3L/21R in 1950, the original 3/21 became 3R/21L. With the opening of the new east side Runway 3R/21L in 1976, it became 3C/21C. With the opening of Runway 4L/22R in December 2001 and the splitting of the field into two sectors (3/21 on the east and 4/22 on the west), Runway 3C/21C became Runway 3L/21R.
In 2009, Detroit Metro Airport launched its firstsocial mediaefforts with participation in Twitter, Facebook, and YouTube networks.
Detroit was a major hub forNorthwest Airlinesfrom 1986 to 2010; Northwest merged with Delta Air Lines, and Detroit became Delta's second-largest hub.
In April 2011Lufthansalaunched a unique curbside check-in and baggage check service for premium customers from DTW's North Terminal to Frankfurt and beyond. Lufthansa became the only airline allowing international customers departing from DTW to check their bags and receive a boarding pass at the curb, while DTW became Lufthansa's first North American gateway with this service.[19]
Detroit's economy plunged in theGreat Recession,causing airlines such asBritish Airwaysto drop flights toLondon–Heathrowand other airlines such asKLM Royal Dutch AirlinesandVirgin Atlanticto use codeshare flights throughDelta Air Lines.The city has lost population, but Detroit Metropolitan Airport has since re-grown, and airlines are looking to expand or resume service.JetBlue Airwaysbegan flights toBostonin February 2014.Spirit Airlineshas grown at DTW, adding service to more East and West Coast cities. Spirit has increased its market share to over 10%, widening the gap as Metro Airport's second largest carrier.[20]
Royal Jordanianwas the first airline to schedule theBoeing 787 Dreamlinerinto Detroit, on December 1, 2014.[21]
One ofDelta Connectioncarriers,Compass Airlineschose to close its operating base in Detroit to move operations to the new Seattle hub in early 2015. Delta has replaced many of the existing Compass flights with mainline Delta flights to allowSkyWest AirlinesandGoJetto open Detroit bases.[22]
Beginning in January 2018Suburban Mobility Authority for Regional Transportation,or SMART Bus, began providing a direct connection from the airport to the Rosa Parks Transit Center indowntown Detroitvia route 261, also known as the Michigan Ave FAST bus, with stations at both the McNamara and Evans terminals.[23]
On June 26, 2015, Spirit Airlines announced the construction of a new maintenance facility, saying it would bring $31.5 million and 82 jobs to the area. Spirit previously had a hangar that closed, forcing the airline to do maintenance at the gate with contract workers. With the new facility, which opened in May 2017, Spirit will retain its operating base at Metro Airport and bring more flights.[24]Spirit was also the first airline to regularly fly theA320neoin the US, the first route was Detroit to Los Angeles as well as add self-tagging luggage kiosks at DTW.
In 2017,WOW Airannounced service toReykjavíkon the Airbus A321. This marked the first ever entrance of a modern European low-cost carrier to DTW. In the summer of 2018, Reykjavík went from the 55th most traveled destination to the fifth due to this flight's popularity. Passengers could connect onwards in Reykjavík, boosting travel to European destinations. In March 2019, the airline ceased operations, leaving Metro Airport with no low-cost nonstop to Europe; the airport looked for replacement service to begin in 2020, but due to the COVID pandemic, that effort ceased until 2022, whenIcelandairand Delta announced seasonal flights to Reykjavík starting in 2023.[25]
Since the Great Recession of 2008, Southeast Michigan has gone through an economic and industrial resurgence leading to several new airlines and services including service by Icelandair, Sun Country, Turkish, and WestJet. In October 2021,Turkish Airlinesannounced the intent to serve Detroit. Service began on November 13, 2023.[26]In February 2023, WestJet announced seasonal service to Calgary, later adding seasonal service to Vancouver.[27]
Facilities
editDTW has 2 passenger terminals and 4 concourses with a total of 147 gates.
Edward H. McNamara Terminal
editThe McNamara Terminal, also once known as theNorthwest WorldGateway,opened February 24, 2002. Designed bySmithGroupand built byHunt Construction Group,it replaced the aged Davey Terminal. During development, the terminal was known as the Midfield Terminal.[14]The terminal is used exclusively by Delta (which merged with Northwest) and Delta partnersAeromexico,Air France,andWestJet.This terminal has three concourses, A, B, and C, which house 121 gates with shopping and dining in the center of A concourse (known as the Central Link), as well as throughout the concourses. It houses five Delta Sky Clubs located throughout Concourse A, and 1 located in Concourses B and C.[28]At nearly 1 mi (1.6 km) in length, Concourse A in McNamara Terminal is the second-longest airport concourse in the world (the longest is in Terminal 1 ofKansai International Airportin Japan).[29][30]In addition tomoving walkwaysspaced along the length of each concourse, Concourse A has apeople mover,theExpressTram.It transports passengers between each end of Concourse A in just over three minutes. Trams arrive almost simultaneously at theTerminal Station,in the midpoint of the concourse and depart in opposite directions to theNorth Stationand theSouth Station,then return.[31]The McNamara Terminal opened a new baggage sorting facility in October 2008, which has improved the screening of baggage through 14 new explosive detection system devices along a fully automated conveyor system. Northwest Airlines said that it reduced the amount of lost baggage, and it improved the timeliness of bags getting to their correct flight.[32][33]
AnAAAFour StarWestinhotel is connected to the A concourse. Additionally, overnight guests at the hotel who are not flying can obtain a pass to enter the concourses to visit shops and restaurants. Called theAirport Access Authorization to Commercial Establishments Beyond the Screen Checkpoint(AAACE), registered guests must be cleared through the same security background check (Secure Flight) andTSAscreening process as travelers to access the terminal area.Dallas/Fort Worth International Airportis the only other airport participating in this program.[34]
The A concourse houses 78 gates with 12 gates used for international departures and arrivals processing.[31]The A concourse is intended for all aircraft. At the midpoint of the concourse is a large, laminar flow water feature designed byWET.[35]The concourse contains over 1.5 miles (2.4 km) of moving walkways. The A concourse also includes a pet relief area for passengers traveling with pets and service animals.[citation needed]Signage through the terminal is in English, along with Japanese, due to a large number of business travelers from Japan. Izumi Suzuki, aSheratonemployee, and several colleagues provided the Japanese translations used by the airport. In previous eras many Japanese travelers going through Detroit missed connections due to a lack ofEnglish comprehension.[36]Also, messages reminding travelers to configure watches to theEastern Time Zoneregularly broadcast through thepublic address systemare said in English, Japanese, and Mandarin.
