This article includes a list ofgeneral references,butit lacks sufficient correspondinginline citations.(November 2022) |
Anell(fromProto-Germanic*alinō,cognate withLatinulna)[1]is a northwestern Europeanunit of measurement,originally understood as acubit(the combined length of the forearm and extended hand). The word literally means "arm", and survives in the modern English word "elbow" (arm-bend). Later usage through the 19th century refers to several longer units,[2][3]some of which are thought to derive from a "double ell".[4][5]
| Ell | |
|---|---|
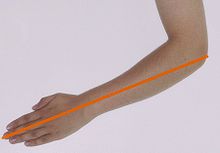 The ell was originally acubit,later replaced by the cloth-ell or "double ell". | |
| General information | |
| Unit of | Length |
| Conversions (imperial) | |
| 1 imp unitin... | ... is equal to... |
| Inch | 45 |
| Metre | 1.143 |


Anell-wandorellwandwas a rod of length one ell used for official measurement.Edward I of Englandrequired that every town have one. In Scotland, theBelt of Orionwas called "the King's Ellwand".[6][7]An iron ellwand is preserved in the entrance toStånga Churchon the Swedish island ofGotland,indicating the role that rural churches had in disseminating uniform measures.[8]
Several national forms existed, with different lengths, including theScottish ell(≈37 inches or 94 centimetres),theFlemishell [el](≈27 in or 68.6 cm),theFrenchell [aune](≈54 in or 137.2 cm),[9]thePolishell(≈31 in or 78.7 cm),theDanishalen(24Danishinches or 2 Danish fod: 62.7708 cm),theSwedishaln(2 Swedish fot 59.38 cm)and the German ell [Elle] of different lengths in Frankfurt (54.7 cm), Cologne, Leipzig (Saxony) or Hamburg.
Select customs were observed by Englishimportersof Dutchtextiles;although all cloths were bought by the Flemish ell,linenwas sold by the English ell, buttapestrywas sold by the Flemish ell.[9]
The Viking ell was the measure from the elbow to the tip of the middle finger, about 18 inches (460 mm). The Viking or primitive ell was used in Iceland up to the 13th century. By the 13th century, a law set the "stika" as equal to 2 ells which was the English ell of the time.[10]
Historic use
editEngland
editIn England, the ell was usually exactly 45 in (1.143 m), or a yard and a quarter. It was mainly used in thetailoringbusiness but is now obsolete. Although the exact length was never defined in English law, standards were kept; the brass ell examined at theExchequerby Graham in the 1740s had been in use "since the time of Queen Elizabeth".[11]
Other English measures called an ell include the "yard and handful", or 40 in. ell, abolished in 1439; the yard and inch, or 37 in. ell (a cloth measure), abolished after 1553 and known later as the Scotch ell=37·06; and the cloth ell of 45 in., used until 1600.[12]Seeyardfor details.
Scots
editTheScottish ell(Scottish Gaelic:slat Albannach) is approximately 37 inches (0.94 m). The Scottish ell was standardised in 1661, with the exemplar to be kept in the custody of Edinburgh.[13]It comes fromMiddle Englishelle.[14]
It was used in the popular expression "Gie 'im an inch, an he'll tak an ell" (equivalent to "Give him an inch and he'll take a mile" or "... he'll take ayard."
The Ell Shop(1757) inDunkeld,Perth and Kinross(National Trust for Scotland), is so called from the 18th-century iron ell-stick attached to one corner, once used to measure cloth and other commodities in the adjacent market-place. The shaft of the 17th-century Kincardinemercat crossstands in the square ofFettercairn,and is notched to show the measurements of an ell.
Scottish measures were made obsolete, and English measurements made standard in Scotland, by an Act of Parliament, theWeights and Measures Act 1824.
