This article has multiple issues.Please helpimprove itor discuss these issues on thetalk page.(Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
Arespiratory therapistis a specializedhealthcare practitionertrained incritical careand cardio-pulmonary medicine in order to work therapeutically with people who have acute critical conditions,cardiacandpulmonary disease.Respiratory therapists graduate from a college or university with a degree in respiratory therapy and have passed a national board certifying examination. The NBRC (National Board for Respiratory Care) is responsible for credentialing as a CRT (certified respiratory therapist), or RRT (registered respiratory therapist) in the United States. The CBRC (Canadian Board for Respiratory Care) is responsible for credentialing as an RRT in Canada.
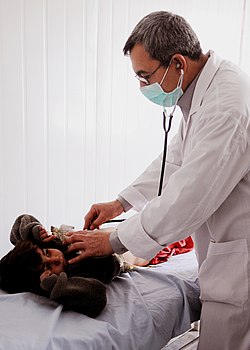 A clinician listening to the chest of a pediatric patient. | |
| Occupation | |
|---|---|
| Names |
|
Occupation type | Specialty |
Activity sectors | Resporation Therapy,Medicine,Allied Health,Pulmonology,Critical care medicine |
| Description | |
Education required |
|
Fields of employment |
Flight Transport, Air Ambulance Teaching or nursing home |
Related jobs | |
The specialty certifications of respiratory therapy include: CPFT and RPFT (Certified or Registered Pulmonary Function Technologist), ACCS (Adult Critical Care Specialist), NPS (Neonatal/Pediatric Specialist), and SDS (Sleep Disorder Specialist).
Respiratory therapists work in hospitals in the intensive care units (Adult, Pediatric, and Neonatal), on hospital floors, in emergency departments, in pulmonary functioning laboratories (PFTs), are able to intubate patients, work in sleep labs (polysomnography) (PSG) labs, and in home care specifically DME (durable medical equipment) and home oxygen.
Respiratory therapists are specialists and educators in many areas includingcardiology,pulmonology,and sleep therapy. Respiratory therapists are clinicians trained in advancedairway management;establishing and maintaining the airway during management of trauma, and intensive care.
Respiratory therapists initiate and managelife supportfor people in intensive care units and emergency departments, stabilizing, treating and managing pre-hospital and hospital-to-hospital patient transport by air or ground ambulance.
In the outpatient setting respiratory therapists work as educators in asthma clinics, ancillary clinical staff in pediatric clinics, and sleep-disorder diagnosticians in sleep-clinics, they also serve as clinical providers in cardiology clinics and cath-labs, as well as working in pulmonary rehabilitation.
Clinical practice
editRespiratory therapy, done by respiratory therapists, is a large variety of treatments to help with breathing and support the heart's work. Giving oxygen and drugs to ease breathing are two examples. Respiratory therapists also do patient assessments.
Intensive care and operating room
editRespiratory therapists educate, assist in diagnosis, and treat people who have heart and lung problems. Specialized in both cardiac and pulmonary care, respiratory therapists often collaborate with specialists inpulmonologyandanaesthesiain various aspects of clinical care of patients. Respiratory therapists provide a vital role in bothmedicineandnursingsuch as the initiation and maintenance of mechanical ventilation.
Outpatient clinical practice
editRespiratory therapists are also primary clinicians in conducting tests to measure lung function and teaching people to manageasthma,chronic obstructive pulmonary disorderamong other cardiac and lung functions.
Internationally, respiratory therapists that providelung function testingare termed respiratory scientists, but in North America, they may be a respiratory therapist.
Home-health care
editOutside of clinics and hospitals, respiratory therapists often manage home oxygen needs of patients and their families, providing around the clock support for home ventilators and other equipment for conditions likesleep apnea.
In the clinic or outpatient setting respiratory therapists assist with diagnosis and serve as an educator for patients with cardiac and respiratory illness.[1]In theUnited States,respiratory therapists with certification asregistered respiratory therapistsevaluate and treat patients with a great deal of autonomy under the direction of apulmonologist.[2]In facilities that maintain critical care transport teams respiratory therapists are a preferred addition to all types ofsurfaceorair transport.[3]
Public education
editIn other settings respiratory therapists are found in schools as asthma educators, working with teachers and coaches about childhood symptoms of asthma and how to spot an emergency. In the United States, legislation has been unsuccessfully introduced several times to allow respiration therapists certified as asthma specialists with registered respiratory therapist certification to prescribe and manage previously diagnosed respiratory patients in physician clinics.[4][5]In sleep clinics, respiratory therapists work with physicians in the diagnosis of sleep-related illnesses. Respiratory therapists in the United States are migrating toward a role with autonomy similar to the extension of the physician like thephysician assistant.[6]Respiratory therapists are frequently utilized as complete cardiovascular specialists to place and manage arterial accesses along with peripherally-inserted central catheters.[7]
Credentialing and licensure
editUnited States and Canada
editIn theUnited StatesandCanada,respiratory therapists are healthcare practitioners who, after receiving their education, complete a credentialing process and become a certified respiratory therapists (CRT) or registered respiratory therapists (RRTs).
After satisfactorily completing the required examinations and being added to a registry, the practitioner is then eligible to apply for a license to practice in the region governed by their respective licensing body.
