The submandibular ganglion (or submaxillary ganglion in older texts) is part of the human autonomic nervous system. It is one of four parasympathetic ganglia of the head and neck. (The others are the otic ganglion, pterygopalatine ganglion, and ciliary ganglion).
| Submandibular ganglion | |
|---|---|
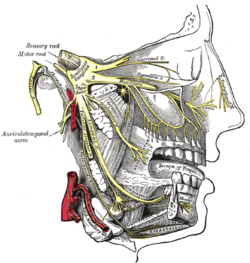 Distribution of the maxillary and mandibular nerves, and the submaxillary ganglion. (Submandibular ganglion visible at bottom left, but not labeled.) | |
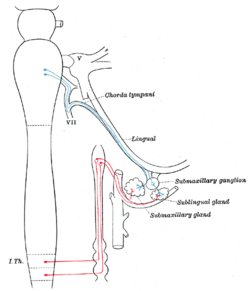 Parasympathetic connections of the submaxillary and superior cervical ganglia. (Submaxillary ganglion labeled at center right.) | |
| Details | |
| Innervates | Submandibular gland, sublingual gland |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | ganglion submandibulare |
| TA98 | A14.3.02.009 |
| TA2 | 6667 |
| FMA | 6966 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
Location and relations
editThe submandibular ganglion is small and fusiform in shape. It is situated above the deep portion of the submandibular gland, on the hyoglossus muscle, near the posterior border of the mylohyoid muscle.
The ganglion 'hangs' by two nerve filaments from the lower border of the lingual nerve (itself a branch of the mandibular nerve, CN V3). It is suspended from the lingual nerve by two filaments, one anterior and one posterior. Through the posterior of these it receives a branch from the chorda tympani nerve which runs in the sheath of the lingual nerve.
Fibers
editLike other parasympathetic ganglia of the head and neck, the submandibular ganglion is the site of synapse for parasympathetic fibers and carries other types of nerve fiber that do not synapse in the ganglion. In summary, the fibers carried in the ganglion are:
- Sympathetic fibers from the external carotid plexus, via the facial nerve and its branches. These do not synapse in this ganglion.
- Preganglionic parasympathetic fibers from the superior salivatory nucleus of the Pons, via the chorda tympani and lingual nerve, which synapse at this ganglion.
- Postganglionic parasympathetic fibers to the oral mucosa and the submandibular and sublingual salivary glands. They are secretomotor to these glands. Some of the postganglionic fibers reach the sublingual gland after they re-enter the lingual nerve.[1]
Additional images
edit-
Mandibular division of trifacial nerve, seen from the middle line.
-
Diagram of efferent sympathetic nervous system.
References
edit- ^ I. B. Singh (2008). "The Facial Nerve". Essentials of Anatomy. Jaypee Brothers Publishers. p. 395. ISBN 9788184484618.
External links
edit- Anatomy figure: 27:03-10 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- cranialnerves at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (V, VII)
- Autonomics of the Head and Neck – Page 9 of 14 anatomy module at med.umich.edu