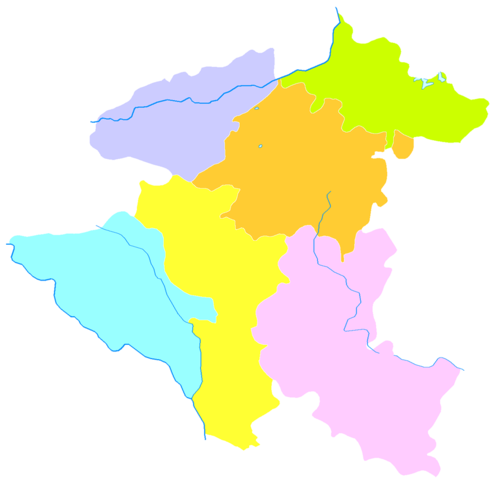
Anshun
This articleneeds additional citations forverification.(August 2012) |
Anshun
An thuận thị | |
|---|---|
 | |
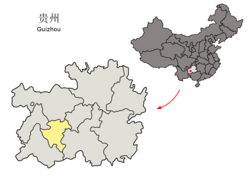 Location of Anshun City jurisdiction in Guizhou | |
| Coordinates (Anshun municipal government):26°15′11″N105°56′51″E/ 26.2531°N 105.9476°E | |
| Country | People's Republic of China |
| Province | Guizhou |
| Municipal seat | Xixiu District |
| Area | |
| •Prefecture-level city | 9,269 km2(3,579 sq mi) |
| • Urban | 1,724.24 km2(665.73 sq mi) |
| • Metro | 1,724.24 km2(665.73 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 1,380 m (4,530 ft) |
| Population (2010 census)[2] | |
| •Prefecture-level city | 2,297,339 |
| • Density | 250/km2(640/sq mi) |
| •Urban | 765,313 |
| • Urban density | 440/km2(1,100/sq mi) |
| •Metro | 765,313 |
| • Metro density | 440/km2(1,100/sq mi) |
| GDP[3] | |
| •Prefecture-level city | CN¥96.7 billion US$14.0 billion |
| • Per capita | CN¥ 39,160 US$ 5,678 |
| Time zone | UTC+8(China Standard) |
| Area code | 0851 |
| ISO 3166 code | CN-GZ-04 |
| Website | anshun |
Anshun(simplified Chinese:An thuận;traditional Chinese:An thuận;pinyin:Ānshùn) is aprefecture-level citylocated in southwesternGuizhouprovince,southwest China,near theHuangguoshu Waterfall,the tallest in China. As of the 2010 census, it had a population of 2,297,339. The city proper had a population of 765,313. Within the prefecture are attractions such as The Long Gong Dragon Caves and the Getu River.
History[edit]
During theWarring States period,the area belonged to the independent kingdom ofYelang.[4]TheRecords of the Grand Historianstates that of all the independent kingdoms in the area, Yelang was the largest.[4]The kingdom was located alongZangke River(now called Beipan River), andNanpan River.[citation needed]Bamboo Worship, Cow Totems, bullfights and dogfights were the culture traditions of the Yelang Empire.[citation needed]In 111 BCE, Yelang was conquered by theHan dynasty,and incorporated asZangke Commandery.[4]From 28 BCE to 25 BCE, an insurrection againstEmperor Chengcalled for the reinstatement of the Yelang Kingdom, but was crushed by Han forces.[4]
In theThree Kingdoms period,the area was split between the county of Yelang and the county ofQielanwithinYi Province.[4]
Under theJin dynasty,the area of present-day Anshun would fall under the jurisdiction of Guangtan County (Quảng đàm huyện) within Yi Province.[4]
During the Sui dynasty, the area belonged to Binhua County (Tân hóa huyện), located within Zangke Commandery,Zang Province.[4]
This organization of the region remained intact until the latter portion of the Tang dynasty, when it was re-organized under thePuning Commandery.[4]The area would remain under the Puning Commandery until 1292, when, under theYuan dynasty,the area would fall underPuding Prefecture,which it would remain under until 1372.[4]
Anshun Prefecturewas established during the earlyMing dynastyto govern the region, and would remain until 1602, when it was replaced by the Anshun Military and Civil Administration (An thuận quân dân phủ).[4]The area was incorporated into the Qing dynasty in 1658, and a newAnshun Prefecturewas established.[4]In April 1638,Xu Xiake,the greatest travel writer and geographer of ancient China, traveled to Anshun.[5]
In 1673, the area became engulfed under theRevolt of the Three Feudatories,during which, significant fighting took place in Anshun.[4]
The Anshun Prefecture would remain until January 15, 1913, when theRepublic of Chinarevoked the prefecture system.[4]After a short-lived implementation of a county to govern Anshun, the city was placed underGuizhou West Circuit,until reverting to the county system.[4]
In 1950,Anshun Prefecturewas established, governing 6county-level divisions.[6]In 1958, Anshun County (An thuận huyện) was upgraded to serve as acounty-level city.[4][6]In 1970, Anshun Prefecture was re-organized as Anshun Area (An thuận địa khu), which it would remain until June 23, 2000, when it was re-organized as aprefecture-level city.[4][6]
Geography and climate[edit]
Anshun's administrative area spans latitude 25° 21′−26° 38′ N and longitude 105° 13′−106° 34′ E and contains sizeable areas ofkarstformation. It bordersGuiyang,the provincial capital, andQiannan Buyei and Miao Autonomous Prefectureto the east,Liupanshuito the west,Qianxinan Buyei and Miao Autonomous Prefectureto the south, andBijieto the north. Within the prefecture, the elevation ranges from 1,102 to 1,694 metres (3,615 to 5,558 ft).
