Open access

Open access(OA) is a set of principles and a range of practices through which nominallycopyrightablepublications are delivered to readers free of access charges or other barriers.[1]With open access strictly defined (according to the 2001 definition), orlibreopen access, barriers to copying or reuse are also reduced or removed by applying anopen licensefor copyright, which regulates post-publication uses of the work.[1]
The main focus of the open access movement has been on "peer reviewedresearch literature ", and more specifically onacademic journals.[2]because such publicationshave been:
1) a subject ofserials crisis,unlikenewspapers,magazinesandfiction writing.The main difference between these two groups is indemand elasticity:whereas a teacher of English literature can substitute in her class a copyrightedHarry Potter and the Philosopher's Stonewith a ca. 300-year old free-domainA Voyage to Lilliputwithout a detrimental effect on the students, anemergency roomphysiciantreating a patient for a life-threateningurushiolpoisoning can not substitute the most recent, butpaywalledreview article on this topic[3]for a 90 year-old copyright-expired article,[4]that was published before the invention ofprednisonein 1954.
2) the authors of research papers are not paid in any way, so they do not suffer any monetary losses, when they switch frombehind paywallto open access publishing, especially, if they usediamond open accessmedia.
3) the cost ofelectronic publishing,which has been the main form of distribution ofjournal articlessince ca. 2000, is incommensurably smaller, than the cost of on-paper publishing and distribution, which is still preferred by manyfiction literaturereaders.
Whereas non-open access journals cover publishing costs throughaccess tollssuch as subscriptions, site licenses orpay-per-viewcharges, open-access journals are characterised by funding models which do not require the reader to pay to read the journal's contents, relying instead onauthor feesor on public funding, subsidies and sponsorships. Open access can be applied to all forms of published research output, includingpeer-reviewedand non peer-reviewedacademic journalarticles,conference papers,theses,[5]book chapters,[1]monographs,[6]research reportsand images.[7]
Definitions
[edit]There are different models of open access publishing and publishers may use one or more of these models.
Colour naming system
[edit]Different open access types are currently commonly described using a colour system. The most commonly recognised names are "green", "gold", and "hybrid" open access; however, several other models and alternative terms are also used.[8]
Gold OA
[edit]In the gold OA model, the publisher makes all articles and related content available for free immediately on the journal's website. In such publications, articles are licensed for sharing and reuse viaCreative Commonslicenses or similar.[1]
Many gold OA publishers charge anarticle processing charge(APC), which is typically paid through institutional or grant funding. The majority of gold open access journals charging APCs follow an "author-pays" model,[13] although this is not an intrinsic property of gold OA.[14]
Green OA
[edit]Self-archivingby authors is permitted under green OA. Independently from publication by a publisher, the author also posts the work to a website controlled by the author, the research institution that funded or hosted the work, or to an independent central open repository, where people can download the work without paying.[15]
Green OA is free of charge for the author. Some publishers (less than 5% and decreasing as of 2014) may charge a fee for an additional service[15]such as afree licenseon the publisher-authored copyrightable portions of the printed version of an article.[16]
If the author posts the near-final version of their work after peer review by a journal, the archived version is called a "postprint".This can be the accepted manuscript as returned by the journal to the author after successful peer review.[17]
Hybrid OA
[edit]Hybrid open-access journalscontain a mixture of open access articles and closed access articles.[18][19]A publisher following this model is partially funded by subscriptions, and only provide open access for those individual articles for which the authors (or research sponsor) pay a publication fee.[20]Hybrid OA generally costs more than gold OA and can offer a lower quality of service.[21]A particularly controversial practice in hybrid open access journals is "double dipping",where both authors and subscribers are charged.[22]For these reasons, hybrid open access journals have been called a "Mephistophelianinvention ",[23]and publishing in hybrid OA journals often do not qualify for funding underopen access mandates,as libraries already pay for subscriptions thus have no financial incentive to fund open access articles in such journals.[24]
Bronze OA
[edit]Bronze open access articles are free to read only on the publisher page, but lack a clearly identifiable license.[25]Such articles are typically not available for reuse.
Diamond/platinum OA
[edit]Journals that publish open access without charging authors article processing charges are sometimes referred to as diamond[26][27][28]or platinum[29][30]OA. Since they do not charge either readers or authors directly, such publishers often require funding from external sources such as the sale ofadvertisements,academic institutions,learned societies,philanthropistsorgovernment grants.[31][32][33]There are now over 350 platinum OA journals withimpact factorsover a wide variety of academic disciplines, giving most academics options for OA with no APCs.[34]Diamond OA journals are available for most disciplines, and are usually small (<25 articles per year) and more likely to be multilingual (38%); thousands of such journals exist.[28]
Black OA
[edit]
The growth of unauthorized digital copying by large-scale copyright infringement has enabled free access topaywalledliterature.[36][37]This has been done via existing social media sites (e.g. the#ICanHazPDFhashtag) as well as dedicated sites (e.g.Sci-Hub).[36]In some ways this is a large-scale technical implementation of pre-existing practice, whereby those with access to paywalled literature would share copies with their contacts.[38][39][40][41]However, the increased ease and scale from 2010 onwards have changed how many people treat subscription publications.[42]
Gratis and libre
[edit]Similar to thefree contentdefinition, the terms'gratis' and 'libre'were used in theBudapest Open Access Initiativedefinition to distinguish between free to read versus free to reuse.[43]
Gratis open access (![]() ) refers to free online access, to read, free of charge, without re-use rights.[43]
) refers to free online access, to read, free of charge, without re-use rights.[43]
Libre open access (![]() ) also refers to free online access, to read, free of charge, plus some additional re-use rights,[43]covering the kinds of open access defined in theBudapest Open Access Initiative,theBethesda Statement on Open Access Publishingand theBerlin Declaration on Open Access to Knowledge in the Sciences and Humanities.The re-use rights of libre OA are often specified by various specificCreative Commons licenses;[44]all of which require as a minimumattribution of authorshipto the original authors.[43][45]In 2012, the number of works under libre open access was considered to have been rapidly increasing for a few years, though mostopen-access mandatesdid not enforce any copyright license and it was difficult to publish libre gold OA in legacy journals.[2]However, there are no costs nor restrictions for green libre OA as preprints can be freely self-deposited with a free license, and most open-access repositories useCreative Commonslicenses to allow reuse.[46]The biggest drawback of many Open Access licenses is a prohibition ondata mining.For this reason, manybig datastudies of various technologies performed byeconomists( as well asmachine learningbycomputer scientists) are limited topatent analysis,since the patent documents are not subject to copyright at all.
