Anatolia
Anadolu | |
|---|---|
 Anatolia, also known as Asia Minor, has two definitions. It is either bounded by an imprecise line from theGulf of Iskenderunto theBlack Sea,or it is the entirety of the Asiatic territory of Turkey.[1][2] | |
| Etymology | "the East", from Greek |
| Geography | |
| Location | Turkey |
| Coordinates | 39°N35°E/ 39°N 35°E |
| Area | 756,000 km2(292,000 sq mi)[3] (incl.SoutheasternandEastern Anatolia Region) |
| Administration | |
Turkey | |
| Largest city | Ankara(pop. 5,700,000[4]) |
| Demographics | |
| Demonym | Anatolian (Turkish:Anadolulu[5]) |
| Languages | Turkish Minority:Kurdish,Armenian,Greek,Kabardian,North Caucasian languages,variousothers |
| Ethnic groups | Turks,Kurds,Armenians,Chechens,Circassians,Greeks,Laz,variousothers |
| Additional information | |
| Time zone | |
Anatolia(Turkish:Anadolu), also known asAsia Minor,[a]is apeninsulaofTurkeysituated inWestern Asia.It is the westernmost protrusion of theAsiancontinent, and constitutes the majority of contemporary territory of Turkey. Geographically, Anatolia is bounded by theMediterranean Seato the south, theAegean Seato the west, theTurkish Straitsto the northwest, and theBlack Seato the north. The eastern and southeastern limits has either been expanded to the entirety of Asiatic Turkey,[1]or to an imprecise line from theBlack SeatoGulf of Iskenderun.[2]Topographically, theSea of Marmaraconnects the Black Sea with the Aegean Sea through theBosporusstrait and theDardanellesstrait, and separates Anatolia fromThracein theBalkan peninsulaofSoutheastern Europe.
Anatolia was an early centre for the development of farming during theNeolithicperiod following its origination in the adjacentFertile Crescent.Beginning around 9,000 years ago there was major migration ofAnatolian Neolithic Farmersinto Europe, with their descendants coming to dominate Europe as far west as the Iberian Peninsula and the British Isles.
The ancientAnatolian peoplesspoke the now-extinctAnatolian languagesof theIndo-Europeanlanguage family, which were largely replaced by theGreek languageduringclassical antiquityas well as during theHellenistic,Roman,andByzantineperiods. The major Anatolian languages includedHittite,Luwian,andLydian,while other, poorly attested local languages includedPhrygianandMysian.Hurro-Urartian languageswere spoken in the southeastern kingdom ofMitanni,whileGalatian,aCeltic language,was spoken inGalatia,central Anatolia. Ancient peoples in the region includedGalatians,Hurrians,Assyrians,Armenians,Hattians,Cimmerians,as well asIonian,Dorian,andAeolic Greeks.TheTurkificationof Anatolia began under the rule of theSeljuk Empirein the late 11th century, continued under theOttoman Empirebetween the late 13th and early 20th centuries, and continues today under theRepublic of Türkiye.However, various non-Turkic languages continue to be spoken by minorities in Anatolia, includingKurdish,Neo-Aramaic,Armenian,North Caucasian languages,Laz,Georgian,andGreek.
Geography
[edit]
Traditionally, Anatolia is considered to extend in the east to an indefinite line running from theGulf of Alexandrettato theBlack Sea,[9]coterminous with theAnatolian Plateau.This traditional geographical definition is used, for example, in the latest edition ofMerriam-Webster's Geographical Dictionary.[2]Under this definition, Anatolia is bounded to the east by theArmenian Highlands,and theEuphratesbefore that river bends to the southeast to enterMesopotamia.[10]To the southeast, it is bounded by the ranges that separate it from theOrontesvalley inSyriaand the Mesopotamian plain.[10]
Following theArmenian genocide,Western Armeniawas renamedtheEastern Anatolia Regionby the newly established Turkish government.[11][12]In 1941, with theFirst Geography Congresswhich divided Turkey intoseven geographical regionsbased on differences in climate and landscape, the easternprovinces of Turkeywere placed into theEastern Anatolia Region,[13]which largely corresponds to the historical region ofWestern Armenia(named as such after the division ofGreater Armeniabetween theRoman/Byzantine Empire(Western Armenia) andSassanid Persia(Eastern Armenia) in 387 AD). Vazken Davidian terms the expanded use of "Anatolia" to apply to territory in eastern Turkey that was formerly referred to asArmenia(which had a sizeableArmenianpopulation before theArmenian genocide) an "ahistorical imposition" and notes that a growing body of literature is uncomfortable with referring to the Ottoman East as "Eastern Anatolia".[14][11][12]
The highest mountain in theEastern Anatolia Region(also the highest peak in theArmenian Highlands) isMount Ararat(5123 m).[15]TheEuphrates,Aras,KarasuandMurat riversconnect the Armenian Highlands to theSouth Caucasusand the Upper Euphrates Valley. Along with theÇoruh,these rivers are the longest in the Eastern Anatolia Region.[16]
Etymology
[edit]The English-language nameAnatoliaderives from theGreekἈνατολή(Anatolḗ) meaning "the East" and designating (from a Greek point of view) eastern regions in general. The Greek word refers to the direction where the sun rises, coming fromἀνατέλλωanatello'(Ι) rise up', comparable to terms in other languages such as "levant"from Latinlevo'to rise', "orient"from Latinorior'to arise, to originate',Hebrewמִזְרָחmizraḥ'east' fromזָרַחzaraḥ'to rise, to shine',Aramaicמִדְנָחmidnaḥfromדְּנַחdenaḥ'to rise, to shine'.[17][18]
The use of Anatolian designations has varied over time, perhaps originally referring to theAeolian,IonianandDoriancolonies situated along the eastern coasts of theAegean Sea,but also encompassing eastern regions in general. Such use of Anatolian designations was employed during the reign of Roman EmperorDiocletian(r. 284–305), who created theDiocese of the East,known in Greek as the Eastern Diocese, but completely unrelated to the regions of Asia Minor. In their widest territorial scope, Anatolian designations were employed during the reign of Roman EmperorConstantine I(306–337), who created thePraetorian prefecture of the East,known in Greek as the Eastern Prefecture, encompassing all eastern regions of theLate Roman Empireand spanning fromThracetoEgypt.
Only after the loss of other eastern regions during the 7th century and the reduction ofByzantineeastern domains to Asia Minor, that region became the only remaining part of theByzantine East,and thus commonly referred to (in Greek) as the Eastern part of the Empire. At the same time, theAnatolic Theme(Ἀνατολικὸν θέμα/ "the Eastern theme" ) was created, as a province (theme) covering the western and central parts of Turkey's present-dayCentral Anatolia Region,centered aroundIconium,but ruled from the city ofAmorium.[19][20]
The Latinized form "Anatolia",with its-iaending, is probably aMedieval Latininnovation.[18]The modern Turkish formAnadoluderives directly from the Greek nameAνατολή(Anatolḗ). The Russian male nameAnatoly,the FrenchAnatoleand plainAnatol,all stemming from saintsAnatolius of Laodicea(d. 283) andAnatolius of Constantinople(d. 458; the firstPatriarch of Constantinople), share the same linguistic origin.
