Afeedwater heateris apower plantcomponent used to pre-heat water delivered to asteamgeneratingboiler.[1][2][3]Preheating the feedwater reduces the irreversibilities involved in steam generation and therefore improves thethermodynamic efficiencyof the system.[4]This reduces plant operating costs and also helps to avoidthermal shockto the boiler metal when the feedwater is introduced back into the steam cycle.
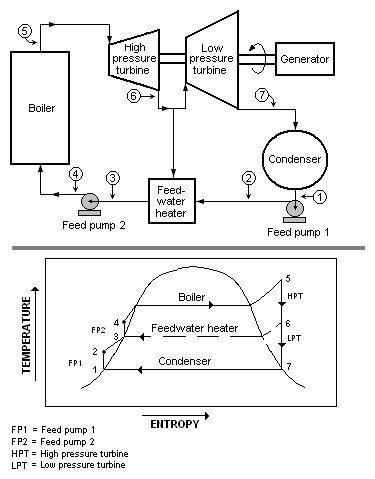
In a steam power plant (usually modeled as a modifiedRankine cycle), feedwater heaters allow the feedwater to be brought up to the saturation temperature very gradually. This minimizes the inevitable irreversibilities associated with heat transfer to the working fluid (water). See the article on thesecond law of thermodynamicsfor a further discussion of suchirreversibilities.
Cycle discussion and explanation
editThe energy used to heat the feedwater is usually derived from steam extracted between the stages of thesteam turbine.Therefore, the steam thatwould be usedto perform expansion work in the turbine (and therefore generate power) is not utilized for that purpose. The percentage of the total cycle steam mass flow used for the feedwater heater is termed theextraction fraction[4]and must be carefully optimized for maximum power plantthermal efficiencysince increasing this fraction causes a decrease in turbine power output.
Feedwater heaters can also be"open"or"closed" heat exchangers.An open heat exchanger is one in which extracted steam is allowed to mix with the feedwater. This kind of heater will normally require a feed pump at both the feed inlet and outlet since the pressure in the heater is between the boiler pressure and thecondenserpressure. Adeaeratoris a special case of the open feedwater heater which is specifically designed to remove non-condensable gases from the feedwater.
Closed feedwater heaters are typicallyshell and tube heat exchangerswhere the feedwater passes throughout the tubes and is heated by turbine extraction steam. These do not require separate pumps before and after the heater to boost the feedwater to the pressure of the extracted steam as with an open heater. However, the extracted steam (which is most likely almost fully condensed after heating the feedwater) must then be throttled to the condenser pressure, anisenthalpicprocess that results in someentropygain with a slight penalty on overall cycle efficiency:
Many power plants incorporate a number of feedwater heaters and may use both open and closed components. Feedwater heaters are used in both fossil- and nuclear-fueled power plants.
Economizer
editAn economizer serves a similar purpose to a feedwater heater, but is technically different as it does not use cycle steam for heating. In fossil-fuel plants, the economizer uses the lowest-temperatureflue gasfrom thefurnaceto heat the water before it enters the boiler proper. This allows for the heat transfer between the furnace and the feedwater to occur across a smaller average temperature gradient (for the steam generator as a whole). System efficiency is therefore further increased when viewed with respect to actual energy content of the fuel.
Most nuclear power plants do not have an economizer. However, the Combustion EngineeringSystem 80+ nuclear plant design and its evolutionary successors, (e.g.Korea Electric Power Corporation'sAPR-1400) incorporate an integral feedwater economizer. This economizer preheats the steam generator feedwater at the steam generator inlet using the lowest-temperature primary coolant.
Testing
editA widely use Code for the procedures, direction, and guidance for determining the thermo-hydraulic performance of a closed feedwater heater is the ASME PTC 12.1 Feedwater Heater Standard.
See also
editASME Codes
editThe American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), publishes the following Code:
- PTC 4.4 Gas Turbine Heat Recovery Steam Generators
References
edit- ^British Electricity International (1991).Modern Power Station Practice: incorporating modern power system practice(3rd Edition (12 volume set) ed.). Pergamon.ISBN0-08-040510-X.
- ^Babcock & Wilcox Co. (2005).Steam: Its Generation and Use(41st ed.).ISBN0-9634570-0-4.
- ^Thomas C. Elliott, Kao Chen, Robert Swanekamp (coauthors) (1997).Standard Handbook of Powerplant Engineering(2nd ed.). McGraw-Hill Professional.ISBN0-07-019435-1.
{{cite book}}:CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^abFundamentals of Steam PowerArchived2007-04-22 at theWayback Machineby Kenneth Weston,University of Tulsa