In theUnited States,specialist respiratory therapists are clinicians who hold National Board for Respiratory Care specialty credentials, which may include neonatal/pediatric specialist (CRT-NPS or RRT-NPS), adult critical care specialist (RRT-ACCS), sleep disorder specialist (CRT-SDS or RRT-SDS), and pulmonary function technologist (CPFT or RPFT). The NBRC's RRT-ACCS examination is the newest NBRC examination: it was introduced in 2012.
In theUnited States,one must obtain a degree in respiratory care and must then sit for the board exams to become a RRT. RRT is issued by theNational Board for Respiratory Careafter passing the Therapist Multiple-Choice ExaminationNBRC-TMCand Clinical Simulation ExaminationNBRC-CSEexaminations.[8]Eligibility for the NBRC-CSE examination is based on scoring high enough on the NBRC-TMC, and holding at least anAssociate of Science in Respiratory Care.Professional credentials denoted as a Certified Asthma Educator (AE-C) may also be earned by passing the National Asthma Educator Certification Board[9](NAECB) exam.
In some parts of Canada, one may practice as a provisional respiratory therapist after graduating, until writing and passing the CBRC exam. The RRT certification is granted by examination from theCanadian Society of Respiratory Therapists.
Scope of practice
editThe registered respiratory therapist is typically governed by their medical director for clinical services and their licensing body for laboratory, rehabilitation and home-health services.[10]Trained in cardiology and pulmonology medicine. The registered respiratory therapist is prepared didactically and clinically to perform advanced procedures and emergency management.[11]Actual scope of practice varies by region and institution.[12]
International respiratory care
editExcept for the United States and Canada, very few countries have a dedicated professional role for respiratory health. In these countries, respiratory care is provided by physiotherapists, nurses and physicians that have chosen to specialize in this field. In many countries this recognition is in a transition stage; as an example, in 2011, a journal from China claimed that hospitals inBeijing, Chinabegan a recruitment drive to acquire respiratory therapists for their intensive care units where previously nurses were the only clinician.[13]
Canada
editUpon graduation from an accredited school of respiratory therapy, the graduate is then eligible to write the national exam administered by theCanadian Board for Respiratory Care.
Success on this examination will then allow the respiratory therapist to register with any licensing body in Canada. Alberta, Manitoba, New Brunswick, Newfoundland and Labrador, Nova Scotia, Ontario, Quebec and Saskatchewan are the Canadian provinces with provincial licensing bodies; in these provinces, it is illegal to practice the profession of Respiratory Care without first being licensed as a full or provisional member with the provincial licensing body.
These provinces are so-called regulated provinces. In some provinces, one may work provisionally upon graduating, until writing and passing the exam. In all other jurisdictions, the licensing body for the profession of Respiratory Care is theCanadian Society for Respiratory Therapy.
Registration as a full member is optional for respiratory therapists living in regulated provinces, however, for respiratory therapists living in non-regulated provinces, registration as a full member with the CSRT is compulsory. Registration with the provincial regulatory body or the CSRT (in non-regulated provinces) confers upon the respiratory therapist the title of registered respiratory therapist (RRT). Canada and the United States recognize each of their cardio-pulmonary education structure as equal, however, a qualifying exam must be written in order to practice in either nation.
There is pressure for the program to become a degree, like other therapies (physical therapy,occupational therapy) now require a master's degree or greater. However, in some places such asAlberta,Canada the cardio-pulmonary course work is only offered at technical schools that are unable to grant a formal degree.
France
editRespiratory therapy is a sub-specialty ofphysical therapyin France.[14]Respiratory care as a specialty is regulated by the Fédération Française des Masseurs Kinésithérapeutes Rééducateurs.
Germany
editTheGerman Respiratory Society[15]first issued a resolution to develop the dedicated respiratory therapist (RT) role in 2004 as a means to increase the quality of patient care, delegate physician duties and respond to the observed increase in respiratory conditions and diseases. In 2006, a year-long pilot training program was offered to established nurses and physiotherapists.[16]Researchers report that significant additional work is necessary to define and position the role of the respiratory therapist within the current healthcare system.[17]
Italy
editIn Italy, the title of the respiratory therapist can be acquired applying to the master's degree in respiratory therapy.[18]It consists of frontal lessons and various internships throughout Italian hospitals.
Philippines
editInPhilippinesrespiratory therapists are clinicians who have been awarded at minimum aBachelor of Science in Respiratory Caredegree.[19]Licenses to practice respiratory care are regulated by the Professional Regulatory Board of Respiratory therapy and Professional Regulation Commission which is established and legally maintained by thePhilippine Respiratory Therapy Act(Republic Act No. 10024).[20]
United Arab Emirates
editInUnited Arab Emiratesrespiratory therapists must have been awarded aBachelor of Science in Respiratory Care.An additional two-years of experience is required for foreign applicants. Licenses are maintained and awarded by theDubai Health Authority.TheDubai Health Authorityrestricts respiratory therapists to working only in physical medicine and rehabilitation Centers, in hospitals, in surgical clinics with cardio-thoracic surgeons and with physicians in family/general practice or pulmonology.[21]
Saudi Arabia
editSaudi Arabia utilizes respiratory therapists in a similar fashion to Canada and the U.S. Some respiratory therapists from North America travel to Saudi Arabia for temporary need.