Names
[edit]The oldest known name for any region within Anatolia is related to its central area, known as the "Land ofHatti"– a designation that was initially used for the land of ancientHattians,but later became the most common name for the entire territory under the rule of ancientHittites.[21]
The first recorded name the Greeks used for the Anatolian peninsula, though not particularly popular at the time, wasἈσία(Asía),[22]perhaps from an Akkadian expression for the "sunrise" or possibly echoing the name of theAssuwa leaguein western Anatolia.[citation needed]The Romans used it as the name of theirprovince,comprising the west of the peninsula plus the nearbyAegean Islands.As the name "Asia" broadened its scope to apply to the vaster region east of the Mediterranean, some Greeks inLate Antiquitycame to use the name Asia Minor (Μικρὰ Ἀσία,Mikrà Asía), meaning "Lesser Asia" to refer to present-day Anatolia, whereas the administration of the Empire preferred the description Ἀνατολή (Anatolḗ;lit. 'the East').
TheendonymῬωμανία (Rōmanía"the land of the Romans, i.e. the Eastern Roman Empire" ) was understood as another name for the province by the invadingSeljuq Turks,who founded aSultanate of Rûmin 1077. Thus (land of the)Rûmbecame another name for Anatolia. By the 12th century Europeans had started referring to Anatolia asTurchia.[23]
During the era of theOttoman Empire,many mapmakers referred to the mountainous plateau in eastern Anatolia asArmenia.Other contemporary sources called the same areaKurdistan.[24]Geographers have used East Anatolian Plateau,Armenian Plateauand the Iranian Plateau to refer to the region; the former two largely overlap.[25]While a standard definition of Anatolia refers to the entire Asian side of Turkey, according to archaeologist Lori Khatchadourian, this difference in terminology "primarily result[s] from the shifting political fortunes and cultural trajectories of the region since the nineteenth century".[25]
Turkey'sFirst Geography Congressin 1941 created twogeographical regions of Turkeyto the east of the Gulf of Iskenderun-Black Sea line, theEastern Anatolia Regionand theSoutheastern Anatolia Region,[26]the former largely corresponding to the western part of the Armenian Highlands, the latter to the northern part of the Mesopotamian plain. According toRichard Hovannisian,this changing of toponyms was "necessary to obscure all evidence" of theArmenianpresence as part of the policy ofArmenian genocide denialembarked upon by the newly established Turkish government and what Hovannisian calls its "foreign collaborators".[27]
History
[edit]Prehistoric Anatolia
[edit]
Human habitation in Anatolia dates back to thePaleolithic.[28]Neolithic settlements includeÇatalhöyük,Çayönü,Nevali Cori,Aşıklı Höyük,Boncuklu Höyük,Hacilar,Göbekli Tepe,Norşuntepe,Köşk Höyük,andYumuktepe.Çatalhöyük (7.000 BCE) is considered the most advanced of these.[29]Recent advances in archaeogenetics have confirmed that thespread of agriculturefrom the Middle East to Europe was strongly correlated with themigrationofearly farmers from Anatoliaabout 9,000 years ago, and was not just a cultural exchange.[30]Anatolian Neolithic farmers derived most of their ancestry from localAnatolian hunter-gatherers,suggesting that agriculture was adopted in site by these hunter-gatherers and not spread bydemic diffusioninto the region.[31]Anatolian derived Neolithic Farmers would subsequently spread across Europe, as far west as the Iberian Peninsula and the British Isles,[32][33]as well as to theMaghreb.[34]Most modern Europeans derive a significant part of their ancestry from these Neolithic Anatolian farmers.[35]
NeolithicAnatolia has beenproposedas thehomelandof theIndo-European language family,although linguists tend to favour alater originin the steppes north of the Black Sea. However, it is clear that theAnatolian languages,the earliest attested branch of Indo-European, have been spoken in Anatolia since at least the 19th century BCE.[36][37]
Ancient Anatolia
[edit]The earliest historical data related to Anatolia appear during theBronze Ageand continue throughout theIron Age.The most ancient period in thehistory of Anatoliaspans from the emergence of ancientHattians,up to the conquest of Anatolia by theAchaemenid Empirein the 6th century BCE.
Hattians and Hurrians
[edit]The earliest historically attested populations of Anatolia were theHattiansin central Anatolia, andHurriansfurther to the east. The Hattians were an indigenous people, whose main center was the city ofHattush.Affiliation ofHattian languageremains unclear, whileHurrian languagebelongs to a distinctive family ofHurro-Urartian languages.All of those languages are extinct; relationships with indigenouslanguages of the Caucasushave been proposed,[38]but are not generally accepted. The region became famous for exporting raw materials. Organized trade between Anatolia andMesopotamiastarted to emerge during the period of theAkkadian Empire,and was continued and intensified during the period of theOld Assyrian Empire,between the 21st and the 18th centuries BCE. Assyrian traders were bringing tin and textiles in exchange for copper, silver or gold. Cuneiform records, datedc. 20th century BCE,found in Anatolia at the Assyrian colony ofKanesh,use an advanced system of trading computations and credit lines.[39][40][41]
Hittite Anatolia (18th–12th century BCE)
[edit]
Unlike the Akkadians and Assyrians, whose Anatolian trading posts were peripheral to their core lands inMesopotamia,theHittiteswere centered atHattusa(modern Boğazkale) in north-central Anatolia by the 17th century BCE. They were speakers of an Indo-European language, theHittite language,ornesili(the language of Nesa) in Hittite. The Hittites originated from local ancient cultures that grew in Anatolia, in addition to the arrival of Indo-European languages. Attested for the first time in the Assyrian tablets ofNesaaround 2000 BCE, they conquered Hattusa in the 18th century BCE, imposing themselves over Hattian- and Hurrian-speaking populations. According to the widely acceptedKurgan theoryon theProto-Indo-European homeland,however, the Hittites (along with the other Indo-Europeanancient Anatolians) were themselves relatively recentimmigrantsto Anatolia from the north. However, they did not necessarily displace the population genetically; they assimilated into the former peoples' culture, preserving the Hittite language.