) also refers to free online access, to read, free of charge, plus some additional re-use rights,[43]covering the kinds of open access defined in theBudapest Open Access Initiative,theBethesda Statement on Open Access Publishingand theBerlin Declaration on Open Access to Knowledge in the Sciences and Humanities.The re-use rights of libre OA are often specified by various specificCreative Commons licenses;[44]all of which require as a minimumattribution of authorshipto the original authors.[43][45]In 2012, the number of works under libre open access was considered to have been rapidly increasing for a few years, though mostopen-access mandatesdid not enforce any copyright license and it was difficult to publish libre gold OA in legacy journals.[2]However, there are no costs nor restrictions for green libre OA as preprints can be freely self-deposited with a free license, and most open-access repositories useCreative Commonslicenses to allow reuse.[46]The biggest drawback of many Open Access licenses is a prohibition ondata mining.For this reason, manybig datastudies of various technologies performed byeconomists( as well asmachine learningbycomputer scientists) are limited topatent analysis,since the patent documents are not subject to copyright at all.
FAIR
[edit]FAIRis an acronym for 'findable, accessible, interoperable and reusable', intended to more clearly define what is meant by the term 'open access' and make the concept easier to discuss.[47][48]Initially proposed in March 2016, it has subsequently been endorsed by organisations such as theEuropean Commissionand theG20.[49][50]
Features
[edit]The emergence ofopen scienceoropen researchhas brought to light a number of controversial and hotly-debated topics.
Scholarly publishing invokes various positions and passions. For example, authors may spend hours struggling with diverse article submission systems, often converting document formatting between a multitude of journal and conference styles, and sometimes spend months waiting for peer review results. The drawn-out and often contentious societal and technological transition to Open Access and Open Science/Open Research, particularly across North America and Europe (Latin America has already widely adopted "Acceso Abierto" since before 2000[51]) has led to increasingly entrenched positions and much debate.[52]
The area of (open) scholarly practices increasingly sees a role for policy-makers and research funders[53][54][55]giving focus to issues such as career incentives, research evaluation and business models for publicly funded research.Plan SandAmeliCA[56](Open Knowledge for Latin America) caused a wave of debate in scholarly communication in 2019 and 2020.[57][58]
Licenses
[edit]
Subscription-based publishing typically requirestransfer of copyrightfrom authors to thepublisherso that the latter can monetise the process via dissemination and reproduction of the work.[60][61][62][63]With OA publishing, typically authors retain copyright to their work, andlicenseits reproduction to the publisher.[64]Retention of copyright by authors can supportacademic freedomsby enabling greater control of the work (e.g. for image re-use) or licensing agreements (e.g. to allow dissemination by others).[65]
The most common licenses used in open access publishing areCreative Commons.[66]The widely used CC BY license is one of the most permissive, only requiring attribution to be allowed to use the material (and allowing derivations and commercial use).[67]A range of more restrictive Creative Commons licenses are also used. More rarely, some of the smaller academic journals use custom open access licenses.[66][68]Some publishers (e.g.Elsevier) use "author nominal copyright" for OA articles, where the author retains copyright in name only and all rights are transferred to the publisher.[69][70][71]
Funding
[edit]Since open access publication does not charge readers, there are many financial models used to cover costs by other means.[72]Open access can be provided by commercial publishers, who may publish open access as well as subscription-based journals, or dedicated open-access publishers such asPublic Library of Science(PLOS) andBioMed Central.Another source of funding for open access can be institutional subscribers. One example of this is theSubscribe to Openpublishing model introduced byAnnual Reviews;if the subscription revenue goal is met, the given journal's volume is published open access.[73]
Advantages and disadvantages of open access have generated considerable discussion amongst researchers, academics, librarians, university administrators, funding agencies, government officials, commercialpublishers,editorial staff andsocietypublishers.[74]Reactions of existing publishers to open access journal publishing have ranged from moving with enthusiasm to a new open access business model, to experiments with providing as much free or open access as possible, to active lobbying against open access proposals. There are many publishers that started up as open access-only publishers, such as PLOS,Hindawi Publishing Corporation,Frontiers in...journals,MDPIand BioMed Central.
Article processing charges
[edit]

Some open access journals (under the gold, and hybrid models) generate revenue by charging publication fees in order to make the work openly available at the time of publication.[75][26][27]The money might come from the author but more often comes from the author'sresearch grantor employer.[76]While the payments are typically incurredper article published(e.g.BMCorPLOSjournals), some journals apply themper manuscript submitted(e.g.Atmospheric Chemistry and Physicsuntil recently) orper author(e.g.PeerJ).
