Geosynchronous orbit

Ageosynchronous orbit(sometimes abbreviatedGSO) is an Earth-centeredorbitwith anorbital periodthat matchesEarth's rotationon its axis, 23 hours, 56 minutes, and 4 seconds (onesidereal day). The synchronization of rotation and orbital period means that, for an observer on Earth's surface, an object in geosynchronous orbit returns to exactly the same position in the sky after a period of one sidereal day. Over the course of a day, the object's position in the sky may remain still or trace out a path,typically in a figure-8 form,whose precise characteristics depend on the orbit'sinclinationandeccentricity.A circular geosynchronous orbit has a constant altitude of 35,786 km (22,236 mi).[1]
A special case of geosynchronous orbit is thegeostationary orbit(often abbreviatedGEO), which is a circular geosynchronous orbit in Earth'sequatorial planewith both inclination and eccentricity equal to 0. A satellite in a geostationary orbit remains in the same position in the sky to observers on the surface.[1]
Communications satellitesare often given geostationary or close-to-geostationary orbits, so that thesatellite antennasthat communicate with them do not have to move but can be pointed permanently at the fixed location in the sky where the satellite appears.[1]
History
[edit]
In 1929,Herman Potočnikdescribed both geosynchronous orbits in general and the special case of the geostationary Earth orbit in particular as useful orbits forspace stations.[2]The first appearance of a geosynchronousorbitin popular literature was in October 1942, in the firstVenus Equilateralstory byGeorge O. Smith,[3]but Smith did not go into details. Britishscience fictionauthorArthur C. Clarkepopularised and expanded the concept in a 1945 paper entitledExtra-Terrestrial Relays – Can Rocket Stations Give Worldwide Radio Coverage?,published inWireless Worldmagazine. Clarke acknowledged the connection in his introduction toThe Complete Venus Equilateral.[4][5]The orbit, which Clarke first described as useful for broadcast and relay communications satellites,[5]is sometimes called the Clarke Orbit.[6]Similarly, the collection of artificial satellites in this orbit is known as the Clarke Belt.[7]
In technical terminology, the geosynchronous orbits are often referred to as geostationary if they are roughly over the equator, but the terms are used somewhat interchangeably.[8][9]Specifically,geosynchronous Earth orbit(GEO) may be a synonym forgeosynchronousequatorial orbit,[10]orgeostationary Earth orbit.[11]
The first geosynchronous satellite was designed byHarold Rosenwhile he was working atHughes Aircraftin 1959. Inspired bySputnik 1,he wanted to use a geostationary (geosynchronous equatorial) satellite to globalise communications. Telecommunications between the US and Europe was then possible between just 136 people at a time, and reliant onhigh frequencyradios and anundersea cable.[12]
Conventional wisdom at the time was that it would require too muchrocketpower to place a satellite in a geosynchronous orbit and it would not survive long enough to justify the expense,[13]so early efforts were put towards constellations of satellites inlowormediumEarth orbit.[14]The first of these were the passiveEcho balloon satellitesin 1960, followed byTelstar 1in 1962.[15]Although these projects had difficulties with signal strength and tracking that could be solved through geosynchronous satellites, the concept was seen as impractical, so Hughes often withheld funds and support.[14][12]
By 1961, Rosen and his team had produced a cylindrical prototype with a diameter of 76 centimetres (30 in), height of 38 centimetres (15 in), weighing 11.3 kilograms (25 lb); it was light, and small, enough to be placed into orbit by then-available rocketry, wasspin stabilisedand used dipole antennas producing a pancake-shaped waveform.[16]In August 1961, they were contracted to begin building the working satellite.[12]They lostSyncom 1to electronics failure, but Syncom 2 was successfully placed into a geosynchronous orbit in 1963. Although itsinclined orbitstill required moving antennas, it was able to relay TV transmissions, and allowed for US PresidentJohn F. Kennedyto phone Nigerian prime ministerAbubakar Tafawa Balewafrom a ship on August 23, 1963.[14][17]