The Hittites adopted the Mesopotamiancuneiform script.In the Late Bronze Age,Hittite New Kingdom(c. 1650 BCE) was founded, becoming an empire in the 14th century BCE after the conquest ofKizzuwatnain the south-east and the defeat of theAssuwa leaguein western Anatolia. The empire reached its height in the 13th century BCE, controlling much of Asia Minor, northwesternSyria,and northwest upper Mesopotamia. However, the Hittite advance toward the Black Sea coast was halted by the semi-nomadic pastoralist and tribalKaskians,a non-Indo-European people who had earlier displaced thePalaic-speakingIndo-Europeans.[42]Much of the history of the Hittite Empire concerned war with the rival empires ofEgypt,Assyriaand theMitanni.[43]
TheAncient Egyptianseventually withdrew from the region after failing to gain the upper hand over the Hittites and becoming wary of the power of Assyria, which had destroyed the Mitanni Empire.[43]The Assyrians and Hittites were then left to battle over control of eastern and southern Anatolia and colonial territories inSyria.The Assyrians had better success than the Egyptians, annexing much Hittite (and Hurrian) territory in these regions.[44]
Post-Hittite Anatolia (12th–6th century BCE)
[edit]After 1180 BCE, during theLate Bronze Age collapse,the Hittite Empire disintegrated into several independentSyro-Hittite states,subsequent to losing much territory to theMiddle Assyrian Empireand being finally overrun by thePhrygians,another Indo-European people who are believed to have migrated from theBalkans.The Phrygian expansion into southeast Anatolia was eventually halted by the Assyrians, who controlled that region.[44]
- Luwians
Another Indo-European people, theLuwians,rose to prominence in central and western Anatoliac. 2000BCE.Their languagebelonged to the same linguistic branch asHittite.[49]The general consensus amongst scholars is that Luwian was spoken across a large area of western Anatolia, including (possibly)Wilusa(Troy), the Seha River Land (to be identified with theHermosand/orKaikosvalley), and the kingdom of Mira-Kuwaliya with its core territory of the Maeander valley.[50]From the 9th century BCE, Luwian regions coalesced into a number of states such asLydia,Caria,andLycia,all of which hadHellenicinfluence.
- Arameans
Arameansencroached over the borders of south-central Anatolia in the century or so after the fall of the Hittite empire, and some of the Syro-Hittite states in this region became an amalgam of Hittites and Arameans. These became known asSyro-Hittite states.
- Neo-Assyrian Empire

From the 10th to late 7th centuries BCE, much of Anatolia (particularly the southeastern regions) fell to theNeo-Assyrian Empire,including all of theSyro-Hittite states,Tabal,Commagene,theCimmeriansandScythians,and swathes ofCappadocia.
The Neo-Assyrian empire collapsed due to a bitter series of civil wars followed by a combined attack byMedes,Persians,Scythians and their ownBabylonianrelations. The last Assyrian city to fall wasHarranin southeast Anatolia. This city was the birthplace of the last king ofBabylon,the AssyrianNabonidusand his son and regentBelshazzar.Much of the region then fell to the short-lived Iran-basedMedian Empire,with the Babylonians and Scythians briefly appropriating some territory.
- Cimmerian and Scythian invasions
From the late 8th century BCE, a new wave of Indo-European-speaking raiders entered northern and northeast Anatolia: theCimmeriansandScythians.The Cimmerians overranPhrygiaand the Scythians threatened to do the same toUrartuandLydia,before both were finally checked by the Assyrians.
- Early Greek presence
The north-western coast of Anatolia was inhabited by Greeks of theAchaean/Mycenaeanculture from the 20th century BCE, related to the Greeks of southeastern Europe and theAegean.[51]Beginning with theBronze Age collapseat the end of the 2nd millennium BCE, the west coast of Anatolia was settled byIonian Greeks,usurping the area of the related but earlierMycenaean Greeks.Over several centuries, numerous Ancient Greekcity-stateswere established on the coasts of Anatolia. Greeks started Western philosophy on the western coast of Anatolia (Pre-Socratic philosophy).[51]
Classical Anatolia
[edit]InClassical antiquity,Anatolia was described by the Ancient Greek historianHerodotusand later historians as divided into regions that were diverse in culture, language, and religious practices.[52]The northern regions includedBithynia,Paphlagonia,andPontus;to the west wereMysia,Lydia,and Caria; andLycia,Pamphylia,andCiliciabelonged to the southern shore. There were also several inland regions:Phrygia,Cappadocia,Pisidia,andGalatia.[52]Languages spoken included the late survivingAnatolic languages,Isaurian,[53]andPisidian,Greek in western and coastal regions,Phrygianspoken until the 7th century CE,[54]local variants ofThracianin the northwest, theGalatian variant of GaulishinGalatiauntil the 6th century CE,[55][56][57]Cappadocianin the homonymous region,[58]Armenianin the east, andKartvelian languagesin the northeast.
Anatolia is known as the birthplace of mintedcoinage(as opposed to unminted coinage, which first appears inMesopotamiaat a much earlier date) as a medium of exchange, some time in the 7th century BCE in Lydia. The use of minted coins continued to flourish during theGreekandRomaneras.[59][60]
During the 6th century BCE, all of Anatolia was conquered by thePersianAchaemenid Empire,the Persians having usurped theMedesas thedominant dynasty of Persia.In 499 BCE, theIoniancity-states on the west coast of Anatolia rebelled against Persian rule. TheIonian Revolt,as it became known, though quelled, initiated theGreco-Persian Wars,which ended in a Greek victory in 449 BCE, and the Ionian cities regained their independence. By thePeace of Antalcidas(387 BCE), which ended theCorinthian War,Persia regained control over Ionia.[61][62]
In 334 BCE, theMacedonianGreek kingAlexander the Greatconquered the Anatolian peninsula from the Achaemenid Persian Empire.[63]Alexander's conquest opened up the interior of Asia Minor to Greek settlement and influence.

Following the death of Alexander the Great and the subsequent breakup of theMacedonian Empire,Anatolia was ruled by a series of Hellenistic kingdoms, such as theAttalids of Pergamumand theSeleucids,the latter controlling most of Anatolia. A period of peacefulHellenizationfollowed, such that the local Anatolian languages had been supplanted by Greek by the 1st century BCE. In 133 BCE the last Attalid king bequeathed his kingdom to theRoman Republic;western and central Anatolia came underRoman control,butHellenistic cultureremained predominant.
Mithridates VI Eupator,ruler of theKingdom of Pontusin northern Anatolia, waged war against theRoman Republicin the year 88 BCE in order to halt the advance of Romanhegemonyin theAegean Searegion. Mithridates VI sought to dominate Asia Minor and theBlack Searegion, waging several hard-fought but ultimately unsuccessful wars (theMithridatic Wars) to break Roman dominion over Asia and theHellenic world.[64]He has been called the greatest ruler of the Kingdom of Pontus.[65]Further annexations by Rome, in particular of the Kingdom of Pontus byPompey,brought all of Anatolia underRoman control,except for the southeastern frontier with theParthian Empire,which remained unstable for centuries, causing a series of military conflicts that culminated in theRoman–Parthian Wars(54 BCE – 217 CE).