Charges typically range from $1,000–$3,000 ($5,380 forNature Communications)[77][59][78]but can be under $10,[79]close to $5,000[80]or well over $10,000.[81]APCs vary greatly depending on subject and region and are most common in scientific and medical journals (43% and 47% respectively), and lowest in arts and humanities journals (0% and 4% respectively).[82]APCs can also depend on a journal's impact factor.[83][84][85][86]Some publishers (e.g.eLifeandUbiquity Press) have released estimates of their direct and indirect costs that set their APCs.[87][88]Hybrid OA generally costs more than gold OA and can offer a lower quality of service.[21]A particularly controversial practice in hybrid open access journals is "double dipping",where both authors and subscribers are charged.[22]
By comparison, journal subscriptions equate to $3,500–$4,000 per article published by an institution, but are highly variable by publisher (and some charge page fees separately). This has led to the assessment that there is enough money "within the system" to enable full transition to OA.[89]However, there is ongoing discussion about whether the change-over offers an opportunity to become more cost-effective or promotes more equitable participation in publication.[90]Concern has been noted that increasing subscription journal prices will be mirrored by rising APCs, creating a barrier to less financially privileged authors.[91][92][93]
The inherent bias of the current APC-based OA publishing perpetuates this inequality through the 'Matthew effect' (the rich get richer, and the poor get poorer). The switch from pay-to-read to pay-to-publish has left essentially the same people behind, with some academics not having enough purchasing power (individually or through their institutions) for either option.[94]Some gold OA publishers will waive all or part of the fee for authors fromless developed economies.Steps are normally taken to ensure thatpeer reviewersdo not know whether authors have requested, or been granted, fee waivers, or to ensure that every paper is approved by an independent editor with no financial stake in the journal.[citation needed]The main argument against requiring authors to pay a fee, is the risk to thepeer reviewsystem, diminishing the overall quality of scientific journal publishing.[citation needed]
Subsidized or no-fee
[edit]No-fee open access journals, also known as "platinum" or "diamond"[26][27]do not charge either readers or authors.[95]These journals use a variety ofbusiness modelsincluding subsidies, advertising, membership dues, endowments, or volunteer labour.[96][90]Subsidising sources range from universities, libraries and museums to foundations,societiesor government agencies.[96]Some publishers may cross-subsidise from other publications or auxiliary services and products.[96]For example, most APC-free journals in Latin America are funded by higher education institutions and are not conditional on institutional affiliation for publication.[90]Conversely,Knowledge Unlatchedcrowdsources funding in order to make monographs available open access.[97]
Estimates of prevalence vary, but approximately 10,000 journals without APC are listed in DOAJ[98]and theFree Journal Network.[99][100]APC-free journals tend to be smaller and more local-regional in scope.[101][102]Some also require submitting authors to have a particular institutional affiliation.[101]
Preprint use
[edit]
A "preprint"is typically a version of a research paper that is shared on an online platform prior to, or during, a formal peer review process.[103][104][105]Preprint platforms have become popular due to the increasing drive towards open access publishing and can be publisher- or community-led. A range of discipline-specific or cross-domain platforms now exist.[106]The posting of pre-prints (and/or authors' manuscript versions) is consistent with the Green Open Access model.[citation needed]
Effect of preprints on later publication
[edit]A persistent concern surrounding preprints is that work may be at risk of being plagiarised or "scooped" – meaning that the same or similar research will be published by others without proper attribution to the original source – if publicly available but not yet associated with a stamp of approval from peer reviewers and traditional journals.[107]These concerns are often amplified as competition increases for academic jobs and funding, and perceived to be particularly problematic for early-career researchers and other higher-risk demographics within academia.[citation needed]
However, preprints, in fact, protect against scooping.[108]Considering the differences between traditional peer-review based publishing models and deposition of an article on a preprint server, "scooping" is less likely for manuscripts first submitted as preprints. In a traditional publishing scenario, the time from manuscript submission to acceptance and to final publication can range from a few weeks to years, and go through several rounds of revision and resubmission before final publication.[109]During this time, the same work will have been extensively discussed with external collaborators, presented at conferences, and been read by editors and reviewers in related areas of research. Yet, there is no official open record of that process (e.g., peer reviewers are normally anonymous, reports remain largely unpublished), and if an identical or very similar paper were to be published while the original was still under review, it would be impossible to establish provenance.[citation needed]
Preprints provide a time-stamp at the time of publication, which helps to establish the "priority of discovery" for scientific claims (Vale and Hyman 2016). This means that a preprint can act as proof of provenance for research ideas, data, code, models, and results.[110]The fact that the majority of preprints come with a form of permanent identifier, usually adigital object identifier(DOI), also makes them easy to cite and track. Thus, if one were to be "scooped" without adequate acknowledgement, this would be a case of academic misconduct and plagiarism, and could be pursued as such.
There is no evidence that "scooping" of research via preprints exists, not even in communities that have broadly adopted the use of thearXivserver for sharing preprints since 1991. If the unlikely case of scooping emerges as the growth of the preprint system continues, it can be dealt with as academic malpractice.ASAPbioincludes a series of hypothetical scooping scenarios as part of its preprint FAQ, finding that the overall benefits of using preprints vastly outweigh any potential issues around scooping.[note 1]Indeed, the benefits of preprints, especially for early-career researchers, seem to outweigh any perceived risk: rapid sharing of academic research, open access without author-facing charges, establishing priority of discoveries, receiving wider feedback in parallel with or before peer review, and facilitating wider collaborations.[108]
Archiving
[edit]The "green" route to OA refers to author self-archiving, in which a version of the article (often the peer-reviewed version before editorial typesetting, called "postprint" ) is posted online to an institutional and/or subject repository. This route is often dependent on journal or publisher policies,[note 2]which can be more restrictive and complicated than respective "gold" policies regarding deposit location, license, and embargo requirements. Some publishers require an embargo period before deposition in public repositories,[111]arguing that immediate self-archiving risks loss of subscription income.