Singapore
editIn Singapore, a respiratory therapist is an allied health professional who plays an integral role in the care of critically ill patients in the Intensive Care Units, managing patients on invasive and non-invasive mechanical ventilation, and other respiratory supportive devices. Respiratory therapists are recognized domain experts pertaining to respiratory care and are responsible to facilitate learning and training for respiratory care topics (mechanical ventilation management, artificial airway management, lung protective strategies, diagnostic procedures, etc) for medical students, nursing students, and health care colleagues (nurses, physicians, allied health professions) in the hospitals.
As part of their duties, some of the respiratory therapists are also routinely assigned to staff the emergency department, outpatient ambulatory clinics, diagnostic polysomnography laboratories, as well as the pulmonary function test laboratories to assist with the diagnostic procedures for patients.
All respiratory therapists in Singapore have a baccalaureate degree in respiratory therapy awarded by accredited institutions across the region and the United States and hold board certifications in their country of training. In 2010, the Association of Respiratory Therapists Singapore (ARTS) was established as the national professional organization for respiratory therapists working in Singapore and is a recognized international affiliate of the American Association for Respiratory Therapists (AARC). In 2022, ARTS was also inducted as a council member into the International Council for Respiratory Therapists, with two established leaders serving as co-governors to represent the interests of respiratory therapists in Singapore.
As of 2024, services and care provided by respiratory therapists can be found in all public hospitals in the country and is continuing to grow at with demand.
United States
editIn the United States, a respiratory therapist is a clinician who has at a minimum completed anAssociate of Science in Respiratory Caredegree along with a certification process. After satisfactorily completing required examinations either administered by theNational Board for Respiratory Careor directly by the individual state licensing board (either the medical examiner's board or a special state respiratory care board), the practitioner is then eligible to apply for a license to practice in the region governed by their respective licensing body.
There are two recognized governing bodies in the United States: the State Board of Respiratory Care in the state in which a respiratory therapist is licensed to practice and theNational Board for Respiratory Care(NBRC), a non-profit organization which regulates two levels of certification along with some additional specialist certifications.
TheCertified Respiratory Therapist(CRT) is the certification given after successfully passing the Therapist Multiple ChoiceNBRC-TMCexam; theRegistered Respiratory Therapist(RRT) certification is given after first making the RRT cut-off score on the TMC exam, and passing the Clinical Simulation ExamNBRC-CSE.
Most state boards of respiratory care require proof of the appropriate NBRC credential and award various license titles, including (but not limited to) respiratory care practitioner, licensed registered respiratory therapist, and licensed certified respiratory therapist.
There has been a substantial push to standardize the state licensure by theAmerican Association for Respiratory Care.[22]The NBRC credential is renewed every 5 years for a fee in addition to fees assessed by the state boards of respiratory care.
United Kingdom
editRespiratory therapy in the UK is not a recognized specific profession, but a specialization route available to physicians, nurses, physiotherapists, and occupational therapists.
Common titles include cardio-respiratoryphysiotherapist,clinical respiratoryphysiologist(as well as other healthcare scientists), respiratorynurseand cardio-respiratoryoccupational therapist.
All UK trainedphysiotherapistsreceive advanced training in respiratory therapy theory and practice as a core component of their pre-registration physiotherapy degree program. Following qualification and a period of rotations throughout the core areas of physiotherapy practice, they may then follow a career pathway specializing in respiratory physiotherapy. Areas of practice include critical care, respiratory medicine, cystic fibrosis, asthma, hyperventilation syndrome, general and specialized surgery, non-invasive ventilation, ventilation weaning, cardiac and pulmonary rehab, respiratory therapy outpatient clinics and community respiratory therapy. The Association of Chartered Physiotherapists interested in respiratory care is the specialist interest group for UK physiotherapists working within the field of respiratory therapy.[23]All physiotherapists working within the United Kingdom must be registered with theHealth and Care Professions Council,regardless of their area of clinical practice, in order to be allowed to work in both the public and private sectors. Respiratory physiotherapy postgraduate master's degree and PhD programs exist within the United Kingdom for suitably qualified and experienced therapists.
The main grouping of healthcare scientists working in areas similar to respiratory therapists are respiratory and sleep physiologists.[24]They perform the majority of comprehensive pulmonary physiological assessments (including cardiopulmonary exercise tests) as well as sleep studies. They might also manage non-invasive ventilation services and undertake allergy testing. Similarly, critical care scientists are involved in many aspects of patient critical care that respiratory therapists might, including the management and application of invasive ventilation technologies and other respiratory adjuncts as ell as point-of-care blood testing (including interpreting the results for other clinicians), but are also involved in other areas of critical care, such renal replacement therapy and non-respiratory related patient monitoring; Critical care scientists might also be involved in the provision of non-invasive ventilation services and pre-operative cardiopulmonary exercise testing.[25][26][27]Other healthcare science groupings might also occasionally be involved in some of the physiological investigations mentioned above e.g. neurophysiologists might perform sleep studies to investigate neurological reasons for sleep disturbance, while cardiac scientist might perform cardiopulmonary exercise testing focused on the diagnosis of cardiac issues. Since the advent of modernising scientific careers, there have been a largely unitary model of accreditation pathway for Healthcare Scientists in the UK.[28]The framework can be roughly divided into four stages: an associate/assistant stage (usually not holding any professional registration), a BSc-level practitioner stage eligible for voluntary registration (e.g.with the Registration Council for Clinical Physiologists or the Academy for Healthcare Science Healthcare Science Practitioner Register), an MSc-level Scientist stage where individuals are eligible for state registration as Clinical Scientists with theHealth and Care Professions Council,and a doctoral-level stage that in addition to registration with theHealth and Care Professions Councilinvolves registration on the Academy for Healthcare Science Higher Specialist Scientist Register.[28][29][30]Those on the Higher Specialist Scientist Register are largely equivalent in seniority to medical consultants, though they cannot prescribe; in Respiratory Science this might e.g. involve the advising on the provision of non-invasive ventilation to complex patients.[31][32][33]Healthcare Scientists are usually trained to work with all patient age groups.