Today there are hundreds of geosynchronous satellites providingremote sensing,navigation and communications.[12][1]
Although most populated land locations on the planet now have terrestrial communications facilities (microwave,fiber-optic), which often have latency and bandwidth advantages, and telephone access covering 96% of the population and internet access 90% as of 2018,[18]some rural and remote areas in developed countries are still reliant on satellite communications.[19][20]
Types
[edit]Geostationary orbit
[edit]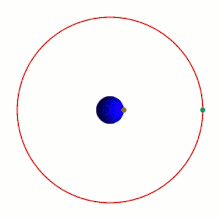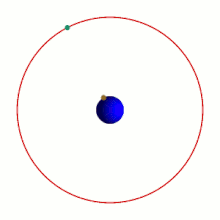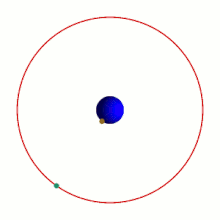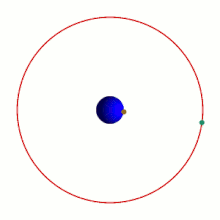
A geostationary equatorial orbit (GEO) is a circular geosynchronous orbit in the plane of the Earth's equator with a radius of approximately 42,164 km (26,199 mi) (measured from the center of the Earth).[21]: 156 A satellite in such an orbit is at an altitude of approximately 35,786 km (22,236 mi) above mean sea level. It maintains the same position relative to the Earth's surface. If one could see a satellite in geostationary orbit, it would appear to hover at the same point in the sky, i.e., not exhibitdiurnal motion,while the Sun, Moon, and stars would traverse the skies behind it. Such orbits are useful fortelecommunications satellites.[22]
A perfectly stable geostationary orbit is an ideal that can only be approximated. In practice the satellite drifts out of this orbit because of perturbations such as thesolar wind,radiation pressure,variations in the Earth's gravitational field, and thegravitationaleffect of theMoonandSun,and thrusters are used to maintain the orbit in a process known asstation-keeping.[21]: 156
Eventually, without the use of thrusters, the orbit will become inclined, oscillating between 0° and 15° every 55 years. At the end of the satellite's lifetime, when fuel approaches depletion, satellite operators may decide to omit these expensive manoeuvres to correct inclination and only control eccentricity. This prolongs the life-time of the satellite as it consumes less fuel over time, but the satellite can then only be used by ground antennas capable of following the N-S movement.[21]: 156
Geostationary satellites will also tend to drift around one of two stable longitudes of 75° and 255° without station keeping.[21]: 157
Elliptical and inclined geosynchronous orbits
[edit]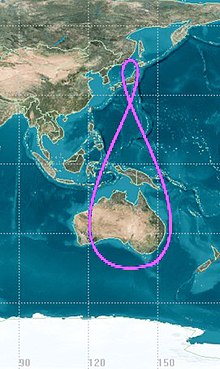
Many objects in geosynchronous orbits have eccentric and/or inclined orbits. Eccentricity makes the orbit elliptical and appear to oscillate E-W in the sky from the viewpoint of a ground station, while inclination tilts the orbit compared to the equator and makes it appear to oscillate N-S from a groundstation. These effects combine to form ananalemma(figure-8).[21]: 122
Satellites in elliptical/eccentric orbits must be tracked by steerableground stations.[21]: 122
Tundra orbit
[edit]The Tundra orbit is an eccentric geosynchronous orbit, which allows the satellite to spend most of its time dwelling over one high latitude location. It sits at an inclination of 63.4°, which is afrozen orbit,which reduces the need forstationkeeping.[23]At least two satellites are needed to provide continuous coverage over an area.[24]It was used by theSirius XM Satellite Radioto improve signal strength in the northern US and Canada.[25]
Quasi-zenith orbit
[edit]TheQuasi-Zenith Satellite System(QZSS) is a four-satellite system that operates in a geosynchronous orbit at an inclination of 42° and a 0.075 eccentricity.[26]Each satellite dwells overJapan,allowing signals to reach receivers inurban canyonsthen passes quickly over Australia.[27]
Launch
[edit]EchoStar XVII·Earth.
