Cumulus oophorus
| Cumulus oophorus | |
|---|---|
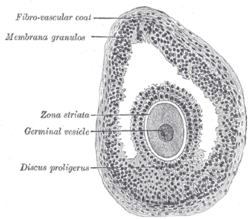 Section of vesicularovarian follicleof acat.X 50. (Discus proligerus labeled at lower left.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | cumulus oophorus discus proliger |
| FMA | 18659 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Thecumulus oophorus(discus proligerus) is a cluster of cells that surround theoocyteboth in theovarian follicleand afterovulation.In theantral follicle,it may be regarded as an extension of themembrana granulosa.The innermost layer of these cells is thecorona radiata.[1]
This layer of cells must be penetrated byspermatozoaforfertilizationto occur.
Functions
[edit]Functions of the cumulus oophorus include coordination of follicular development and oocyte maturation.[2]Mechanisms of the latter include stimulation ofamino acid transportandsterolbiosynthesisand regulation of oocytegene transcription.[2]
It also provides energy substrates for oocyte meiotic resumption and promotes glycolysis.[2]
Cumulus oophorus cells contribute heavily to the maturation and eventual fertilization of an oocyte. As a follicle grows in size and the antrum develops, more layers of cumulus oophorus cells accumulate around the oocyte to aid in the acrosome reaction and sperm penetration into the oocyte. The proximity between the cumulus oophorus cells and the oocyte favors bidirectional communication, which is vital for oocyte development.
Gene expression profiling
[edit]As a part of the process ofin vitro fertilization,gene expression profilingof cumulus cells can be performed to estimate oocyte quality and the efficiency of anovarian hyperstimulationprotocol, and may indirectly predict oocyteaneuploidy,embryo development and pregnancy outcomes. Increased knowledge in these aspects is useful in, for example,embryo selection.[citation needed]
In geneexpression profilingof cumulus cells, genes where increased expression is correlated with higher oocyte competence or better pregnancy outcomes, include:HAS2,GREM1andPTGS2.
In contrast, genes where increased expression is correlated with lower oocyte competence or worse pregnancy outcomes include:BDNF,CCND2,CXCR4,GPX3,HSPB1,DVL3,DHCR7,CTNND1,TRIM28,STAR,AREG,CX43,PTGS2,SCD1andSCD5.[citation needed]
References
[edit]- ^Gilbert, Scott F.Developmental Biology(Ninth ed.). Sinauer Associates, Inc. p. 126.ISBN978-0878933846.
- ^abcThe Evian Annual Reproduction (EVAR) Workshop Group 2010; Fauser, B. C. J. M.; Diedrich, K.; Bouchard, P.; Domínguez, F.; Matzuk, M.; Franks, S.; Hamamah, S.; Simón, C.; Devroey, P.; Ezcurra, D.; Howles, C. M. (2011)."Contemporary genetic technologies and female reproduction".Human Reproduction Update.17(6): 829–847.doi:10.1093/humupd/dmr033.PMC3191938.PMID21896560.
{{cite journal}}:CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link)
External links
[edit]- Anatomy photo: Reproductive/mammal/ovary5/ovary3- Comparative Organology at University of California, Davis - "Mammal, bovine ovary (LM, Medium)"
- Swiss embryology(fromUL,UB,andUF)dbefruchtung/objectbefru01
- UIUC Histology Subject366
- Histology image: 18404loa– Histology Learning System at Boston University - "Female Reproductive System: ovary, cumulus oophorus"
