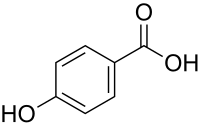
4-Hydroxybenzoic acid
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
4-Hydroxybenzoic acid | |
| Other names
p-Hydroxybenzoic acid
para-Hydroxybenzoic acid PHBA 4-hydroxybenzoate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.550 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChemCID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard(EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H6O3 | |
| Molar mass | 138.122g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White crystalline solid |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Density | 1.46g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 214.5 °C (418.1 °F; 487.6 K) |
| Boiling point | N/A, decomposes[1] |
| 0.5g/100 mL | |
| Solubility |
|
| logP | 1.58 |
| Acidity(pKa) | 4.54 |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health(OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
Irritant |
| NFPA 704(fire diamond) | |
| 250 °C (482 °F; 523 K) | |
| Lethal doseor concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50(median dose)
|
2200mg/kg (oral, mouse) |
| Safety data sheet(SDS) | HMDB |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in theirstandard state(at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
4-Hydroxybenzoic acid,also known asp-hydroxybenzoic acid(PHBA), is amonohydroxybenzoic acid,a phenolic derivative of benzoic acid. It is a white crystalline solid that is slightly soluble in water andchloroformbut more soluble in polar organic solvents such asalcoholsandacetone.4-Hydroxybenzoic acid is primarily known as the basis for the preparation of itsesters,known asparabens,which are used as preservatives in cosmetics and some ophthalmic solutions. It isisomericwith 2-hydroxybenzoic acid, known assalicylic acid,a precursor toaspirin,and with3-hydroxybenzoic acid.
Natural occurrences
[edit]It is found in plants of the genusVitexsuch asV. agnus-castusorV. negundo,and inHypericum perforatum(St John's wort). It is also found inSpongiochloris spongiosa,a freshwater green alga.
The compound is also found inGanoderma lucidum,amedicinal mushroomwith the longest record of use.
Cryptanaerobacter phenolicusis a bacterium species that producesbenzoatefromphenolvia 4-hydroxybenzoate.[2]
Occurrences in food
[edit]4-Hydroxybenzoic acid can be found naturally incoconut.[3]It is one of the main catechinsmetabolitesfound in humans after consumption ofgreen teainfusions.[4]It is also found inwine,[5]invanilla,inMacrotyloma uniflorum(horse gram),carob[6]and inPhyllanthus acidus(Otaheite gooseberry).
Açaí oil,obtained from the fruit of theaçaí palm(Euterpe oleracea), is rich inp-hydroxybenzoic acid (892±52 mg/kg).[7]It is also found incloudy olive oil[citation needed]and in the edible mushroomRussula virescens(green-cracking russula).[citation needed]
Related compounds
[edit]p-Hydroxybenzoic acid glucosidecan be found in mycorrhizal and non-mycorrhizal roots of Norway spruces (Picea abies).[8]
Violdelphinis an anthocyanin, a type of plant pigments, found in blue flowers and incorporating twop-hydroxybenzoic acid residues, onerutinosideand twoglucosidesassociated with adelphinidin.
Agnusideis the ester ofaucubinandp-hydroxybenzoic acid.[9]
Biosynthesis
[edit]Chorismate lyaseis an enzyme that transformschorismateinto 4-hydroxybenzoate and pyruvate. This enzyme catalyses the first step inubiquinonebiosynthesis inEscherichia coliand other Gram-negative bacteria.
Benzoate 4-monooxygenaseis an enzyme that utilizesbenzoate,NADPH, H+and O2to produce 4-hydroxybenzoate, NADP+and H2O. This enzyme can be found inAspergillus niger.
4-Hydroxybenzoate also arises from tyrosine.[10]
Metabolism
[edit]As an intermediate
[edit]The enzyme4-methoxybenzoate monooxygenase (O-demethylating)transforms4-methoxybenzoate,an electron acceptor AH2and O2into 4-hydroxybenzoate, formaldehyde, the reduction product A and H2O. This enzyme participates in2,4-dichlorobenzoatedegradation inPseudomonas putida.