Early Christian period
[edit]
After thefirst division of the Roman Empire,Anatolia became part of theEastern Roman Empire,otherwise known as the Byzantine Empire orByzantium.[67]In the 1st century CE, Anatolia becameone of the first places where Christianity spread,so that by the 4th century CE, western and central Anatolia were overwhelmingly Christian and Greek-speaking.[67]
Byzantine Anatolia was one of the wealthiest and most densely populated places in theLater Roman Empire.Anatolia's wealth grew during the 4th and 5th centuries thanks, in part, to thePilgrim's Roadthat ran through the peninsula. Literary evidence about the rural landscape stems from theChristian hagiographiesof the 6th-centuryNicholas of Sionand 7th-centuryTheodore of Sykeon.Large and prosperous urban centers of Byzantine Anatolia includedAssos,Ephesus,Miletus,Nicaea,Pergamum,Priene,Sardis,andAphrodisias.[67]
From the mid-5th century onwards, urbanism was affected negatively and began to decline, while the rural areas reached unprecedented levels of prosperity in the region.[67]Historians and scholars continue to debate the cause of the urban decline in Byzantine Anatolia between the 6th and 7th centuries,[67]variously attributing it to thePlague of Justinian(541), theByzantine–Sasanian War(602–628), and theArab invasion of the Levant(634–638).[68]
Medieval period
[edit]
In the 10 years following theBattle of Manzikertin 1071, theSeljuk Turksfrom Central Asia migrated over large areas of Anatolia, with particular concentrations around the northwestern rim.[69]The Turkish language and the Islamic religion were gradually introduced as a result of the Seljuk conquest, and this period marks the start of Anatolia's slow transition from predominantly Christian and Greek-speaking, to predominantly Muslim and Turkish-speaking (although ethnic groups such as Armenians, Greeks, and Assyrians remained numerous and retained Christianity and their native languages). In the following century, the Byzantines managed to reassert their control in western and northern Anatolia. Control of Anatolia was then split between the Byzantine Empire and the SeljukSultanate of Rûm,with the Byzantine holdings gradually being reduced.[70]

In 1255, theMongolsswept through eastern and central Anatolia, and would remain until 1335. TheIlkhanategarrison was stationed nearAnkara.[70][71]After the decline of the Ilkhanate from 1335 to 1353, theMongol Empire's legacy in the region was theUyghurEretna Dynastythat was overthrown byKadi Burhan al-Dinin 1381.[72]
By the end of the 14th century, most of Anatolia was controlled by variousAnatolian beyliks.Smyrna fell in 1330, and the last Byzantine stronghold in Anatolia, Philadelphia, fell in 1390. TheTurkmenBeyliks were under the control of the Mongols, at least nominally, through declining Seljuk sultans.[73][74]The Beyliks did not mint coins in the names of their own leaders while they remained under the suzerainty of theMongolIlkhanids.[75]TheOsmanlirulerOsman Iwas the first Turkish ruler who minted coins in his own name in 1320s; they bear the legend "Minted by Osman son of Ertugrul".[76]Since the minting of coins was a prerogative accorded in Islamic practice only to asovereign,it can be considered that the Osmanli, or Ottoman Turks, had become formally independent from the Mongol Khans.[77]
Ottoman Empire
[edit]
Among theTurkishleaders, theOttomansemerged as great power underOsman Iand his sonOrhan.[78][79]TheAnatolian beylikswere successively absorbed into the risingOttoman Empireduring the 15th century.[80]It is not well understood how the Osmanlı, orOttoman Turks,came to dominate their neighbours, as the history of medieval Anatolia is still little known.[81]The Ottomans completed the conquest of the peninsula in 1517 with the taking ofHalicarnassus(modernBodrum) from theKnights of Saint John.[82]
Modern times
[edit]
With the acceleration of the decline of the Ottoman Empire in the early 19th century, and as a result of the expansionist policies of theRussian Empirein theCaucasus,many Muslim nations and groups in that region, mainlyCircassians,Tatars,Azeris,Lezgis,Chechensand severalTurkicgroups left their homelands and settled in Anatolia. As the Ottoman Empire further shrank in theBalkanregions and then fragmented during theBalkan Wars,much of the non-Christian populations of its former possessions, mainly Balkan Muslims (Bosniaks,Albanians,Turks,Muslim BulgariansandGreek Muslimssuch as theVallahadesfromGreek Macedonia), were resettled in various parts of Anatolia, mostly in formerly Christian villages throughout Anatolia.
A continuous reverse migration occurred since the early 19th century, when Greeks from Anatolia,Constantinopleand Pontus area migrated toward the newly independentKingdom of Greece,and also towards theUnited States,the southern part of theRussian Empire,Latin America, and the rest of Europe.
Following the Russo-Persian Treaty of Turkmenchay (1828) and the incorporation of Eastern Armenia into the Russian Empire, another migration involved the large Armenian population of Anatolia, which recorded significant migration rates from Western Armenia (Eastern Anatolia) toward the Russian Empire, especially toward its newly established Armenian provinces.
Anatolia remainedmulti-ethnicuntil the early 20th century (see therise of nationalism under the Ottoman Empire). During World War I, theArmenian genocide,theGreek genocide(especially inPontus), and theAssyrian genocidealmost entirely removed the ancient indigenous communities ofArmenian,Greek,andAssyrianpopulations in Anatolia and surrounding regions. Following theGreco-Turkish War of 1919–1922,most remaining ethnic Anatolian Greeks were forced out during the 1923population exchange between Greece and Turkey.Of the remainder, most have left Turkey since then, leaving fewer than 5,000 Greeks in Anatolia today.[83]
Geology
[edit]
Anatolia's terrain is structurally complex. A centralmassifcomposed of uplifted blocks and downfoldedtroughs,covered by recentdepositsand giving the appearance of a plateau with rough terrain, is wedged between two folded mountain ranges that converge in the east. True lowland is confined to a few narrow coastal strips along the Aegean, Mediterranean, and the Black Sea coasts. Flat or gently sloping land is rare and largely confined to the deltas of theKızıl River,the coastal plains ofÇukurovaand the valley floors of theGediz Riverand theBüyük Menderes Riveras well as some interior high plains in Anatolia, mainly aroundLake Tuz(Salt Lake) and theKonyaBasin (Konya Ovasi).
There are two mountain ranges in southern Anatolia: theTaurusand theZagrosmountains.[84]
Climate
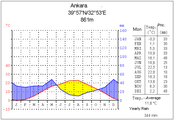
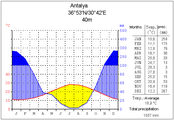
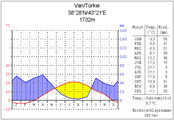
[edit]Anatolia has a varied range of climates. The central plateau is characterized by a continental climate, with hot summers and cold snowy winters. The south and west coasts enjoy a typical Mediterranean climate, with mild rainy winters, and warm dry summers.[85]The Black Sea and Marmara coasts have a temperate oceanic climate, with warm, foggy summers and much rainfall throughout the year.
Ecoregions
[edit]

There is a diverse number of plant and animal communities.
The mountains and coastal plain of northern Anatolia experience a humid and mild climate. There aretemperate broadleaf, mixedandconiferousforests. The central and eastern plateau, with its driercontinental climate,has deciduous forests and forest steppes. Western and southern Anatolia, which have aMediterranean climate,containMediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrubecoregions.