In addition to the ticketing level, there's an additional ticketing and security area for passengers using the parking structures.
The terminal houses ten international gates that are capable of dualjet bridgeloading and unloading. The gates contain two exit configurations depending on the arriving flight. Domestic arrivals follow an upper path directly into the terminal, while international arrivals proceed downstairs to customs and immigration screening. TheCustoms and Border Protectionprocessing center located in the terminal's lower level is designed to accommodate as many as 3,200 passengers per hour. International arriving passengers connecting to another flight are screened byTSAat a dedicated screening checkpoint within the international arrivals facility. Those passengers then exit directly back into the center of the A concourse.[37]Passengers arriving from international destinations who end their trip in Detroit (or connecting to a flight via Evans Terminal) exit directly into a dedicated International Arrivals Hall on the lower level of the terminal.
The B and C concourses currently have 41 gates that are used for Delta's regional flights that employ smaller aircraft. All regional flights havejet bridges,eliminating the need for outdoor boarding.[citation needed]
The B and C concourses are connected to the main terminal building and the A concourse by a pedestrian walkway under theairport ramp.This walkway, known as theLight Tunnel,features an elaborate multi-colored light show behind sculpted glass panels extending the entire length of the walkway, as well as severalmoving walkways.The light patterns are synchronized with an original musical score composed by Victor Alexeeff,[38]which runs for nearly 30 minutes before repeating. This installation, one of the first large-scale uses of color-changingLED lightingin the United States, was produced byMills James Productionswith glasswork by Foxfire Glass Works ofPontiac, Michigan.[39]The display won multiple lighting design awards, including the prestigious Guth Award of Merit. For passengers prone to medical conditions such as seizures, buttons at each end of the tunnel will suspend the light show for five minutes so they can pass through with no adverse effects.
The terminal has undergone updates that include new electronic terminal directories to assist passengers better. A unique feature of this is that passengers can scan their boarding passes, and the screen will direct them to the gate from which their plane departs. The passenger can also choose to view the information in other languages. Passengers may select a restaurant on the touch screen, and a menu will show what items the restaurant serves. Mini tablet devices and phone/tablet apps have been installed in food court areas, where travelers may order food and have it delivered to their table.[40]
There are five Delta Sky Clubs located in the McNamara terminal. The largest is located above the central link across from gate A38. Next to that, across from gate A43, houses a smaller Sky Club. There are two satellite Sky Clubs in Concourse A located on the upper level near gates A18 and A68, across from their respective ExpressTram stations. An additional Sky Club is located in Concourse C, at gate level near the entrance to Concourse C. This lounge services Delta Connection flights in concourses B & C.[41]
Warren Cleage Evans Terminal
editThe Evans Terminal, formerly known as theNorth Terminal,was designed byGenslerand built by Walbridge/Barton Malow Joint Venture,[42]opened September 17, 2008, as the replacement for the aged Berry and Smith terminals, which housed all non-SkyTeamairlines. It used to be known as the North Terminal until it was renamed in 2022.[43]Initially,Wayne County Airport Authoritysought bids for thenaming rightsof the North Terminal. After two years with no successful offers, however, the effort ceased and theNorth Terminalname remained.[44] The terminal currently houses all non-SkyTeam airlines serving the airport and is considered D Concourse. (Concourses A, B, and C are housed in the McNamara Terminal) The concourse has 29 gates, two of which opened in the middle of 2009 to accommodate international wide-body aircraft, and three of which were added to the north end of the concourse in 2022. The two gates were unusable at the building's opening because they were extremely close to Smith Terminal's C concourse, which was demolished after operations moved to the new facility. The terminal features four long segments of moving walkways on the departures level and another moving walkway on the lower level, for international arriving passengers to access the Federal Inspection Services area.
Airlines that utilize the North Terminal includeAir Canada,Alaska,American,American Eagle,Frontier,Icelandair,JetBlue,Lufthansa,Royal Jordanian,Southwest,Spirit,Sun Country,Turkish,United,United Express,and all non-SkyTeamand non-Delta partner charters.
The Evans Terminal houses two six-lane security checkpoints. The terminal also has U.S.Customs & Border Protectioninspection facilities located on the lower level for arriving international flights.[45]
This terminal includes a brand new service pet relief area to accommodate passengers traveling with pets.
The Evans Terminal has five common-use domestic baggage carousels on the lower level. Two additional carousels are located inside the Federal Inspection Services area for international flights, and a central Oversize Baggage Claim is adjacent to both the international and domestic carousel areas.
On January 29, 2010, the Evans Terminal was named winner of the "Build Michigan" award project.[46]
The Evans Terminal is home to a Lufthansa Business and Senator Lounge located between Gates D7 and D8. This lounge is accessible to passengers flying in Lufthansa premium cabins as well as select Lufthansa and Star Alliance elite members. This lounge also grants access to Priority Pass members outside of peak hours.[47]
Historical terminals
editMichael Berry Terminal
editThe Berry Terminal, named for a former airport commissioner, was designed by Detroit architect Louis G. Redstone, and opened in 1974 as the international terminal at DTW. It was decommissioned on September 17, 2008, and replaced by the Evans Terminal; however, the airport authority voted May 20, 2009, to renovate the terminal to house its offices.[48]All international passengers would arrive at this terminal, pass through customs and immigration inspection, and continue on to their connecting flights by bus to adjacent terminals.
