TheTruckee Riveris ariverin theU.S. statesofCaliforniaandNevada.The river flows northeasterly and is 121 miles (195 km) long.[3][6]The Truckee is the sole outlet ofLake Tahoeand drains part of the highSierra Nevada,emptying intoPyramid Lakein theGreat Basin.Its waters are an important source ofirrigationalong its valley and adjacent valleys.
| Truckee River | |
|---|---|
 The Truckee River just east ofTruckee, California | |
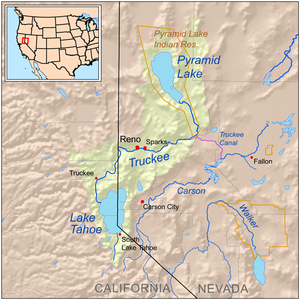 Map of the Pyramid Lake drainage basin | |
| Etymology | Named after thePaiutechiefTruckee |
| Native name |
|
| Location | |
| Country | United States |
| State | California,Nevada |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | Lake Tahoe |
| • location | Sierra Nevada,California |
| • coordinates | 39°10′3″N120°8′39″W/ 39.16750°N 120.14417°W[2] |
| • elevation | 6,233 ft (1,900 m)[3] |
| Mouth | Pyramid Lake |
• location | Nevada |
• coordinates | 39°51′27″N119°26′53″W/ 39.85750°N 119.44806°W[2] |
• elevation | 3,793 ft (1,156 m)[2] |
| Length | 121 mi (195 km)[3] |
| Basin size | 3,060 sq mi (7,900 km2)[4] |
| Discharge | |
| • location | USGSgage 10350000, Truckee River at Vista, NV[5] |
| • average | 804 cu ft/s (22.8 m3/s)[5] |
| • minimum | 7 cu ft/s (0.20 m3/s) |
| • maximum | 17,400 cu ft/s (490 m3/s) |
Naming of the river
editANorthern Paiuteword for the Truckee is Kuyuinahukwa. Kuyui- refers to theCui-ui,a species of fish endemic toPyramid Lakewhich is central to the lives of theNorthern Paiuteband called the Kuyui Dükadü (cui-ui-fish-eaters).[7]
In theWasho language,different parts of the river have different names. Two names, ‘Át’abi wá’t’a and Á’waku wá’t’a translate to "trout stream."[8]The latter name refers to the river at and aroundPyramid Lake.[9]At the outlet at Lake Tahoe, there are multiple names as well. Dawbayódok is said to refer to the area when one is situated "on the down side" of the outlet, while Dawbayóduwé is used when one is "on the up side." Debeyúmewe, translated as "coming out," is less specific.[10]
WhenJohn C. FrémontandKit Carsonascended the Truckee River on January 16, 1844, they called it the Salmon Trout River,[1]after the hugeLahontan cutthroat trout(Oncorhynchus clarki henshawi) that ran up the river from Pyramid Lake to spawn. However, the river was ultimately named after aPaiutechief known asTruckee,who in 1844 guided an emigrant party from the headwaters of theHumboldt Riverto California via the Truckee River,Donner Lake,andDonner Pass.Appreciative of their Native American guide's services, the party named the river after him.[11]The chief's real name might not have been Truckee, but perhapsTru-ki-zo,which could have become distorted as "Truckee". There are numerous other theories about Chief Truckee and his name.[12]
Course and watershed
editThe Truckee River's source is the outlet ofLake Tahoe,at the dam on the northwest side of the lake nearTahoe City, California.It flows generally northeast through the mountains toTruckee, California,then turns sharply to the east and flows into Nevada, throughRenoandSparksand along the northern end of theCarson Range.AtFernleyit turns north, flowing along the east side of thePah Rah Range.It empties into the southern end of Pyramid Lake, a remnant of prehistoricLake Lahontan,in northernWashoe Countyin thePyramid Lake Indian Reservation.[13]
The Truckee River'sendorheicdrainage basinis about 3,060 square miles (7,900 km2), of which about 2,300 square miles (6,000 km2) are in Nevada.[4]The Middle Watershed is regarded as the 15 miles (24 km) of river and its tributaries from Tahoe City inPlacer County,through the Town of Truckee inNevada County,to the state line betweenSierraandWashoecounties. The major tributaries to the Truckee River in California from the Lake Tahoe outlet and heading downstream include:Bear Creek,Squaw Creek, Cabin Creek, Pole Creek,Donner Creek,Trout Creek,Martis Creek,Prosser Creek, the Little Truckee River, Gray Creek, and Bronco Creek. Major lakes and reservoirs in the California part of the watershed include Lake Tahoe,Donner Lake,Independence Lake (California),Webber Lake,Boca Reservoir,Stampede Reservoir,Prosser Creek Reservoir,and Martis Creek Reservoir.[14]In the Lower Watershed,Steamboat Creek,which drainsWashoe Lake,is the major tributary to the Truckee River.