- Euxine-Colchic deciduous forests:These temperate broadleaf and mixed forests extend across northern Anatolia, lying between the mountains of northern Anatolia and the Black Sea. They include the enclaves oftemperate rainforestlying along the southeastern coast of the Black Sea in eastern Turkey and Georgia.[86]
- Northern Anatolian conifer and deciduous forests:These forests occupy the mountains of northern Anatolia, running east and west between the coastal Euxine-Colchic forests and the drier, continental climate forests of central and eastern Anatolia.[87]
- Central Anatolian deciduous forests:These forests of deciduous oaks and evergreen pines cover the plateau of central Anatolia.[88]
- Central Anatolian steppe:These dry grasslands cover the drier valleys and surround the saline lakes of central Anatolia, and includehalophytic(salt tolerant) plant communities.[89]

- Eastern Anatolian deciduous forests:This ecoregion occupies the plateau of eastern Anatolia. The drier and more continental climate is beneficial for steppe-forests dominated by deciduous oaks, with areas of shrubland, montane forest, and valley forest.[90]
- Anatolian conifer and deciduous mixed forests:These forests occupy the western, Mediterranean-climate portion of the Anatolian plateau. Pine forests and mixed pine and oak woodlands and shrublands are predominant.[91]
- Aegean and Western Turkey sclerophyllous and mixed forests:These Mediterranean-climate forests occupy the coastal lowlands and valleys of western Anatolia bordering the Aegean Sea. The ecoregion has forests ofTurkish pine(Pinus brutia),oak forests and woodlands, andmaquis shrublandof Turkish pine and evergreensclerophylloustrees and shrubs, includingOlive(Olea europaea),Strawberry Tree(Arbutus unedo),Arbutus andrachne,Kermes Oak(Quercus coccifera),andBay Laurel(Laurus nobilis).[92]
- Southern Anatolian montane conifer and deciduous forests:These mountain forests occupy the Mediterranean-climateTaurus Mountainsof southern Anatolia. Conifer forests are predominant, chiefly Anatolian black pine(Pinus nigra),Cedar of Lebanon(Cedrus libani),Taurus fir(Abies cilicica),andjuniper(Juniperus foetidissimaandJ. excelsa).Broadleaf trees include oaks,hornbeam,andmaples.[93]
- Eastern Mediterranean conifer-sclerophyllous-broadleaf forests:This ecoregion occupies the coastal strip of southern Anatolia between the Taurus Mountains and the Mediterranean Sea. Plant communities include broadleaf sclerophyllous maquis shrublands, forests of Aleppo Pine(Pinus halepensis)and Turkish Pine(Pinus brutia),and dry oak(Quercusspp.) woodlands and steppes.[94]
Demographics
[edit]The largest cities in Anatolia (aside from the Asian side ofIstanbul) areAnkara,İzmir,Bursa,Antalya,Konya,Adana,İzmit,Mersin,Manisa,Kayseri,Samsun,Balıkesir,Kahramanmaraş,Aydın,Adapazarı,Denizli,Muğla,Eskişehir,Trabzon,Ordu,Afyonkarahisar,Sivas,Tokat,Zonguldak,Kütahya,Çanakkale,OsmaniyeandÇorum.All have populations of more than 500,000.[citation needed]
See also
[edit]- Aeolis
- Anatolian hypothesis
- Anatolianism
- Anatolian leopard
- Anatolian Plate
- Anatolian Shepherd
- Ancient kingdoms of Anatolia
- Antigonid dynasty
- Doris (Asia Minor)
- Empire of Nicaea
- Empire of Trebizond
- Gordium
- Lycaonia
- Midas
- Miletus
- Myra
- Pentarchy
- Pontic Greeks
- Rumi
- Saint Anatolia
- Saint John
- Saint Nicholas
- Saint Paul
- Seleucid Empire
- Seven churches of Asia
- Seven Sleepers
- Tarsus
- Troad
- Turkic migration
Explanatory notes
[edit]- ^Additional alternative names includeAsian Turkey,theAnatolian Peninsula,and theAnatolian Plateau.
References
[edit]Citations
[edit]- ^ab
- McColl 2014,p. 922: "Thrace, its European area, is about the size of VERMONT at 9,412 square mi (24,378 square km). Its Asian area (Asia Minor) is called Anatolia and covers 291,971 square mi (756,202 square km)"
- Cohen 2008,p. 125: "Anatolia, [Gr.=sunrise], Asiatic part of Turkey; its area covers 97% of all Turkey"
- Tockner, Uehlinger & Robinson 2009:"About 97% of the country is in Asia Minor (Anatolia) and 3% in Europe (Thrace)"
- "Turkey".The World Factbook.Central Intelligence Agency.Retrieved20 February2024.:"the 97% of the country in Asia is referred to as Anatolia"
- "Anatolia".Encyclopedia Britannica.Retrieved29 February2024.:"Anatolia, the peninsula of land that today constitutes the Asian portion of Turkey"
- Steadman & McMahon 2011,p. 466
- Howard 2016,p. 7
- Helen Chapin Metz, ed. (1995)."Turkey: A Country Study | Geography".Washington: GPO for the Library of Congress.Retrieved31 May2024.:"The Asian part of the country is known by a variety of names--Asia Minor, Asiatic Turkey, the Anatolian Plateau, and Anatolia (Anadolu)"
- ^abcHopkins, Daniel J.; Staff, Merriam-Webster; 편집부 (2001).Merriam-Webster's Geographical Dictionary.Merriam-Webster. p. 46.ISBN978-0-87779-546-9.Archivedfrom the original on 28 November 2021.Retrieved18 May2001.
Anatolia: The part of Turkey in Asia equivalent to the peninsula of Asia Minor up to indefinite line on E from Gulf of Iskenderun to Black Sea comprising about three fifths of Turkey's provinces
- ^Sansal, Burak."History of Anatolia".Archivedfrom the original on 6 April 2002.Retrieved7 December2017.
- ^"Turkish Statistical Institute The Results of Address Based Population Registration System 2017".www.turkstat.gov.tr.Archivedfrom the original on 2 May 2019.Retrieved2 September2020.
- ^Güncel Türkçe Sözlük,s.v. Anadolu
- ^abc"Illustration of the Lake (later Sea) of Marmara and the formation of the Turkish Straits after the Black Sea deluge".www.ncdc.noaa.gov.26 January 2014.Archivedfrom the original on 31 August 2021.Retrieved22 May2021.
- ^abcDimitrov P., 2003."The Black Sea – a Clue to the Secret of World Flood".Archived21 May 2021 at theWayback Machine.Oceanology,4, 52–57.
- ^abcDimitrov P., D. Dimitrov. 2004.The Black Sea The Flood and the ancient myths.Archived15 May 2021 at theWayback Machine."Slavena", Varna,ISBN954579335X,91 pp.,doi:10.13140/RG.2.2.18954.16327.
- ^Philipp Niewohner (2017).The Archaeology of Byzantine Anatolia: From the End of Late Antiquity until the Coming of the Turks.Oxford University Press. pp. 18–.ISBN978-0190610470.Archivedfrom the original on 11 March 2020.Retrieved7 December2018.