Originally containing six gates (two of which were removed in 2003 to allow for construction of an adjacent Northwest Airlines maintenance hangar), the terminal was later used for scheduled and charter flights. There were still several international scheduled flights on low cost carriers to destinations in theCaribbeanand other warm-weathered places in the early 2000s (decade), including flights fromChampion Air,Ryan International Airlines,andUSA3000 Airlines.Four charter airlines also used this terminal.
Since its closure in 2008, the Berry Terminal has become a popular space for commercial film and television production. Films such asUp in the Air(2009),Machine Gun Preacher(2011), andThis Must Be the Placehave used the now-vacant terminal as a set (in addition to shooting in and around the airport's active terminals).
L. C. Smith Terminal
editThe Smith Terminal, named for Detroit-Wayne Major airport visionary Leroy C. Smith, was built in 1958. Though cited as the oldest of Metro Airport's terminals, that designation belongs to theExecutive Terminalbuilding located near Middlebelt Road and Lucas Drive, one-quarter-mile east. The Executive Terminal was built in the late 1920s and is still in operation today as home to ASIG, a flight support company.
The Smith Terminal's thirty-two gates originally housed Northwest Orient Airlines,Allegheny Airlines(forerunner toUS Airways),Eastern Airlines,andPan-Am,among others. A control tower was included in the construction, and served its purpose until the late 1980s, when a new control tower was built near the site of the new McNamara Terminal.
In later years, Smith Terminal hosted North American airlines other than Northwest, Continental, and later Delta, which relocated to the McNamara Terminal in 2002 before its merger with Northwest.
State of the art for its time, the Smith Terminal eventually became victim to airline expansion. The design of the building did not allow for physical expansion of the ticketing area. To accommodate additional airlines, ticketing counters were constructed on the sides of the lobby in areas that previously held lounges and retail.[49]In contrast, the North Terminal was constructed with future expansion in mind.
Spirit Airlines,which operated out of many of the gates once used by Northwest, made few upgrades to the gate areas in those parts of the terminal. The Northwest Airlines display boards near check-in counters at each gate remained in place, with the Northwest logos removed, and a Spirit information board simply affixed over the old signage.
On September 10, 2008,The Detroit Newsreported that Smith Terminal itself will not be demolished due to the airport authority offices remaining on the upper floors. However, theDetroit Free Pressof October 9, 2008, stated that maintaining the terminal in its present condition would cost upwards of $4 million annually in utilities, a sore spot for airlines at DTW who foot the bill, in part, through airport landing fees; the airlines were hoping for a greater cost savings once the Smith and Berry Terminals were decommissioned.[50]On May 20, 2009, the airport authority formally voted to totally vacate the Smith Terminal, while retaining and renovating the Berry Terminal for its offices.[48]
Discussions were also raised regarding proposed construction of a new structure to house the Airport Authority offices and Airport Police, with a preliminary price tag of $31.5 million.
James M. Davey Terminal
editThe Davey Terminal was built in 1966 and was first known as "Terminal 2" or the "North Terminal". Designed by the firm ofSmith, Hinchman and Grylls,it was said to be the largest post tensioned building in the world. Tapering cruciform columns around the perimeter and curved beams supported five large concrete roof panels. The lack of columns allowed maximum flexibility in the interior space. The spaces between the roof panels and exterior columns were filled with glass to allow abundant natural light into the building.[51]It was renamed the "J. M. Davey Terminal" in 1975 in honor of former airport manager James M. Davey. It originally contained three concourses labeled C to E, as well as a Host Hotel which later was rebrandedMarriott.[14]In the early 1980s, a separate ticketing area was constructed to the north of the Davey Terminal, along with Concourses F and G to eventually accommodateNorthwest Airlines' regional jet fleet.
Over time, the terminal and added concourse began showing its age due to its layout and poor maintenance, hastened further by increased aircraft traffic, which it was not designed to handle efficiently. Despite this, more gates were added to Concourse C in a short-term expansion project in the early 1990s, making it 26 gates in length. This concourse was considered the worst by most travelers due to its long distance from the center of the terminal, and for its length.
The Davey Terminal was originally the principal base of operations forRepublic Airlines,which merged with Northwest Orient Airlines to becomeNorthwest Airlinesin 1986. Upon relocation of Northwest operations to the McNamara Terminal, the Davey Terminal was mothballed for three years before demolition of the ticketing area and Concourse G began October 17, 2005, to prepare for the North Terminal project. All concourses of the Davey Terminal and adjoining Marriott hotel, except gates 1 to 11 of Concourse C, were subsequently demolished in 2005–06 (the remaining gates were in use bySpirit Airlinesuntil the new North Terminal (now Evans Terminal) opened on September 17, 2008).[14]
Ground transportation
editThe airport is accessible fromI-94via Merriman Road (exit 198), which is the nearest entrance to the Evans Terminal, and fromI-275via Eureka Road (exit 15), which is closer to the McNamara Terminal. Both entrances and the terminals are connected by John D. Dingell Drive, an expressway completed in 1999 and named afterthe longtime Congressman.[52]Cell phone lotsare located near both entrances.[53]
Free shuttle buses are available between the two terminals, and also connect to the Green parking lots. Rental car companies provide their own shuttles, as do private offsite parking lots and most hotels in the airport's vicinity.