River modifications
editLike many other rivers in the western United States, the Truckee's flow is highly regulated, with most river flow fully allocated through a system ofwater rights,set in 2015 by the Truckee River Operating Agreement. This system over-allocates available water during low flow periods. Disputes occur among those asserting rights to the water. In the early 20th century, theNewlands Reclamation Actinstituted a diversion that removed river flows from the Truckee River watershed and transferred them to the Carson River watershed.[15]Currently theTruckee–Carson Irrigation Districtsupervises the diversion of approximately one-third of the river flow at theDerby Damto theLahontan Valleyto irrigate alfalfa and pastures. Truckee River water is also supplied to the resort communities surrounding Lake Tahoe, the greater metropolitan area of Reno and Sparks, and the Pyramid Lake Paiute Indian Reservation. TheU.S. Fish and Wildlife Serviceuses some of the water to inducespawningof the endangered fishcui-uiand to provide drought relief.
Ecology
editBeavers were re-introduced to the Truckee River watershed andTahoeBasin by theCalifornia Department of Fish and Game(CDFG) and theU. S. Forest Servicebetween 1934 and 1949 in order to prevent stream degradation and to promote wetland restoration. That beaver were once native to the area is supported by the fact that theWashohave a word for beaver,c'imhélhel[16][17]and thenorthern PaiuteofWalker Lake,Honey LakeandPyramid Lakehave a word for beaversu-i'-tu-ti-kut'-teh.[18]WhenStephen Powersvisited the northern Paiute to collect Indian materials for theSmithsonian Institutionin preparation for theCentennial Exhibition of 1876,he reported that the northern Paiute wrapped their hair in strips of beaver fur, made medicine from parts of beaver and that their creation legend included beaver.[18]In addition, fur trapperStephen Hall Meek"set his traps on the Truckee River in 1833", which strongly suggests that he saw a beaver or beaver sign.[19]Supporting this line of evidence, Tappe records in 1941 an eyewitness who said beaver were plentiful on the eastern slope of the Sierra Nevada on the upper part of the Carson River and its tributaries inAlpine Countyuntil 1892 when they fell victim to heavy trapping.[20]James "Grizzly" Adams' also reports trapping beaver in the lowerCarson Riveraround 1860, "In the evening we caught a fine lot of salmon-trout (Cutthroat trout), using grasshoppers for bait, and in the night killed half a dozen beavers, which were very tame. "[21]Recent novel physical evidence of beaver's historic presence in the Sierra Nevada was the discovery of beaver dams dating to the 1850s inRed Clover Creekin theFeather Riverwatershed.[22]The presence of beaver dams has been shown to either increase the number of fish, their size, or both, in a study of brook, rainbow and brown trout in nearbySagehen Creek,which flows into theLittle Truckee Riverat an altitude of 5,800 feet (1,800 m) and is a stream typical of the eastern slope of the northernSierra Nevada.[23]Not only have aspen and cottonwood survived ongoing beaver colonization but a recent study of ten Tahoe streams utilizing aerial multispectral videography, includingTrout Creekand Cold Creek, has shown that deciduous, thick and thin herbaceous vegetation has increased near beaver dams, whereas coniferous trees are decreased.[24]Benefits of beaver dams include removal of sediment and excessive pollutants travelling downstream, which improves water clarity, which was shown to worsen when beaver dams were recently removed in nearbyTaylor CreekandWard Creek.[25]Flooding from beaver dams is relatively inexpensively controlled withflow devices.