Geosynchronous satellites are launched to the east into a prograde orbit that matches the rotation rate of the equator. The smallest inclination that a satellite can be launched into is that of the launch site's latitude, so launching the satellite from close to the equator limits the amount ofinclination changeneeded later.[28]Additionally, launching from close to the equator allows the speed of the Earth's rotation to give the satellite a boost. A launch site should have water or deserts to the east, so any failed rockets do not fall on a populated area.[29]
Mostlaunch vehiclesplace geosynchronous satellites directly into ageosynchronous transfer orbit(GTO), an elliptical orbit with anapogeeat GSO height and a lowperigee.On-board satellite propulsion is then used to raise the perigee, circularise and reach GSO.[28][30]
Once in a viable geostationary orbit, spacecraft can change their longitudinal position by adjusting their semi-major axis such that the new period is shorter or longer than a sidereal day, in order to effect an apparent "drift" Eastward or Westward, respectively. Once at the desired longitude, the spacecraft's period is restored to geosynchronous.[31]
Proposed orbits
[edit]Statite proposal
[edit]Astatiteis a hypothetical satellite that usesradiation pressurefrom the Sun against asolar sailto modify its orbit.[32]
It would hold its location over the dark side of the Earth at a latitude of approximately 30 degrees. It would return to the same spot in the sky every 24 hours from an Earth-based viewer's perspective, so be functionally similar to a geosynchronous orbit.[32][33]
Space elevator
[edit]A further form of geosynchronous orbit is the theoreticalspace elevator.When one end is attached to the ground, for altitudes below the geostationary belt the elevator maintains a shorter orbital period than by gravity alone.[34]
Retired satellites
[edit]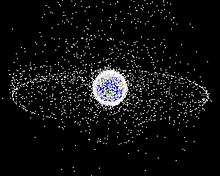
Geosynchronous satellites require somestation-keepingin order to remain in position, and once they run out of thruster fuel and are no longer useful they are moved into a highergraveyard orbit.It is not feasible to deorbit geosynchronous satellites, for to do so would take far more fuel than would be used by slightly elevating the orbit; and atmospheric drag is negligible, giving GSOs lifetimes of thousands of years.[35]
The retirement process is becoming increasingly regulated and satellites must have a 90% chance of moving over 200 km above the geostationary belt at end of life.[36]
Space debris
[edit]Space debris in geosynchronous orbits typically has a lower collision speed than at LEO since most GSO satellites orbit in the same plane, altitude and speed; however, the presence of satellites ineccentric orbitsallows for collisions at up to 4 km/s. Although a collision is comparatively unlikely, GSO satellites have a limited ability to avoid any debris.[37]
Debris less than 10 cm in diameter cannot be seen from the Earth, making it difficult to assess their prevalence.[38]
Despite efforts to reduce risk, spacecraft collisions have occurred. TheEuropean Space Agencytelecom satelliteOlympus-1was struck by ameteoroidon August 11, 1993, and eventually moved to agraveyard orbit,[39]and in 2006 the RussianExpress-AM11communications satellite was struck by an unknown object and rendered inoperable,[40]although its engineers had enough contact time with the satellite to send it into a graveyard orbit. In 2017 bothAMC-9andTelkom-1broke apart from an unknown cause.[41][38][42]
Properties
[edit]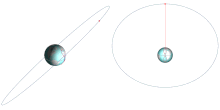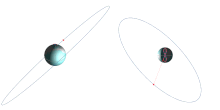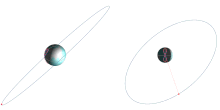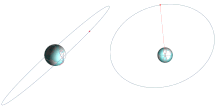
A geosynchronous orbit has the following properties:
- Period: 1436 minutes (onesidereal day)
- Semi-major axis:42,164 km[21]: 121
Period
[edit]All geosynchronous orbits have an orbital period equal to exactly one sidereal day.[43]This means that the satellite will return to the same point above the Earth's surface every (sidereal) day, regardless of other orbital properties.[44][21]: 121 This orbital period, T, is directly related to the semi-major axis of the orbit through the formula:
where:
- ais the length of the orbit's semi-major axis
- is thestandard gravitational parameterof the central body[21]: 137
Inclination
[edit]A geosynchronous orbit can have any inclination.
Satellites commonly have an inclination of zero, ensuring that the orbit remains over the equator at all times, making it stationary with respect to latitude from the point of view of a ground observer (and in theECEFreference frame).[21]: 122
Another popular inclinations is 63.4° for a Tundra orbit, which ensures that the orbit'sargument of perigeedoes not change over time.[23]
Ground track
[edit]In the special case of a geostationary orbit, theground trackof a satellite is a single point on theequator.In the general case of a geosynchronous orbit with a non-zeroinclinationoreccentricity,the ground track is a more or less distorted figure-eight, returning to the same places once per sidereal day.[21]: 122
See also
[edit]- Geostationary orbit
- Geosynchronous satellite
- Graveyard orbit
- High Earth orbit
- List of orbits
- List of satellites in geosynchronous orbit
- Low Earth orbit
- Medium Earth orbit
- Molniya orbit
- Subsynchronous orbit
- Supersynchronous orbit
- Synchronous orbit
References
[edit]- ^abcdHowell, Elizabeth."What Is a Geosynchronous Orbit?".Space.com.RetrievedJuly 15,2022.