Public transit
editMetro Airport is accessible by public transit, served by theRTA'sDetroit Air Xpress (DAX),an express bus to downtown Detroit; andSMART'sFAST Michigan,alimited-stopbusroute connecting the airport to Detroit and Dearborn, with connections to the region's wider transit network.[54][55]
Two local bus routes, operated by SMART, also serve the airport: route 125, to communities in theDownriverregion of southern Wayne County, serving both terminals; and route 280, to downtown Romulus and other suburbs in western Wayne County, serving only the Evans Terminal.[56]
Transit toAnn Arbor,Brighton,andEast Lansingis available with theMichigan Flyer,anintercity busoperated byIndian Trailsin partnership withTheRide.[57]Service to destinations in southern Ontario, Canada, includingWindsorandLondon,is offered by Robert Q Airbus, a private operator.[58]
Transit buses board from the Ground Transportation Center at the Evans Terminal, and from the departures drop-off area at McNamara.[59]
Airlines and destinations
editPassenger
editCargo
edit| Airlines | Destinations |
|---|---|
| Atlas Air | Cincinnati |
| FedEx Express | Columbus–Rickenbacker,Indianapolis,Memphis,Newark |
| UPS Airlines | Chicago/Rockford,Louisville,Philadelphia |
Statistics
editTop destinations
edit| Rank | City | Passengers | Carriers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Atlanta, Georgia | 836,000 | Delta, Frontier, Spirit |
| 2 | Orlando, Florida | 671,000 | Delta, Frontier, Southwest, Spirit |
| 3 | New York-LaGuardia, New York | 528,000 | American, Delta, Spirit |
| 4 | Dallas/Fort Worth, Texas | 497,000 | American, Delta, Frontier, Spirit |
| 5 | Las Vegas, Nevada | 492,000 | Delta, Southwest, Spirit |
| 6 | Los Angeles, California | 454,000 | Delta, Spirit |
| 7 | Denver, Colorado | 446,000 | Delta, Frontier, Southwest, United |
| 8 | Ft. Lauderdale, Florida | 419,000 | Delta, Spirit |
| 9 | Chicago O'Hare, Illinois | 414,000 | American, Delta, Spirit, United |
| 10 | Phoenix-Sky Harbor, Arizona | 383,000 | Delta, Southwest, Spirit |
| Rank | Airport | Passengers | Carriers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Amsterdam, Netherlands | 347,856 | Delta |
| 2 | Paris–Charles de Gaulle, France | 314,063 | Air France, Delta |
| 3 | Cancún, Mexico | 306,594 | Delta, Frontier, Spirit |
| 4 | Toronto–Pearson, Canada | 153,619 | Air Canada, Delta |
| 5 | Frankfurt, Germany | 145,448 | Delta, Lufthansa |
| 6 | Seoul–Incheon, South Korea | 130,620 | Delta |
| 7 | Montréal-Trudeau, Canada | 128,873 | Air Canada, Delta |
| 8 | London–Heathrow, United Kingdom | 115,796 | Delta |
| 9 | Mexico City–Benito Juárez, Mexico | 72,619 | Delta |
| 10 | Munich, Germany | 50,340 | Delta |
Airline market share
edit| Rank | Airline | Passengers | Market Share |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Delta Air Lines | 16,010,000 | 55.70% |
| 2 | Spirit Airlines | 3,780,000 | 11.75% |
| 3 | SkyWest Airlines | 2,651,000 | 9.22% |
| 4 | Endeavor Air | 1,706,000 | 5.93% |
| 5 | American Airlines | 1,416,000 | 4.93% |
| 6 | Others | 3,582,000 | 12.46% |
Annual traffic
editGraphs are unavailable due to technical issues. Updates on reimplementing the Graph extension, which will be known as the Chart extension, can be found onPhabricatorand onMediaWiki.org. |
| Year | Passengers | Year | Passengers | Year | Passengers |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1995 | 28,298,215 | 2005 | 36,383,514 | 2015 | 33,440,112 |
| 1996 | 27,408,666 | 2006 | 35,972,673 | 2016 | 34,401,254 |
| 1997 | 30,732,871 | 2007 | 36,013,478 | 2017 | 34,701,497 |
| 1998 | 30,803,158 | 2008 | 35,135,828 | 2018 | 35,236,676 |
| 1999 | 33,967,819 | 2009 | 31,357,388 | 2019 | 36,769,279 |
| 2000 | 35,535,080 | 2010 | 32,377,064 | 2020 | 14,105,007 |
| 2001 | 32,631,463 | 2011 | 32,406,159 | 2021 | 23,610,765 |
| 2002 | 32,477,694 | 2012 | 32,242,473 | 2022 | 28,160,572 |
| 2003 | 32,738,900 | 2013 | 32,389,544 | 2023 | 31,453,486 |
| 2004 | 35,229,705 | 2014 | 32,513,555 | 2024 | 32,971,060 |
Accidents and incidents
edit- December 30, 1963, aZantop Air TransportC-46 Commandowith 4 occupants crashed 2.2 miles SW of DTW, killing all aboard. A loss of control during a night instrument approach in adverse weather was the probable cause.[105]
- June 12, 1972, after a stopover in Detroit,American Airlines Flight 96,a McDonnell DouglasDC-10-10with 56 passengers and 11 crew fromLos Angeles International Airporten route toBuffalo, New York,suffered a cargo door failure and explosive decompression shortly after departure from Detroit Metropolitan Airport while flying overWindsor, Ontario.It is thus sometimes referred to as the Windsor incident.[106]The aircraft sustained damage that left the pilots without full flight controls but the plane returned to Detroit for a successful emergency landing. There were no fatalities but several serious to minor injuries.
- July 31, 1972,Delta Air Lines Flight 841;members of theBlack Liberation Armytook over the airplane in flight using weapons smuggled on board, including a Bible, cut out to hold a handgun. The plane held seven crew and 94 passengers, none of whom was killed during the hijacking. Five hijackers who had boarded with three children took over the plane. The plane flew to Miami, where the passengers were exchanged for $1 million in ransom. The plane was then flown on to Boston, where it refueled before flying to Algeria. Algeria seized the plane and ransom, which they returned to the U.S., but the hijackers were released after a few days.
