| Main page | New articles & Tasks |
 The Energy Portal Welcome to Wikipedia's Energy portal, your gateway to energy. This portal is aimed at giving you access to all energy related topics in all of its forms.
|
Page contents: Selected article • Selected image • Selected biography • Did you know? • General images • Quotations • Related portals • Wikiprojects • Major topics • Categories • Help • Associated Wikimedia |
Introduction
Energy (from Ancient Greek ἐνέργεια (enérgeia) 'activity') is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of heat and light. Energy is a conserved quantity—the law of conservation of energy states that energy can be converted in form, but not created or destroyed; matter and energy may also be converted to one another. The unit of measurement for energy in the International System of Units (SI) is the joule (J).
Common forms of energy include the kinetic energy of a moving object, the potential energy stored by an object (for instance due to its position in a field), the elastic energy stored in a solid object, chemical energy associated with chemical reactions, the radiant energy carried by electromagnetic radiation, and the internal energy contained within a thermodynamic system. All living organisms constantly take in and release energy.
Due to mass–energy equivalence, any object that has mass when stationary (called rest mass) also has an equivalent amount of energy whose form is called rest energy, and any additional energy (of any form) acquired by the object above that rest energy will increase the object's total mass just as it increases its total energy.
Human civilization requires energy to function, which it gets from energy resources such as fossil fuels, nuclear fuel, or renewable energy. The Earth's climate and ecosystems processes are driven by the energy the planet receives from the Sun (although a small amount is also contributed by geothermal energy). (Full article...)
Selected article
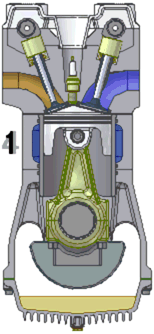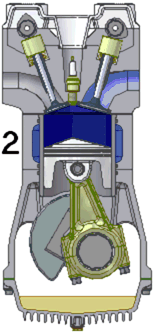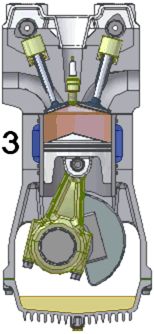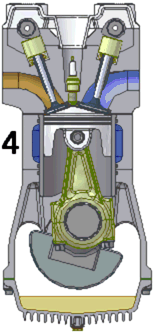
The defining feature of an internal combustion engine is that useful work is performed by the expanding hot gases acting directly to cause movement, for example by acting on pistons, rotors, or even by pressing on and moving the entire engine itself.
Internal combustion engines are most commonly used for mobile propulsion systems, where their high power-to-weight ratios, together with excellent fuel energy-density, are advantageous. They have appeared in almost all automobiles, motorbikes, many boats, and in a wide variety of aircraft and locomotives. Where very high power is required, such as jet aircraft, helicopters and large ships, they appear mostly in the form of gas turbines. They are also used for electric generators and by industry.
The most common fuels in use today are hydrocarbons derived from petroleum including diesel, gasoline and liquified petroleum gas. Most internal combustion engines designed for gasoline can run on natural gas or liquified petroleum gases without modifications except for the fuel delivery components. Liquid and gaseous biofuels, including ethanol and biodiesel can also be used, and trials of hydrogen fuel have been in progress for some years.
Selected image

Photo credit: Andreas Tille
Geysers erupt periodically due to surface water being heated by geothermal heat.
Did you know?
- During World War I, the German Army produced shale oil from Yarmouk oil shale deposits in Jordan to operate the Hijazi Railway (pictured)?
- Dennis Spurgeon, formerly chief operating officer at uranium supplier USEC Inc., became the United States Assistant Secretary for Nuclear Energy in 2006?
- Japan Canada Oil Sands Limited was the first offshore oil company to exploit the Athabasca oil sands in Canada?
- Teesside Power Station is the largest combined-cycle gas turbine (CCGT) plant in Europe.?
- The Klaipėda Geothermal Demonstration Plant in Lithuania was the first geothermal plant in the Baltic Sea region?
- Hitachi Zosen Corporation built the first oil tanker in Japan in 1908 per an order by Standard Oil Company?
- Coalbed methane is a form of natural gas extracted from coal beds?
- When constructed in 1906, the Baku–Batumi pipeline was the world's longest kerosene pipeline?
Selected biography
Hansen studied at the University of Iowa, obtaining a B.A. in Physics and Mathematics, an M.S. in Astronomy and a Ph.D. in Physics. He was elected to the National Academy of Sciences in 1996 and received the Heinz Environment Award for his research on global warming in 2001.
Hansen is a vocal critic of the Bush Administration's ideology on climate change. In 2005 and 2006, he claimed that NASA administrators have tried to influence his public statements about the causes of climate change. He has also claimed that the White House edited climate-related press releases from federal agencies to make global warming seem less threatening, and that he is unable to speak 'freely', without the backlash of other government officials.
Hansen has said that a global tipping point will be reached by 2016 if levels of greenhouse gases are not reduced. After this point global warming becomes unstoppable. As a result he claims that there may be a rise in sea levels by as much as 10 feet (3 metres) by 2100.
In the news
- 10 July 2024 – Russian invasion of Ukraine
- Two Ukrainians are killed by Russian drone and missile attacks on a port in southern Odesa Oblast, Ukraine, which damaged port infrastructure, an energy facility, and a civilian ship. (Reuters)
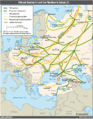
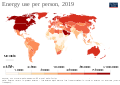
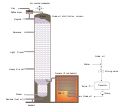
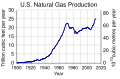
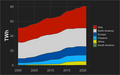
General images
Quotations
- "We simply must balance our demand for energy with our rapidly shrinking resources. By acting now we can control our future instead of letting the future control us." – Jimmy Carter, 1977
- "It is sensible to improve energy efficiency and to develop alternative and sustainable sources of supply; it's sensible to replant the forests which we consume; it's sensible to re-examine industrial processes; it's sensible to tackle the problem of waste. I understand that the latest vogue is to call them 'no regrets' policies. Certainly we should have none in putting them into effect." – Margaret Thatcher, 1990
- "We have the opportunity and potential to create an oil-free future today, it is potentially right around the corner - and, more often than not, the technology is already here." – John Kerry, 2003
Related portals
WikiProjects
WikiProjects connected with energy:
Other WikiProjects that may be of interest:
Major topics
Major categories
National energy supply, use & conservation
National electricity sector
Politics, economics, environment
- Climate change
- Energy conservation
- Energy economics
- Energy crises
- Energy development
- Energy policy
- Peak oil
Energy sources
- Fuels
- Biofuels
- Fossil fuels
- Fusion power
- Nuclear technology
- Renewable energy
- Energy conversion
- Electric power
- Energy storage
Energy-related design
Scientific usage
Help

Puzzled by energy?
Can't answer your question?
Don't understand the answer?
- Ask at the reference desk
- Read the Wikipedia help pages
For further ideas, to leave a comment, or to learn how you can help improve and update this portal, see the talk page.
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus