Fascia dentata
Appearance
| Fascia dentata | |
|---|---|
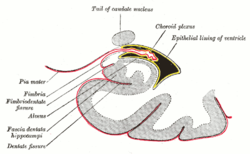 Coronal section of inferior horn of lateral ventricle. (Fascia dentata labeled at bottom left.) | |
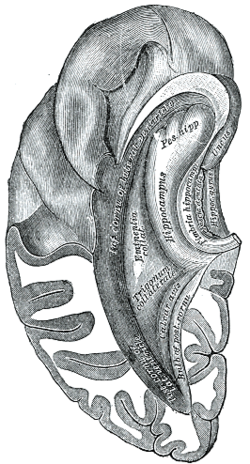 Inferior and posterior cornua, viewed from above. (Fascia dentata labeled at center right.) | |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy |
Thefascia dentatais the earliest stage of the hippocampal circuit.[1][2]Its primary input is theperforant pathfrom the superficial layers ofentorhinal cortex.Its principal neurons are tinygranule cellswhich give rise tounmyelinatedaxons called themossy fiberswhich project to thehilusand CA3. The fascia dentata of the rat contains approximately 1,000,000 granule cells. It receives feedback connections from mossy cells in the hilus at distant levels in the septal and temporal directions. The fascia dentata and the hilus together make up thedentate gyrus.As with all regions of the hippocampus, the dentate gyrus also receivesGABAergicandcholinergicinput from themedial septumand thediagonal band of Broca.
References
[edit]- ^Zimmer, Jens (1978-01-01), Corner, M. A.; Baker, R. E.; Vandepoll, N. E.; Swaab, D. F. (eds.),"Development of the Hippocampus and Fascia Dentata: Morphological and Histochemical Aspects",Progress in Brain Research,Maturation of the Nervous System, vol. 48, Elsevier, pp. 171–190,doi:10.1016/s0079-6123(08)61022-5,ISBN978-0-444-80036-7,PMID370906,retrieved2023-03-29
- ^Zimmer, J.; Gähwiler, B. H. (1984-09-20)."Cellular and connective organization of slice cultures of the rat hippocampus and fascia dentata: HIPPOCAMPAL SLICE CULTURES".Journal of Comparative Neurology.228(3): 432–446.doi:10.1002/cne.902280310.PMID6148364.S2CID6827956.