- ^abStephen Mitchell (1995).Anatolia: Land, Men, and Gods in Asia Minor. The Celts in Anatolia and the impact of Roman rule.Clarendon Press, 266 pp.ISBN978-0198150299[1]Archived29 March 2017 at theWayback Machine
- ^abSahakyan, Lusine (2010).Turkification of the Toponyms in the Ottoman Empire and the Republic of Turkey.Montreal: Arod Books.ISBN978-0969987970.
- ^abHovannisian, Richard (2007).The Armenian Genocide: Cultural and Ethical Legacies.New Brunswick, NJ: Transaction Publishers. p. 3.ISBN978-1412835923.Archivedfrom the original on 10 October 2017.Retrieved10 September2015.
- ^A Comparative Analysis Regarding Pictures Included in Secondary School Geography Textbooks Taught in Turkey.Archived13 April 2015 at theWayback Machine,Okan Yasar and Mehmet Seremet,International Research in Geographical and Environmental Education,2007.
- ^Vazken Khatchig Davidian, "Imagining Ottoman Armenia: Realism and Allegory in Garabed Nichanian's Provincial Wedding in Moush and Late Ottoman Art Criticism", p. 7 & footnote 34, inÉtudes arméniennes contemporainesvolume 6, 2015.
- ^Fevzi Özgökçe; Kit Tan; Vladimir Stevanović (2005). "A new subspecies of Silene acaulis (Caryophyllaceae) from East Anatolia, Turkey".Annales Botanici Fennici.42(2): 143–149.JSTOR23726860.
- ^Palumbi, Giulio (5 September 2011). McMahon, Gregory; Steadman, Sharon (eds.)."The Chalcolithic of Eastern Anatolia".The Oxford Handbook of Ancient Anatolia.1.doi:10.1093/oxfordhb/9780195376142.013.0009.Archivedfrom the original on 12 May 2018.Retrieved6 May2018.
- ^Henry George Liddell; Robert Scott."ἀνατολή".A Greek-English Lexicon.Archivedfrom the original on 26 May 2007.Retrieved20 February2021.
- ^ab"Anatolia | Origin and meaning of the name Anatolia".Online Etymology Dictionary.Archivedfrom the original on 13 July 2017.Retrieved14 May2021.
- ^"On the First Thema, called Anatolikón. This theme is called Anatolikón or Theme of the Anatolics, not because it is above and in the direction of the east where the sun rises, but because it lies to the East of Byzantium and Europe."Constantine VII Porphyrogenitus,De Thematibus,ed. A. Pertusi. Vatican:Vatican Library,1952, pp. 59 ff.
- ^John Haldon,Byzantium, a History,2002, p. 32.
- ^Bryce 2009,pp. 297–98.
- ^Henry George Liddell, Robert Scott,Ἀσία.Archived27 April 2011 at theWayback Machine,A Greek-English Lexicon,on Perseus.
- ^Everett-Heath, John (2018)."Anatolia".The Concise Dictionary of World Place-Names.Vol. 1. Oxford University Press.doi:10.1093/acref/9780191866326.001.0001.ISBN978-0191866326.Archivedfrom the original on 6 December 2018.Retrieved5 December2018.
- ^Suny, Ronald Grigor (2015).'They Can Live in the Desert but Nowhere Else': A History of the Armenian Genocide.Princeton University Press. p. 31.ISBN978-1400865581.
- ^abSteadman & McMahon 2011,p. 466
- ^Ali Yiğit, "Geçmişten Günümüze Türkiye'yi Bölgelere Ayıran Çalışmalar ve Yapılması Gerekenler",Ankara Üniversitesi Türkiye Coğrafyası Araştırma ve Uygulama Merkezi, IV. Ulural Coğrafya Sempozyumu, "Avrupa Birliği Sürecindeki Türkiye'de Bölgesel Farklılıklar",pp. 34–35.Archived9 November 2013 at theWayback Machine.
- ^Hovannisian, Richard G. (1998).Remembrance and Denial: The Case of the Armenian Genocide.Wayne State University Press.ISBN978-0814327777.Archivedfrom the original on 10 March 2020.Retrieved5 December2018.
- ^Stiner, Mary C.; Kuhn, Steven L.; Güleç, Erksin (2013). "Early Upper Paleolithic shell beads at Üçağızlı Cave I (Turkey): Technology and the socioeconomic context of ornament life-histories".Journal of Human Evolution.64(5): 380–98.Bibcode:2013JHumE..64..380S.doi:10.1016/j.jhevol.2013.01.008.ISSN0047-2484.PMID23481346.
- ^Whitehouse, Harvey; Martin, Luther H. (2004).Theorizing Religions Past: Archaeology, History, and Cognition.Rowman Altamira. p. 38.ISBN978-0-7591-0621-5.
- ^Curry, Andrew (August 2019)."The first Europeans weren't who you might think".National Geographic.Archived fromthe originalon 19 March 2021.
- ^Krause, Johannes; Jeong, Choongwon; Haak, Wolfgang; Posth, Cosimo; Stockhammer, Philipp W.; Mustafaoğlu, Gökhan; Fairbairn, Andrew; Bianco, Raffaela A.; Julia Gresky (19 March 2019)."Late Pleistocene human genome suggests a local origin for the first farmers of central Anatolia".Nature Communications.10(1): 1218.Bibcode:2019NatCo..10.1218F.doi:10.1038/s41467-019-09209-7.ISSN2041-1723.PMC6425003.PMID30890703.
- ^Brace, Selina; Diekmann, Yoan; Booth, Thomas J.; van Dorp, Lucy; Faltyskova, Zuzana; Rohland, Nadin; Mallick, Swapan; Olalde, Iñigo; Ferry, Matthew; Michel, Megan; Oppenheimer, Jonas; Broomandkhoshbacht, Nasreen; Stewardson, Kristin; Martiniano, Rui; Walsh, Susan (15 April 2019)."Ancient genomes indicate population replacement in Early Neolithic Britain".Nature Ecology & Evolution.3(5): 765–771.Bibcode:2019NatEE...3..765B.doi:10.1038/s41559-019-0871-9.ISSN2397-334X.PMC6520225.PMID30988490.
- ^Olalde, Iñigo; Mallick, Swapan; Patterson, Nick; Rohland, Nadin; Villalba-Mouco, Vanessa; Silva, Marina; Dulias, Katharina; Edwards, Ceiridwen J.; Gandini, Francesca; Pala, Maria; Soares, Pedro; Ferrando-Bernal, Manuel; Adamski, Nicole; Broomandkhoshbacht, Nasreen; Cheronet, Olivia (15 March 2019)."The genomic history of the Iberian Peninsula over the past 8000 years".Science.363(6432): 1230–1234.Bibcode:2019Sci...363.1230O.doi:10.1126/science.aav4040.ISSN0036-8075.PMC6436108.PMID30872528.
