ThePeace River(French:rivière de la Paix) is a 1,923-kilometre-long (1,195 mi) river inCanadathat originates in theRocky Mountainsof northernBritish Columbiaand flows to the northeast throughnorthern Alberta.The Peace River joins theAthabasca Riverin thePeace-Athabasca Deltato form theSlave River,a tributary of theMackenzie River.TheFinlay River,the main headwater of the Peace River, is regarded as the ultimate source of the Mackenzie River. The combined Finlay–Peace–Slave–Mackenzie river system is the13th longest river system in the world.
| Peace River | |
|---|---|
 Peace River Valley in BC | |
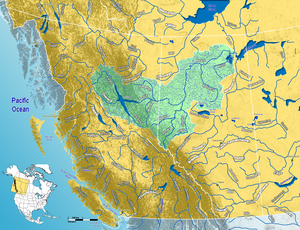 Map of the Peace River watershed in western Canada | |
| Etymology | Peace Point, Alberta,where a treaty marking the river as the boundary betweenBeaverandCreewas signed in 1781 |
| Native name | |
| Location | |
| Country | Canada |
| Province | British Columbia,Alberta |
| Cities | Fort Saint John, British Columbia,Peace River, Alberta |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | Finlay River |
| • location | Thutade Lake,British Columbia |
| • coordinates | 57°04′29″N126°53′36″W/ 57.07472°N 126.89333°W |
| • elevation | 1,140 m (3,740 ft) |
| 2nd source | Parsnip River |
| • location | Near Mount Barton, British Columbia |
| • coordinates | 54°30′02″N121°26′26″W/ 54.50056°N 121.44056°W |
| • elevation | 1,716 m (5,630 ft) |
| Source confluence | Williston Lake |
| • coordinates | 55°59′21″N123°50′08″W/ 55.98917°N 123.83556°W |
| • elevation | 748 m (2,454 ft)(Elevation of Williston Lake) |
| Mouth | Slave River |
• location | Confluence of Peace withAthabasca River,Alberta |
• coordinates | 59°00′01″N111°24′38″W/ 59.00028°N 111.41056°W |
| Length | 1,923 km (1,195 mi) |
| Basin size | 306,000 km2(118,000 sq mi)[2] |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Peace Point, Alberta[3] |
| • average | 2,110 m3/s (75,000 cu ft/s)[3] |
| • minimum | 344 m3/s (12,100 cu ft/s) |
| • maximum | 9,790 m3/s (346,000 cu ft/s) |
| Basin features | |
| River system | Mackenzie Riverwatershed |
| Tributaries | |
| • left | Finlay River,Halfway River,Beatton River,Clear River (Alberta), Ponton River |
| • right | Parsnip River,Pine River,Kiskatinaw River,Pouce Coupé River,Smoky River,Wabasca River,Mikkwa River |
History
editThe regions along the river are the traditional home of theDane-zaa people,called the Beaver by the Europeans. Thefur traderPeter Pondis believed to have visited the river in 1785. In 1788 Charles Boyer of theNorth West Companyestablished afur tradingpost at the river's junction with theBoyer River.
In 1792 and 1793, the explorerAlexander Mackenzietravelled up the river to theContinental Divide.[4]Mackenzie referred to the river asUnjegah,from the Dane-zaa meaning "large river."
The decades of hostilities between the Dane-zaa and theCree,(in which the Cree dominated the Dane-zaa), ended in 1781 when asmallpox epidemicdecimated the Cree. The Treaty of the Peace was celebrated by the smoking of aceremonial pipe.The treaty made the Peace River a border, with the Dane-zaa to the North and the Cree to the South.[5]
In 1794, a fur trading post was built on the Peace River atFort St. John;it was the first settlement established on the British Columbia mainland by Europeans.
Post-settlement
editThe rich soils of the Peace River valley in Alberta have been producingwheatcrops since the late 19th century. In the early 21st century, theBC Grain Producers Associationwas researching the productivity of wheat and other grain crops nearDawson Creek.[6]The Peace River region is also an important centre ofoilandnatural gasproduction. There are alsopulpand paper plants along the river in Alberta and British Columbia.