The enzyme4-hydroxybenzaldehyde dehydrogenaseuses4-hydroxybenzaldehyde,NAD+and H2O to produce 4-hydroxybenzoate, NADH and H+.This enzyme participates intolueneandxylenedegradation in bacteria such asPseudomonas mendocina.It is also found in carrots (Daucus carota).
The enzyme that2,4'-dihydroxyacetophenone dioxygenasetransforms2,4'-dihydroxyacetophenoneand O2into 4-hydroxybenzoate andformate.This enzyme participates inbisphenol Adegradation. It can be found inAlcaligenesspecies.
The enzyme4-chlorobenzoate dehalogenaseuses4-chlorobenzoateand H2O to produce 4-hydroxybenzoate andchloride.It can be found inPseudomonasspecies.
The enzyme4-hydroxybenzoyl-CoA thioesteraseutilizes4-hydroxybenzoyl-CoAand H2O to produce 4-hydroxybenzoate and CoA. This enzyme participates in2,4-dichlorobenzoatedegradation. It can be found inPseudomonasspecies.
The enzyme4-hydroxybenzoate polyprenyltransferaseuses a polyprenyl diphosphate and 4-hydroxybenzoate to produce diphosphate and4-hydroxy-3-polyprenylbenzoate.This enzyme participates inubiquinonebiosynthesis.
The enzyme4-hydroxybenzoate geranyltransferaseutilizesgeranyl diphosphateand 4-hydroxybenzoate to produce3-geranyl-4-hydroxybenzoateand diphosphate. Biosynthetically,alkanninis produced in plants from the intermediates 4-hydroxybenzoic acid andgeranyl pyrophosphate.This enzyme is involved inshikoninbiosynthesis. It can be found inLithospermum erythrorhizon.
The enzyme3-hydroxybenzoate—CoA ligaseuses ATP,3-hydroxybenzoateand CoA to produce AMP, diphosphate and3-hydroxybenzoyl-CoA.The enzyme works equally well with 4-hydroxybenzoate. It can be found inThauera aromatica.
Biodegradation
[edit]The enzyme4-hydroxybenzoate 1-hydroxylasetransforms 4-hydroxybenzoate, NAD(P)H, 2 H+and O2intohydroquinone,NAD(P)+,H2O and CO2.This enzyme participates in2,4-dichlorobenzoatedegradation. It can be found inCandida parapsilosis.
The enzyme4-hydroxybenzoate 3-monooxygenasetransforms 4-hydroxybenzoate, NADPH, H+and O2intoprotocatechuate,NADP+and H2O. This enzyme participates inbenzoatedegradation via hydroxylation and2,4-dichlorobenzoatedegradation. It can be found inPseudomonas putidaandPseudomonas fluorescens.
The enzyme4-hydroxybenzoate 3-monooxygenase (NAD(P)H)utilizes 4-hydroxybenzoate, NADH, NADPH, H+and O2to produce 3,4-dihydroxybenzoate (protocatechuic acid), NAD+,NADP+and H2O. This enzyme participates inbenzoatedegradation via hydroxylation and2,4-dichlorobenzoatedegradation. It can be found inCorynebacterium cyclohexanicumand inPseudomonassp.
The enzyme4-hydroxybenzoate decarboxylaseuses 4-hydroxybenzoate to producephenoland CO2.This enzyme participates inbenzoatedegradation viacoenzyme A(CoA) ligation. It can be found inKlebsiella aerogenes(Aerobacter aerogenes).
The enzyme4-hydroxybenzoate—CoA ligasetransforms ATP, 4-hydroxybenzoate and CoA to produce AMP, diphosphate and4-hydroxybenzoyl-CoA.This enzyme participates inbenzoatedegradation via CoA ligation. It can be found inRhodopseudomonas palustris.
Coniochaeta hoffmanniiis a plant pathogen that commonly inhabits fertile soil. It is known to metabolize aromatic compounds of low molecular weight, such asp-hydroxybenzoic acid.
Glycosylation
[edit]The enzyme4-hydroxybenzoate 4-O-beta-D-glucosyltransferasetransformsUDP-glucoseand 4-hydroxybenzoate into UDP and4-(beta-D-glucosyloxy)benzoate.It can be found in the pollen ofPinus densiflora.
