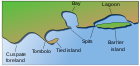
Intertidal wetland
Appearance
Anintertidal wetlandis an area along a shoreline that is exposed toairatlow tideand submerged athigh tide.This type ofwetlandis defined by anintertidal zoneand includes its ownintertidal ecosystems.
Description
[edit]The main types of intertidal wetlands aremudflats(e.g.,mangrove swamps) andsalt marshes.The mangrove swamps are encountered alongtropicalshores and are characterized bytreevegetation, while salt marshes are mostly found intemperatezones and are mostlygrassecosystems.[1]
Intertidal wetlands are commonly encountered in mostestuaries.Intertidal wetlandecosystemsare amongst the most productive plant communities and often constitute a large part of the estuary areas.[1][2][3] [4]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^abDay, John W. Jr.; Hall, Charles A. S.; Kemp, W. Michael; Yáñez-Arancibia, Alejandro (May 9, 1989)."Chapter 5: Intertidal Wetlands: Salt Marshes and Mangrove Swamp".Estuarine Ecology.John Wiley & Sons.ISBN978-0-471-06263-9.
- ^Dionne, Jean-Claude (2004)."Âge et taux moyen d'accrétion verticale des schorres du Saint-Laurent estuarien, en particulier ceux de Montmagny et de Sainte-Anne-de-Beaupré, Québec"[Age and Mean Rate of Vertical Accretion of Intertidal Marshes of the St. Lawrence Estuary, Particularly those at Montmagny and Sainte-Anne-de-Beaupré].Géographie physique et Quaternaire(in French).58(1): 73–108.doi:10.7202/013111ar.ISSN0705-7199.
- ^Ross, Pauline; Adam, Paul (March 19, 2013)."Climate Change and Intertidal Wetlands".Biology.2(1): 445–480.doi:10.3390/biology2010445.ISSN2079-7737.PMC4009871.PMID24832670.
- ^Rayner, Duncan; Glamore, William; Grandquist, Lisa; Ruprecht, Jamie; Waddington, Katrina; Khojasteh, Danial (April 2021)."Intertidal wetland vegetation dynamics under rising sea levels".Science of the Total Environment.766:144237.Bibcode:2021ScTEn.766n4237R.doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144237.ISSN0048-9697.PMID33421788.