Embargo periods
[edit]
Embargoesare imposed by between 20 and 40% of journals,[113][114]during which time an article is paywalled before permitting self-archiving (green OA) or releasing a free-to-read version (bronze OA).[115][116]Embargo periods typically vary from 6–12 months inSTEMand >12 months inhumanities,artsandsocial sciences.[90]Embargo-freeself-archivinghas not been shown to affectsubscription revenue,[117]and tends to increase readership and citations.[118][119]Embargoes have been lifted on particular topics for either limited times or ongoing (e.g. Zika outbreaks[120]or indigenous health[121]).Plan Sincludes zero-length embargoes on self-archiving as a key principle.[90]
Motivations
[edit]Open access (mostly green and gratis) began to be sought and provided worldwide by researchers when the possibility itself was opened by the advent ofInternetand theWorld Wide Web.The momentum was further increased by a growing movement for academic journal publishing reform, and with it gold and libre OA.[citation needed]
The premises behind open access publishing are that there are viable funding models to maintain traditionalpeer reviewstandards of quality while also making the following changes:
- Rather than making journal articles accessible through asubscription business model,all academic publications could be made free to read and published with some other cost-recovery model, such as publication charges, subsidies, or charging subscriptions only for the print edition, with the online editiongratisor "free to read".[122]
- Rather than applying traditional notions ofcopyrightto academic publications, they could belibreor "free to build upon".[122]
An obvious advantage of open access journals is the free access to scientific papers regardless of affiliation with a subscribing library and improved access for the general public; this is especially true in developing countries. Lower costs for research in academia and industry have been claimed in theBudapest Open Access Initiative,[123]although others have argued that OA may raise the total cost of publication,[124]and further increase economic incentives for exploitation in academic publishing.[125]The open access movement is motivated by the problems of social inequality caused by restricting access to academic research, which favor large and wealthy institutions with the financial means to purchase access to many journals, as well as the economic challenges and perceived unsustainability of academic publishing.[122][126]
Stakeholders and concerned communities
[edit]The intended audience of research articles is usually other researchers. Open access helps researchers as readers by opening up access to articles that their libraries do not subscribe to. All researchers benefit from open access as no library can afford to subscribe to everyscientific journaland most can only afford a small fraction of them – this is known as the "serials crisis".[127]
Open access extends the reach of research beyond its immediate academic circle. An open access article can be read by anyone – aprofessionalin the field, aresearcherin another field, ajournalist,a politician orcivil servant,or an interested layperson. Indeed, a 2008 study revealed thatmental health professionalsare roughly twice as likely to read a relevant article if it is freely available.[128]
Research funders
[edit]Research fundingagencies and universities want to ensure that the research they fund and support in various ways has the greatest possible research impact.[129]As a means of achieving this, research funders are beginning to expect open access to the research they support. Many of them (including all UK Research Councils) have already adoptedopen-access mandates,and others are on the way to do so (seeROARMAP).
Universities
[edit]A growing number of universities are providing institutional repositories in which their researchers can deposit their published articles. Some open access advocates believe that institutional repositories will play a very important role in responding to open-access mandates from funders.[130]
In May 2005, 16 majorDutch universitiescooperatively launchedDAREnet,the Digital Academic Repositories, making over 47,000 research papers available.[131]From 2 June 2008, DAREnet has been incorporated into the scholarly portalNARCIS.[132]By 2019, NARCIS provided access to 360,000 open access publications from all Dutch universities,KNAW,NWOand a number of scientific institutes.[133]
In 2011, a group of universities in North America formed the Coalition of Open Access Policy Institutions (COAPI).[134]Starting with 21 institutions where the faculty had either established an open access policy or were in the process of implementing one, COAPI now has nearly 50 members. These institutions' administrators, faculty and librarians, and staff support the international work of the Coalition's awareness-raising and advocacy for open access.
In 2012, the Harvard Open Access Project released its guide to good practices for university open-access policies,[135]focusing on rights-retention policies that allow universities to distribute faculty research without seeking permission from publishers. As of November 2023, Rights retention policies are being adopted by an increasing number of UK universities as well. For a list of institutions worldwide currently espousing rights retention, see the list atUniversity rights-retention OA policies.
In 2013 a group of nine Australian universities formed the Australian Open Access Strategy Group (AOASG) to advocate, collaborate, raise awareness, and lead and build capacity in the open access space in Australia.[136]In 2015, the group expanded to include all eight New Zealand universities and was renamed the Australasian Open Access Support Group.[137]It was then renamed theAustralasian Open Access Strategy GroupArchived10 February 2018 at theWayback Machine,highlighting its emphasis on strategy. The awareness raising activities of the AOASG include presentations, workshops, blogs, and awebinar seriesArchived5 February 2018 at theWayback Machineon open access issues.[138]
Libraries and librarians
[edit]As information professionals,librariansare often vocal and active advocates of open access. These librarians believe that open access promises to remove both the price and permission barriers that undermine library efforts to provide access to scholarship, as well as helping to address theserials crisis.[139]Open access provides a complement to library access services such asinterlibrary loan,supporting researchers' needs for immediate access to scholarship.[140]Librarians and library associations also lead education and outreach initiatives to faculty, administrators, the library community, and the public about the benefits of open access.
Many library associations have either signed major open access declarations or created their own. For example,IFLAhave produced a Statement on Open Access.[141]TheAssociation of Research Librarieshas documented the need for increased access to scholarly information, and was a leading founder of theScholarly Publishing and Academic Resources Coalition(SPARC).[142][143]Librarians and library associations also develop and share informational resources on scholarly publishing and open access to research; the Scholarly Communications Toolkit[144]developed by theAssociation of College and Research Librariesof theAmerican Library Associationis one example of this work.
At most universities, the library manages the institutional repository, which provides free access to scholarly work by the university's faculty. TheCanadian Association of Research Librarieshas a program[145]to develop institutional repositories at all Canadian university libraries. An increasing number of libraries providepublishingor hosting services for open access journals, with the Library Publishing Coalition as a membership organisation.[146]
In 2013, open access activistAaron Swartzwas posthumously awarded the American Library Association'sJames Madison Awardfor being an "outspoken advocate for public participation in government and unrestricted access to peer-reviewed scholarly articles".[147][148]In March 2013, the entire editorial board and the editor-in-chief of theJournal of Library Administrationresigned en masse, citing a dispute with the journal's publisher.[149]One board member wrote of a "crisis of conscience about publishing in a journal that was not open access" after the death of Aaron Swartz.[150][151]
Public
[edit]The public may benefit from open access to scholarly research for many reasons. Advocacy groups such asSPARC's Alliance for Taxpayer Access in the US argue that most scientific research is paid for by taxpayers throughgovernment grants,who have a right to access the results of what they have funded.[152]Examples of people who might wish to read scholarly literature include individuals with medical conditions and their family members, serious hobbyists or "amateur" scholars (e.g.amateur astronomers), and high school andjunior collegestudents. Additionally, professionals in many fields, such as those doing research in private companies,start-ups,and hospitals, may not have access to publications behind paywalls, and OA publications are the only type that they can access in practice.
