This articleneeds additional citations forverification.(March 2015) |
In computing and insystems theory,first in, first out(the first in is the first out),acronymizedasFIFO,is a method for organizing the manipulation of a data structure (often, specifically adata buffer) where the oldest (first) entry, or "head" of thequeue,is processed first.
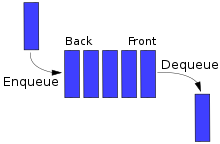
Such processing is analogous to servicing people in aqueue areaon afirst-come, first-served(FCFS) basis, i.e. in the same sequence in which they arrive at the queue's tail.
FCFS is also thejargonterm for the FIFOoperating system schedulingalgorithm, which gives every processcentral processing unit(CPU) time in the order in which it is demanded.[1]FIFO's opposite isLIFO,last-in-first-out, where the youngest entry or "top of the stack" is processed first.[2]Apriority queueis neither FIFO or LIFO but may adopt similar behaviour temporarily or by default.Queueing theoryencompasses these methods for processingdata structures,as well as interactions between strict-FIFO queues.
Computer science
editDepending on the application, a FIFO could be implemented as a hardware shift register, or using different memory structures, typically acircular bufferor a kind oflist.For information on the abstract data structure, seeQueue (data structure).Most software implementations of a FIFO queue are notthread safeand require a locking mechanism to verify the data structure chain is being manipulated by only one thread at a time.
The following code shows alinked listFIFOC++language implementation. In practice, a number of list implementations exist, including popular Unix systems C sys/queue.h macros or the C++standard librarystd::list template, avoiding the need for implementing the data structure from scratch.
#include<memory>
#include<stdexcept>
usingnamespacestd;
template<typenameT>
classFIFO{
structNode{
Tvalue;
shared_ptr<Node>next=nullptr;
Node(T_value):value(_value){}
};
shared_ptr<Node>front=nullptr;
shared_ptr<Node>back=nullptr;
public:
voidenqueue(T_value){
if(front==nullptr){
front=make_shared<Node>(_value);
back=front;
}else{
back->next=make_shared<Node>(_value);
back=back->next;
}
}
Tdequeue(){
if(front==nullptr)
throwunderflow_error("Nothing to dequeue");
Tvalue=front->value;
front=move(front->next);
returnvalue;
}
};
In computing environments that support thepipes-and-filtersmodel forinterprocess communication,a FIFO is another name for anamed pipe.
Disk controllers can use the FIFO as adisk schedulingalgorithm to determine the order in which to service diskI/Orequests, where it is also known by the same FCFS initialism as for CPU scheduling mentioned before.[1]
Communicationnetwork bridges,switchesandroutersused incomputer networksuse FIFOs to hold data packets in route to their next destination. Typically at least one FIFO structure is used per network connection. Some devices feature multiple FIFOs for simultaneously and independently queuing different types of information.[3]
Electronics
editFIFOs are commonly used inelectroniccircuits for buffering and flow control between hardware and software. In its hardware form, a FIFO primarily consists of a set of read and writepointers,storage and control logic. Storage may bestatic random access memory(SRAM),flip-flops,latches or any other suitable form of storage. For FIFOs of non-trivial size, a dual-port SRAM is usually used, where one port is dedicated to writing and the other to reading.
The first known FIFO implemented in electronics was by Peter Alfke in 1969 atFairchild Semiconductor.[4]Alfke was later a director atXilinx.
Synchronicity
editA synchronous FIFO is a FIFO where the same clock is used for both reading and writing. An asynchronous FIFO uses different clocks for reading and writing and they can introducemetastabilityissues. A common implementation of an asynchronous FIFO uses aGray code(or any unit distance code) for the read and write pointers to ensure reliable flag generation. One further note concerning flag generation is that one must necessarily use pointer arithmetic to generate flags for asynchronous FIFO implementations. Conversely, one may use either aleaky bucketapproach or pointer arithmetic to generate flags in synchronous FIFO implementations.
A hardware FIFO is used for synchronization purposes. It is often implemented as acircular queue,and thus has twopointers:
- Read pointer / read address register
- Write pointer / write address register
Status flags
editExamples of FIFO status flags include: full, empty, almost full, and almost empty. A FIFO is empty when the readaddress registerreaches the write address register. A FIFO is full when the write address register reaches the read address register. Read and write addresses are initially both at the first memory location and the FIFO queue isempty.
In both cases, the read and write addresses end up being equal. To distinguish between the two situations, a simple and robust solution is to add one extrabitfor each read and write address which is inverted each time the address wraps. With this set up, the disambiguation conditions are:
- When the read address register equals the write address register, the FIFO is empty.
- When the read and write address registers differ only in the extramost significant bitand the rest are equal, the FIFO is full.
See also
editReferences
edit- ^abAndrew S. Tanenbaum; Herbert Bos (2015).Modern Operating Systems.Pearson.ISBN978-0-13-359162-0.
- ^Kruse, Robert L. (1987) [1984].Data Structures & Program Design (second edition).Joan L. Stone, Kenny Beck, Ed O'Dougherty (production process staff workers) (second (hc) textbook ed.). Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey: Prentice-Hall, Inc. div. of Simon & Schuster. p. 150.ISBN0-13-195884-4.
- ^James F. Kurose; Keith W. Ross (July 2006).Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach.Addison-Wesley.ISBN978-0-321-41849-4.
- ^"Peter Alfke's post at comp.arch.fpga on 19 Jun 1998".