Ammonium metavanadate

| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Ammonium trioxovanadate(V)
| |
| Other names
Ammonium vanadate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.329 |
PubChemCID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2859 |
CompTox Dashboard(EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| NH4VO3 | |
| Molar mass | 116.98 g/mol |
| Appearance | white |
| Density | 2.326 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | >200 °C (392 °F; 473 K)[1](decomposes) |
| 4.8 g/100 ml (20 °C)[1] | |
| Solubility | soluble indiethanolamine,ethanolamine |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health(OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
possiblemutagen,dangerous for the environment |
| GHSlabelling: | |
 
| |
| Danger | |
| H301,H332,H340,H361,H370,H372,H412 | |
| P201,P202,P260,P261,P264,P270,P271,P273,P281,P301+P310,P304+P312,P304+P340,P307+P311,P308+P313,P312,P314,P321,P330,P405,P501 | |
| NFPA 704(fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| Lethal doseor concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50(median dose)
|
58.1 mg/kg, oral (rat) |
| Related compounds | |
Otheranions
|
Ammonium orthovanadate Ammonium hexavanadate |
Othercations
|
Sodium metavanadate Potassium metavanadate |
Related compounds
|
Vanadium pentoxide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in theirstandard state(at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Ammonium metavanadateis theinorganic compoundwith the formula NH4VO3.It is a white salt, although samples are often yellow owing to impurities of V2O5.It is an important intermediate in the purification of vanadium.[2]
Synthesis and structure
[edit]The compound is prepared by the addition of ammonium salts to solutions of vanadate ions, generated by dissolution ofV2O5in basic aqueous solutions, such as hot sodium carbonate. The compound precipitates as a colourless solid.[3][4]This precipitation step can be slow.
The compound adopts a polymeric structure consisting of chains of [VO3]−,formed as corner-sharing VO4tetrahedra. These chains are interconnected viahydrogen bondswithammoniumions.[5]
 |
 |
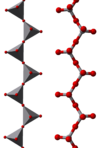
|
| ball-and-stick model | polyhedral model | [(VO3)n]n−chains |
Uses
[edit]Vanadium is often purified from aqueous extracts of slags and ore by selective precipitation of ammonium metavanadate. The material is then roasted to givevanadium pentoxide:[2]
- 2 NH4VO3→ V2O5+ 2 NH3+ H2O
Other
[edit]Vanadates can behave as structural mimics of phosphates, and in this way they exhibit biological activity.[6][7]
Ammonium metavanadate is used to prepareMandelin reagent,a qualitative test foralkaloids.[citation needed]
References
[edit]- ^abJohn Rumble (June 18, 2018).CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics(99th ed.). CRC Press. pp. 4–40.ISBN978-1138561632.
- ^abGünter Bauer, Volker Güther, Hans Hess, Andreas Otto, Oskar Roidl, Heinz Roller, Siegfried Sattelberger "Vanadium and Vanadium Compounds" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2005, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim.doi:10.1002/14356007.a27_367
- ^G. Brauer "Ammonium Metavanadate" in Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry, 2nd Ed. Edited by G. Brauer, Academic Press, 1963, NY. Vol. 1. p. 1272.
- ^Robert H. Baker, Harry Zimmerman, R. N. Maxson "Ammonium Metavanadate" Inorganic Syntheses, 1950, Vol. 3, 117-118.doi:10.1002/9780470132340.ch30
- ^Vladimír Syneček and František Hanic (1954). "The crystal structure of ammonium metavanadate".Czechoslovak Journal of Physics.4(2): 120–129.Bibcode:1954CzJPh...4..120S.doi:10.1007/BF01687750.S2CID97890604.
- ^Korbecki, Jan; Baranowska-Bosiacka, Irena; Gutowska, Izabela; Chlubek, Dariusz "Biochemical and medical importance of vanadium compounds" Acta Biochimica Polonica 2012, vol. 59, pp. 195-200.
- ^Crans, D. C.; Chatterjee, P. B. "Vanadium Biochemistry" Reedijk, Jan;Poeppelmeier, Kenneth,Eds. Comprehensive Inorganic Chemistry II (2013), 3, 323-342.doi:10.1016/B978-0-08-097774-4.00324-7