The Peace River has two navigable sections, separated by theVermilion Chutes,nearFort Vermilion.[7] The first steam-powered vessel to navigate the Peace River was theGrahame,aHudson's Bay Companyvessel built atFort Chipewyan,onLake Athabasca.Brothers of theOblate Order of Mary Immaculatebuilt theSt. Charlesto navigate the upper reaches of the River, from Fort Vermilion toHudson's Hope.Approximately a dozen vessels were to navigate the river. Most of the early vessels were wood-burning steamships, fueled by wood cut from the river's shore. The last cargo vessel was theWatson's Lake,retired in 1952.
Hydroelectric development
editHydroelectricdevelopment began on the Peace River in 1968 and continues to be an important source of renewable energy for British Columbia's main electricity provider,BC Hydro.The river’s first dam, theW. A. C. Bennett Dam,was completed in 1968 and is British Columbia's largest dam and the third-largest hydroelectric facility in Canada. It supplies over 30% of British Columbia's total power demand. Engineers took advantage of the W. A. C. Bennet Dam's large reservoir storage to further develop the river with thePeace Canyon Damopened in 1980.[8]TheSite C damis under construction and scheduled to be finished in 2025; it will further benefit from the upstream dams and generate additional electrical capacity to meet British Columbia's growing demand for green energy and reduce the carbon footprint of residents.[9]As of 2020[update]both the Alberta government and private producers were studying the possibility of hydroelectric development on the Alberta stretch of the river with onerun-of-the-riverproject currently being proposed.[10]
| Name | Height | Capacity
(MW) |
Province | Year completed | Owner | Reservoir name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W. A. C. Bennett Dam | 186 m | 2730 | B.C. | 1968 | BC Hydro | Williston Lake |
| Peace Canyon Dam | 50 m | 694 | B.C. | 1980 | BC Hydro | Dinosaur Lake |
| Site C Dam | 60 m | 1100 | B.C. | 2025 planned | BC Hydro | TBD |
| Amisk Dam | 24 m | 370 | Alberta | late 2020s | Concord Green Energy | TBD |
Geography
editCourse
editThis river is 1,923 kilometres (1,195 mi) long (from the head ofFinlay Riverto Lake Athabasca). It drains an area of approximately 302,500 square kilometres (116,800 sq mi).[11]At Peace Point, where it drains in theSlave River,it has an annual discharge of 68.2 billion cubic metres (55.3 million acre-feet).[12]
A large man-made lake,Williston Lake,has been formed on the upper reaches by the construction of theW. A. C. Bennett Damforhydroelectricpowergeneration. Prior to its flooding, the confluence of the Finlay andParsnip RiversatFinlay Forkswas distinct. A half mile east of that location were the half-mile long Finlay Rapids and a further seven miles east is thePeace Pass,which separates theMuskwa Rangesand theHart Rangesof theCanadian Rockies.
The only river cutting completely through the Rockies,[13][14]it nowadays flows into Dinosaur Lake, a reservoir for thePeace Canyon Dam.After the dams, the river flows east into Alberta and then continues north and east into thePeace-Athabasca DeltainWood Buffalo National Park,at the western end of Lake Athabasca. Water from the delta flows into the Slave River east of Peace Point and reaches theArctic Oceanvia theGreat Slave LakeandMackenzie River.
Communities
editCommunities located directly on the river include:
- Hudson's Hope, British Columbia
- Taylor, British Columbia
- Peace River, Alberta
- Fort Vermilion, Alberta
Manyprovincial parksand wildland reserves are established on the river, such asButler Ridge Provincial Park,Taylor Landing Provincial Park,Beatton River Provincial Park,Peace River Corridor Provincial Parkin British Columbia andDunvegan Provincial Park,Dunvegan West Wildland Provincial Park,Peace River Wildland Provincial Park,Greene Valley Provincial Park,Notikewin Provincial Park,Wood Buffalo National Park in Alberta.
A fewIndian reservesare also on the river banks, among themBeaver Ranch 163,John D'Or Prairie 215,Fox Lake 162,Peace Point 222andDevil's Gate 220.
