From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Chemical compound
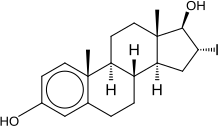
16α-Iodo-E2
(8R,9S,13S,14S,16R,17R)-16-iodo-13-methyl-6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-decahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,17-diol
CAS Number PubChem CID ChemSpider ChEMBL CompTox Dashboard (EPA ) Formula C 18 H 23 I O 2 Molar mass −1 3D model (JSmol )
C[C@]12CC[C@H]3[C@H]([C@@H]1C[C@H]([C@@H]2O)I)CCC4=C3C=CC(=C4)O
InChI=1S/C18H23IO2/c1-18-7-6-13-12-5-3-11(20)8-10(12)2-4-14(13)15(18)9-16(19)17(18)21/h3,5,8,13-17,20-21H,2,4,6-7,9H2,1H3/t13-,14-,15+,16-,17+,18+/m1/s1
Key:SSYGGPAGDDGXAF-ZXXIGWHRSA-N
16α-Iodo-E2 ,or16α-iodoestradiol ,is asynthetic ,steroidal ,potentestrogen with slight preference for theERα over theERβ that is used inscientific research .[1] [2] D of 16α-iodo-E2 for the ERα is 0.6 nM and for the ERβ is 0.24 nM, a 4-fold difference inaffinity ,whereasestradiol is considered to have similar affinity for the two receptor subtypes.[2] estriol (16α-hydroxyestradiol), 16α-iodo-E2 is considered to be equipotent with estradiol in terms of estrogenic activity.[3] Radiolabeled [16α-125 I]iodo-E2 has been employed inimaging to study theestrogen receptor .[4]
^ Manas ES, Unwalla RJ, Xu ZB, Malamas MS, Miller CP, Harris HA, Hsiao C, Akopian T, Hum WT, Malakian K, Wolfrom S, Bapat A, Bhat RA, Stahl ML, Somers WS, Alvarez JC (2004). "Structure-based design of estrogen receptor-beta selective ligands".J. Am. Chem. Soc .126 (46): 15106–19.doi :10.1021/ja047633o .PMID 15548008 . ^a b Chen GG, Vlantis AC, Zeng Q, van Hasselt CA (2008). "Regulation of cell growth by estrogen signaling and potential targets in thyroid cancer".Curr Cancer Drug Targets .8 (5): 367–77.doi :10.2174/156800908785133150 .PMID 18690843 . ^ Hochberg RB, Zielinski JE, Duax WL, Strong P (1986). "The molecular structure of 16 alpha-iodo-17 beta-estradiol, a high affinity ligand for the estrogen receptor".J. Steroid Biochem .25 (5A): 615–8.doi :10.1016/0022-4731(86)90002-6 .PMID 3795941 . ^ Cummins CH (1993). "Radiolabeled steroidal estrogens in cancer research".Steroids .58 (6): 245–59.doi :10.1016/0039-128x(93)90069-y .PMID 8212070 .S2CID 29080385 .
