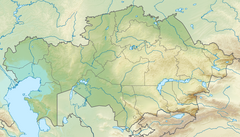
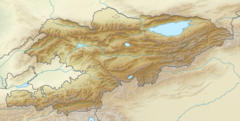
Chu (river)
| Chu | |
|---|---|
 In the Chüy Valley belowTokmok | |
| Native name | |
| Location | |
| Country | Kyrgyzstan,Kazakhstan |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | Confluence ofJoon ArykandKochkor |
| • location | Kochkor District,Naryn Region,Kyrgyzstan |
| • coordinates | 42°13′15.60″N75°44′29″E/ 42.2210000°N 75.74139°E |
| • elevation | 1,802 m (5,912 ft) |
| Mouth | Ashchykol Depression |
• location | Turkistan Region,Kazakhstan |
• coordinates | 44°59′N67°43′E/ 44.983°N 67.717°E |
• elevation | 135 m (443 ft) |
| Length | 1,067 km (663 mi) |
| Basin size | 62,500 km2(24,100 sq mi) |
| Basin features | |
| Tributaries | |
| • left | Ysyk-Ata,Alamüdün,Ala-Archa,Ak-Suu |
| • right | Chong-Kemin,Kichi-Kemin |
TheChu[a]is a river in NorthernKyrgyzstanand SouthernKazakhstan.Of its total length of 1,067 kilometres (663 mi),[1]the first 115 kilometres are in Kyrgyzstan, then for 221 kilometres the river serves as the border between Kyrgyzstan and Kazakhstan and the last 731 kilometres are in Kazakhstan. It is one of the longestriversin Kyrgyzstan and in Kazakhstan. It has adrainage basinof 62,500 square kilometres (24,100 sq mi).[1]
TheChüy Region,the northernmost and most populous administrative region of Kyrgyzstan, is named after the river; so areChüy Avenue,the main street of the Kyrgyz capital ofBishkekand the city ofShuin Kazakhstan'sJambyl Region.
Course
[edit]The Chu is formed by the confluence of the riversJoon ArykandKochkor,[1]in theKochkor Districtof theNaryn Region.After approaching within a few kilometres of LakeIssyk-Kul(nearBalykchy), without either flowing into the lake or draining it, it turns towards the northwest. In the 1950s an old riverbed called Ketmaldy (also Buugan) linked the Chu River and Issyk Kul. During floods part of Chu water would reach the lake, but such outflow has not been seen since the construction of theOrto-Tokoy Reservoir.After passing through the narrowBoom Gorge(Russian:Боомское ущелье,Boomskoye ushchelye), the river enters the comparatively flatChüy Valley,within which lie the Kyrgyz capital Bishkek and the Kazakh city ofShu.Much of the Chu's water is diverted into a network of canals, such as theGreat Chüy Canal,to irrigate the fertile black soils of the Chüy Valley for farming, on both the Kyrgyz and Kazakh sides of the river.
As the Chu flows through the Chüy Valley, it forms the border between Kyrgyzstan and Kazakhstan for more than a hundred kilometres, but then it leavesKyrgyzstanand flows intoKazakhstan,where it flows at the northern edge of theMoiynkum Desert,with lakeKokuydynkolclose to its channel. In wet years it may reach theendorheicsalt lakeAkzhaykyn,located among the vastsolonchaksof theAshchykol Depression.[2]
History
[edit]
The area of this river was originally home to theIranianSughdswho spokeSoghdian,an EastIranian language.[3]
During theMiddle Ages,the area was strategically important. It was the setting ofSuyab,the capital of theWestern Turkic KhaganateandBalasagun,the capital of theQara Khitai(Western Liao dynasty).
The Chu River posed a risk of flooding for settlements located in the Chu Valley. In the winter of 1878, an ice gorge formed on the Chu River upstream fromTokmok,the administrative centre of Semirechye Province. This was followed by severe flooding that damaged the town and the province's capital was moved to Pishpek (Bishkek).[4]
Dams
[edit]The river flow is regulated by the dam atOrto-Tokoy Reservoirin Kyrgyzstan built in 1957 and the dam at Tasotkel Reservoir in Kazakhstan built in 1974.
Ecology and environment
[edit]Environmental monitoring
[edit]The Kyrgyz State Agency for Hydrometeorology and the Kazakhstan Hydrometeorological Service (Kazhydromet) operate a number of water quality monitoring stations on the Chu River and its tributaries.[5]
Water quality
[edit]According to the Kyrgyz State Agency for Hydrometeorology, in 2004–08 the water pollution index of the Chu River in the Chu Valley ranged from 0.25 to 0.7 units, which is interpreted as Class II ( "Clean water" ). The only exception was a monitoring point downstream of Vasilyevka village where the water pollution index ranged from 0.4 to 1.2 units and water quality was assessed as Class II(Clean)/Class III ( "Moderately polluted" ).[5]
According to the Kazakhstan Hydrometeorological Service (Kazhydromet), the water pollution index of the Shu (Chu) River in theJambyl Regionof Kazakhstan amounted to 2.01 (Class III, "Moderately polluted" ) in 2008, and 1.83 (Class III, "Moderately polluted" ) in 2009. Such water quality parameters asbiochemical oxygen demand,nitrites,copper,andphenolsexceeded the maximum allowable concentrations.[6]
Major tributaries
[edit]In Kyrgyzstan, 4892 rivers and canals flow into Chu River.[7]The main tributaries are, from source to mouth:
- Kochkor(left)
- Joon Aryk(right)
- Chong-Kemin(right)
- Kichi-Kemin(right)
- Kara-Konguz(right)
- Shamshy(left)
- Ysyk-Ata(left)
- Alamüdün(left)
- Ala-Archa(left)
- Jylamysh(left)
- Kakpatas(right)
- Ak-Suu(left)
- Kuragaty(left)
Gallery
[edit]-
In theBoom Gorge
-
A medievalbalbalnearBurana Towerin the Chüy Valley
-
In the Chüy Valley nearMilyanfan
-
NearKordayborder crossing
-
NearShu,Kazakhstan
See also
[edit]Notes
[edit]References
[edit]- ^abcЧу (река),Great Soviet Encyclopedia
- ^"L-42 Topographic Chart (in Russian)".Retrieved8 November2022.
- ^Barthold, W."Balāsāg̲h̲ūn or Balāsaḳūn." Encyclopaedia of Islam.Brill Online. Universiteitsbibliotheek Leiden: Brill Academic Publishers.[permanent dead link]
- ^"Profile of town Tokmok (in Russian)".Archived fromthe originalon 2010-04-19.Retrieved2010-03-10.
- ^ab"Kyrgyz State Agency for Hydrometeorology: water quality".Archived fromthe originalon 2011-07-22.Retrieved2010-03-10.
- ^Department of Ecological Monitoring (2010).Information Bulletin on Status of the Environment in the Republic of Kazakhstan in 2009(Report). Ministry of Environment Protection of the Republic of Kazakhstan.[permanent dead link]
- ^Чүй облусу:Энциклопедия[Encyclopedia of Chüy Oblast] (in Kyrgyz and Russian). Bishkek: Chief Editorial Board of Kyrgyz Encyclopedia. 1994. p. 718.ISBN5-89750-083-5.