Taiwan
editInTaiwan,the respiratory therapist is one of the allied health professionals who need minimum four-years Bachelor of Science in respiratory therapy (Care) for the license. According to the Health Professionals Act and Respiratory Therapist Act lawed in 2002,[34][35]respiratory therapists require "Senior Professional and Technical Examinations" bythe Ministry of Examinationto get the license.[36]
Most respiratory therapists in Taiwan participate in adult, neonatal and pediatricICUcare for artificial airway maintenance, invasive or non-invasive ventilation management, aerosol therapy, oxygen therapy, inhaled Nitric oxide therapy,CPR,chest physiotherapy, artery blood gas analysis, pulmonary rehabilitation, and lung expansion therapy, etc.
Some respiratory therapists also will be available inPFT (Pulmonary Function Testing)room or RCC (Respiratory Care Center) and RCW (Respiratory Care Ward) built for focusing on difficult-weaning patients' ventilator weaning.[37]Moreover, after 5 years of experience in hospital, respiratory therapists can set up a home respiratory care office by themselves.
Nowadays, there are five colleges with the Department of Respiratory Therapy including Chang Gung University, Taipei Medical University, Kao Hsiung Medical University, Chang Gung University of Science and Technology (ChiaYi Campus), and Fu Jen Catholic University.[35]
Yemen
editRespiratory care inYemenhas started in 2005 and the profession has accredited by Yemeni Medical Council in 2020 as one of allied medical professions.
Respiratory care professionals need to complete either minimum three yearsAssociate of Science in Respiratory Careor four-yearsBachelor of Science in respiratory care(BsRC) for the license called YRCLE.[citation needed]there are currently 3 accredited programs in bachelor degree and one postgraduate program asmaster of science in respiratory carein Yemen.
Yemen has joinedInternational Council For Respiratory carein 2020 as the third Arabic country afterSaudi Arabia&UAE.It has currently full member ofInternational Council For Respiratory careand Saleem N. Hamilah, BS, RCP, FNIV, MsRC is the official governor for Yemen.[citation needed]
Respiratory Care Services Administration
editThe Respiratory Care Services Administration (RCSA) is a governmental administration at Yemen's Ministry of Public Health & Population established in July 2019.[38]
Yemeni Association For Respiratory Care
editThe Yemeni Association for Respiratory Care (YARC) is anon profit organizationand is the only professional organization supportingRespiratory Carein the Yemen. In addition to attempting to help respiratory therapists nationally and locally, the YARC is trying to promote the profession as a whole to increase interest and membership. The YARC established in 2017.[citation needed]
Specialist respiratory therapists
editAnesthesia assistants
editThe traditional role of the operating room respiratory therapist has included providing technical support to theanesthesiologistfor the proper use and maintenance of theanestheticgas machine, in addition to also providingairway management.In Ontario, Canada, this role in the operating room has evolved to include a more advanced and specialized role with increasing responsibilities to the respiratory therapist. This "anesthesia assistant" is a distinct occupation from the American "anesthesiologist assistant". These Canadian respiratory therapists are academically prepared to perform activities such as sedation by the administration of anesthetic gases and medications, insertion and management of vascular (arterial and venous) access and assessment of the depth ofanesthesiaunder the guidance of ananesthesiologist.[39]This role is similar to thenurse anesthetist,[40]except that an anesthesia assistant must have ananesthesiologistsupervising them and anurse anesthetist,does not.[41]
Asthma specialists
editAsthmaspecialists work with clinics, hospitals and schools as an educator for teachers, parents, patients and practitioners on asthma and allergies. Respiratory therapists in the role as an asthma educator additionally help diagnose and treat asthma and other respiratory illness.[42]Additionally, an asthma educator is the resource clinician in inpatient and outpatient environments for evaluating and advising physicians on treatment plans and helping facilitate patient understanding and compliance with the plan.[43]In the United States, certified asthma educators (AE-C) are credentialed by theNational Asthma Education Certification Board(NAECB).[44]
In Canada, the Canadian Network for Respiratory Care administers two certifications for the specialization as respiratory therapist asthma educator, the certified asthma educator (CAE) (preferred by practitioners with a pediatric focus) and the certified respiratory educator (CRE), which comprises the CAE program with additional training inCOPD.[45]
Cystic fibrosis
editRespiratory therapists work with people whocystic fibrosisin clinics and hospitals[46]by educating them about their disease and working with them on a treatment plan. While admitted to a hospital, patients with cystic fibrosis have their treatment schedule modified and maintained by respiratory therapists. Maintaining a healthy schedule for pharmacokinetic and physical therapeutic airway clearance typically more frequent than home treatment plans because admissions are usually due to an increased need for therapy during the stay.