- December 15, 1972, aZantop International AirlinesLearjet 23,a ferry flight, crashed after failing to climb from runway 3R, hitting a fuel storage tank. Both occupants on board and 1 on the ground were killed. Cause undetermined.[107]
- January 19, 1979, aLearjet 25operated byMassey Fergusonrolled violently and crashed on approach to runway 09. The probable causes were icing,wake vortexby a precedingMcDonnell Douglas DC-9and a delayed application of engine thrust during an attempted go-around. All six occupants (two crew, four passengers) were killed.[108]
- On April 4, 1979,TWA Flight 841 (1979)went into a dive aboveSaginaw, Michigan.The flight made an emergency landing at DTW.
- January 11, 1983,United Airlines Flight 2885,aMcDonnell Douglas DC-8F cargo flight with 3 occupants aboard crashed after takeoff due to a mistrimmed stabilizer causing a loss of control, all on board were killed.[109]
- March 4, 1987,Northwest Airlink Flight 2268,operated by Fischer Brothers Aviation, aCASA 212was on a scheduled flight fromMansfieldto Detroit with an intermediate stop inClevelandwhen it crashed while landing at Detroit Metropolitan Wayne County Airport. The plane yawed violently to the left about 70 feet (21 m) above the runway, skidded to the right, hit three ground support vehicles in front of Concourse F, and caught fire. Of 19 occupants onboard (16 passengers and three crew), nine were killed. The cause of the crash was determined to be pilot error.[110]
- August 16, 1987, aMcDonnell Douglas MD-82operating asNorthwest Airlines Flight 255,[111]bound forPhoenix, Arizona,crashed on take-off from Metro's 8,500-foot-long (2,600 m) Runway 3 Center (Now Runway 3L). All but one passenger on the aircraft were killed; the lone survivor was a young girl,Cecelia Cichan,who lost both of her parents and her brother. The NTSB determined that the accident resulted from flight crew's failure to deploy the aircraft's flaps prior to take-off, resulting in a lack of necessary lift. The aircraft slammed into an overpass bridge onI-94just northeast of the departure end of the runway.[112]
- December 3, 1990, aMcDonnell Douglas DC-9-14operating asNorthwest Airlines Flight 1482,bound forPittsburgh,collided with aBoeing 727-200 Adv.operating as Northwest Airlines Flight 299, bound forMemphis,on runway 03C. Seven passengers and a flight attendant on Flight 1482 were killed. The cause of the accident is listed as "pilot error".[113][114]
- January 9, 1997, anEmbraer EMB 120 Brasiliaaircraft operating asComair Flight 3272crashed nose down 18 miles (29 km) from the airport while on approach into Detroit. All 26 passengers and 3 crew members were killed. The cause is listed to be the "FAA's failure to establish adequate aircraft certification standards for flight in icing conditions, the FAA's failure to ensure that an FAA/CTA-approved procedure for the accident airplane's deice system operation was implemented by U.S.-based air carriers, and the FAA's failure to require the establishment of adequate minimum airspeeds for icing conditions."[115]
- March 17, 2001, anAirbus A320-200operating as Northwest Airlines Flight 985 bound forMiami,Florida,prematurely rotated during takeoff from runway 3C. The captain aborted the takeoff, and the aircraft skidded off the runway. All 151 occupants survived. The cause of the accident was the captain's delayed rejection of the takeoff, and the flight crew had incorrectly set the trim of the horizontal stabilizer.[116]
- December 25, 2009,NigeriannationalUmar Farouk Abdulmutallabattempted to detonate an explosive device onNorthwest Airlines Flight 253,anAirbus A330fromAmsterdamto Detroit as the plane was approaching Detroit. The device failed to go off correctly, and the suspect suffered burns to his lower body. Three other passengers had minor injuries. The White House said it considered the incident an attempted terrorist attack.[117]
See also
editNotes
editReferences
editThis article incorporatespublic domain materialfrom theAir Force Historical Research Agency
- ^"Airport Statistics 2024".Wayne County Airport Authority. 2024.RetrievedJanuary 23,2025.
- ^abFAA Airport Form 5010 for DTWPDFeffective January 23, 2025.
- ^"DTW airport data at skyvector.com".skyvector.com.FAA data effective January 23, 2025.
- ^"Detroit Metropolitan Wayne County Airport".Delta News Hub.Archivedfrom the original on January 7, 2016.RetrievedJanuary 13,2016.
- ^"Annual Report for the period ending 12/31/11"(PDF).Spirit Airlines. February 23, 2012. Archived fromthe original(PDF)on October 2, 2013.RetrievedJanuary 10,2013.
- ^ab"Press Room: Facts".Wayne County Airport Authority. Archived fromthe originalon January 20, 2013.RetrievedJanuary 10,2013.
- ^"Detroit Metropolitan Airport, Twin Bay Boeing 747 Hangar".Walbridge Construction.Archivedfrom the original on July 13, 2013.RetrievedJanuary 10,2013.
- ^"Travel Tips & Security Information: FAQ-Directions".Wayne County Airport Authority. Archived fromthe originalon February 24, 2009.RetrievedJanuary 10,2013.
- ^Pawlowski, Agnes (February 24, 2010)."Detroit Tops Airport Satisfaction Study".CNN.Archivedfrom the original on February 3, 2014.RetrievedJanuary 10,2013.
- ^Abdel-Baqui, Omar."DTW ranked No. 1 for customer satisfaction in survey".Detroit Free Press.Archivedfrom the original on September 25, 2019.RetrievedSeptember 25,2019.
- ^"DTW named best airport in North America for customer satisfaction".September 20, 2023.
