Typhoon Angela,known in thePhilippinesasSuper Typhoon Rosing,was an extremely powerful and catastrophictropical cyclonethat impacted the Philippines in November 1995, and the most intense tropical cycloneworldwide in 1995.Typhoon Angela was the third storm in a row that struck the Philippines, followingYvetteandZack.Typhoon Angela was the twenty-ninthtropical cyclone,and the fifth super typhoon of the moderately active1995 Pacific typhoon season.
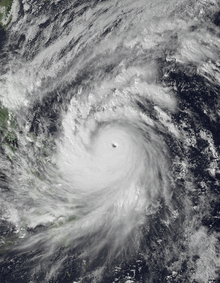 Angela at peak intensity nearing the Philippines on November 1 | |
| Meteorological history | |
|---|---|
| Formed | October 25, 1995 |
| Dissipated | November 7, 1995 |
| Violent typhoon | |
| 10-minute sustained(JMA) | |
| Highest winds | 215 km/h (130 mph) |
| Lowest pressure | 910hPa(mbar); 26.87inHg |
| Category 5-equivalent super typhoon | |
| 1-minute sustained(SSHWS/JTWC) | |
| Highest winds | 285 km/h (180 mph) |
| Lowest pressure | 879hPa(mbar); 25.96inHg |
| Overall effects | |
| Fatalities | 936 total |
| Damage | $315 million |
| Areas affected | |
| IBTrACS | |
Part of the1995 Pacific typhoon season | |
Angela causedPHP9.33 billion worth of damage across the Philippines, in addition to 882 fatalities. It was the strongest typhoon to hit the Philippines sinceTyphoon Joanin 1970, and the costliest sinceTyphoon Mikein 1990.
Meteorological history
editTropical storm (39–73 mph, 63–118 km/h)
Category 1 (74–95 mph, 119–153 km/h)
Category 2 (96–110 mph, 154–177 km/h)
Category 3 (111–129 mph, 178–208 km/h)
Category 4 (130–156 mph, 209–251 km/h)
Category 5 (≥157 mph, ≥252 km/h)
Unknown
The monsoon trough that developed Yvette and Zack spawned another tropical depression on October 25 in conjunction with a tropical disturbance that originated in the Marshall Islands. It moved to the west, organizing very slowly, becoming a tropical storm on October 26.[1]Two days later, Angela further intensified into a typhoon, and between October 31 and November 1, Angela rapidly intensified into a Category 5-equivalent super typhoon with 1-minute sustained winds of 285 km/h (180 mph), while theJapan Meteorological Agencyreported peak 10-minute sustained winds of 215 km/h (130 mph). It maintained that intensity before gradually weakening as it tracked westward, making landfall in the Philippines on November 2 with 1-minute sustained winds of 260 km/h (160 mph) –still at Category 5-equivalent intensity.[2]Angela continued to the west-northwest, where upper-level winds caused it to dissipate on November 7 over theGulf of Tonkin.[3]
Impact, records, and retirement
editMore than 900 people died due to the typhoon. It wreaked havoc overMetro Manila,CalabarzonandBicol Region.It caused a total of 10.829 billionpesosin damage.[4]
More than 96,000 houses were destroyed throughout the affected area, along with bridges and roads. The worst impact was in theBicol Region.Angela passed almost right over Manila, causing a significant impact both there and inCatanduanes.InCalauag,storm surgesand flooding from adam failurekilled 121 people. In nearbyParacale,mudslides killed more than a hundred people.Power outagesaffected one-third of the country.[5]
Although the JMA, which is the officialregional specialized meteorological centerof the western Pacific, estimated a minimum central pressure of 910 mbar (26.87 inHg), the JTWC unofficially estimated a central pressure of 879 mbar (25.96 inHg), which would rank it high on thelist of most intense tropical cyclones,but still behindTyphoon Tip,[6]the most intense tropical cyclone ever recorded.[7]However, Angela is an unofficial contender for world's most intense tropical cyclone. In a study utilizing theDvorak techniquefor analysis of post-1987 typhoons, the authors concluded that Angela and1992's Gaywere higher on the scale than Tip. The authors also thought that Angela might have been slightly more intense than Gay, and hence Tip.[8]
Angela was the strongest typhoon to hit the Philippines since1970's Joan.[1]A weather observatory inCatanduanesreported a gust of 259 km/h (161 mph). This makes it the typhoon with third-highest gust recorded in the Philippines.[9]
Due to the high death toll and catastrophic damages,PAGASAofficially retired the nameRosingfrom the rotating naming lists. It was replaced byRening,which was used once in the1999 season.