- ^Simões, Luciana G.; Günther, Torsten; Martínez-Sánchez, Rafael M.; Vera-Rodríguez, Juan Carlos; Iriarte, Eneko; Rodríguez-Varela, Ricardo; Bokbot, Youssef; Valdiosera, Cristina; Jakobsson, Mattias (15 June 2023)."Northwest African Neolithic initiated by migrants from Iberia and Levant".Nature.618(7965): 550–556.Bibcode:2023Natur.618..550S.doi:10.1038/s41586-023-06166-6.ISSN0028-0836.PMC10266975.PMID37286608.
- ^Allentoft, Morten E.; Sikora, Martin; Refoyo-Martínez, Alba; Irving-Pease, Evan K.; Fischer, Anders; Barrie, William; Ingason, Andrés; Stenderup, Jesper; Sjögren, Karl-Göran; Pearson, Alice; Sousa da Mota, Bárbara; Schulz Paulsson, Bettina; Halgren, Alma; Macleod, Ruairidh; Jørkov, Marie Louise Schjellerup (11 January 2024)."Population genomics of post-glacial western Eurasia".Nature.625(7994): 301–311.Bibcode:2024Natur.625..301A.doi:10.1038/s41586-023-06865-0.ISSN0028-0836.PMC10781627.PMID38200295.
- ^"Indo-European Daughter Languages: Anatolian".www.historyfiles.co.uk.Archivedfrom the original on 13 May 2021.Retrieved26 January2021.
- ^"Anatolian languages".Encyclopedia Britannica.Archivedfrom the original on 6 September 2015.Retrieved26 January2021.
- ^Bryce 2005,p. 12.
- ^Freeman, Charles (1999).Egypt, Greece and Rome: Civilizations of the Ancient Mediterranean.Oxford University Press.ISBN978-0198721949.
- ^Akurgal 2001.
- ^Barjamovic 2011.
- ^Carruba, O.Das Palaische. Texte, Grammatik, Lexikon.Wiesbaden: Harrassowitz, 1970. StBoT 10
- ^abGeorges Roux – Ancient Iraq
- ^abGeorges Roux,Ancient Iraq.Penguin Books, 1966.[ISBN missing]
- ^"History of the Past: World History".
- ^Paul Lunde (May–June 1980)."The Seven Wonders".Saudi Aramco World. Archived fromthe originalon 13 October 2009.Retrieved12 September2009.
- ^Mark Cartwright."Celsus Library".World History Encyclopedia.Retrieved2 February2017.
- ^"The Temple of Artemis at Ephesus: The Un-Greek Temple and Wonder".World History Encyclopedia.Retrieved17 February2017.
- ^Melchert 2003
- ^Watkins 1994; id. 1995:144–51; Starke 1997; Melchert 2003; for the geography Hawkins 1998
- ^abCarl Roebuck,The World of Ancient Times
- ^abYavuz, Mehmet Fatih (2010)."Anatolia".The Oxford Encyclopedia of Ancient Greece and Rome.Oxford University Press.doi:10.1093/acref/9780195170726.001.0001.ISBN978-0195170726.Archivedfrom the original on 6 December 2018.Retrieved5 December2018.
- ^Honey, Linda (5 December 2016)."Justifiably Outraged or Simply Outrageous? The Isaurian Incident of Ammianus Marcellinus".Violence in Late Antiquity: Perceptions and Practices.Routledge. p. 50.ISBN978-1351875745.Archivedfrom the original on 19 May 2022.Retrieved8 November2020.
- ^Swain, Simon; Adams, J. Maxwell; Janse, Mark (2002).Bilingualism in Ancient Society: Language Contact and the Written Word.Oxford [Oxfordshire]: Oxford University Press. pp. 246–66.ISBN0199245061.
- ^Freeman, Philip,The Galatian Language,Edwin Mellen, 2001, pp. 11–12.
- ^Clackson, James. "Language maintenance and language shift in the Mediterranean world during the Roman Empire." Multilingualism in the Graeco-Roman Worlds (2012): 36–57. p. 46: The second testimonium for the late survival of Galatian appears in the Life of Saint Euthymius, who died in ad 487.
- ^Norton, Tom.[2]Archived2 November 2018 at theWayback Machine| A question of identity: who were the Galatians?. University of Wales. p. 62: The final reference to Galatian comes two hundred years later in the sixth century CE when Cyril of Scythopolis attests that Galatian was still being spoken eight hundred years after the Galatians arrived in Asia Minor. Cyril tells of the temporary possession of a monk from Galatia by Satan and rendered speechless, but when he recovered he spoke only in his native Galatian when questioned: 'If he were pressed, he spoke only in Galatian'.180 After this, the rest is silence, and further archaeological or literary discoveries are awaited to see if Galatian survived any later. In this regard, the example of Crimean Gothic is instructive. It was presumed to have died out in the fifth century CE, but the discovery of a small corpus of the language dating from the sixteenth century altered this perception.
- ^J. Eric Cooper, Michael J. Decker,Life and Society in Byzantine CappadociaISBN0230361064,p. 14
- ^Howgego, C. J.(1995).Ancient History from Coins.Routledge.ISBN978-0415089920.
- ^Asia Minor CoinsArchived17 March 2020 at theWayback Machine– an index of Greek and Roman coins from Asia Minor (ancient Anatolia)
- ^Dandamaev, M. A.(1989).A Political History of the Achaemenid Empire.Brill. p. 294.ISBN978-9004091726.
- ^Schmitt, R.(1986)."ARTAXERXES II".Encyclopaedia Iranica, Vol. II, Fasc. 6.pp. 656–58.Archivedfrom the original on 9 April 2019.Retrieved21 April2019.
- ^Roisman, Joseph; Worthington, Ian (2010).A Companion to Ancient Macedonia.John Wiley and Sons.ISBN978-1405179362.Archivedfrom the original on 16 April 2020.Retrieved20 June2015.
- ^"Mithradates VI Eupator",Encyclopædia Britannica
- ^Hewsen, Robert H. (2009). "Armenians on the Black Sea: The Province of Trebizond". In Richard G. Hovannisian (ed.).Armenian Pontus: The Trebizond-Black Sea Communities.Costa Mesa, CA: Mazda Publishers, Inc. pp. 41, 37–66.ISBN978-1-56859-155-1.
- ^Bennett, Julian (1997).Trajan: Optimus Princeps: a Life and Times.Routledge.ISBN978-0-415-16524-2..Fig. 1. Regions east of theEuphratesriver were held only in the years 116–117.
- ^abcdeNiewöhner, Philipp (2017)."Chapter 3: Urbanism – The Archaeology of Byzantine Anatolia".In Niewöhner, Philipp (ed.).The Archaeology of Byzantine Anatolia: From the End of Late Antiquity until the Coming of the Turks.OxfordandNew York:Oxford University Press.pp. 39–59.doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780190610463.003.0004.ISBN9780190610487.
- ^Thonemann, Peter (2018)."Anatolia".The Oxford Dictionary of Late Antiquity.Vol. 1. Oxford University Press.doi:10.1093/acref/9780198662778.001.0001.ISBN978-0198662778.Archivedfrom the original on 6 December 2018.Retrieved6 December2018.