Cardiovascular perfusionist
editRespiratory therapists are able to fulfill the role of perfusionist with appropriate training. The perfusionist is a highly trained member of the cardiothoracic surgical team (often time an RT with extra training) which consists ofcardiac surgeons,anesthesiologists,physician assistants,surgical technicians,otherrespiratory therapists,andnurses.The perfusionist's main responsibility is to support the physiological and metabolic needs of the cardiac surgical patient so that thecardiac surgeonmay operate on a still, unbeatingheart.Perfusionist certifications are maintained and awarded by TheAmerican Board of Cardiovascular Perfusion.[47]
Extra-corporeal membrane oxygenation
editExtracorporeal membrane oxygenation(ECMO) is a modifiedcardiopulmonary bypasstechnique used for the treatment of life-threatening cardiac or respiratory failure. An ECMO Clinical Specialist is a technical specialist trained to manage the ECMO system including blood pump, tubing, artificial oxygenator, and related equipment.
The ECMO Specialist is also responsible for the clinical needs of the patient on ECMO which may include bedside management of oxygenation and carbon dioxide removal, maintenance of normal acid-base balance, administration of medications, blood and blood products, and maintenance of appropriate anticoagulation therapies for the blood.[48][49]This ECMO Clinical Specialist may be the bedside critical care nurse specifically trained in ECMO patient and circuit management,[50]or the ECMO system may be primarily managed by aregistered respiratory therapist,[51]or physicians with training as ECMO clinical specialists.[50]
Neonatal & pediatric intensive care
editMuch like adult intensivist respiratory therapists, neonatal and pediatric specialists deal primarily with managing life support for the pediatric or neonatal patient.[52]Pediatric respiratory therapists are trained extensively in antenatal and intrapartum patients and family.[52]In the United States a specialist certification exists and is awarded by theNational Board for Respiratory Care.Available to respiratory therapists holding certification as acertified respiratory therapistorregistered respiratory therapisthowever the registered respiratory therapist is preferred by most institutions.[52][53][54]
Sleep disorder specialist
editRespiratory therapists monitor, interpret and diagnose findings from asleep study,as well as the medical history and physical exam to make the diagnosis and decide on treatment related to sleep-disorders. A sleep study can also help diagnosenarcolepsy.[55]
In the United States a sleep disorder specialist can be aregistered respiratory therapistwith the sleep disorder specialist certification (RRT-SDS) who performs sleep disorders testing and therapeutic intervention along with a diagnosis of sleep-related disease such asObstructive Sleep ApneaorCentral Apnea.In Canada, it is often an RT with additional training to become a Registered Polysomnography Technician (RPSGT)
Case management
editCase management is a collaborative process that assesses, plans, implements, coordinates, monitors, and evaluates the options and services required to meet the client's health and human services needs. It is characterized by advocacy, communication, and resource management and promotes quality and cost-effective interventions and outcomes. Eligibility and certification is maintained by the Commission for Case Management Certification, a body certifying healthcare professionals in the United States.[56]
Surface & air transport specialist
editRespiratory therapists work with nurses, physicians, and paramedics inemergency flightand ground transport.[57][58]They are a vital practitioner delivering care inside helicopters, air ambulance or ground ambulance working to pick up a patient and move them to a facility that has what they need. In the United States certification for transport (C-NPT) is currently awarded by The National Certification Corporation.[59]
Pulmonary research and science
editRespiratory therapists are sometimes referred to as respiratory scientists who are specialists in pulmonary function.[60]Respiratory therapists work withPulmonologistsin both clinical and general research of therespiratory system,ranging from the anatomy of therespiratory epitheliumto the most effective treatment ofpulmonary hypertensionin pediatrics. Scientific research also takes place to look for causes and possible treatment in diseases such asasthmaandlung cancer.[61]
History of respiratory care
editTheprofession of respiratory carewas officially established in the United Statesc. 1930;[22]and respiratory research has officially existed since the early 1900s.[62]During the early years, respiratory therapists were referred to as "oxygen technicians", and most of their activities involved moving cylinders of compressed gas and administering oxygen via nasal catheter or oxygen tent.[63]Most oxygen technicians were trained on the job, although brief training programs began to appear in the late 1940s and 1950s.[64][65]
Today the profession hardly resembles what it was in the 1940s. Respiratory therapists provide direct care, patient education, and care coordination. They are academically trained in respiratory nursing and respiratory medicine. They practice in acute care facilities, long-term acute care facilities, skilled nursing facilities, assisted-living centers, subacute care units, rehabilitation centers, diagnostics units, and in the home.[66]Respiratory therapist training has also dramatically changed. Current accreditation standards require Respiratory therapists to have, at minimum, anAssociate of Science in Respiratory Caredegree from an accredited program.[67]Legal requirements to practice respiratory therapy have also dramatically changed. 49 states now legally recognize respiratory therapists.[68]Limited permits or state licenses are now required in all states except Alaska, which has no statutory authority over the practice of respiratory care. All states that have licensure requirements also require continuing education.
