This article includes a list ofgeneral references,butit lacks sufficient correspondinginline citations.(July 2011) |
Grain size(orparticle size) is thediameterof individual grains ofsediment,or thelithifiedparticles inclastic rocks.The term may also be applied to othergranular materials.This is different from thecrystallitesize, which refers to the size of a singlecrystalinside a particle or grain. A single grain can be composed of severalcrystals.Granular material can range from very smallcolloidal particles,throughclay,silt,sand,gravel,andcobbles,toboulders.
| Granulometry | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Basic concepts | |
| Particle size,Grain size,Size distribution,Morphology | |
| Methods and techniques | |
| Mesh scale,Optical granulometry,Sieve analysis,Soil gradation | |
Related concepts | |
| Granulation,Granular material,Mineral dust,Pattern recognition,Dynamic light scattering | |
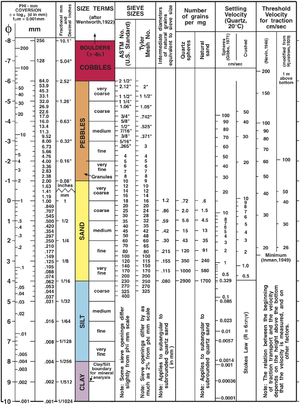

Krumbein phi scale
editSize ranges define limits of classes that are given names in the Wentworth scale (or Udden–Wentworth scale named after geologists Chester K. Wentworth andJohan A. Udden) used in theUnited States.The Krumbeinphi(φ) scale, a modification of the Wentworth scale created byW. C. Krumbein[1]in 1934, is alogarithmic scalecomputed by the equation
where
- is the Krumbein phi scale,
- is thediameterof the particle or grain in millimeters (Krumbein and Monk's equation)[2]and
- is a reference diameter, equal to 1 mm (to make the equationdimensionally consistent).
This equation can be rearranged to find diameter using φ:
| φ scale | Size range (metric) |
Size range (approx. inches) |
Aggregate name (Wentworth class) |
Other names |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| <−8 | >256 mm | >10.1 in | Boulder | |
| −6 to −8 | 64–256 mm | 2.5–10.1 in | Cobble | |
| −5 to −6 | 32–64 mm | 1.26–2.5 in | Very coarsegravel | Pebble |
| −4 to −5 | 16–32 mm | 0.63–1.26 in | Coarse gravel | Pebble |
| −3 to −4 | 8–16 mm | 0.31–0.63 in | Medium gravel | Pebble |
| −2 to −3 | 4–8 mm | 0.157–0.31 in | Fine gravel | Pebble |
| −1 to −2 | 2–4 mm | 0.079–0.157 in | Very fine gravel | Granule |
| 0 to −1 | 1–2 mm | 0.039–0.079 in | Very coarsesand | |
| 1 to 0 | 0.5–1 mm | 0.020–0.039 in | Coarse sand | |
| 2 to 1 | 0.25–0.5 mm | 0.010–0.020 in | Medium sand | |
| 3 to 2 | 125–250μm | 0.0049–0.010 in | Fine sand | |
| 4 to 3 | 62.5–125 μm | 0.0025–0.0049 in | Very fine sand | |
| 8 to 4 | 3.9–62.5 μm | 0.00015–0.0025 in | Silt | Mud |
| 10 to 8 | 0.98–3.9 μm | 3.8×10−5–0.00015 in | Clay | Mud |
| 20 to 10 | 0.95–977nm | 3.8×10−8–3.8×10−5in | Colloid | Mud |
In some schemes, gravel is anything larger than sand (comprising granule, pebble, cobble, and boulder in the table above).
International scale
editISO14688-1:2017, establishes the basic principles for identifying and classifying soils based on those material and mass characteristics most commonly used for soils for engineering purposes. ISO 14688-1 applies to natural soilsin situ,similar man-made materialsin situand soils redeposited by people.[3]
| Name | Size range (mm) | Size range (approx. in) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Very coarse soil | Large boulder | lBo | >630 | >24.8031 | |
| Boulder | Bo | 200–630 | 7.8740–24.803 | ||
| Cobble | Co | 63–200 | 2.4803–7.8740 | ||
| Coarse soil | Gravel | Coarse gravel | cGr | 20–63 | 0.78740–2.4803 |
| Medium gravel | mGr | 6.3–20 | 0.24803–0.78740 | ||
| Fine gravel | fGr | 2.0–6.3 | 0.078740–0.24803 | ||
| Sand | Coarse sand | cSa | 0.63–2.0 | 0.024803–0.078740 | |
| Medium sand | mSa | 0.2–0.63 | 0.0078740–0.024803 | ||
| Fine sand | fSa | 0.063–0.2 | 0.0024803–0.0078740 | ||
| Fine soil | Silt | Coarse silt | cSi | 0.02–0.063 | 0.00078740–0.0024803 |
| Medium silt | mSi | 0.0063–0.02 | 0.00024803–0.00078740 | ||
| Fine silt | fSi | 0.002–0.0063 | 0.000078740–0.00024803 | ||
| Clay | Cl | ≤0.002 | ≤0.000078740 | ||
Sorting
editAn accumulation of sediment can also be characterized by the grain size distribution. A sediment deposit can undergo sorting when a particle size range is removed by an agency such as a river or the wind. The sorting can be quantified using the Inclusive Graphic Standard Deviation:[4]
where
- is the Inclusive Graphic Standard Deviation in phi units
- is the 84th percentile of the grain size distribution in phi units, etc.
The result of this can be described using the following terms:
| Diameter (phi units) | Description |
|---|---|
| < 0.35 | very well sorted |
| 0.35 << 0.50 | well sorted |
| 0.50 << 1.00 | moderately sorted |
| 1.00 << 2.00 | poorly sorted |
| 2.00 << 4.00 | very poorly sorted |
| 4.00 < | extremely poorly sorted |
See also
editReferences
edit- ^Krumbein, W. C. (1934). "Size frequency distributions of sediments".Journal of Sedimentary Petrology.2(4).doi:10.1306/D4268EB9-2B26-11D7-8648000102C1865D.
- ^PetroWiki: Estimating permeability based on grain size
- ^"ISO 14688-1:2017 – Geotechnical investigation and testing – Identification and classification of soil – Part 1: Identification and description".International Organization for Standardization (ISO).
- ^Folk, Robert L.; Ward, William C. (1957)."Brazos River bar: a study in the significance of grain-size parameters"(PDF).Journal of Sedimentary Petrology.27(1):3–26.Bibcode:1957JSedR..27....3F.doi:10.1306/74d70646-2b21-11d7-8648000102c1865d.Archived fromthe original(PDF)on 12 May 2014.Retrieved11 May2014.
External links
edit- R D Dean & R A Dalrymple,Coastal Processes with Engineering Applications(Cambridge University Press, 2002)
- W C Krumbein & L L Sloss,Stratigraphy and Sedimentation,2nd edition (Freeman, San Francisco, 1963).
- Udden, J. A. (1914). "Mechanical composition of clastic sediments".Geological Society of America Bulletin.25(1):655–744.Bibcode:1914GSAB...25..655U.doi:10.1130/GSAB-25-655.
- Wentworth, C. K. (1922)."A Scale of Grade and Class Terms for Clastic Sediments".The Journal of Geology.30(5):377–392.Bibcode:1922JG.....30..377W.doi:10.1086/622910.JSTOR30063207.S2CID128682870.