Theconfluence of sinuses(Latin:confluens sinuum),torcular Herophili,ortorculais the connecting point of thesuperior sagittal sinus,straight sinus,andoccipital sinus.It is below theinternal occipital protuberanceof theskull.It drainsvenous bloodfrom thebraininto thetransverse sinuses.It may be affected byarteriovenous fistulas,athrombus,major trauma,or surgical damage, and may be imaged with manyradiologytechniques.
| Confluence of sinuses | |
|---|---|
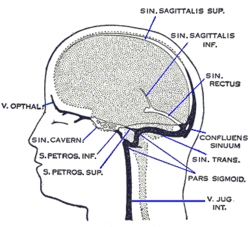 Dural veins. (Labeled with "confluens sinuum" ) | |
 Sagittal section of the skull, showing the sinuses of the dura. (Labeled with "torcula herophili".) | |
| Details | |
| Source | Superior sagittal sinus,straight sinus,occipital sinus |
| Drains to | Transverse sinuses |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | confluens sinuum, torcula herophili |
| TA98 | A12.3.05.103 |
| TA2 | 4852 |
| FMA | 50784 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Structure
editThe confluence of sinuses is found deep to theinternal occipital protuberanceof theoccipital boneof theskull.[1]This puts it inferior to theoccipital lobesof thebrain,and posterosuperior to thecerebellum.[1]It connects the ends of thesuperior sagittal sinus,thestraight sinus,and theoccipital sinus.[1]Blood from it can drain into the left and righttransverse sinuses.[1]It is lined withendothelium,with somesmooth muscle.[1]
Variation
editThe confluence of sinuses shows significant variation.[1]Most commonly, there is a continuous connection between all of the sinuses.[1][2]A very common variant is thesuperior sagittal sinusonly draining into the righttransverse sinus- more rarely, it may also only drain into the left transverse sinus.[1][2]Another variation involves a continuous connection, but where most blood from the superior sagittal sinus drains into the right transverse sinus, and most blood from theoccipital sinusdrains into the left transverse sinus.[1]Other less common variations also exist.[1]
Development
editThe confluence of sinuses develops from the anterior plexus and the middle plexus.[1]These fuse so that the anterior plexus becomes a remnant.[1]
Function
editThe confluence of sinuses is important in drainage ofvenous bloodfrom thebrain.[1]It drains most of the blood from the brain.[3]
Clinical significance
editThe confluence of sinuses may be affected byarteriovenous fistulas.[1]This is treated with surgery toemboliseof the fistula.[1]It may also be affected by athrombus.[1]This can be treated withanticoagulants.[1]It may be injured by a variety ofmajor trauma.[3]It may also be damaged during surgery, such as that to remove ameningioma.[3]
The confluence of sinuses can be imaged withradiology.[1]Angiography,CT scan,magnetic resonance imaging,medical ultrasound,orinterventional radiologymay be used.[1]
History
editThe confluence of sinuses may also be known as the confluens sinuum (fromLatin), or the torcular Herophili (or more simply the torcula). The last term is older, and describes the veins as a gutter or canal. This is named afterHerophilos,theGreekanatomistwho first usedcadaversfor the systematic study ofanatomy.This term more precisely refers to the concavity in the bone, which is the location of the confluence of sinuses.[4]
Additional images
edit-
Confluence of sinuses
References
edit- ^abcdefghijklmnopqrsGranger, Andre; Tubbs, R. Shane (2020)."7 - The Torcular Herophili (Confluence of Sinuses)".Anatomy, Imaging and Surgery of the Intracranial Dural Venous Sinuses.Elsevier.pp. 71–85.doi:10.1016/B978-0-323-65377-0.00007-6.ISBN978-0-323-65377-0.S2CID198402766.
- ^abJoseph, Shamfa C.; Rizk, Elias; Tubbs, R. Shane (2020)."25 - Variations of the Intracranial Dural Venous Sinuses".Anatomy, Imaging and Surgery of the Intracranial Dural Venous Sinuses.Elsevier.pp. 205–220.doi:10.1016/B978-0-323-65377-0.00025-8.ISBN978-0-323-65377-0.S2CID198283297.
- ^abcMortazavi, Martin M.; Surya, Sajid S.; Hami, Farzad; Sadati, Mohsen; Jazi, Ghazaleh Ahmadi; Tubbs, R. Shane (2020)."27 - Surgical Nuances in Management of Intracranial Venous Sinus Injuries".Anatomy, Imaging and Surgery of the Intracranial Dural Venous Sinuses.Elsevier.pp. 231–236.doi:10.1016/B978-0-323-65377-0.00027-1.ISBN978-0-323-65377-0.S2CID198282914.
- ^Tubbs, R.S. Neuroanatomy, 2002:1, 14
External links
edit- Anatomy figure: 28:03-07at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- http://neuroangio.org/venous-brain-anatomy/venous-sinuses/