In 2007 theAmerican Association for Respiratory Care(AARC) began developing recommendations for the promotion of the field of respiratory care in the United States[22]in response to increased concern regarding licensure and credentialing issues as well as international recognition of those practicing in the United States.[6]The task force decided to recommend that by 2015 the minimum education requirement for licensure and certification as a respiratory therapist be abachelor of science in respiratory therapy(BSRT).[69]The AARC task force also recommended theAmerican Respiratory Care Foundationchange its scholarship policies and only award assistance and grants to those working toward a bachelor's degree. TheCommittee on Accreditation for Respiratory Care(CoARC) was asked by the AARC task force to change its accreditation standards and no longer accredit associates level respiratory care programs.[69]The CoARC replied by a press release rejecting the recommendation.[70]In 2011 legislation introduced by the AARC will help improve the use of respiratory therapists in clinical applications by allowing them to manage patients withasthmaandCOPDseeing a clinic for routine checkups.[71]Similar billshave been introduced before and have died in committee.[4][5][72]
See also
editReferences
edit- ^"PCC Notes: Respiratory students train".The Reflector.Archivedfrom the original on 5 August 2016.Retrieved6 November2011.
- ^Harbrecht BG, Delgado E, Tuttle RP, Cohen-Melamed MH, Saul MI, Valenta CA (2009). "Improved outcomes with routine Respiratory Therapist evaluation of non-intensive-care-unit surgery patients".Respiratory Care.54(7):861–7.doi:10.4187/002013209793800457.PMID19558737.S2CID32274631.
- ^O'Malley RJ, Rhee KJ (1993)."Contribution of air medical personnel to the airway management of injured patients".Air Med J.12(11–12):425–8.doi:10.1016/S1067-991X(05)80138-5.PMID10130326.
- ^ab112th Congress (2011) (Mar 8, 2011)."H.R. 941".Legislation.GovTrack.us.Archivedfrom the original on November 17, 2011.RetrievedAugust 28,2011.
Medicare Respiratory Therapy Initiative Act of 2011
{{cite web}}:CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ab110th Congress (2007) (Oct 25, 2007)."H.R. 3968".Legislation.GovTrack.us.Archivedfrom the original on November 17, 2011.RetrievedAugust 28,2011.
Medicare Respiratory Therapy Initiative Act of 2007
{{cite web}}:CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^abShelledy DC, Wiezalis CP (2005)."Education and credentialing in respiratory care: where are we and where should we be headed?".Respiratory Care Clinics of North America.11(3):517–30.doi:10.1016/j.rcc.2005.04.003.PMID16168918.
- ^Rowley DD, Mayo DF, Durbin CG (May 2000). "Initial experience with a Respiratory Therapist arterial line placement service".Respiratory Care.45(5):482–5.PMID10813223.
- ^Barnes TA, Kacmarek RM, Kageler WV, Morris MJ, Durbin CG (2011)."Transitioning the respiratory therapy workforce for 2015 and beyond".Respir Care.56(5):681–90.doi:10.4187/respcare.01169.PMID21276324.
- ^"National Asthma Educator Certification Board".NAECB.Retrieved2022-05-10.
- ^Kacmarek RM, Durbin CG, Barnes TA, Kageler WV, Walton JR, O'Neil EH. Creating a vision for respiratory care in 2015 and beyond. Respir Care 2009;54(3):375-389.
- ^Barnes TA, Gale DD, Kacmarek RM, Kageler WV. Competencies needed by graduate respiratory therapists in 2015 and beyond. Respir Care 2010;55(5):601-616.
- ^American Association for Respiratory Care. AARC 2009 respiratory therapist human resource study. Irving, Texas: AARC; June 2009.
- ^Li J, Zhan QY, Liang ZA, Tu ML, Sun B, Yao XL, et al. (2011)."Respiratory Care Practices and Requirement for Respiratory Therapists in Beijing ICUs".Respiratory Care.57(3):370–6.doi:10.4187/respcare.01093.PMID22005194.S2CID1646513.
- ^World Confederation for Physical Therapy. Federation Francaise des Masseurs Kinesitherapeutes Reeducateurs
- ^"Master Universitario in fisioterapia e riabilitazione respiratoria | ARIR Associazione riabilitatori della insufficienza respiratoria".www.arirassociazione.org(in Italian).Archivedfrom the original on 2017-12-31.Retrieved2017-12-30.
- ^Karg O, Bubulj C, Esche B, Geiseler J, Bonnet R, Mäder I. [The Respiratory Therapist]. Pneumologie. 2008;62(11):685-9.
- ^Karg, O., Bubulj, C., Esche, B., Geiseler, J., Bonnet, R., Mader, I., 2008. Karg, O., Bonnet, R., Magnussen, H., Kohler, D., 2008
- ^Sapienza E."Master Universitario in fisioterapia e riabilitazione respiratoria | ARIR Associazione riabilitatori della insufficienza respiratoria".www.arirassociazione.org(in Italian).Archivedfrom the original on 2017-12-31.Retrieved2017-12-30.
- ^American Association for Respiratory Care(2010-03-12)."Philippines Enacts Licensure for RTs".Archivedfrom the original on 2011-12-05.Retrieved2012-02-12.