- ^Noordung, Hermann (1929).Das Problem der Befahrung des Weltraums: Der Raketen-Motor(PDF).Berlin: Richard Carl Schmidt & Co. pp. 98–100.
- ^"(Korvus's message is sent) to a small, squat building at the outskirts of Northern Landing. It was hurled at the sky.... It... arrived at the relay station tired and worn,... when it reached a space station only five hundred miles above the city of North Landing."Smith, George O.(1976).The Complete Venus Equilateral.New York:Ballantine Books.pp. 3–4.ISBN978-0-345-28953-7.
- ^"It is therefore quite possible that these stories influenced me subconsciously when... I worked out the principles of synchronous communications satellites...",McAleer, Neil (1992).Arthur C. Clarke.Contemporary Books. p. 54.ISBN978-0-809-24324-2.
- ^abClarke, Arthur C.(October 1945)."Extra-Terrestrial Relays – Can Rocket Stations Give Worldwide Radio Coverage?"(PDF).Wireless World.pp. 305–308. Archived fromthe original(PDF)on March 18, 2009.RetrievedMarch 4,2009.
- ^Phillips Davis (ed.)."Basics of Space Flight Section 1 Part 5, Geostationary Orbits".NASA.RetrievedAugust 25,2019.
- ^Mills, Mike (August 3, 1997)."Orbit Wars: Arthur C. Clarke and the Global Communications Satellite".The Washington Post Magazine.pp. 12–13.RetrievedAugust 25,2019.
- ^Kidder, S.Q. (2015). "Satellites and satellite remote senssing:[vague]--> Orbits ". In North, Gerald; Pyla, John; Zhang, Fuqing (eds.).Encyclopedia of Atmospheric Sciences(2 ed.). Elsiver. pp. 95–106.doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-382225-3.00362-5.ISBN978-0-12-382225-3.
- ^Brown, C.D. (1998).Spacecraft Mission Design(2nd ed.). AIAA Education Series. p. 81.ISBN978-1-60086-115-4.
- ^"Ariane 5 User's Manual Issue 5 Revision 1"(PDF).Ariane Space. July 2011. Archived fromthe original(PDF)on October 4, 2013.RetrievedJuly 28,2013.
- ^"What is orbit?".NASA.October 25, 2001. Archived fromthe originalon April 6, 2013.RetrievedMarch 10,2013.
Satellites that seem to be attached to some location on Earth are in Geosynchronous Earth Orbit (GEO)...Satellites headed for GEO first go to an elliptical orbit with an apogee about 23,000 miles. Firing the rocket engines at apogee then makes the orbit round. Geosynchronous orbits are also called geostationary.
- ^abcdMcClintock, Jack (November 9, 2003)."Communications: Harold Rosen – The Seer of Geostationary Satellites".Discover Magazine.RetrievedAugust 25,2019.
- ^Perkins, Robert (January 31, 2017).Harold Rosen, 1926–2017.Caltech.RetrievedAugust 25,2019.
- ^abcVartabedian, Ralph (July 26, 2013)."How a satellite called Syncom changed the world".Los Angeles Times.RetrievedAugust 25,2019.
- ^Glover, Daniel R. (1997)."Chapter 6: NASA Experimental Communications Satellites, 1958-1995".In Andrew J Butrica (ed.).Beyond The Ionosphere: Fifty Years of Satellite Communication.NASA.Bibcode:1997bify.book.....B.
- ^David R. Williams (ed.)."Syncom 2".NASA.RetrievedSeptember 29,2019.
- ^"World's First Geosynchronous Satellite Launched".History Channel.Foxtel. June 19, 2016. Archived fromthe originalon December 7, 2019.RetrievedAugust 25,2019.
- ^"ITU releases 2018 global and regional ICT estimates".International Telecommunication Union.December 7, 2018.RetrievedAugust 25,2019.
- ^Thompson, Geoff (April 24, 2019)."Australia was promised superfast broadband with the NBN. This is what we got".ABC.RetrievedAugust 25,2019.
- ^Tibken, Shara (October 22, 2018)."In farm country, forget broadband. You might not have internet at all. 5G is around the corner, yet pockets of America still can't get basic internet access".CNET.RetrievedAugust 25,2019.
- ^abcdefghijkWertz, James Richard; Larson, Wiley J. (1999). Larson, Wiley J.; Wertz, James R. (eds.).Space Mission Analysis and Design.Microcosm Press and Kluwer Academic Publishers.Bibcode:1999smad.book.....W.ISBN978-1-881883-10-4.