Chemistry
[edit]TheHammett equationdescribes a linear free-energy relationship relating reaction rates and equilibrium constants for many reactions involving benzoic acid derivatives with meta- and para-substituents.
Chemical production
[edit]4-Hydroxybenzoic acid is produced commercially from potassiumphenoxideandcarbon dioxidein theKolbe-Schmitt reaction.[11]It can also be produced in the laboratory by heatingpotassium salicylatewithpotassium carbonateto 240 °C, followed by treating with acid.[12]
Chemical reactions
[edit]4-Hydroxybenzoic acid has about one tenth the acidity ofbenzoic acid,having anacid dissociation constantKa=3.3×10−5Mat 19 °C.[citation needed]Its acid dissociation follows this equation:
- HOC6H4CO2H⇌HOC6H4CO−2+H+
Chemical use
[edit]Vectranis a manufactured fiber, spun from aliquid crystal polymer.Chemically it is an aromatic polyester produced by the polycondensation of 4-hydroxybenzoic acid and6-hydroxynaphthalene-2-carboxylic acid.The fiber has been shown to exhibit strong radiation shielding used byBigelow Aerospaceand produced byStemRad.[13]
4,4′-Dihydroxybenzophenoneis generally prepared by the rearrangement ofp-hydroxyphenylbenzoate. Alternatively,p-hydroxybenzoic acid can be converted top-acetoxybenzoyl chloride.This acid chloride reacts with phenol to give, after deacetylation, 4,4′-dihydroxybenzophenone.
Examples of drugs made from PHBA includenifuroxazide,orthocaine,ormeloxifeneandproxymetacaine.
Bioactivity and safety
[edit]4-Hydroxybenzoic acid is a popular antioxidant in part because of its low toxicity. TheLD50is 2200 mg/kg in mice (oral).[14]
4-Hydroxybenzoic acid hasestrogenicactivity bothin vitroandin vivo,[15]and stimulates the growth of humanbreast cancercell lines.[16][17]It is a common metabolite ofparabenesters,such asmethylparaben.[15][16][17]The compound is a relatively weak estrogen, but can produceuterotrophywith sufficient doses to an equivalent extent relative toestradiol,which is unusual for a weakly estrogenic compound and indicates that it may be afull agonistof theestrogen receptorwith relatively lowbinding affinityfor the receptor.[16][18][19]It is about 0.2% to 1% as potent as an estrogen as estradiol.[18]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^"4-Hydroxybenzoic acid"(PDF).International Programme on Chemical Safety (IPCS).Archived fromthe original(PDF)on 24 September 2015.Retrieved10 January2015.
- ^Juteau, P.; Côté, V.; Duckett, M.-F.; Beaudet, R.; Lépine, F.; Villemur, R.; Bisaillon, J.-G. (January 2005)."Cryptanaerobacter phenolicusgen. nov., sp. nov., an anaerobe that transforms phenol into benzoate via 4-hydroxybenzoate ".International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology.55(1): 245–250.doi:10.1099/ijs.0.02914-0.PMID15653882.
- ^Dey, G.; Chakraborty, M.; Mitra, A. (April 2005). "Profiling C6–C3 and C6–C1 phenolic metabolites inCocos nucifera".Journal of Plant Physiology.162(4): 375–381.doi:10.1016/j.jplph.2004.08.006.PMID15900879.
- ^Pietta, P. G.; Simonetti, P.; Gardana, C.; Brusamolino, A.; Morazzoni, P.; Bombardelli, E. (1998). "Catechin metabolites after intake of green tea infusions".BioFactors.8(1–2): 111–118.doi:10.1002/biof.5520080119.PMID9699018.S2CID37684286.
- ^Tian, R.-R.; Pan, Q.-H.; Zhan, J.-C.; Li, J.-M.; Wan, S.-B.; Zhang, Q.-H.; Huang, W.-D. (2009)."Comparison of phenolic acids and flavan-3-ols during wine fermentation of grapes with different harvest times".Molecules.14(2): 827–838.doi:10.3390/molecules14020827.PMC6253884.PMID19255542.