Anshun has amonsoon-influencedhumid subtropical climate(KöppenCwa) bordering on asubtropical highland climate(KöppenCwb), tempered by its rather high altitude and having frequent rain (falling on just over half of the days of the year) and high humidity year-round. Winters are short, cool and damp, while summers are very warm. The monthly 24-hour mean temperature ranges from 4.5 °C (40.1 °F) in January to 22.0 °C (71.6 °F) in July, and the annual mean is 14.22 °C (57.6 °F). Over two-thirds of the annual rainfall occurs from May to August.
| Climate data for Anshun, elevation 1,431 m (4,695 ft), (1991–2020 normals, extremes 1971–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 21.9 (71.4) |
26.1 (79.0) |
31.8 (89.2) |
32.2 (90.0) |
33.4 (92.1) |
31.0 (87.8) |
32.4 (90.3) |
32.5 (90.5) |
31.7 (89.1) |
27.7 (81.9) |
24.0 (75.2) |
22.3 (72.1) |
33.4 (92.1) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 7.5 (45.5) |
10.8 (51.4) |
15.4 (59.7) |
20.3 (68.5) |
22.9 (73.2) |
24.4 (75.9) |
25.9 (78.6) |
26.2 (79.2) |
23.5 (74.3) |
18.5 (65.3) |
14.9 (58.8) |
9.5 (49.1) |
18.3 (65.0) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 4.3 (39.7) |
6.9 (44.4) |
10.7 (51.3) |
15.5 (59.9) |
18.6 (65.5) |
20.6 (69.1) |
22.0 (71.6) |
21.9 (71.4) |
19.4 (66.9) |
15.1 (59.2) |
11.2 (52.2) |
6.2 (43.2) |
14.4 (57.9) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 2.3 (36.1) |
4.3 (39.7) |
7.8 (46.0) |
12.3 (54.1) |
15.5 (59.9) |
18.1 (64.6) |
19.5 (67.1) |
19.0 (66.2) |
16.5 (61.7) |
12.8 (55.0) |
8.7 (47.7) |
3.9 (39.0) |
11.7 (53.1) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −5.2 (22.6) |
−4.8 (23.4) |
−5.9 (21.4) |
1.3 (34.3) |
6.7 (44.1) |
11.1 (52.0) |
10.7 (51.3) |
13.6 (56.5) |
8.5 (47.3) |
3.7 (38.7) |
−2.4 (27.7) |
−5.7 (21.7) |
−5.9 (21.4) |
| Averageprecipitationmm (inches) | 25.6 (1.01) |
21.3 (0.84) |
33.5 (1.32) |
67.7 (2.67) |
170.8 (6.72) |
297.3 (11.70) |
237.8 (9.36) |
171.8 (6.76) |
113.0 (4.45) |
95.5 (3.76) |
35.2 (1.39) |
19.0 (0.75) |
1,288.5 (50.73) |
| Average precipitation days(≥ 0.1 mm) | 16.1 | 13.4 | 15.3 | 14.4 | 17.3 | 18.7 | 17.5 | 15.0 | 12.5 | 16.1 | 11.7 | 12.9 | 180.9 |
| Average snowy days | 4.5 | 2.7 | 0.4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.2 | 1.6 | 9.4 |
| Averagerelative humidity(%) | 84 | 81 | 78 | 76 | 76 | 81 | 81 | 79 | 78 | 82 | 80 | 81 | 80 |
| Mean monthlysunshine hours | 45.1 | 66.2 | 95.4 | 129.1 | 133.6 | 105.5 | 153.1 | 172.3 | 126.3 | 80.5 | 89.2 | 61.3 | 1,257.6 |
| Percentpossible sunshine | 14 | 21 | 26 | 34 | 32 | 26 | 37 | 43 | 35 | 23 | 28 | 19 | 28 |
| Source 1:China Meteorological Administration[7][8] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Weather China[9] | |||||||||||||
Administrative divisions[edit]
Anshun administers onedistrict,twocounties,and threeautonomous counties.In addition, there are two other administrative areas: theAnshun Economic Development Zone(An thuận kinh tế khai phát khu) and the national-levelHuangguoshu Scenic Area(Hoàng quả thụ phong cảnh danh thắng khu).