Recreation
editThe river is heavily used for recreation, includingwhitewater raftingandfly fishing.A common rafting run is the River Ranch Run. Starting from the outlet gates at Lake Tahoe stretching about 3 miles (4.8 km), the run ends at the River Ranch Restaurant. These rapids are almost all class 1 and class 2. In downtown Reno the river has been sculpted into a half-mile Class 2/3 whitewater park, and is used mainly forkayaking.[26]
The Truckee River is western Nevada's largest river. It supports a large sport fishing population each year. Kim Tisdale of theNevada Department of Wildlife(NDOW), is the state's Western Regions Fishery Supervisor; she commented that NDOW's goal is for a catch rate of one to two fish per hour in the Truckee. To accomplish this, NDOW stocks a total of 105,000 trout per year. 70,000 of those are nativeLahontan cutthroat trout(Oncorhynchus clarki henshawi) and the rest are non-nativeRainbow trout(Oncorhynchus mykiss).[27]The Truckee also boasts a healthy, self-sustaining non-nativeBrown trout(Salmo trutta) population.[27]
Hydrology and water quality
editBecause of the endangered species present and because theLake Tahoe Basincomprises the headwaters of the Truckee River, the river has been the focus of several water quality investigations, the most detailed starting in the mid-1980s. Under the direction of theU.S. Environmental Protection Agency,a comprehensive dynamichydrology transport modelwas developed by Earth Metrics Inc.[28]The model's name was subsequently changed toDSSAM,and it was applied to analyze land use, and wastewater management decisions throughout the Truckee River Basin of 3,120 square miles (8,081 km2) and to provide guidance in other U.S. river basins.[29]Analytes addressed includednitrogen,reactivephosphate,dissolved oxygen,total dissolved solidsand nine other parameters. Based on the use of the model, some decisions have been influenced to enhance riverine quality and aid the viability of associatedbiota.Impacts upon the receiving waters ofPyramid Lakewere also analyzed. It is thought that dumping raw sewage into the Truckee River is a detriment to the water quality in several communities.
See also
editReferences
edit- ^abJohn Charles Fremont (1847).Narrative of the exploring expedition to the Rocky mountains: in the year 1842, and to Oregon and north California in the years 1843–44.Hall & Dickson. p.309.Retrieved2010-12-13.
salmon trout river.
- ^abcU.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: Truckee River
- ^abcU.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline data.The National Map,accessed October 20, 2012
- ^abRigby, Jim G. (1998).The 1997 New Year's Floods in Western Nevada.Nevada Bureau of Mines and Geology. p. 5.ISBN978-1-888035-03-2.
- ^ab"Water resources data for the United States, Water Year 2009; gage 10350000, Truckee River at Vista, NV"(PDF).USGS.Retrieved4 August2010.
- ^Justin Bartlett; John J. Warwick (August 2009). "Assessing the Impacts of Nutrient Load Uncertainties on Predicted Truckee River Water Quality".Journal of Environmental Engineering.135(8): 636–644.doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9372(2009)135:8(636).
- ^Ginny Bengston (2002).Northern Paiute and Western Shoshone Land Use in Northern Nevada: A Class I Ethnographic/Ethnohistoric Overview(PDF). SWCA Environmental Consultants. pp. 6, 50. Retrieved 2022-12-30.
- ^Natalie E. Davenport (2019).Naming, Remembering, and Experiencing We’ lmelt’ iʔ [northern Washoe] Cultural Spaces in Wa she shu It Deh [Washoe Land](PDF).ScholarWorks, University of Nevada, Reno. p. 235.Retrieved2022-12-31.
Ahwacoo watah, means "trout stream" (Lindström 1992a, 196 from Freed 1966; Nevers 1976, 4; Dixon, Schablitsky, and Novak 2011, 257).... 'Át'abi wá't'a (d'Azevedo 1956, 57/#134) was also translated as "trout stream" (Lindström 1992a, 196; from Freed 1966).