- ^Meyer, Zlati (August 31, 2014)."This week in Michigan history: Detroit's airport is dedicated".Detroit Free Press.Archivedfrom the original on September 2, 2014.RetrievedSeptember 3,2014.
- ^"Detroit-area aerial pics".Wayne State University.Archivedfrom the original on February 14, 2015.RetrievedSeptember 14,2012.
- ^abcde"Detroit Metropolitan Wayne County Airport Chronological History".Wayne County Airport Authority. Archived fromthe originalon February 4, 2009.RetrievedJanuary 10,2013.
- ^Christoff, Chris (October 18, 1984)."Republic will make Metro its major hub".Detroit Free Press.p. A-3.RetrievedNovember 24,2024– viaNewspapers.com.
- ^"DTW WORLDGATEWAY 20TH ANNIVERSARY".Northwest Airlines History.April 10, 2022.RetrievedApril 13,2022.
- ^"Airline offers link to flight to Tokyo".Battle Creek Enquirer.April 11, 1987. p. 6B.RetrievedNovember 24,2024– viaNewspapers.com.
- ^Creager, Ellen (May 16, 2011)."Northwest Airlines Artifacts Soar in Value".USA Today.Archivedfrom the original on October 29, 2012.RetrievedJanuary 10,2013.
- ^"Lufthansa Launches Curbside Check-In Service at Detroit Metropolitan Airport"(PDF)(Press release). Wayne County Airport Authority. Archived fromthe original(PDF)on July 22, 2012.RetrievedJanuary 10,2013.
- ^Williams, Candice (February 5, 2019)."Detroit Metro Airport sees most passengers in decade".The Detroit News.Archivedfrom the original on April 3, 2019.RetrievedApril 3,2019.
- ^Cardenas, Edward (December 1, 2014)."Metro Airport Welcomes Its First Boeing 787 Flight".WWJ-TVNews.Archivedfrom the original on May 18, 2015.RetrievedMay 13,2015.
- ^Abdel-Razzaq, Lauren (April 3, 2015)."Delta feeder airline shuttering Detroit crew base".The Detroit News.Archivedfrom the original on February 7, 2016.RetrievedJuly 3,2017.
- ^"SMART Unveils New Service!".Suburban Mobility Authority for Regional Transportation.December 27, 2018. Archived fromthe originalon February 3, 2018.RetrievedJanuary 4,2018.
- ^Reindl, JC (June 26, 2015)."Detroit Metro Airport to get new hangar, 80 jobs".Detroit Free Press.Archivedfrom the original on June 30, 2015.RetrievedJune 27,2015.
- ^"Icelandic budget airline WOW Air ceases operations, grounding flights in Detroit".March 28, 2019.Archivedfrom the original on April 3, 2019.RetrievedApril 3,2019.
- ^"Turkish Airlines Broadens U.S. Presence with Launch of 13th U.S. Gateway in Detroit".November 13, 2023.RetrievedAugust 9,2024.
- ^"WestJet brings new U.S. Destinations and enhanced domestic connectivity to summer schedule as airline's new growth strategy takes flight | Wayne County Airport Authority".
- ^"Detroit".www.delta.com.RetrievedJune 23,2022.
- ^Keraghosian, Greg (January 21, 2016)."Airports You'll Enjoy Being Stranded at During Winter Storm Jonas".Yahoo!.Archived fromthe originalon October 11, 2018.RetrievedOctober 11,2018.
- ^"Osaka Kansai International Airport".Skyscanner.May 31, 2018. Archived fromthe originalon October 11, 2018.RetrievedOctober 11,2018.
- ^ab"McNamara Terminal Map"(PDF).Wayne County Airport Authority. Archived fromthe original(PDF)on February 27, 2009.RetrievedJanuary 10,2013.
- ^"Detroit (DTW) McNamara Terminal Northwest World Gateway Baggage Handling System"(PDF)(Press release). BNP Associates. Archived fromthe original(PDF)on March 15, 2013.RetrievedJanuary 10,2013.
- ^Hurst, Nathan (March 20, 2009)."New, Faster Baggage Screening".The Detroit News.Archivedfrom the original on May 22, 2014.RetrievedJanuary 10,2013.
- ^"Privacy Impact Assessment for the Airport Access Authorization To Commercial Establishments Beyond The Screening Checkpoint (AAACE) Program"(PDF).Department of Homeland Security. April 5, 2007.Archived(PDF)from the original on May 24, 2012.RetrievedJanuary 10,2013.
- ^"Water Feature".Wayne County Airport Authority.Archivedfrom the original on September 5, 2015.RetrievedAugust 30,2015.
- ^Kelly, Natalie; Zetzsche, Jost (October 2, 2012).Found in Translation: How Language Shapes Our Lives and Transforms the World.Penguin Books.ISBN978-1101611920.Archivedfrom the original on September 28, 2016.RetrievedAugust 7,2017.
Back in the 1980s, waves of Japanese businessmen started to arrive in Detroit[...]one local hotel, part of the Sheraton chain, was lucky enough to have an employee, Izumi Suzuki, who spoke Japanese[...]Eventually, she and some colleagues translated all of the signs that appear in the more modern airport that Detroit boasts today,[...]
- ^"McNamara Terminal Restaurants, Shops and Services".Wayne County Airport Authority. Archived fromthe originalon February 2, 2013.RetrievedJanuary 10,2013.
- ^Wuebker, Marcus (November 18, 2008)."The McNamara Tunnel, Detroit Airport".JimOnLight.com.Archivedfrom the original on May 6, 2012.RetrievedJanuary 10,2013.
- ^"Northwest Airlines Passenger Tunnel: 2001–present".ColorKinetics.RetrievedApril 13,2022.
- ^Gordon, Guy (November 23, 2015)."Detroit Metro Airport (DTW) has variety of new food choices".WDIV News.Archivedfrom the original on November 26, 2015.RetrievedAugust 4,2017.