| Map | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Division code[10] | English name | Simp. Chinese | Trad. Chinese | Pinyin | Area in km2[11] | Seat | Postal code | Divisions[12] | |||||
| Subdistricts | Towns | Townships | Ethnic townships | Residential communities | Villages | ||||||||
| 520400 | Anshun | An thuận thị | An thuận thị | Ānshùn Shì | 9253.06 | Xixiu District | 561000 | 7 | 44 | 36 | 11 | 106 | 1837 |
| 520402 | Xixiu District | Tây tú khu | Tây tú khu | Xīxiù Qū | 1724.24 | Dongguan Subdistrict(Đông quan nhai đạo) | 561000 | 7 | 10 | 7 | 5 | 57 | 498 |
| 520403 | Pingba District | Bình bá khu | Bình bá khu | Píngbà Xiàn | 985.49 | Anping Subdistrict(An bình nhai đạo) | 561100 | 2 | 7 | 2 | 17 | 193 | |
| 520422 | Puding County | Phổ định huyện | Phổ định huyện | Pǔdìng Xiàn | 1090.49 | Chengguan(Thành quan trấn) | 562100 | 5 | 6 | 4 | 10 | 317 | |
| 520423 | Zhenning Buyei and Miao Autonomous County |
Trấn ninh bố y tộc miêu tộc tự trị huyện | Trấn ninh bố y tộc miêu tộc tự trị huyện | Zhènníng Bùyīzú Miáozú Zìzhìxiàn |
1709.42 | Chengguan(Thành quan trấn) | 561200 | 8 | 8 | 6 | 365 | ||
| 520424 | Guanling Buyei and Miao Autonomous County |
Quan lĩnh bố y tộc miêu tộc tự trị huyện | Quan lĩnh bố y tộc miêu tộc tự trị huyện | Guānlǐng Bùyīzú Miáozú Zìzhìxiàn |
1470.49 | Guansuo Subdistrict(Quan tác nhai đạo) | 561300 | 8 | 5 | 8 | 241 | ||
| 520425 | Ziyun Miao and Buyei Autonomous County |
Tử vân miêu tộc bố y tộc tự trị huyện | Tử vân miêu tộc bố y tộc tự trị huyện | Zǐyún Miáozú Bùyīzú Zìzhìxiàn |
2272.94 | Songshan(Tùng sơn trấn) | 550800 | 5 | 7 | 6 | 223 | ||
| Note: Xixiu District includes one subdistrict and two towns of the Anshun Economic Development Zone, while the two towns of Huangguoshu Scenic Area, Huangguoshu (Hoàng quả thụ trấn) and Baishui (Bạch thủy trấn), are administered by Zhenning and Guanling Counties, respectively. | |||||||||||||
Economy[edit]
As of 2019, the city'sGDPtotaled 92.394 billionYuan,an increase of 8.1% from 2018.[13]17.0% of the city's GDP came from theprimary sector,31.7% from thesecondary sector,and 51.3% from thetertiary sector.[13]
Major agricultural products grown in Anshun includerice,yams,maize,rapeseed,watermelons,and variousvegetables.[13]The city is also home to a sizable animal husbandry industry, which produces mostly pork, but also significant amounts of beef, poultry, and mutton.[13]
Anshun's industry produces bothconsumer goodsandintermediate goods.[13]Major consumer goods produced in the city includedetergent,various paper products,liquors,Chinese traditional medicine,andmobile phones.[13]Major intermediate goods produced in the city includeconstruction materialssuch as stone and cement, rawaluminium,barium salt,androlling bearings.[13]
In recent years, the city has played an important role in the development of military aircraft, with significant production taking place in the city, and withAnshun Huangguoshu Airportserving as a testing ground for new military aircraft.[14][15]In 2019, the city government announced an initiative to further increase the city's aerospace industry over the next few years.[16]
Demographics[edit]
| Name | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Residence population[17](Nov. 2010) | Hukoupopulation[18] (end of 2010) | |||
| Total | % | Population density (persons/km2) | ||
| Anshun | 2297339 | 100 | 247.91 | 2797871 |
| Xixiu District | 765313 | 33.31 | 449.13 | 868669 |
| Pingba County | 298034 | 12.97 | 298.33 | 353777 |
| Puding County | 378288 | 16.47 | 346.42 | 459605 |