Even those who do not read scholarly articles benefit indirectly from open access.[153]For example, patients benefit when their doctor and otherhealth careprofessionals have access to the latest research. Advocates argue that open access speeds research progress, productivity, and knowledge translation.[154]
Low-income countries
[edit]In developing nations, open access archiving and publishing acquires a unique importance. Scientists, health care professionals, and institutions in developing nations often do not have the capital necessary to access scholarly literature.
Many open access projects involve international collaboration. For example, theSciELO(Scientific Electronic Library Online),[155]is a comprehensive approach to full open access journal publishing, involving a number ofLatin Americancountries.Bioline International,anon-profit organizationdedicated to helping publishers in developing countries is a collaboration of people in the UK, Canada, and Brazil; the Bioline International Software is used around the world.Research Papers in Economics(RePEc), is a collaborative effort of over 100 volunteers in 45 countries. ThePublic Knowledge Projectin Canada developed theopen-sourcepublishing softwareOpen Journal Systems(OJS), which is now in use around the world, for example by theAfrican Journals Onlinegroup, and one of the most active development groups is Portuguese. This international perspective has resulted in advocacy for the development ofopen-source appropriate technologyand the necessary open access to relevant information forsustainable development.[156][157]
History
[edit]This section should include a summary of, or be summarized in,History of open access.(May 2018) |

Extent
[edit]Various studies have investigated the extent of open access. A study published in 2010 showed that roughly 20% of the total number of peer-reviewed articles published in 2008 could be found openly accessible.[159]Another study found that by 2010, 7.9% of all academic journals withimpact factorswere gold open access journals and showed a broad distribution of Gold Open Access journals throughout academic disciplines.[160]A study of random journals from thecitations indexesAHSCI, SCI and SSCI in 2013 came to the result that 88% of the journals were closed access and 12% were open access.[26]In August 2013, a study done for theEuropean Commissionreported that 50% of a random sample of all articles published in 2011 as indexed byScopuswere freely accessible online by the end of 2012.[161][162][163]A 2017 study by theMax Planck Societyput the share of gold access articles in pure open access journals at around 13 percent of total research papers.[164]
In 2009, there were approximately 4,800 active open access journals, publishing around 190,000 articles.[165]As of February 2019, over 12,500 open access journals are listed in theDirectory of Open Access Journals.[166]

A 2013-2018 report (GOA4) found that in 2018 over 700,000 articles were published in gold open access in the world, of which 42% was in journals with no author-paid fees.[77]The figure varies significantly depending on region and kind of publisher: 75% if university-run, over 80% in Latin America, but less than 25% in Western Europe.[77]However, Crawford's study did not count open access articles published in "hybrid" journals (subscription journals that allow authors to make their individual articles open in return for payment of a fee). More comprehensive analyses of the scholarly literature suggest that this resulted in a significant underestimation of the prevalence of author-fee-funded OA publications in the literature.[169]Crawford's study also found that although a minority of open accessjournalsimpose charges on authors, a growing majority of open accessarticlesare published under this arrangement, particularly in the science disciplines (thanks to the enormous output of open access "mega journals", each of which may publish tens of thousands of articles in a year and are invariably funded by author-side charges—see Figure 10.1 in GOA4).
According toScopusdatabase in August, 2024, 46.2% of works, indexed therein and published in 2023, had some form of open access. More than half of the OA publications (27.5% of all indexed works in 2023) were in fully Gold Open Access sources, 16.7% of all were in Green OA sources (i.e. which allow for self-archiving by authors), 9.2 % in Hybrid Gold OA sources (such as journals, which have open access and behind-paywall articles in the same issue), and 10.6 % were in Bronze OA sources (free-to-read on the publishers' websites).[170]

The adoption of Open Access publishing varies significantly from publisher to publisher, as shown in Fig. OA-Plot, where only the oldest (traditional) publishers are shown, but not the newer publishers, that use the Open Access model exclusively. This plot shows, that since 2010 theInstitute of Physicshas the largest percentage of OA publications, while theAmerican Chemical Societyhas the lowest. Both theIOPand theACSare non-profit publishers. The increase in OA percentage for articles published before ca. 1923 is related to the expiration of a 100-yearcopyright term.Some publishers (e.g.IOPandACSmade many such articles available as Open Access, while others (Elsevierin particular) did not.