See also
edit- Typhoons in the Philippines
- Typhoon Mike (Ruping, 1990)
- Typhoon Xangsane (Milenyo, 2006)
- Typhoon Nesat (Pedring, 2011)
- Typhoon Bopha (Pablo, 2012)
- Typhoon Haiyan (Yolanda, 2013)
- Typhoon Megi (Juan, 2010)
- Typhoon Rai (Odette, 2021)
- Typhoon Rammasun (Glenda, 2014)
- Typhoon Tembin (Vinta, 2017)
- Typhoon Ketsana (Ondoy, 2009)
- Typhoon Nock-ten (Nina, 2016)
- Typhoon Doksuri (Egay, 2023)
- Typhoon Mangkhut (Ompong, 2018)
- Typhoon Kammuri (Tisoy, 2019)
- Typhoon Goni (Rolly, 2020)– had a similar track and landfall date (late October to early November) in 2020.
- Typhoon Noru (Karding, 2022)– also took a similar track.
References
edit- ^ab"Super Typhoon Angela (29W)"(PDF).1995 Annual Tropical Cyclone Report.Joint Typhoon Warning Center.p. 170. Archived fromthe original(PDF)on 2011-06-07.Retrieved2008-11-02.
- ^"Super Typhoon Angela (29W)"(PDF).1995 Annual Tropical Cyclone Report.Joint Typhoon Warning Center.p. 171. Archived fromthe original(PDF)on 2011-06-07.Retrieved2008-11-02.
- ^"Super Typhoon Angela (29W)"(PDF).1995 Annual Tropical Cyclone Report.Joint Typhoon Warning Center.p. 173. Archived fromthe original(PDF)on 2011-06-07.Retrieved2008-11-02.
- ^David Michael Padua & Dominic Alojado (2008-06-10)."11 Worst Typhoons in the Philippines".Typhoon2000. Archived fromthe originalon 2008-10-16.Retrieved2007-02-04.
- ^"Super Typhoon Angela (29W)"(PDF).1995 Annual Tropical Cyclone Report.Joint Typhoon Warning Center.p. 175. Archived fromthe original(PDF)on 2011-06-07.Retrieved2008-11-02.
- ^Dunnavan."Typhoon Tip (23)"(PDF).1979 Annual Typhoon Report.Joint Typhoon Warning Center.p. 73. Archived fromthe original(PDF)on 2011-06-07.Retrieved2008-10-31.
- ^Chris Landsea(2006-11-28)."Subject:E1) Which is the most intense tropical cyclone on record?".FAQ: Hurricanes, Typhoons, and Tropical Cyclones.Atlantic Oceanographic and Meteorological LaboratoryHurricane Research Division.Retrieved2008-10-31.
- ^Karl Hoarau; Gary Padgett & Jean-Paul Hoarau."Have There Been Any Typhoons Stronger Than Super Typhoon Tip?"(PDF).American Meteorological Society.
- ^David Michael Padua & Dominic Alojado (2008-06-11)."Strongest Typhoons of the Philippines (1947 - 2006)".Typhoon2000. Archived fromthe originalon 2008-09-28.Retrieved2008-10-31.
External links
edit- JMA General Informationof Typhoon Angela (9520) from Digital Typhoon
- JMA Best Track Data (Graphics)of Typhoon Angela (9520)
- JMA Best Track Data (Text)
- JTWC Best Track Dataof Super Typhoon 29W (Angela)