- ^Kabiling, Genalyn (2010-03-19)."Gov't regulates practice of respiratory therapy".Manila Bulletin.Philippines.Archivedfrom the original on 2010-03-26.Retrieved2012-02-10.
- ^Dubai Health Authority."Allied Healthcare Professionals' Licensure"(PDF).Dubai Health Authority (DHA). Archived fromthe original(PDF)on 2012-04-17.Retrieved2012-02-03.
- ^abcKacmarek RM, Durbin CG, Barnes TA, Kageler WV, Walton JR, O'Neil EH (2009). "Creating a vision for respiratory care in 2015 and beyond".Respiratory Care.54(3):375–89.PMID19245732.
- ^http://www.acprc.org.ukArchived2014-12-18 at theWayback Machineretrieved 23 November 2014
- ^"Respiratory physiology and sleep sciences".Health Careers.NHS.
- ^"Critical care science".25 March 2015.
- ^Fowler N, Ali R, Bannard-Smith J, Jennings C, Playfor S, Pruski M (February 2021)."Critical care scientists: Role, training and future directions".Journal of the Intensive Care Society.22(1):1–7.doi:10.1177/1751143720903232.PMC7890759.PMID33643426.
- ^"GPICS".
- ^ab"An overview of Modernising Scientific Careers".GOV.UK. 2 December 2010.
- ^"Home".searchtheregister.rccp.co.uk.
- ^"Join the Register".
- ^Shakespeare J, Parkes E, Bryce M, Hull JH (December 2019)."Advanced roles in respiratory healthcare science: it's not just spirometry".Breathe.15(4):267–269.doi:10.1183/20734735.0310-2019.PMC6885340.PMID31803258.
- ^"Specialty: HPS1-3-2-20—Higher Specialist Scientist Training | Curriculum Library | NSHCS".
- ^"Specialty: HPS1-3-1-20—Higher Specialist Scientist Training | Curriculum Library | NSHCS".
- ^"Toàn quốc pháp quy tư liêu khố".
- ^abVõng nhuyễn cổ phân hữu hạn công tư:www.npois.com.tw."Đài loan hô hấp trị liệu học hội".Đài loan hô hấp trị liệu học hội.Archived fromthe originalon 2020-11-27.Retrieved2020-03-22.
- ^"Khảo tuyển bộ".
- ^"Đài loan hô hấp khí trường kỳ sử dụng khái huống"(PDF).Toàn dân kiện khang bảo hiểm tranh nghị thẩm nghị ủy viên hội tranh nghị thẩm nghị báo đạo.Archived(PDF)from the original on 2020-03-22.
- ^Hamilah, Saleem N; Al Ahmari, Mohammed; Alsabri, Mohammed A; Alrubaiee, Gamil G (August 2021)."Respiratory Care Profession in Yemen: Past, Present, and Future".Indian Journal of Critical Care Medicine.25(8):891–892.
- ^"Respiratory Therapists as Anesthesia Assistants"(PDF).Archived(PDF)from the original on 2013-03-27.Retrieved2012-03-26.
- ^"Five facts about AAs".American Academy of Anesthesiologist Assistants. Archived fromthe originalon 2006-09-26.Retrieved2010-11-25.
- ^United States Code of Federal Regulations (42 C.F.R. § 482.52 Condition of participation: Anesthesia services)
- ^"Pediatric asthma clinic team | Children's Hospital Vanderbilt".Archivedfrom the original on 2012-03-19.Retrieved2011-08-17.Vanderbilt Children's Asthma Clinic
- ^Davis JJ, Bailey WC (2006)."Teach a man to fish and you have fed him for a lifetime".Chest.129(2):220–1.doi:10.1378/chest.129.2.220.PMID16478832.
- ^http://www.naecb.orgArchived2011-08-09 at theWayback MachineNational Asthma Education Certification Board (NAECB)
- ^"Canadian Network for Respiratory Care | Réseau canadien pour les soins respiratoire".Archivedfrom the original on 2012-10-09.Retrieved2012-01-07.Canadian Network for Respiratory Care Certification for Asthma and Respiratory Educators (CAEs and CREs)
- ^"Children's Hospital Vanderbilt | Our Services | A to Z Listing | Allergy, Immunology, and Pulmonary Medicine | Clinics and Programs | Cystic Fibrosis Diagnosis and Treatment Center | Meet Our Team".Archivedfrom the original on 2012-03-19.Retrieved2011-08-17.Vanderbilt Children's Hospital Cystic Fibrosis Clinic
- ^"Clinical Perfusionists Currently Certified by the American Board of Cardiovascular Perfusion through December 31, 2010".American Board of Cardiovascular Perfusion. Archived fromthe originalon February 13, 2010.Retrieved2010-02-15.
- ^Dalton HJ (2011)."Extracorporeal life support: moving at the speed of light".Respiratory Care.56(9):1445–53, discussion 1453–6.doi:10.4187/respcare.01369.PMID21944690.
- ^"ECMO Program - Respiratory Care Services - Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center".Archivedfrom the original on 2011-09-07.Retrieved2011-08-18.Wake Forrest Baptist Health
- ^abExtracorporeal Life Support Organization, ELSO."ELSO Guidelines for ECMO Centers"(PDF).University of Michigan Health System. Archived fromthe original(PDF)on 2012-04-26.
