This articleneeds additional citations forverification.(October 2020) |
Themakiwara(Quyển cảo) is a padded striking post used as a training tool in various styles of traditionalkarate.It is thought to be uniquelyOkinawanin origin. The makiwara is one form ofhojo undō,a method of supplementary conditioning used by Okinawanmartial artists.
Use
editThe makiwara is used by karate practitioners to practice strikes in much the same way as a boxer uses aheavy bag.The makiwara develops one's striking ability by letting them experience resistance to punches, kicks and other strikes. A poor punch will bounce off the makiwara if the body is not in a position to support the energy generated by the strike. It also develops targeting, and focus, which is the ability to penetrate the target (i.e., opponent) to varying degrees of force.
The makiwara is very versatile, and can accommodate practice of open/closed hand strikes,kicks,knee strikes and elbow strikes. Okinawan methods emphasize striking from different angles. Mostsourcesrecommend a regimen of hitting the makiwara 50–100 times per day, with each hand. It is especially important to train the weaker side of the body as hard as, or harder than the dominant side.[1]It is important to note that one should not use the makiwara so much that it causes them harm. While abrasions or soreness may be expected in early stages of training, like all good training, there should be no lasting damage.
A round elongated makiwara, traditionally made from rice straw bound with rope, is used by practitioners ofkyūdō,Japanese archery. This makiwara is placed on a stand so that it is near shoulder height, and is used for close range practice from about 5–8 feet away. The archer is practically unable to miss the target from that range, affording thekyūdōpractitioner the opportunity to practice his form, without thought for the target.
Construction
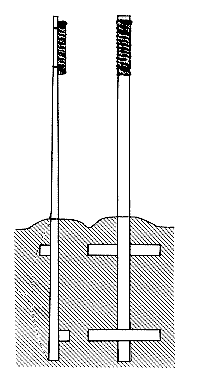
editHistorically, the most common type consists of a single 7-to-8-foot-long (2.1 to 2.4 m) post driven into the ground, so that it is approximately shoulder height. The post is tapered from the bottom to a thickness of 1 cm at the top. Traditionally, a pad of rice straw ( quyển maki "roll" + cảo wara "straw" ) was bound to the top with rope to form a striking surface.
More modern variations of the standing makiwara use a metal or other base;[2]or in some cases a concreted recess into the floor of the dojo. These bases may be constructed to affix the makiwara with through bolts; or capture the makiwara in a clamping action. Today the pad is less often made of straw, and more likely to be leather; often with a layer of rubber, duct tape or other tape over foam rubber; and in some cases black palm rope is used. Modern materials may last longer outdoors.
Soft makiwara construction and use
editSoft makiwara are the type of makiwara that beginners use, but they are still essential for daily speed training for both beginners and experts alike. Soft makiwara are often positioned at a greater angle from vertical and an average punch will straighten the makiwara to a vertical position.
Stiff makiwara construction and use
editAfter the user is well conditioned from using the soft makiwara, they often add additional training on the stiff makiwara to work on power training. The stiff makiwara is constructed by positioning the wood at a small angle from vertical. The average training punch to push the makiwara to a vertical position, or 90 degrees from the ground.
Types of makiwara
editStanding Makiwara
editShuri makiwara
editThe shuri makiwara is a flat board, measured to be as high as the instructor's breast bone. This makiwara is used when punching from a short stance.[3]
Naha makiwara
editThe naha makiwara is also a flat board, but measured to be as high as the instructor'ssolar plexus.This makiwara is used traditionally byGoju Ryupractitioners, who train in a deep stance(Shiko dachi).Goju Ryustudents are far more likely to use sanchin dachi in using the makiwara. The common makiwara in the Jundokan dojo in Naha, ofEiichi Miyazatoare closer to shoulder height.
Ude makiwara
editThe ude makiwara differs in that it is round on all sides. This allows for the practitioner to use a variety of strikes and kicks on the makiwara, that could not be used on flat boards.
Hand Held Makiwara
editMany martial artists use portable or hand held makiwara. Some are pocket sized, some may be mounted temporarily (in a Okinawa Taxi for instance). These makiwara are usually held in one hand and struck with the other. These makiwara allows the practitioner to condition other parts of the hand such as shuto, nukite (finger tips). This provides the capability of hand conditioning and training outside the dojo.[4]
See also
edit- Wolff's law(a possible explanation why bones strengthen with daily makiwara use)
- Stress fracture
- Boxer's fracture
- Mu ren zhuang
References
edit- ^Karate Do Kyohan. Funakoshi Gichin. Page 18.[1]
- ^A metal mounted makiwara at makiwara
- ^Interview with Seikichi Iha
- ^Hand held Makiwara at fightingarts
External links
edit- Detailed instructions onhow to build a makiwara and makiwara pad
- More detailed instructions on how to make one
- Makiwara construction & Technique
(Wayback Machinecopy)