- ^Goulas, V.; Stylos, E.; Chatziathanasiadou, M. V.; Mavromoustakos, T.; Tzakos, A. G. (2016)."Functional Components of Carob Fruit: Linking the Chemical and Biological Space".International Journal of Molecular Sciences.17(11): 1875.doi:10.3390/ijms17111875.PMC5133875.PMID27834921.
- ^Pacheco Palencia, L. A.; Mertens-Talcott, S.; Talcott, S. T. (June 2008). "Chemical composition, antioxidant properties, and thermal stability of a phytochemical enriched oil from Açaí (Euterpe oleraceaMart.) ".Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry.56(12): 4631–4636.doi:10.1021/jf800161u.PMID18522407.
- ^Münzenberger, B.; Heilemann, J.; Strack, D.; Kottke, I.; Oberwinkler, F. (1990). "Phenolics of mycorrhizas and non-mycorrhizal roots of Norway spruce".Planta.182(1): 142–148.doi:10.1007/BF00239996.PMID24197010.S2CID43504838.
- ^Hoberg, E.; Meier, B.; Sticher, O. (September 2000). "An analytical high performance liquid chromatographic method for the determination of agnuside andp-hydroxybenzoic acid contents in Agni-casti fructose ".Phytochemical Analysis.11(5): 327–329.Bibcode:2000PChAn..11..327H.doi:10.1002/1099-1565(200009/10)11:5<327::AID-PCA523>3.0.CO;2-0.
- ^Acosta, Manuel Jesús; Vazquez Fonseca, Luis; Desbats, Maria Andrea; Cerqua, Cristina; Zordan, Roberta; Trevisson, Eva; Salviati, Leonardo (2016)."Coenzyme Q biosynthesis in health and disease".Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Bioenergetics.1857(8): 1079–1085.doi:10.1016/j.bbabio.2016.03.036.PMID27060254.
- ^Edwin Ritzer and Rudolf Sundermann "Hydroxycarboxylic Acids, Aromatic" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2002, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim.doi:10.1002/14356007.a13_519
- ^Buehler, C. A.; Cate, W. E. (1943)."p-Hydroxybenzoic acid ".Organic Syntheses;Collected Volumes,vol. 2, p. 341.
- ^Charles Fishman, Dan Winters (2016-04-11)."This Expandable Structure Could Become the Future of Living in Space".Smithsonian Magazine.Retrieved2020-12-07.
- ^Lewis, R. J., ed. (1996).Sax's Dangerous Properties of Industrial Materials.Vol. 1–3 (9th ed.). New York, NY: Van Nostrand Reinhold. p. 2897.
- ^abKhetan, S. K. (23 May 2014).Endocrine Disruptors in the Environment.Wiley. p. 109.ISBN978-1-118-89115-5.
- ^abcPugazhendhi, D.; Pope, G. S.; Darbre, P. D. (2005). "Oestrogenic activity ofp-hydroxybenzoic acid (common metabolite of paraben esters) and methylparaben in human breast cancer cell lines ".Journal of Applied Toxicology.25(4): 301–309.doi:10.1002/jat.1066.PMID16021681.S2CID12342018.
- ^abGabriel, J. (April 2013).Holistic Beauty from the Inside Out: Your Complete Guide to Natural Health, Nutrition, and Skincare.Seven Stories Press. p. 31.ISBN978-1-60980-462-6.
- ^abLemini, C.; Silva, G.; Timossi, C.; Luque, D.; Valverde, A.; González Martínez, M.; Hernández, A.; Rubio Póo, C.; Chávez Lara, B.; Valenzuela, F. (1997). "Estrogenic effects ofp-hydroxybenzoic acid in CD1 mice ".Environmental Research.75(2): 130–134.Bibcode:1997ER.....75..130L.doi:10.1006/enrs.1997.3782.PMID9417843.
- ^OECD (November 2004).OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals / OECD Series on Testing and Assessment Detailed Background Review of the Uterotrophic Bioassay.OECD Publishing. p. 183.ISBN978-92-64-07885-7.