| Zhenning Buyei and Miao Autonomous County | 283880 | 12.36 | 165.05 | 381192 |
| Guanling Buyei and Miao Autonomous County | 301562 | 13.13 | 205.42 | 366814 |
| Ziyun Miao and Buyei Autonomous County | 270262 | 11.76 | 118.33 | 367814 |
According to theSixth National Population Census of the People's Republic of Chinaconducted in 2010, the residence population was 2,297,339, a reduction of 34,402 (1.48%) from the Fifth Census in 2000. The male-female ratio was 107.34 males per 100 females. Persons aged 0–14 numbered 580,910 (25.29%), 15–64 numbered 1,516,977 (66.03%), and 65+ numbered at 199,452 (8.68%). The urban population was 690,138 (only 30.04%).
Ethnic groups[edit]
Among the residence population, there were 1,466,833 people ofHanethnicity (63.85%), with members of various otherethnic groupstaking up the other 36.15%.
Tunpo People[edit]
The city is home to a significant number ofTunpo People,many of whom live inTianlong Tunbao town.[citation needed]
Transportation[edit]
The city sits on theGuiyang-Kunming railway,a section on theShanghai-Kunming railway.[19]Anshun West railway stationserves as a stop on theShanghai–Kunming high-speed railway,as well as one of two terminals on theAnshun–Liupanshui intercity railway.[20]
Anshun Huangguoshu Airportis located in the city.[19]The airport is a dual-use facilities, offering civilian as well as military air services.[21]The airport's destinations include Chongqing, Guangzhou and Beijing'sDaxing Airport.[citation needed]Most travelers choose to useGuiyang Longdongbao International Airportand take a coach between there and Anshun.[citation needed]
TheG60 Shanghai–Kunming ExpresswayandNational Highway 320both run through Anshun.[19]
Education[edit]
Anshun Normal Universityis the largest local institution of higher education,[citation needed]hosting Peace Corps Volunteer TEFL teachers since 2005.
Famous sites[edit]
Tourist attractions and landmarks in Anshun include:
- AnshunWenmiao:This Ming dynasty Confucian temple, situated within Anshun city, is erected to honor the famous philosopher Confucius and his disciples.
- Huangguoshu Waterfall( "Yellow Fruit Tree Waterfall" ): A waterfall that can be viewed from all angles, even from inside the waterfall. It is the biggest waterfall in Asia.
- Getu River:the river is situated in a mountainous karst area. Along the river one can find Miao villages andkarst caves.It is possible to walk 2000 steps up to theChuangshangcave where one can get a view of the whole area.
- Longgong Cave(Long cung động;"Dragon Palace" ): The cave is situated above sea level and one has to walk 200 meters upwards to reach it. From there one can sail into the cave and experience the stalagmites and stalactites of the karst formation. There is also a waterfall by the foot of the cave.
- Tianlong Tunbao(Truân bảo) Ming Dynasty Town: The town is situated some 25 kilometres (16 mi) from downtown Anshun. The nameTunbaorefers to the places where the troops were stationed to guard the frontiers after putting down the riots during their southern expedition to Guizhou in theHongwureign (1368–1398) of the Ming dynasty. The citizens have stuck to their traditional customs since then. The locals still wear clothes from the Ming dynasty and the houses are also from that era.
- Tiantai Mountain:The mountain lies in Tunbao tourist site. It has a history of approximately 421 years. It is the only one ancient architectural complex in Guizhou Province which is the imitation of Song-dynasty-style. The architectural complex is called The Epic of Stone Architectural. Ming generalWu Sanguionce resided here.