TheRegistry of Open Access Repositories(ROAR) indexes the creation, location and growth of open accessopen access-repositoriesand their contents.[171]As of February 2019, over 4,500 institutional and cross-institutional repositories have been registered in ROAR.[172]
Effects on scholarly publishing
[edit]Article impact
[edit]
Since published articles report on research that is typically funded by government or university grants, the more the article is used, cited, applied and built upon, the better for research as well as for the researcher's career.[180][181]
Some professional organizations have encouraged use of open access: in 2001, theInternational Mathematical Unioncommunicated to its members that "Open access to the mathematical literature is an important goal" and encouraged them to "[make] available electronically as much of our own work as feasible" to "[enlarge] the reservoir of freely available primary mathematical material, particularly helping scientists working without adequate library access".[182]
Readership
[edit]OA articles are generally viewed online and downloaded more often than paywalled articles and that readership continues for longer.[174][183]Readership is especially higher in demographics that typically lack access to subscription journals (in addition to the general population, this includes many medical practitioners, patient groups, policymakers, non-profit sector workers, industry researchers, and independent researchers).[184]OA articles are more read on publication management programs such as Mendeley.[178]Open access practices can reduce publication delays, an obstacle which led some research fields such as high-energy physics to adopt widespread preprint access.[185]
Citation rate
[edit]
A main reason authors make their articles openly accessible is to maximize theircitation impact.[186]Open access articles are typicallycitedmore often than equivalent articles requiring subscriptions.[2][187][188][189][190]This 'citation advantage' was first reported in 2001.[191]Although two major studies dispute this claim,[192][183]the consensus of multiple studies support the effect,[173][193]with measured OA citation advantage varying in magnitude between 1.3-fold to 6-fold depending on discipline.[189][194][195]
Citation advantage is most pronounced in OA articles in hybrid journals (compared to the non-OA articles in those same journals),[196]and with articles deposited in green OA repositories.[159]Notably, green OA articles show similar benefits to citation counts as gold OA articles.[195][190]Articles in gold OA journals are typically cited at a similar frequency to paywalled articles.[197]Citation advantage increases the longer an article has been published.[174]
Altmetrics
[edit]In addition to format academiccitation,other forms of research impact (altmetrics) may be affected by OA publishing,[184][190]constituting a significant "amplifier" effect for science published on such platforms.[179]Initial studies suggest that OA articles are more referenced in blogs,[198]on Twitter,[178]and on English Wikipedia.[179]The OA advantage in altmetrics may be smaller than the advantage in academic citations, although findings are mixed.[199][190][195]
Journal impact factor
[edit]Journal impact factor(JIF) measures the average number of citations of articles in a journal over a two-year window. It is commonly used as a proxy for journal quality, expected research impact for articles submitted to that journal, and of researcher success.[200][201]In subscription journals, impact factor correlates with overall citation count, however this correlation is not observed in gold OA journals.[202]
Open access initiatives likePlan Stypically call on a broader adoption and implementation of theLeiden Manifesto[note 3]and theSan Francisco Declaration on Research Assessment(DORA) alongside fundamental changes in the scholarly communication system.[note 4]
Peer review processes
[edit]Peer reviewof research articles prior to publishing has been common since the 18th century.[203][204]Commonly reviewer comments are only revealed to the authors and reviewer identities kept anonymous.[205][206]The rise of OA publishing has also given rise to experimentation in technologies and processes for peer review.[207]Increasing transparency of peer review and quality control includes posting results topreprint servers,[208]preregistrationof studies,[209]open publishing of peer reviews,[210]open publishing of full datasets and analysis code,[211][212]and other open science practices.[213][214][215]It is proposed that increased transparency of academic quality control processes makes audit of the academic record easier.[210][216]Additionally, the rise of OAmegajournalshas made it viable for their peer review to focus solely on methodology and results interpretation whilst ignoring novelty.[217][218]Major criticisms of the influence of OA on peer review have included that if OA journals have incentives to publish as many articles as possible then peer review standards may fall (as aspect of predatory publishing), increased use of preprints may populate the academic corpus with un-reviewed junk and propaganda, and that reviewers may self-censor if their identity of open. Some advocates propose that readers will have increased skepticism of preprint studies - a traditional hallmark of scientific inquiry.[90]
Predatory publishing
[edit]Predatory publisherspresent themselves as academic journals but use lax or no peer review processes coupled with aggressive advertising in order to generate revenue from article processing charges from authors. The definitions of 'predatory', 'deceptive', or 'questionable' publishers/journals are often vague, opaque, and confusing, and can also include fully legitimate journals, such as those indexed by PubMed Central.[219]In this sense, Grudniewicz et al.[220]proposed a consensus definition that needs to be shared: "Predatory journals and publishers are entities that prioritize self-interest at the expense of scholarship and are characterized by false or misleading information, deviation from best editorial and publication practices, a lack of transparency, and/or the use of aggressive and indiscriminate solicitation practices."
In this way, predatory journals exploit the OA model by deceptively removing the main value added by the journal (peer review) and parasitize the OA movement, occasionally hijacking or impersonating other journals.[221][222]The rise of such journals since 2010[223][224]has damaged the reputation of the OA publishing model as a whole, especially via sting operations where fake papers have been successfully published in such journals.[225]Although commonly associated with OA publishing models, subscription journals are also at risk of similar lax quality control standards and poor editorial policies.[226][227][228]OA publishers therefore aim to ensure quality via auditing by registries such asDOAJ,OASPAandSciELOand comply to a standardised set of conditions. A blacklist of predatory publishers is also maintained byCabell's blacklist(a successor toBeall's List).[229][230]Increased transparency of the peer review and publication process has been proposed as a way to combat predatory journal practices.[90][210][231]
Open irony
[edit]Open irony refers to the situation where a scholarly journal article advocates open access but the article itself is only accessible by paying a fee to the journal publisher to read the article.[232][233][234]This has been noted in many fields, with more than 20 examples appearing since around 2010, including in widely-read journals such asThe Lancet,ScienceandNature.AFlickrgroupcollected screenshots of examples. In 2012 Duncan Hull proposed the Open Access Irony award to publicly humiliate journals that publish these kinds of papers.[235]Examples of these have been shared and discussed on social media using thehashtag#openirony (e.g. onTwitter). Typically, these discussions are humorous exposures of articles/editorials that are pro-open access, but locked behind paywalls. The main concern that motivates these discussions is that restricted access to public scientific knowledge is slowing scientific progress.[234]The practice has been justified as important for raising awareness of open access.[236]
Infrastructure
[edit]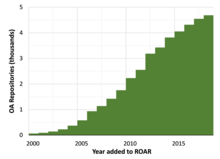
Databases and repositories
[edit]Multiple databases exist for open access articles, journals and datasets. These databases overlap, however each has different inclusion criteria, which typically include extensive vetting for journal publication practices, editorial boards and ethics statements. The main databases of open access articles and journals areDOAJandPMC.In the case of DOAJ, only fully gold open access journals are included, whereas PMC also hosts articles from hybrid journals.
