(85989) 1999 JD6
 | |
| Discovery | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | LONEOS |
| Discovery date | 12 May 1999 |
| Designations | |
| Orbital characteristics[1] | |
| Epoch13 January 2016 (JD2457400.5) | |
| Uncertainty parameter0 | |
| Observation arc | 9167 days (25.10 yr) |
| Aphelion | 1.44183AU(215.695Gm) |
| Perihelion | 0.32425 AU (48.507 Gm) |
| 0.88304 AU (132.101 Gm) | |
| Eccentricity | 0.63280 |
| 0.83yr(303.1d) | |
| 137.83229° | |
| 1.18778°/day | |
| Inclination | 17.05701° |
| 130.21399° | |
| 309.18377° | |
| EarthMOID | 0.0487023 AU (7.28576 Gm) |
| JupiterMOID | 3.86909 AU (578.808 Gm) |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Dimensions | ~0.7 km × 2 km (contact binary) |
| 7.6638h(0.31933d) | |
| ~0.15 | |
| K(SMASS) | |
| ~16–18 | |
| 17.1 | |
(85989) 1999 JD6(provisional designation1999 JD6) is anAten asteroid,near-Earth object,andpotentially hazardous objectin the inner Solar System that makes frequent close approaches to Earth and Venus. On the Earth approach in 2015, it was observed by theGoldstone Solar System Radarand found to be acontact binarywith the largest axis approximately 2 kilometers wide, and each lobe about 200–300 meters large.[2]Although1999 JD6in its current orbit never passes closer than 0.047 AU to Earth, it is listed as a potentially hazardous object because it is large and might pose a threat in the future.
The asteroid is well-observed, having been observed over 2,000 times over a length of over 25 years, and was assigned a numeric designation in August 2004.[3]
July 2015 Earth passage
[edit]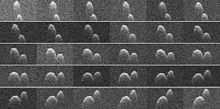
On 24 July 20151999 JD6came as close as 19 lunar distances to Earth.[4]It was imaged by radar, and shown to be a contact binary, about 2 kilometers (1.2 miles) on its long axis.[4]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^"JPL Small-Body Database Browser: 1999 JD6".JPL.NASA.Retrieved7 April2016.
- ^"JPL News: Earth Flyby of 'Space Peanut' Captured in New Video".JPL.NASA.Retrieved1 August2015.
- ^"IAU Minor Planet Center: (85989) 1999 JD6".Minor Planet Center.IAU.Retrieved1 August2015.
- ^abPIA19647
External links
[edit]- PIA19647: Asteroid 1999 JD6(Radar imaged 25 July 2015)
- Radar Movie of the same
- (85989) 1999 JD6atNeoDyS-2, Near Earth Objects—Dynamic Site
- (85989) 1999 JD6atESA–space situational awareness
- (85989) 1999 JD6at theJPL Small-Body Database



