Bezitramide
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChemCID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard(EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.035.744 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
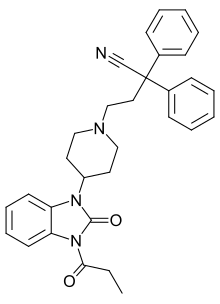
| Formula | C31H32N4O2 |
| Molar mass | 492.623g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Bezitramideis an opioidanalgesic.Bezitramide itself is aprodrugwhich is readilyhydrolyzedin thegastrointestinal tractto itsactive metabolite,despropionyl-bezitramide.[2]Bezitramide was discovered atJanssen Pharmaceuticain 1961.[3][4][5]It is most commonly marketed under the trade nameBurgodin.
The drug was pulled from the shelves in theNetherlandsin 2004 after fatal overdose cases, including one where a five-year-old child took one tablet from his mother's purse, ate it, and promptly died.[6]
Bezitramide is regulated much the same asmorphinein all known jurisdictions and is aSchedule IIsubstance under the United States' Controlled Substances Act of 1970, with an ACSCN of 9800 and zero annual manufacturing quota.[7]However, as of May 2021, it has never been marketed in the United States.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^Anvisa(2023-03-31)."RDC Nº 784 - Listas de Substâncias Entorpecentes, Psicotrópicas, Precursoras e Outras sob Controle Especial"[Collegiate Board Resolution No. 784 - Lists of Narcotic, Psychotropic, Precursor, and Other Substances under Special Control] (in Brazilian Portuguese).Diário Oficial da União(published 2023-04-04).Archivedfrom the original on 2023-08-03.Retrieved2023-08-16.
- ^Meijer DK, Hovinga G, Versluis A, Bröring J, van Aken K, Moolenaar F, Wesseling H (1984). "Pharmacokinetics of the oral narcotic analgesic bezitramide and preliminary observations on its effect on experimentally induced pain".European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology.27(5): 615–8.doi:10.1007/BF00556902.PMID6519169.S2CID23978449.
- ^US patent 3196157,Janssen PA, "Benzimidalinyl Piperidines", published 1963-06-11, issued 1965-07-20
- ^Janssen PA, Niemegeers CJ, Schellekens KH, Marsboom RH, Herin VV, Amery WK, et al. (June 1971). "Bezitramide (R 4845), a new potent and orally long-acting analgesic compound".Arzneimittel-Forschung.21(6): 862–7.PMID5109278.
- ^Knape H (April 1970)."Bezitramide, an orally active analgesic. An investigation on pain following operations for lumbar disc protrusion (preliminary report)".British Journal of Anaesthesia.42(4): 325–8.doi:10.1093/bja/42.4.325.PMID4913411.
- ^de Vos JC, Rohof OJ, Bernsen PJ, Conemans JM, van Unnik AJ (August 1983). "[Death caused by one tablet of Burgodin]".Nederlands Tijdschrift voor Geneeskunde.127(34): 1552–3.PMID6633692.
- ^"Title 21 United States Code (USC) Controlled Substances Act".Archived fromthe originalon 2020-08-30.Retrieved2011-09-29.