There are also a number ofpreprint serverswhich host articles that have not yet been reviewed as open access copies.[238][239]These articles are subsequently submitted for peer review by both open access and subscription journals, however the preprint always remains openly accessible. A list of preprint servers is maintained at ResearchPreprints.[240]
For articles that are published in closed access journals, some authors will deposit a postprint copy in anopen-access repository,where it can be accessed for free.[241][242][243][171][244]Most subscription journals place restrictions on which version of the work may be shared and/or require anembargoperiod following the original date of publication. What is deposited can therefore vary, either apreprintor the peer-reviewedpostprint,either the author's refereed and revised final draft or the publisher'sversion of record,either immediately deposited or after several years.[245]Repositories may be specific to aninstitution,adiscipline(e.g.arXiv), ascholarly society(e.g.MLA's CORE Repository), or a funder (e.g. PMC). Although the practice was first formally proposed in 1994,[246][247]self-archiving was already being practiced by some computer scientists in localFTParchives in the 1980s (later harvested byCiteSeer).[248]TheSHERPA/RoMEOsite maintains a list of the different publisher copyright and self-archiving policies[249]and theROARdatabase hosts an index of the repositories themselves.[250][251]
Representativeness in proprietary databases
[edit]Uneven coverage of journals in the major commercial citation index databases (such asWeb of Science,Scopus,andPubMed)[252][253][254][255]has strong effects on evaluating both researchers and institutions (e.g. the UKResearch Excellence FrameworkorTimes Higher Education ranking[note 5][256][257]). While these databases primarily select based on process and content quality, there has been concern that their commercial nature may skew their assessment criteria and representation of journals outside of Europe and North America.[90][70]At the time of that study in 2018, there were no comprehensive, open source or non-commercial academic databases.[258]However, in more recent years,The Lensemerged as a suitable outside-paywalls universal academic database.
Distribution
[edit]Like the self-archived green open access articles, most gold open access journal articles are distributed via theWorld Wide Web,[1]due to low distribution costs, increasing reach, speed, and increasing importance for scholarly communication.Open source softwareis sometimes used foropen-access repositories,[259]open access journal websites,[260]and other aspects of open access provision and open access publishing.
Access to online content requires Internet access, and this distributional consideration presents physical and sometimes financial barriers to access.
There are various open access aggregators that list open access journals or articles.ROAD(the Directory of Open Access Scholarly Resources)[261]synthesizes information about open access journals and is a subset of theISSNregister.SHERPA/RoMEOlists international publishers that allow the published version of articles to be deposited ininstitutional repositories.TheDirectory of Open Access Journals(DOAJ) contains over 12,500 peer-reviewed open access journals for searching and browsing.[262][166]
Open access articles can be found with aweb search,using any generalsearch engineor those specialized for the scholarly and scientific literature, such asGoogle Scholar,OAIster,base-search.net,[263]andCORE[264]Many open-access repositories offer a programmable interface to query their content. Some of them use a generic protocol, such asOAI-PMH(e.g., base-search.net[263]). In addition, some repositories propose a specific API, such as thearXivAPI, the Dissemin API, theUnpaywall/oadoi API, or the base-search API.
In 1998, several universities founded thePublic Knowledge Projectto foster open access, and developed the open-source journal publishing systemOpen Journal Systems,among other scholarly software projects. As of 2010, it was being used by approximately 5,000 journals worldwide.[265]
Several initiatives provide an alternative to the English language dominance of existing publication indexing systems, includingIndex Copernicus(Polish),SciELO(Portuguese, Spanish) andRedalyc(Spanish).
Policies and mandates
[edit]Many universities, research institutions and research funders have adopted mandates requiring their researchers to make their research publications open access.[266]For example, Research Councils UK spent nearly £60m on supporting their open access mandate between 2013 and 2016.[267]New mandates are often announced during the Open Access Week, that takes place each year during the last full week of October.
The idea of mandating self-archiving was raised at least as early as 1998.[268]Since 2003[269]efforts have been focused on open access mandating by the funders of research: governments,[270]research funding agencies,[271]and universities.[272]Some publishers and publisher associations have lobbied against introducing mandates.[273][274][275]
In 2002, the University of Southampton's School of Electronics & Computer Science became one of the first schools to implement a meaningful mandatory open access policy, in which authors had to contribute copies of their articles to the school's repository. More institutions followed suit in the following years.[2]In 2007, Ukraine became the first country to create a national policy on open access, followed by Spain in 2009. Argentina, Brazil, and Poland are currently in the process of developing open access policies. Making master's and doctoral theses open access is an increasingly popular mandate by many educational institutions.[2]
In the US, theNIH Public Access Policyhas required since 2008 that papers describing research funded by the National Institutes of Health must be available to the public free throughPubMed Central(PMC) within 12 months of publication. In 2022, US PresidentJoe Biden'sOffice of Science and Technology Policyissued a memorandum calling for the removal of the 12-month embargo.[276]By the end of 2025, US federal agencies must require all results (papers, documents and data) produced as a result of US government-funded research to be available to the public immediately upon publication.[277]
In 2023, the Council of theEuropean Unionrecommended the implementation of an open-access and not-for-profit model for research publishing by theEuropean Commissionand member states. These recommendations are not legally binding and received mixed reactions. While welcomed by some members of the academic community,publishersargued that the suggested model is unrealistic due to the lack of crucial funding details. Furthermore, the council's recommendations raised concerns within the publishing industry regarding the potential implications, and they also emphasized the importance of research integrity and the need for member states to addresspredatory journalsandpaper mills.[278]
In 2024, theGates Foundationannounced a "preprint-centric" open access policy, and their intention to stop paying APCs.[279]In 2024, the government of Japan also announced a Green open access policy, requiring that government-funded research be made freely available on institutional preprint repositories from April 2025.[280]
Compliance
[edit]As of March 2021,open-access mandateshave been registered by over 100 research funders and 800 universities worldwide, compiled in theRegistry of Open Access Repository Mandates and Policies.[281]As these sorts of mandates increase in prevalence, collaborating researchers may be affected by several at once. Tools such asSWORDcan help authors manage sharing between repositories.[2]
Compliance rates withvoluntaryopen access policies remain low (as low as 5%).[2]However it has been demonstrated that more successful outcomes are achieved by policies that are compulsory and more specific, such as specifying maximum permissible embargo times.[2][282]Compliance with compulsory open-access mandates varies between funders from 27% to 91% (averaging 67%).[2][283]From March 2021,Google Scholarstarted tracking and indicating compliance with funders' open-access mandates, although it only checks whether items are free-to-read, rather than openly licensed.[284]
Inequality and open access
[edit]Gender inequality
[edit]Gender inequality still exists in the modern system of scientific publishing. In terms of citation and authorship position, gender differences favoring men can be found in many disciplines such as political science, economics and neurology, and critical care research. For instance, in critical care research, 30.8% of the 18,483 research articles published between 2008 and 2018 were led by female authors and were more likely to be published in lower-impact journals than those led by male authors.[285]Such disparity can adversely affect the scientific career of women and underrate their scientific impacts for promotion and funding. Open access (OA) publishing can be a tool to help female researchers increase their publications' visibility, measure impact, and help close the gendered citation gap. OA publishing is a well-advocated practice for providing better accessibility to knowledge (especially for researchers in low- and middle-income countries) as well as increasing transparency along with the publishing procedure [21,22]. Publications' visibility can be enhanced through OA publishing due to its high accessibility by removing paywalls compared to non-OA publishing.