Tributaries
editTributaries of the Peace River include:
- Finlay River
- Omineca River
- Ingenika River
- Ospika River
- Parsnip River
- Manson River
- Nation River
- Clearwater Creek
- Nabesche River
- Carbon Creek
- Northeastern British Columbia
- Gething Creek, Moosbar Creek, Johnson Creek, Starfish Creek, Bullrun Creek, Portage Creek, Maurice Creek, Lynx Creek, Farrell Creek
- Halfway River
- Cache Creek, Wilder Creek, Tea Creek
- Moberly River
- Pine River
- Eight Mile Creek
- Beatton River
- Golata Creek, Mica Creek
- Kiskatinaw River
- Alces River
- Alberta
- Moonlight Creek
- Pouce Coupe River
- Clear River
- Sneddon Creek
- Montagneuse River
- Fourth Creek, Hamelin Creek
- Ksituan River
- Hines Creek, Dunvegan Creek, Boucher Creek
- Leith River(Little Burnt River)
- Saddle River(Burnt River)
- Griffin Creek, Mcallister Creek, Strong Creek
- Smoky River
- Heart River
- Pat's Creek,Three Creeks, Carmon Creek
- Whitemud River
- Cadotte River
- Buchanan Creek, Keppler Creek
- Notikewin River
- Scully Creek
- Wolverine River
- Buffalo River
- Keg River
- Steephill Creek
- Boyer River
- Caribou River
- Beaver Ranch Creek
- Wabasca River
- Lawrence River
- Mikkwa River(Little Red River)
- Dummy Creek, Waldo Creek
- Pakwanutik River
- Garden Creek, Drolet Creek, Swan River, Vermilion River, Trident Creek,Portage River
- Jackfish River
- Jodoin Creek
- Claire River
- Lake Claire
- Lake Claire
- Birch River
- McIvor River
- Mamawi Lake
- Baril River
- Chenal Des Quatre Fourches
- Revolution Coupe
- Scow Channel
See also
edit- List of rivers of Alberta
- List of rivers of British Columbia
- List of longest rivers of Canada
- Steamboats of the Peace River
Footnotes
edit- ^David W., Leonard."Peace River".The Canadian Encyclopedia.Historica Canada.Retrieved4 December2021.
- ^Bennett, R.M.; Card, J.R.; Hornby, D.M. (1973-03-09)."Hydrology of Lake Athabasca: Past, Present and Future"(PDF).Hydrological Sciences Bulletin, XVIII.International Association of Hydrological Science. Archived fromthe original(PDF)on 2013-05-16.Retrieved2010-10-08.
- ^ab"Peace River at Peace Point".R-ArcticNet. 1959–2000.Retrieved2010-10-08.
- ^"Peace River",Encyclopædia Britannica,2006. Retrieved September 12, 2006, from Encyclopædia Britannica Premium Service
- ^Coutts, M. E. (1958).Dawson Creek: Past and Present, An Historical Sketch.Edmonton: Dawson Creek Historical Society.
- ^"BC Peace Region 2018 Field Crop Variety Performance"(PDF).bcgrain.BC Grain Producers Association.
- ^Edward L. Affleck."Steamboating on the Peace River"(PDF).British Columbia History.Archived fromthe original(PDF)on 2013-09-21.Retrieved2012-12-06.
The brothers built a fleet of small primitive steamers, extending by 1903 to the waters of the Peace above the Vermilion Chutes. In that year the pint—sized sternwheeler St. Charles began to work the 526 mile stretch from Fort Vermilion to Hudson's Hope, carrying lumber and supplies for the Mission at Fort St. John in British Columbia, as well as goods for the Northwest Mounted Police.
- ^"Peace Region".BC Hydro.
- ^"About the Site C project".Site C Clean Energy Project.
- ^"Home".Amisk Hydro Project.2020.
- ^Atlas of Canada."Rivers in Canada".Retrieved2007-05-01.
- ^Alberta EnvironmentArchived2007-01-16 at theWayback Machine- Alberta river basins
- ^Fort George Tribune, 20 Jun 1914
- ^Prince George Citizen, 26 Sep 1916