- ^"Orbits".ESA.October 4, 2018.RetrievedOctober 1,2019.
- ^abMaral, Gerard; Bousquet, Michel (August 24, 2011). "2.2.1.2 Tundra Orbits".Satellite Communications Systems: Systems, Techniques and Technology.John Wiley & Sons.ISBN978-1-119-96509-1.
- ^Jenkin, A.B.; McVey, J.P.; Wilson, J.R.; Sorge, M.E. (2017).Tundra Disposal Orbit Study.7th European Conference on Space Debris. ESA Space Debris Office. Archived fromthe originalon October 2, 2017.RetrievedOctober 2,2017.
- ^"Sirius Rising: Proton-M Ready to Launch Digital Radio Satellite Into Orbit".AmericaSpace.October 18, 2013.Archivedfrom the original on June 28, 2017.RetrievedJuly 8,2017.
- ^Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (July 14, 2016),Interface Specifications for QZSS,version 1.7, pp. 7–8, archived fromthe originalon April 6, 2013
- ^"Quasi-Zenith Satellite Orbit (QZO)".Archivedfrom the original on March 9, 2018.RetrievedMarch 10,2018.
- ^abFarber, Nicholas; Aresini, Andrea; Wauthier, Pascal; Francken, Philippe (September 2007).A general approach to the geostationary transfer orbit mission recovery.20th International Symposium on Space Flight Dynamics. p. 2.
- ^"Launching Satellites".EUMETSAT.Archived fromthe originalon December 21, 2019.RetrievedJanuary 26,2020.
- ^Davis, Jason (January 17, 2014)."How to get a satellite to geostationary orbit".The Planetary Society.RetrievedOctober 2,2019.
- ^"Repositioning geostationary satellites".Satellite Signals.February 22, 2022.Archivedfrom the original on November 27, 2022.RetrievedMay 23,2023.
- ^abUS patent 5183225,Forward, Robert, "Statite: Spacecraft That Utilizes Sight Pressure and Method of Use", published February 2, 1993
- ^"Science: Polar 'satellite' could revolutionise communications".New Scientist.No. 1759. March 9, 1991.RetrievedOctober 2,2019.
- ^Edwards, Bradley C. (March 1, 2003)."The Space Elevator NIAC Phase II Final Report"(PDF).NASA Institute for Advanced Concepts.p. 26.Archived(PDF)from the original on October 9, 2022.
- ^"Frequently Asked Questions: Orbital Debris".NASA. September 2, 2011. Archived fromthe originalon March 23, 2020.RetrievedFebruary 9,2020.
- ^EUMETSAT(April 3, 2017)."Where old satellites go to die".phys.org.
- ^Stephens, Marric (December 12, 2017)."Space debris threat to geosynchronous satellites has been drastically underestimated".Physics World.
- ^abHenry, Caleb (August 30, 2017)."ExoAnalytic video shows Telkom-1 satellite erupting debris".SpaceNews.com.
- ^"N° 40–1993: OLYMPUS: End of mission"(Press release).ESA.August 26, 1993. 40–1993.Archivedfrom the original on October 31, 2022.RetrievedMay 23,2023.
- ^"Notification for Express-AM11 satellite users in connection with the spacecraft failure".Russian Satellite Communications Company. April 19, 2006 – via Spaceref.[permanent dead link]
- ^Dunstan, James E. (January 30, 2018)."Do we care about orbital debris at all?".SpaceNews.com.
- ^"AMC 9 Satellite Anomaly associated with Energetic Event & sudden Orbit Change – Spaceflight101".spaceflight101.com.June 20, 2017. Archived fromthe originalon December 26, 2019.RetrievedJanuary 27,2020.
- ^Chobotov, Vladimir, ed. (1996).Orbital Mechanics(2nd ed.). Washington, DC: AIAA Education Series. p. 304.ISBN9781563471797.OCLC807084516.
- ^ Vallado, David A. (2007).Fundamentals of Astrodynamics and Applications.Hawthorne, CA: Microcosm Press. p. 31.OCLC263448232.
External links
[edit]- Satellites currently in Geosynchronous Orbit, list updated daily
- Science@NASA – Geosynchronous Orbit
- NASA – Planetary Orbits
- Science Presse data on Geosynchronous Orbits (including historical data and launch statistics)
- Orbital Mechanics(Rocket and Space Technology)
- NASA Astronomy Picture of the Day: Time lapse of Geostationary Satellites Beyond the Alps (11 April 2012)




