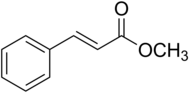
Methyl cinnamateis themethylesterofcinnamic acidand is a white or transparent solid with a strong, aromatic odor. It is found naturally in a variety of plants, including in fruits, likestrawberry,and some culinary spices, such asSichuan pepperand some varieties ofbasil.[4]Eucalyptus olidahas the highest known concentrations of methyl cinnamate (98%) with a 2–6% fresh weight yield in the leaf and twigs.[5]
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Methyl (2E)-3-phenylprop-2-enoate | |
| Other names
Methyl cinnamate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.813 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChemCID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard(EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H10O2 | |
| Molar mass | 162.188g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.092g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 34–38 °C (93–100 °F; 307–311 K) |
| Boiling point | 261–262 °C (502–504 °F; 534–535 K) |
| Insoluble | |
| Hazards | |
| GHSlabelling:[3] | |

| |
| Warning | |
| H317 | |
| P261,P272,P280,P302+P352,P321,P333+P313,P363,P501 | |
| Flash point | > 110 °C (230 °F; 383 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in theirstandard state(at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Methyl cinnamate is used in the flavor and perfume industries. The flavor is fruity and strawberry-like; and the odor is sweet, balsamic with fruity odor, reminiscent of cinnamon and strawberry.[1]
It is known to attract males of variousorchid bees,such asAglae caerulea.[6]

List of plants that contain the chemical
edit- Eucalyptus olida'Strawberry Gum'
- Ocotea quixosSouth American (Ecuadorian) Cinnamon, Ishpingo[7]
- Ocimum americanumcv. Purple Lovingly (Querendona Morada)
- Ocimum americanumcv. Purple Castle (Castilla Morada)
- Ocimum americanumcv. Purple Long-legged (Zancona morada)
- Ocimum americanumcv. Clove (Clavo)
- Ocimum basilicumcv. Sweet Castle (Dulce de Castilla)
- Ocimum basilicumcv. White Compact (Blanca compacta)
- Ocimum basilicumcv. large green leaves (verde des horjas grandes)
- Ocimum micranthumcv. Cinnamon (Canela)
- Ocimum minimumcv. Little Virgin (Virgen pequena)
- Ocimum minimumcv. Purple Virgin (Virgen morada)
- Ocimumsp. cv. Purple ruffle (Crespa morada)
- Ocimumsp. cv. White Ruffle (Crespa blanca)
- Stanhopea embreei,an orchid
- Vanilla
Toxicology and safety
editModerately toxic by ingestion. The oralLD50for rats is 2610 mg/kg.[8] It is combustible as a liquid, and when heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes.
Compendial status
editSee also
edit- Eucalyptus oil
- Ralf Sieckmann v Deutsches Patent und Markenamt,a court case concerning a company attempting totrademark the chemical compound.
References
edit- ^abMethyl cinnamate,at goodscents.com
- ^Methyl cinnamate,at Sigma-Aldrich
- ^"Methyl cinnamate".pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.
- ^Viña, Amparo; Murillo, Elizabeth (2003)."Essential oil composition from twelve varieties of basil (Ocimum spp) grown in Colombia".Journal of the Brazilian Chemical Society.14(5): 744–9.doi:10.1590/S0103-50532003000500008.
- ^Boland DJ, Brophy JJ, House APN (1991).Eucalyptus Leaf Oils.ISBN978-0-909605-69-8.
- ^Williams, N.H.; Whitten, W.M. (1983)."Orchid floral fragrances and male euglossine bees: methods and advances in the last sesquidecade".Biol. Bull.164(3): 355–395.doi:10.2307/1541248.JSTOR1541248.
- ^Bruni, Renato; Medici, Alessandro; Andreotti, Elisa; Fantin, Carlo; Muzzoli, Mariavittoria; Dehesa, Marco; Romagnoli, Carlo; Sacchetti, Gianni (2004). "Chemical composition and biological activities of Ishpingo essential oil, a traditional Ecuadorian spice from Ocotea quixos (Lam.) Kosterm. (Lauraceae) flower calices".Food Chemistry.85(3): 415–21.doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2003.07.019.hdl:11381/1449234.
- ^Richard J. Lewis (1989).Food Additives Handbook.Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 304–.ISBN978-0-442-20508-9.
- ^Therapeutic Goods Administration(1999)."Approved Terminology for Medicines"(PDF).Archived fromthe original(PDF)on 22 May 2006.Retrieved29 June2009.