2019 North Macedonian presidential election
| |||||||||||||||||
| Turnout | 41.67% (first round) 46.65% (second round) | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||
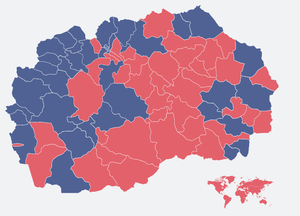 Second round results by municipality | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
 |
|---|
|
|
Presidential elections were held inNorth Macedoniain 2019. Three candidates were on the ballot in the first round, held on 21 April:Stevo Pendarovski,supported by the ruling coalition led by theSocial Democratic Union of Macedonia,including theDemocratic Union for Integration;[1]Gordana Siljanovska-Davkovaof the leading opposition partyVMRO-DPMNE,andBlerim Reka,an independent supported by Albanian opposition partiesAlliance for AlbaniansandBesa Movement.[2]The first round did not result in an absolute majority for any candidate, with Pendarovski receiving the most votes. In the second round held on 5 May, Pendarovski defeated Siljanovska-Davkova with 54% of the vote.[3]
Incumbent PresidentGjorge Ivanovwas constitutionally barred from seeking a third term in office, having previously been elected in2009and2014.
Background
[edit]The elections were the first in North Macedonia after thePrespa agreement on the naming dispute,signed on 17 June 2018. Areferendumwas held on 30 September, in which a majority of voters approved the agreement, although turnout was far below the quorum required to validate the result, mainly because of an organized boycott of the Anti-Prespa agreement bloc. TheAssemblysubsequently approved the change of the country's name to "North Macedonia" on 11 January 2019, and Greece subsequently ratified the agreement and the accession protocol for NATO.
Incumbent President Gjorge Ivanov was a vocal opponent of the name change and refused to sign the laws and amendments on the matter. However, Assembly SpeakerTalat Xhafericlaimed that his signature was enough to enforce the change.[4]
The name change had the support of the government coalition formed by theSocial Democrats(SDSM) and the ethnic AlbanianDemocratic Union for Integration.The nationalistVMRO-DPMNEcoalition led byHristijan Mickoskiwas in favor of NATO integration but against the name change, although the change was approved in the Assembly with at least four VMRO-DPMNE MPs voting in favour.[5]
After her nomination, VMRO-DPMNE candidate Gordana Siljanovska-Davkova had promised to initiate a second referendum and restore the old name to the country if she won.[6]
Electoral system
[edit]The President of North Macedonia is elected using a modifiedtwo-round system;a candidate can only be elected in the first round of voting if they receive the equivalent of over 50% of the vote from all registered voters.[7]In the second round, voter turnout must be at least 40% for the result to be deemed valid.[8]Before 2009, the constitution required turnout in the second round to be 50% to validate the result. However, the XXXI amendment approved on 9 January 2009 lowered the threshold to 40%,[8]as the then-government feared the trend of reducing turnouts would lead to presidential elections being frequently invalidated. In the2009 presidential elections,second round turnout was just 42.6%.[9]
Theconstitutionmandates that the President must be over 40 years of age and have lived in the country for ten of the last fifteen years.
Opinion polls
[edit]Before and between the voting rounds, several opinion polls were conducted. The percentages of the polls below are related to only those voters who declared that they would vote for a certain candidate.
First round
| Date(s) conducted | Polling firm/Client | Sample size/Type | Pendarovski/SDSM | Siljanovska/VMRO-DPMNE | Reka/AA,Besa | Lead |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8-14 Apr 2019 | Rating Agency | 1,112/Face-to-face | 45.5 | 39.5 | 15.0 | 6.0 |
| 7-11 Apr 2019 | IDSCS/Telma&MCMS | 967/Telephone | 44.1 | 38.1 | 17.8 | 6.0 |
| 4-10 Apr 2019 | M-Prospect/MRT | 1,197/Telephone | 43.2 | 38.8 | 18.0 | 4.4 |
| 10 Mar-10 Apr 2019 | Samerimpex Impulses/MCMS | 1,147/Online | 50.4 | 41.4 | 8.2 | 9.0 |
| 23-27 Mar 2019 | IPIS/Sitel | 1,110/Telephone | 45.9 | 42.7 | 11.3 | 3.2 |
| 13-19 Mar 2019 | M-Prospect/Telma&MCMS | 1,001/Telephone | 42.9 | 38.4 | 18.7 | 4.5 |
Second round
| Date(s) conducted | Polling firm/Client | Sample size/Type | Pendarovski/SDSM | Siljanovska/VMRO-DPMNE | Lead |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13-19 Mar 2019 | M-Prospect/Telma&MCMS | 1,001/Telephone | 55.3 | 44.7 | 10.6 |
Results
[edit]To win in the first round, a candidate would have had to receive at least 904,066 votes, equivalent to 50% of the number of registered voters.
| Candidate | Party | First round | Second round | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Votes | % | Votes | % | |||
| Stevo Pendarovski | Social Democratic Union of Macedonia | 322,581 | 44.75 | 435,656 | 53.58 | |
| Gordana Siljanovska-Davkova | VMRO-DPMNE | 318,341 | 44.16 | 377,446 | 46.42 | |
| Blerim Reka | Independent | 79,888 | 11.08 | |||
| Total | 720,810 | 100.00 | 813,102 | 100.00 | ||
| Valid votes | 720,810 | 95.66 | 813,102 | 96.40 | ||
| Invalid/blank votes | 32,697 | 4.34 | 30,406 | 3.60 | ||
| Total votes | 753,507 | 100.00 | 843,508 | 100.00 | ||
| Registered voters/turnout | 1,808,131 | 41.67 | 1,808,131 | 46.65 | ||
| Source:OCSE | ||||||
References
[edit]- ^"Втор обид на Пендаровски, овојпат како консензуален кандидат".Deutsche Welle(in Macedonian). 2 March 2019.Retrieved14 April2022.
- ^"Професорот Блерим Река независен претседателски кандидат, ќе го поддржат Алијанса за Албанците и Беса".Сакам Да Кажам(in Macedonian). 28 February 2019.Retrieved14 April2022.
- ^Supporter of North Macedonia Name Change Wins Presidency.New York Times, 6 May 2019.
- ^"Ivanov: Amnesty is a blackmail for votes for the Prespes Agreement".Independent Balkan News Agency.28 December 2018.
- ^"Deputies agree historic name change for Macedonia".France 24.11 January 2019.
- ^Силјановска ќе игра „втор референдум “за Договорот од Преспа!18.02.2019; Deutsche Welle.
- ^Polls Open in Macedonia Presidential ElectionsBalkan Insight, 13 April 2014
- ^abAmendment XXXIConstitution of North Macedonia
- ^Anna Fruhstorfer & Michael Hein (2016)Constitutional Politics in Central and Eastern Europe: From Post-Socialist Transition to the Reform of Political SystemsSpringer, p235