- ^American Association for Respiratory Care(July 2007) [1998],Respiratory Therapists as Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO) Specialists,archivedfrom the original on 2012-04-05
- ^abcKashani KB, Farmer JC (2006)."The support of severe respiratory failure beyond the hospital and during transportation".Curr Opin Crit Care.12(1):43–9.doi:10.1097/01.ccx.0000198057.35212.3e.PMID16394783.S2CID46191625.
- ^Beninati W, Meyer MT, Carter TE (2008)."The critical care air transport program".Crit Care Med.36(7 Suppl): S370-6.doi:10.1097/CCM.0b013e31817e3143.PMID18594265.S2CID6439109.
- ^DiBlasi RM, Cheifetz IM (2011)."Neonatal and pediatric respiratory care: what does the future hold?"(PDF).Respiratory Care.56(9):1466–80.doi:10.4187/respcare.01505.PMID21944692.Archived(PDF)from the original on 2017-08-09.
- ^Epstein LJ, Kristo D, Strollo PJ, Friedman N, Malhotra A, Patil SP, et al. (2009)."Clinical guideline for the evaluation, management and long-term care of obstructive sleep apnea in adults".J Clin Sleep Med.5(3):263–76.doi:10.5664/jcsm.27497.PMC2699173.PMID19960649.
- ^"Welcome to CCMC".Archived fromthe originalon 2011-08-12.Retrieved2011-08-16.Commission for Case Management Certification
- ^"Search Results"(PDF).Archived(PDF)from the original on 2012-04-13.Retrieved2013-06-19..(Accessed on June 18, 2013).
- ^"Vanderbilt LifeFlight in Nashville, TN - Modes of Transportation".Archived fromthe originalon 2011-10-03.Retrieved2011-08-18.
- ^"Archived copy".Archivedfrom the original on 2011-08-18.Retrieved2011-08-18.
{{cite web}}:CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)The National Certification Corporation - ^Cheifetz IM (2011)."Management of acute lung injury: sharing data between adults and children".Respiratory Care.56(9):1258–68, discussion 1268–72.doi:10.4187/respcare.01413.PMID21944680.
- ^Curley MA (2011)."Respiratory research in the critically ill pediatric patient: why is it so difficult?".Respiratory Care.56(9):1247–54, discussion 1254–7.doi:10.4187/respcare.01255.PMID21944679.
- ^"Smother Small Dog To See it Revived. Successful Demonstration of an Artificial Respiration Machine Cheered in Brooklyn. Women in the Audience, But Most of Those Present Were Physicians. The Dog, Gathered in from the Street, Wagged Its Tail".New York Times.May 29, 1908.Retrieved2007-12-25.
An audience, composed of about thirty men and three or four women, most of the men being physicians, attended a demonstration of Prof. George Poe's machine for producing artificial respiration in the library of the Kings County Medical Society, at 1,313 Bedford Avenue, Brooklyn, last night, under the auspices of the First Legion of the Red Cross Society.
- ^Smith GA. Respiratory care: evolution of a profession. Lenexa, Kansas: AMP; 1989.
- ^Pierson DJ (2001). "The future of respiratory care".Respir Care.46(7):705–18.PMID11403703.
- ^Weilacher RR. History of the respiratory care profession. In: Hess DR, MacIntyre NR, Mishoe SC, Galvin WF, Adams AB, Saposnick AB, editors. Respiratory care: principles and practice. Philadelphia: Saunders; 2002.
- ^American Association for Respir Care. Position statement. Definition of respiratory care. December 2006."Position Statement - Definition of Respiratory Care".Archivedfrom the original on 2012-06-11.Retrieved2012-02-03..Accessed January 7, 2009
- ^Commission on Accreditation of Allied Health Education Programs, or a diploma from an accredited school. Standards and guidelines for the profession of respiratory care. 2003."Archived copy"(PDF).Archived(PDF)from the original on 2009-03-06.Retrieved2012-02-03.
{{cite web}}:CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link).Accessed January 7, 2009. - ^"Hawaii Revised Statutes Chapter 466D-RespiratoryTherapists""Department of Commerce and Consumer Affairs"(PDF).Archived(PDF)from the original on 2010-12-09.Retrieved2011-11-01.;July 2011
- ^abBarnes TA, Kacmarek RM, Kageler WV, Morris MJ, Durbin CG (2011)."Transitioning the respiratory therapy workforce for 2015 and beyond".Respiratory Care.56(5):681–90.doi:10.4187/respcare.01169.PMID21276324.
- ^CoARC Memorandum to Our Communities of Interest Regarding 2015 Recommendations"News and Announcements".Archivedfrom the original on 2011-10-09.Retrieved2011-11-01.November 15, 2010
- ^112th Congress (2011) (Mar 8, 2011)."H.R. 941".Legislation.GovTrack.us.Archivedfrom the original on October 26, 2011.RetrievedAugust 28,2011.
Medicare Respiratory Therapy Initiative Act of 2011
{{cite web}}:CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^110th Congress (2008) (Mar 5, 2008)."S. 2704".Legislation.GovTrack.us.RetrievedAugust 28,2011.
Medicare Respiratory Therapy Initiative Act of 2008
{{cite web}}:CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link)