Other
editSimilar measures include:[12]
- Netherlands: el, 1 metre (Old ell=27.08 inches)
- Jersey: ell, 4 feet
- N. Borneo: ella, 1 yard
- Switzerland: elle, 0.6561 yard
- Ottoman Turkey: Arşın, ~69 cm
In literature
editElls are used for measuring the length of rope inJ. R. R. Tolkien'sThe Lord of the Rings.[15]Since Sam declares that 30 elles are "about" 18 fathoms (108 feet), he seems to be using the 45-inch English ell, which would work out to 112 feet.
In the epic poemSir Gawain and the Green Knight,the Green Knight's axe-head was an ell (45 inches) wide.[16]
Ells were also used in the medieval French playThe Farce of Master Pathelinto measure the size of the clothing Pierre Pathelin bought.[17]
Halldór LaxnessdescribedÖrvar-Oddras twelveDanish ellstall inIndependent People,Part II, "Of the World".[18]
References
edit- ^"ell, n.1".OED Online. December 2011. Oxford University Press. (accessed February 20, 2012).
- ^The Diagonal.Yale University Press. 1920. p. 98.Retrieved6 February2012.
- ^Charlton Thomas Lewis; Hugh Macmaster Kingery (1918).An elementary Latin dictionary.American book company. p.198.Retrieved6 February2012.
forearm, ell, cubit.
- ^James Robinson (of Boston.) (1857).The American elementary arithmetic.J.P. Jewett & co. p. 94.Retrieved6 February2012.
- ^Daniel O'Gorman (1853).Intuitive calculations; the readiest and most concise methods.p.48.Retrieved6 February2012.
- ^infoplease,OEDs.Ell-wand.
- ^AR Littlewood."The measurements of cricket".ESPN cricinfo.
- ^Andrén, Anders (2017).Det Medeltida Gotland. En arkeologisk guidebok[Medieval Gotland. An archaeological guidebook] (in Swedish) (2nd ed.). Lund: Historiska Media. p. 206.ISBN978-91-7545-476-4.
- ^abBrayshaw, Tom S., ed.Brayshaw's Mathematical Desk Companion.Chesterfield, England: Thomas Brayshaw Ltd., Edition 16, 1955
- ^Nancy Marie Brown (2007).The Far Traveller: Voyages of a Viking Woman.Harcourt. pp. 236, 276.OCLC85822467.
- ^Knight, Charles (1840).The Penny magazine of the Society for the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge, Volume 9.London: Society for the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge.
- ^abChisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Weights and Measures"(free fulltext), from theEncyclopædia Britannica.Vol. 01 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
- ^Concise Scots Dictionary,chief editor Mairi Robinson, Aberdeen University Press, 1987, p 817
- ^"Dictionary of the Scots Language".Archived fromthe originalon 2012-03-21.Retrieved2011-08-09.
- ^Tolkien, J. R. R.(1997).The Lord of the Rings.HarperCollins.pp. 595–6.ISBN0-261-10368-7.
Sam paid it out slowly, measuring it with his arms: 'Five, ten, twenty, thirty ells, more or less,... Thirty ells, or say, about eighteenfathom'
- ^Burrow, J. A., ed. (1972).Sir Gawain and the Green Knight.Harmondsworth, England: Penguin. p. 22.ISBN0140806679.OCLC1136028.
The lenkthe of an elnyerde the large hed had
- ^"The farce of Master Pierre Patelin"(PDF).sas.ac.uk.Retrieved11 April2024.
- ^Laxness, Halldór(1997) [1946].Sjálfstætt fólk[Independent People]. Translated byThompson, J. A. (James Anderson).Introduction byBrad Leithauser.New York:Vintage.p. 201.ISBN0-679-76792-4.
- Attribution
Further reading
edit- Collins Encyclopedia of Scotland
- Scottish National DictionaryandDictionary of the Older Scottish Tongue
- Weights and Measures,by D. Richard Torrance, SAFHS, Edinburgh, 1996,ISBN1-874722-09-9(N.B.: The book focusses exclusively on Scottish weights and measures.)
External links
edit- Media related toEllat Wikimedia Commons