- ^"Alert: System Unavailable: Delta Air Lines".Archivedfrom the original on October 19, 2019.RetrievedAugust 9,2019.
- ^"Detroit Metropolitan Airport".Gensler.Archivedfrom the original on May 26, 2012.RetrievedJanuary 10,2013.
- ^"Metro Airport Renames North Terminal in Warren Evans' Honor".The Michigan Chronicle.April 5, 2022. Archived fromthe originalon April 17, 2022.RetrievedJune 3,2022.
- ^Shea, Bill (July 27, 2010)."Detroit Metropolitan Airport Calls Off Plan to Sell Naming Rights".Crain's Detroit Business.Archivedfrom the original on August 7, 2017.RetrievedJanuary 10,2013.
- ^"North Terminal Restaurants, Shops and Services".Wayne County Airport Authority. Archived fromthe originalon February 2, 2013.RetrievedJanuary 10,2013.
- ^"Detroit Metro Airport's North Terminal Named 'Build Michigan' Winner"(Press release). redOrbit. February 1, 2010.Archivedfrom the original on December 25, 2013.RetrievedJanuary 10,2013.
- ^"DTW: Lufthansa Business Lounge".LoungeBuddy.Archivedfrom the original on August 9, 2019.RetrievedAugust 9,2019.
- ^ab"Berry Terminal at Detroit airport gets new life".Crain's Detroit Business.Associated Press. May 20, 2009.RetrievedJanuary 10,2013.
- ^"Smith Terminal Map"(PDF).Wayne County Airport Authority. Archived fromthe original(PDF)on June 5, 2012.RetrievedJanuary 10,2013.
- ^Masson, Mary Frances (September 17, 2008)."Memories of Smith Terminal Not Fond".Detroit Free Press.RetrievedJanuary 10,2013.
- ^Mattingly–Meyer, Katherine; Martin–McElroy, C.P.; W. Hawkins Ferry, Hon A.I.A. (1980).Detroit Architecture A.I.A. Guide Revised Edition.Wayne State University Press.ISBN0-8143-1651-4.
- ^"Maps and Directions".Wayne County Airport Authority. Archived fromthe originalon February 17, 2009.RetrievedJanuary 10,2013.
- ^"Cell Phone Waiting Area".Wayne County Airport Authority. Archived fromthe originalon February 15, 2012.RetrievedJanuary 10,2013.
- ^"Express bus service links Detroit's downtown to airport".Detroit News.December 28, 2017.Archivedfrom the original on January 12, 2018.RetrievedJanuary 5,2018.
- ^SMART."Ride Smart-Fast".www.smartbus.org.Archivedfrom the original on August 31, 2018.RetrievedOctober 8,2018.
- ^"System Map"(PDF).Suburban Mobility Authority for Regional Transportation.September 12, 2022.
- ^Oppenhuizen, Clay (February 24, 2022)."Michigan Flyer, Expanding Connections in Mid-Michigan, Turns 15".East Lansing Info.
- ^"Pickup Locations".Robert Q.
- ^"Public Transportation".Wayne County Airport Authority.RetrievedMarch 25,2024.
- ^"Delta and Aeromexico reactivate flights between Monterrey and Detroit".Aviacionline. September 7, 2022.RetrievedSeptember 7,2022.
- ^"Aeromexico Schedules First Batch Of U.S. Additions".Aviation Week.RetrievedOctober 12,2023.
- ^"Timetables".Aeroméxico.Archivedfrom the original on November 19, 2018.RetrievedMarch 17,2018.
- ^"Flight Schedules".Air Canada.Archivedfrom the original on September 25, 2019.RetrievedApril 5,2017.
- ^"Horaires".Air France.Archivedfrom the original on April 19, 2017.RetrievedApril 5,2017.
- ^"Alaska Airlines announces new flights to Anchorage from Detroit and Sacramento".Alaska Airlines News Hub.January 7, 2025.RetrievedJanuary 7,2025.
- ^"Flight timetable".Alaska Airlines.Archivedfrom the original on February 2, 2017.RetrievedApril 5,2017.
- ^ab"Flight schedules and notifications".American Airlines.Archivedfrom the original on February 2, 2017.RetrievedApril 5,2017.
- ^Wright, Bailey (December 9, 2024)."Dominican Republic among Avelo Airlines' 5 new destinations".RetrievedDecember 9,2024.
- ^"Destinations".Avelo Airlines.Archivedfrom the original on November 7, 2023.RetrievedJanuary 18,2022.
- ^ab"Santa Barbara, Yosemite, Tahoe and more: Get there on Delta with new and returning flights for summer 2024".Delta News Hub.September 15, 2023.RetrievedSeptember 15,2023.
- ^"Delta boosts Summer 2025 schedule with return of seven U.S. And Latin leisure routes | Delta News Hub".December 23, 2024.
- ^"Delta Expands in Europe with First-Ever Nonstop Flights to Catania".Business Traveler.September 20, 2024.RetrievedSeptember 20,2024.
- ^"Getting to the Bahamas from the Midwest is About to Get Easier with a New Direct Flight".
- ^"Delta boosts Summer 2025 schedule with return of seven U.S. And Latin leisure routes | Delta News Hub".December 23, 2024.
- ^"Delta NW24 Caribbean Network Additions".Aeroroutes.RetrievedMay 8,2024.
- ^"Explore more Mexico: New routes to Tulum, Mazatlán, plus expanded Aeromexico service | Delta News Hub".July 30, 2024.
- ^"Delta NS24 New York – Reykjavik Aircraft Changes".
- ^"Delta to Resume Two Domestic Routes".AirlineGeeks.November 8, 2024.RetrievedNovember 9,2024.