- Zhongdong(Trung động;Middle Cave): Twenty families live inside this isolated village, set in a humongous limestone cavern 1,800 metres (5,900 ft) up a mountain. It's thought to be the only year-round settlement inside a naturally occurring cave in China.
- Huajiang Canyon: The only canyon which is famous as the "earth surface crack" canyon. Cliffside inscriptions are in the canyon.
Folk art[edit]
AnshunBatiksare a traditional folk Chinese handicraft art of Buyi Minority. People use wax pen to draw various patterns on white cloth such as flowers, birds and some strange shapes. Then, the cloth will be dipped dyeing in theindigotin.Finally, the patterns will be white shapes on a blue ground. Baktis can be used to make dresses and some other daily used things.
Dixi Operais called the "living fossil ofChinese Opera".The acting style is singing and dancing. The main feature is that all actors wear thexylographicmasks and sing the opera which are the ancient style.[citation needed]
References[edit]
- ^Cox, W (2018).Demographia World Urban Areas. 14th Annual Edition(PDF).St. Louis: Demographia. p. 22.
- ^"China: Guìzhōu (Prefectures, Cities, Districts and Counties) - Population Statistics, Charts and Map".
- ^Quý châu thống kế niên giám (2021).Trung quốc thống kế xuất bản xã.ISBN9787503795558.
- ^abcdefghijklmnopLịch sử duyên cách(in Chinese). Anshun City People's Government.Archivedfrom the original on 2019-11-23.Retrieved2020-07-12.
- ^Xu Xiake (2015).Từ hà khách du ký[Xu Xiake's Travels] (in Chinese). Beijing: Zhong Hua Book Company.ISBN9787101107647.
- ^abcAn thuận thị lịch sử duyên cách.xzqh.org(in Chinese). 2015-02-27.Archivedfrom the original on 2020-07-12.Retrieved2020-07-12.
- ^Trung quốc khí tượng sổ cư võng – WeatherBk Data(in Simplified Chinese).China Meteorological Administration.Retrieved28 April2023.
- ^ Trung quốc khí tượng sổ cư võng(in Simplified Chinese).China Meteorological Administration.Retrieved28 April2023.
- ^An thuận - khí tượng sổ cư - trung quốc thiên khí võng(in Chinese). Weather China.Retrieved21 November2022.
- ^Quốc gia thống kế cục thống kế dụng khu hoa đại mã(in Chinese (China)).National Bureau of Statistics of the People's Republic of China.2011. Archived fromthe originalon 2012-04-07.Retrieved2012-12-29.
- ^《 an thuận thống kế niên giám 2011》[full citation needed]
- ^《 trung quốc dân chính thống kế niên giám 2011》[full citation needed]
- ^abcdefgKinh tế phát triển(in Chinese). Anshun City People's Government.Archivedfrom the original on 2020-07-13.Retrieved2020-07-13.
- ^"China's FTC-2000 aircraft export-version rolls off production line".Xinhua.2017-06-05. Archived fromthe originalon 2020-07-13.Retrieved2020-07-13.
- ^Huang, Panyue (2018-09-30)."New combat aircraft for export makes debut flight".China Military.Archivedfrom the original on 2020-07-13.Retrieved2020-07-13.
- ^《 an thuận thị nhân dân chính phủ quan vu ấn phát an thuận thị bát đại bách ức cấp công nghiệp sản nghiệp chấn hưng hành động phương án đích thông tri 》 giải độc tài liêu(in Chinese). Anshun City People's Government. 2019-07-22.Archivedfrom the original on 2020-07-13.Retrieved2020-07-13.
- ^《 an thuận thị 2010 niên đệ lục thứ toàn quốc nhân khẩu phổ tra chủ yếu sổ cư công báo 》[full citation needed]
- ^《 trung hoa nhân dân cộng hòa quốc toàn quốc phân huyện thị nhân khẩu thống kế tư liêu 2010》[full citation needed]
- ^abcAn thuận thị khái huống địa đồ.xzqh.org(in Chinese). 2015-02-27.Archivedfrom the original on 2020-07-12.Retrieved2020-07-12.
- ^An lục thành tế thiết lộ kim niên tương thông xa.gz.chinanews.com(in Chinese). 2020-01-03.Archivedfrom the original on 2020-07-12.Retrieved2020-07-12.
- ^"Anshun Huangguoshu Airport Profile".centreforaviation.com.Archivedfrom the original on 2020-07-12.Retrieved2020-07-12.