- ^Angold, Michael (1997).The Byzantine Empire 1025–1204.Longman. p. 117.ISBN978-0582294684.
- ^abH. M. BalyuziMuḥammad and the course of Islám,p. 342
- ^John FreelyStorm on Horseback: The Seljuk Warriors of Turkey,p. 83
- ^Clifford Edmund Bosworth-The new Islamic dynasties: a chronological and genealogical manual, p. 234
- ^Mehmet Fuat Köprülü, Gary Leiser-The origins of the Ottoman Empire, p. 33
- ^Peter PartnerGod of battles: holy wars of Christianity and Islam,p. 122
- ^Osman's Dream: The History of the Ottoman Empire,p. 13
- ^Artuk –Osmanli Beyliginin Kurucusu,27f
- ^Pamuk –A Monetary History,pp. 30–31
- ^"Osman I | Ottoman sultan".Encyclopædia Britannica.Archivedfrom the original on 24 April 2018.Retrieved23 April2018.
- ^"Orhan | Ottoman sultan".Encyclopædia Britannica.Archivedfrom the original on 10 March 2018.Retrieved23 April2018.
- ^Fleet, Kate (2010)."The rise of the Ottomans".The rise of the Ottomans (Chapter 11) – The New Cambridge History of Islam.Cambridge Core. pp. 313–31.doi:10.1017/CHOL9780521839570.013.ISBN978-1139056151.Archivedfrom the original on 24 April 2018.Retrieved23 April2018.
- ^Finkel, Caroline (2007).Osman's Dream: The History of the Ottoman Empire.Basic Books. p. 5.ISBN978-0465008506.Archivedfrom the original on 2 January 2014.Retrieved6 June2013.
- ^Genito, Bruno (1 March 2012) [15 December 2003]."Halicarnassus".Encyclopaedia Iranica.Archivedfrom the original on 24 April 2018.Retrieved23 April2018.
- ^"The uncertain future of Greeks in Turkey".archive.is.7 September 2023.Retrieved3 September2024.
- ^Cemen, Ibrahim; Yilmaz, Yucel (2017).Active Global Seismology: Neotectonics and Earthquake Potential of the Eastern Mediterranean Region.John Wiley & Sons.ISBN978-1118945018.
- ^Prothero, W.G. (1920).Anatolia.London: H.M. Stationery Office.Archivedfrom the original on 2 November 2013.Retrieved6 September2013.
- ^"Euxine-Colchic deciduous forests".Terrestrial Ecoregions.World Wildlife Fund.Retrieved25 May2008.
- ^"Northern Anatolian conifer and deciduous forests".Terrestrial Ecoregions.World Wildlife Fund.Retrieved25 May2008.
- ^"Central Anatolian deciduous forests".Terrestrial Ecoregions.World Wildlife Fund.Retrieved25 May2008.
- ^"Central Anatolian steppe".Terrestrial Ecoregions.World Wildlife Fund.Retrieved25 May2008.
- ^"Eastern Anatolian deciduous forests".Terrestrial Ecoregions.World Wildlife Fund.Retrieved25 May2008.
- ^"Anatolian conifer and deciduous mixed forests".Terrestrial Ecoregions.World Wildlife Fund.Retrieved25 May2008.
- ^"Aegean and Western Turkey sclerophyllous and mixed forests".Terrestrial Ecoregions.World Wildlife Fund.Retrieved25 May2008.
- ^"Southern Anatolian montane conifer and deciduous forests".Terrestrial Ecoregions.World Wildlife Fund.Retrieved25 May2008.
- ^"Eastern Mediterranean conifer-sclerophyllous-broadleaf forests".Terrestrial Ecoregions.World Wildlife Fund.Retrieved25 May2008.
Sources
[edit]- Akurgal, Ekrem(2001).The Hattian and Hittite Civilizations.Ankara: Ministry of Culture.ISBN978-9751727565.Archivedfrom the original on 28 April 2021.Retrieved7 January2021.
- Barjamovic, Gojko(2011).A Historical Geography of Anatolia in the Old Assyrian Colony Period.Copenhagen: Museum Tusculanum Press.ISBN978-8763536455.Archivedfrom the original on 28 April 2021.Retrieved7 January2021.
- Bryce, Trevor R.(2005) [1998].The Kingdom of the Hittites(2nd revised ed.). New York: Oxford University Press.ISBN978-0199279081.Archivedfrom the original on 5 May 2021.Retrieved7 January2021.
- Bryce, Trevor R.(2009).The Routledge Handbook of the Peoples and Places of Ancient Western Asia: The Near East from the Early Bronze Age to the fall of the Persian Empire.London & New York: Routledge.ISBN978-1134159079.
- Cohen, Saul B., ed. (2008).The Columbia Gazetteer of the World: Volume 1 A to G(2nd ed.). Columbia University Press.ISBN978-0-231-14554-1.OCLC212893637.
- Howard, Douglas A. (2016).The History of Turkey(2nd ed.). Santa Barbara, California: Greenwood.ISBN978-1-4408-3466-0.
- McColl, R. W. (2014).Encyclopedia of World Geography.Facts On File.ISBN978-0-8160-7229-3.
- Steadman, Sharon R.; McMahon, Gregory (2011). McMahon, Gregory; Steadman, Sharon (eds.).The Oxford Handbook of Ancient Anatolia:(10,000–323 BCE).Oxford University Press Inc.doi:10.1093/oxfordhb/9780195376142.001.0001.hdl:11693/51311.ISBN978-0195376142.
- Tockner, Klement; Uehlinger, Urs; Robinson, Christopher T., eds. (2009).Rivers of Europe.Academic Press.ISBN978-0-08-091908-9.
Further reading
[edit]- Akat, Yücel, Neşe Özgünel, and Aynur Durukan. 1991.Anatolia: A World Heritage.Ankara: Kültür Bakanliǧi.
- Brewster, Harry. 1993.Classical Anatolia: The Glory of Hellenism.London: I. B. Tauris.
- Donbaz, Veysel, and Şemsi Güner. 1995.The Royal Roads of Anatolia.Istanbul: Dünya.
- Dusinberre, Elspeth R. M. 2013.Empire, Authority, and Autonomy In Achaemenid Anatolia.Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Gates, Charles, Jacques Morin, and Thomas Zimmermann. 2009.Sacred Landscapes In Anatolia and Neighboring Regions.Oxford: Archaeopress.
- Mikasa, Takahito, ed. 1999.Essays On Ancient Anatolia.Wiesbaden: Harrassowitz.
- Takaoğlu, Turan. 2004.Ethnoarchaeological Investigations In Rural Anatolia.İstanbul: Ege Yayınları.
- Taracha, Piotr. 2009.Religions of Second Millennium Anatolia.Wiesbaden: Harrassowitz.
- Taymaz, Tuncay, Y. Yilmaz, and Yildirim Dilek. 2007.The Geodynamics of the Aegean and Anatolia.London: Geological Society.
External links
[edit] Media related toAnatoliaat Wikimedia Commons
Media related toAnatoliaat Wikimedia Commons