TheYunnan–Guizhou PlateauorYungui Plateau(simplified Chinese:Vân Quý cao nguyên;traditional Chinese:Vân Quý cao nguyên;pinyin:Yúnguì Gāoyuán) is ahighland regionlocated insouthwest China.The region is primarily spread over theprovincesofYunnanandGuizhou.In the southwest, the Yungui is a true plateau with relatively flatter highland areas, while in the northeast, the Yungui is a generally mountainous area of rolling hills, gorges, andkarst topography.
| Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau | |
|---|---|
| Yungui Plateau | |
 | |
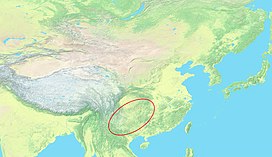 Topographic map of East Asia with Yungui Plateau highlighted | |
| Floor elevation | 500 m (1,600 ft) to 2,500 m (8,200 ft) |
| Geography | |
| Country | China |
| Provinces | Yunnan,Guizhou |
| Region | Southwest China |
| Coordinates | 26°N105°E/ 26°N 105°E |
| Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Chinese | Vân Quý cao nguyên | ||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | Vân Quý cao nguyên | ||||||||
| Postal | Yunnan–Kweichow Plateau | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Yungui Plateau | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Chinese | Vân Quý cao nguyên | ||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | Vân Quý cao nguyên | ||||||||
| Postal | Yunkwei Plateau | ||||||||
| |||||||||

Geography
editDefinition
editUnder the strictest definition, the Yungui Plateau stretches from theRed River Faultin Yunnan in the southwest to theWuling Mountainsin Hunan in the northeast.[1]This plateau region includes most of eastern Yunnan and most of Guizhou. It is common, however, for much of the rest of Yunnan and surrounding highland areas to be referred to as part of the Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau even where there are no plateau-like characteristics.[2]
Under the broader definition of the Yungui Plateau, the provinces would include not only Yunnan and Guizhou but alsoGulin Countyand the southernmost extremes ofSichuan,easternChongqing,southwesternHubei,westernHunan,and northwesternGuangxi.[1]
Human geography
editLocated inSouthwest China,the Yungui Plateau separates theSichuan BasinfromSouth China.The area has long been considered a backwater region of China.[3]Historically, the plateau has been home to manyminority peopleswho have traditionally engaged in intensive agriculture along hills and in valleys. Today, the Yungui region is one of the most economically depressed areas of China and both Guizhou and Yunnan provinces are in the bottom three in rankings for theHuman Development Index in China.[4]Many residents on the Yungui Plateau live in a traditional fashion in rural villages.
Major cities on the Yungui Plateau includeKunming,Guiyang,andZunyi.The Yungui Plateau is home to many extreme engineering feats where railways and expressways have been built to traverse the challenging terrain. Theworld's highest bridge,theBeipan gian g Bridge,is located on the Yunnan-Guizhou border in the heart of the plateau.
Physical geography
editThe Yungui Plateau is a large mountainous region with rugged terrain including steep karst peaks and deep gorges.[5]The plateau is buttressed by the largeHengduan Mountainsto the northwest and by lowland regions to the north, east, and southeast. Other major mountain ranges cross or surround portions of the Yungui Plateau. TheWumeng MountainsandWulian Fengform a barrier through north-central Yungui along theJinsha(UpperYangtze) River. To the north, theDalou Mountainsrun along the Yungui's edge with the Sichuan Basin. TheWuling Mountainsin the northeast form a transitional terrain between the plateau and theYangtze Plain.In the south, theMiao Rangesteps down to the karst hills of South China. Across theRed Riverto the southwest, theAilao Mountainsform a definitive barrier.[1][6]
The high mountain peaks of EasternTibetare the source of many ofAsia's great rivers, which flow southerly towards the Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau.[7]The rivers split around the plateau, with theSalweenandMekongkeeping south and theYangtzeturning northeast. Most of the western Yungui Plateau is drained by theNanpanandBeipanRivers, both headwaters of thePearl River.The eastern Yungui Plateau is largely drained by theWu River,a tributary of the Yangtze.
Major lakes have formed in the Yunnan portions of the Yungui Plateau, includingDian ChiandFuxian Lake.Erhai Lakeis located on the plateau's western edge at the southern base of the Hengduan Mountains.[1]
Climate and ecology
editThe climate gradually transitions from drier in the southwest to rainier in the northeast. In east-central Yunnan, parts of the Yungui Plateau experience asemi-arid climate.In most of Guizhou, the climate is classified ashumid subtropical.The Yungui Plateau is covered bysubtropical evergreen forestsfor much of its Yunnan portions and bymixed broadleaf forestsfor the Guizhou portions.[8][9]
Footnotes
edit- ^abcdAtlas of China.Beijing, China: SinoMaps Press. 2006.ISBN9787503141782.
- ^"Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau".Encyclopædia Britannica.Retrieved2007-08-06.
- ^China's Southwest.Lonely Planet. 2007.ISBN9781741041859.
- ^"China National Human Development Report 2016 Social Innovation for Inclusive Human Development"(PDF).China Publishing Group Corporation China Translation & Publishing House. 2016.
- ^"Chinese History and Statistics - Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau Upland".Retrieved2007-08-06.
- ^Suettinger, Robert Lee; Kuo, Ping-chia."Yunnan".Encyclopædia Britannica.Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.Retrieved31 August2017.
- ^Yang Qinye (2004).Tibetan Geography -- Long Rivers with Distant Sources.ISBN9787508506654.Retrieved2007-12-02.
- ^"Yunnan Plateau subtropical evergreen forests".Global Species.Myers Enterprises II.Retrieved31 July2017.
- ^"Guizhou Plateau broadleaf and mixed forests".Global Species.Myers Enterprises II.Retrieved31 July2017.