- ^"Explore more Mexico: New routes to Tulum, Mazatlán, plus expanded Aeromexico service | Delta News Hub".July 30, 2024.
- ^"Delta Continues Mexico Network Expansion in NW24".Aeroroutes.RetrievedJuly 22,2024.
- ^ab"Flight Schedules".Delta Airlines.Archivedfrom the original on June 21, 2015.RetrievedJune 24,2024.
- ^"Delta adds Detroit flights at Greater Binghamton Airport, LaGuardia discontinued".PressConnects. October 21, 2023.
- ^https://airlinegeeks.com/2024/08/17/delta-adds-two-regional-routes/[bare URL]
- ^"Delta Resumes Detroit – Fort Wayne From June 2024".Aeroroutes.RetrievedApril 1,2024.
- ^"Delta bringing back flights between South Bend, Detroit".June 26, 2023.
- ^"Frontier Airlines Announces New Routes, Expanding Operations Across 38 Airports".
- ^"route map".Frontier.Archivedfrom the original on February 21, 2017.RetrievedJune 24,2024.
- ^"Our Flight Schedule 2022 | Icelandair".
- ^"JetBlue Enhances Summer Travel with New Routes and Destinations, Strengthening its East Coast Network".Business Wire.January 15, 2025.
- ^"JetBlue Airways Timetable".Archivedfrom the original on November 30, 2018.RetrievedDecember 12,2018.
- ^"Timetable".Lufthansa.Archivedfrom the original on January 26, 2017.RetrievedApril 5,2017.
- ^"Route Map".Royal Jordanian Airlines. Archived fromthe originalon August 5, 2018.RetrievedApril 5,2017.
- ^"Check Flight Schedules".Southwest Airlines.Archivedfrom the original on February 2, 2017.RetrievedJune 16,2022.
- ^ab"Spirit Airlines July 2024 Dallas / Detroit Network Expansion".Aeroroutes.RetrievedMay 8,2024.
- ^"Where We Fly".Spirit Airlines.Archivedfrom the original on December 23, 2017.RetrievedApril 5,2017.
- ^"Turkish Airlines to launch Detroit service".June 6, 2023.
- ^"United Resumes San Francisco - Detroit/ St. Louis in Aug 2024".AeroRoutes. April 25, 2024.RetrievedApril 25,2024.
- ^ab"Timetable".United Airlines.Archivedfrom the original on January 28, 2017.RetrievedApril 5,2017.
- ^"WestJet adds U.S. routes to Edmonton and Vancouver while hiking some baggage, seat fees".Global. November 7, 2023.RetrievedNovember 7,2023.
- ^"Direct and Non-Stop Flights".WestJet.RetrievedSeptember 25,2022.
- ^"Detroit, MI: Detroit Metro Wayne County (DTW)".Bureau of Transportation Statistics.RetrievedMay 7,2024.
- ^"International_Report_Passengers | Department of Transportation - Data Portal".data.transportation.gov.RetrievedJuly 26,2021.
- ^"Detroit, MI: Detroit Metro Wayne County (DTW)".www.transtats.bts.gov.Bureau of Transportation Statistics.Archivedfrom the original on March 16, 2013.RetrievedJuly 22,2023.
- ^"Aviation Statistics".Wayne County Airport Authority.Archivedfrom the original on March 23, 2015.RetrievedFebruary 9,2024.
- ^Accident description for N608Zat theAviation Safety Network
- ^Faith, Nicholas (1996).Black Box: Why Airline Safety Is No Accident.Osceola, Wisconsin: Motorbooks International. pp.157–158.ISBN978-0-7603-0400-6.RetrievedNovember 20,2015.
- ^Accident description for N20Mat theAviation Safety Network
- ^Accident description for N137GLat theAviation Safety Network.Retrieved on November 5, 2020.
- ^Accident description for N8053Uat theAviation Safety Network
- ^"9 Killed in Detroit Plane Crash".Chicago Tribune.March 5, 1987.Archivedfrom the original on March 15, 2013.RetrievedJanuary 10,2013.
- ^"Accident Description: Northwest Airlines Flight 255".Aviation-safety.net. August 16, 1987.Archivedfrom the original on October 24, 2012.RetrievedJanuary 10,2013.
- ^"The Crash".Flight255memorial.com.Archivedfrom the original on November 7, 2012.RetrievedJanuary 10,2013.
- ^"Accident Description: Northwest Airlines Flight 1482".Aviation-safety.net. December 3, 1990.Archivedfrom the original on March 15, 2011.RetrievedJanuary 10,2013.
- ^"Accident Description: Northwest Airlines Fight 299".Aviation-safety.net. December 3, 1990.Archivedfrom the original on January 3, 2011.RetrievedJanuary 10,2013.
- ^"Accident Description: Comair Flight 3272".Aviation-safety.net. January 9, 1997.Archivedfrom the original on June 25, 2011.RetrievedJanuary 10,2013.
- ^Ranter, Harro."ASN Aircraft accident Airbus A320-212 N357NW Detroit-Metropolitan Wayne County Airport, MI (DTW)".aviation-safety.net.Aviation Safety Network.Archivedfrom the original on March 18, 2005.RetrievedMarch 30,2021.
- ^"U.S. Security for Air Travel Under New Scrutiny".NBC News.December 28, 2009.RetrievedJanuary 10,2013.
External links
edit- Official website
- Wayne County-Detroit Metro Airport History
- Detroit Spotters
- FAA Airport Diagram(PDF),effective January 23, 2025
- FAA Terminal Procedures for DTW,effective January 23, 2025
- Preferred Development Plan
- Resources for this airport:
- AirNavairport information for KDTW
- ASNaccident history for DTW
- FlightAwareairport informationandlive flight tracker
- NOAA/NWS weather observations:current,past three days
- SkyVectoraeronautical chart for KDTW
- FAAcurrent DTW delay information