- ^Natalie E. Davenport (2019).Naming, Remembering, and Experiencing We’ lmelt’ iʔ [northern Washoe] Cultural Spaces in Wa she shu It Deh [Washoe Land](PDF).ScholarWorks, University of Nevada, Reno. p. 304.Retrieved2022-12-31.
Freed (1966) and Nevers (1976) provided the Washoe name, Ahwacoo watah, "trout stream," for the segment of the Truckee River near Pyramid Lake
- ^Natalie E. Davenport (2019).Naming, Remembering, and Experiencing We’ lmelt’ iʔ [northern Washoe] Cultural Spaces in Wa she shu It Deh [Washoe Land](PDF).ScholarWorks, University of Nevada, Reno. p. 209.Retrieved2022-12-31.
- ^"Truckee River Chronology".State of Nevada Division of Water Resources.Archived fromthe originalon May 27, 2010.RetrievedMay 1,2024.
- ^Chief TruckeeArchived2012-10-28 at theWayback Machine,Truckee–Donner Historical Society
- ^USGStopographic maps
- ^David McGraw; Alan McKay; Guohong Duan; Thomas Bullard; Tim Minor; Jason Kuchnicki (July 2001).Water Quality Assessment and Modeling of the California Portion of the Truckee River Basin McGraw 2001(PDF)(Report). Lahontan Regional Water Quality Control Board.Retrieved2012-10-21.
- ^"Welcome to the TROA – Truckee River Operating Agreement".www.troa.net.Retrieved13 September2017.
- ^"The Washo Project Online Dictionary".Retrieved2012-07-07.
- ^A. L. Kroeber (1919)."30".Handbook of Indians of California.Retrieved2010-08-19.
- ^abDon D. Fowler; Catherine S. Fowler; Stephen Powers (Summer–Autumn 1970). "Stephen Powers'" The Life and Culture of the Washo and Paiutes "".Ethnohistory.17(3/4): 117–149.doi:10.2307/481206.JSTOR481206.
- ^Jesse D. Mason (1881).History of Amador County.Oakland, California: Thompson & West.Retrieved2010-12-24.
- ^Tappe, Donald T. (1942)."The Status of Beavers in California"(PDF).Game Bulletin No. 3.California Department of Fish & Game: 14.Retrieved2010-12-30.
- ^Theodore Henry Hittell (1861).The adventures of James Capen Adams: mountaineer and grizzly bear hunter, of California.Crosby, Nichols, Lee and company. p.250.Retrieved2011-12-24.
salmon-trout.
- ^James, C. D.; Lanman, R. B. (Spring 2012). "Novel physical evidence that beaver historically were native to the Sierra Nevada".California Fish and Game.98(2): 129–132.
- ^Gard R (1961). "Effects of beaver on trout in Sagehen Creek, California".Journal of Wildlife Management.25(3): 221–242.doi:10.2307/3797848.JSTOR3797848.
- ^Michael Benson Ayers (October 1997).Aerial Multispectral Videography for Vegetation Mapping and Assessment of Beaver Distribution within Selected Riparian Areas of the Lake Tahoe Basin(Thesis). University of Nevada at Reno. p. 71.Retrieved2010-08-26.
- ^Sarah Muskopf (October 2007).The Effect of Beaver (Castor canadensis) Dam Removal on Total Phosphorus Concentration in Taylor Creek and Wetland, South Lake Tahoe, California(Thesis). Humboldt State University, Natural Resources.hdl:2148/264.
- ^"Whitewater Park".City of Reno.Retrieved2020-10-05.
- ^abTisdale, Kim. Telephone Interview. 29 June 2012
- ^C. Michael Hogan. Marc Papineau et al.,Development of a dynamic water quality simulation model for the Truckee River,Earth Metrics Inc.,Environmental Protection AgencyTechnology Series, Washington D.C. (1987)
- ^USEPA. 1991. Guidance for water quality-based decisions: The TMDL process. EPA 440/4-91-001. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Water, Washington, DC.