ER Tooltip Estrogen receptor
Agonists
Steroidal: 2-Hydroxyestradiol 2-Hydroxyestrone 3-Methyl-19-methyleneandrosta-3,5-dien-17β-ol 3α-Androstanediol 3α,5α-Dihydrolevonorgestrel 3β,5α-Dihydrolevonorgestrel 3α-Hydroxytibolone 3β-Hydroxytibolone 3β-Androstanediol 4-Androstenediol 4-Androstenedione 4-Fluoroestradiol 4-Hydroxyestradiol 4-Hydroxyestrone 4-Methoxyestradiol 4-Methoxyestrone 5-Androstenediol 7-Oxo-DHEA 7α-Hydroxy-DHEA 7α-Methylestradiol 7β-Hydroxyepiandrosterone 8,9-Dehydroestradiol 8,9-Dehydroestrone 8β-VE2 10β,17β-Dihydroxyestra-1,4-dien-3-one (DHED) 11β-Chloromethylestradiol 11β-Methoxyestradiol 15α-Hydroxyestradiol 16-Ketoestradiol 16-Ketoestrone 16α-Fluoroestradiol 16α-Hydroxy-DHEA 16α-Hydroxyestrone 16α-Iodoestradiol 16α-LE2 16β-Hydroxyestrone 16β,17α-Epiestriol (16β-hydroxy-17α-estradiol) 17α-Estradiol (alfatradiol )17α-Dihydroequilenin 17α-Dihydroequilin 17α-Epiestriol (16α-hydroxy-17α-estradiol) 17α-Ethynyl-3α-androstanediol 17α-Ethynyl-3β-androstanediol 17β-Dihydroequilenin 17β-Dihydroequilin 17β-Methyl-17α-dihydroequilenin Abiraterone Abiraterone acetate Alestramustine Almestrone Anabolic steroids (e.g.,testosterone andesters ,methyltestosterone ,metandienone (methandrostenolone) ,nandrolone andesters ,many others; via estrogenic metabolites)Atrimustine Bolandiol Bolandiol dipropionate Butolame Clomestrone Cloxestradiol
Conjugated estriol Conjugated estrogens Cyclodiol Cyclotriol DHEA DHEA-S ent -EstradiolEpiestriol (16β-epiestriol, 16β-hydroxy-17β-estradiol) Epimestrol Equilenin Equilin ERA-63 (ORG-37663) Esterified estrogens Estetrol Estradiol
Estramustine Estramustine phosphate Estrapronicate Estrazinol Estriol
Estrofurate Estrogenic substances Estromustine Estrone
Etamestrol (eptamestrol) Ethinylandrostenediol
Ethinylestradiol
Ethinylestriol Ethylestradiol Etynodiol Etynodiol diacetate Hexolame Hippulin Hydroxyestrone diacetate Lynestrenol Lynestrenol phenylpropionate Mestranol Methylestradiol Moxestrol Mytatrienediol Nilestriol Norethisterone Noretynodrel Orestrate Pentolame Prodiame Prolame Promestriene RU-16117 Quinestradol Quinestrol Tibolone Xenoestrogens: Anise -related (e.g.,anethole ,anol ,dianethole ,dianol ,photoanethole )Chalconoids (e.g.,isoliquiritigenin ,phloretin ,phlorizin (phloridzin) ,wedelolactone )Coumestans (e.g.,coumestrol ,psoralidin )Flavonoids (incl.7,8-DHF ,8-prenylnaringenin ,apigenin ,baicalein ,baicalin ,biochanin A ,calycosin ,catechin ,daidzein ,daidzin ,ECG ,EGCG ,epicatechin ,equol ,formononetin ,glabrene ,glabridin ,genistein ,genistin ,glycitein ,kaempferol ,liquiritigenin ,mirificin ,myricetin ,naringenin ,penduletin ,pinocembrin ,prunetin ,puerarin ,quercetin ,tectoridin ,tectorigenin )Lavender oil Lignans (e.g.,enterodiol ,enterolactone ,nyasol (cis -hinokiresinol) )Metalloestrogens (e.g.,cadmium )Pesticides (e.g.,alternariol ,dieldrin ,endosulfan ,fenarimol ,HPTE ,methiocarb ,methoxychlor ,triclocarban ,triclosan )Phytosteroids (e.g.,digitoxin (digitalis ),diosgenin ,guggulsterone )Phytosterols (e.g.,β-sitosterol ,campesterol ,stigmasterol )Resorcylic acid lactones (e.g.,zearalanone ,α-zearalenol ,β-zearalenol ,zearalenone ,zeranol (α-zearalanol) ,taleranol (teranol, β-zearalanol) )Steroid -like (e.g.,deoxymiroestrol ,miroestrol )Stilbenoids (e.g.,resveratrol ,rhaponticin )Synthetic xenoestrogens (e.g.,alkylphenols ,bisphenols (e.g.,BPA ,BPF ,BPS ),DDT ,parabens ,PBBs ,PHBA ,phthalates ,PCBs )Others (e.g.,agnuside ,rotundifuran ) MixedSERMs Tooltip Selective estrogen receptor modulators ) Antagonists
Coregulator-binding modulators: ERX-11
GPER Tooltip G protein-coupled estrogen receptor
Agonists Antagonists Unknown