Additionally, because of this high visibility, authors can receive more recognition for their works. OA publishing is also suggested to be advantageous in terms of citation number compared to non-OA publishing, but this aspect is still controversial within the scientific community. The association between OA and a higher number of citations may be because higher-quality articles are self-selected for publication as OA. Considering the gender-based issues in academia and the efforts to improve gender equality, OA can be an important factor when female researchers choose a place to publish their articles. With a proper supporting system and funding, OA publishing is shown to have increased female researchers' productivity.[286]
High-income–low-income country inequality
[edit]A 2022 study has found "most OA articles were written by authors in high-income countries, and there were no articles in Mirror journals by authors in low-income countries."[287]"One of the great ironies of open access is that you grant authors around the world the ability to finally read the scientific literature that was completely closed off to them, but it ends up excluding them from publishing in the same journals" says Emilio Bruna, a scholar at theUniversity of Floridain Gainesville.[288]
By country
[edit]See also
[edit]- Access to knowledge movement
- Altmetrics
- Copyright policies of academic publishers
- Freedom of information
- Guerilla Open Access
- List of open access journals
- Open Access Button
- Open access monograph
- Open Access Scholarly Publishers Association
- Open Access Week
- Open data
- Open educational resources
- Open government
- Predatory open access publishing
- Right to Internet access
- Category:Open access journals
- Category:Open access by country
- Category:Publication management software
Notes
[edit]- ^"ASAPbio FAQ".Archivedfrom the original on 31 August 2020.Retrieved28 August2019..
- ^"SHERPA/RoMEO".Archivedfrom the original on 30 August 2019.Retrieved28 August2019.database.
- ^"The Leiden Manifesto for Research Metrics".Archivedfrom the original on 31 August 2020.Retrieved28 August2019.2015.
- ^"Plan S implementation guidelines".Archivedfrom the original on 31 August 2020.Retrieved28 August2019.,February 2019.
- ^Publications in journals listed in the WoS has a large effect on the UKResearch Excellence Framework.Bibliographic data from Scopus represents more than 36% of assessment criteria inTHE rankings.
References
[edit]- ^abcdeSuber, Peter."Open Access Overview".Archivedfrom the original on 19 May 2007.Retrieved29 November2014.
- ^abcdefghiSwan, Alma (2012)."Policy guidelines for the development and promotion of open access".UNESCO.Archivedfrom the original on 14 April 2019.Retrieved14 April2019.
- ^Diedrich V, Zweerink K, Elder B. Plant Dermatitis. Emerg Med Clin North Am. 2024;42(3):613-38 doi: 10.1016/j.emc.2024.03.001;https://www.emed.theclinics.com/article/S0733-8627(24)00041-5/abstract
- ^Hill GA, Mattacotti V. The Toxic Principle of the Poison Ivy. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 1934;56(12):2736-8 doi: 10.1021/ja01327a064;https://pubs.acs.org/doi/pdf/10.1021/ja01327a064
- ^Schöpfel, Joachim; Prost, Hélène (2013)."Degrees of secrecy in an open environment. The case of electronic theses and dissertations".ESSACHESS – Journal for Communication Studies.6(2(12)): 65–86.Archivedfrom the original on 1 January 2014.
- ^Schwartz, Meredith (2012)."Directory of Open Access Books Goes Live".Library Journal.Archivedfrom the original on 4 October 2013.
- ^"Terms and conditions for the use and redistribution of Sentinel data"(PDF).No. version 1.0. European Space Agency. July 2014.Archived(PDF)from the original on 8 February 2020.Retrieved28 June2020.
- ^Simard, Marc-André; Ghiasi, Gita; Mongeon, Philippe; Larivière, Vincent (9 August 2022). Baccini, Alberto (ed.)."National differences in dissemination and use of open access literature".PLOS One.17(8): e0272730.Bibcode:2022PLoSO..1772730S.doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0272730.ISSN1932-6203.PMC9362937.PMID35943972.
- ^"DOAJ: Directory of Open Access Journals".doaj.org.1 May 2013. Archived fromthe originalon 1 May 2013.
- ^Morrison, Heather (31 December 2018). "Dramatic Growth of Open Access".Scholars Portal Dataverse.hdl:10864/10660.
- ^"PMC full journal list download".National Center for Biotechnology Information.Archivedfrom the original on 7 March 2019.Retrieved10 March2019.
- ^"NLM Catalog".National Center for Biotechnology Information.Archivedfrom the original on 14 January 2019.Retrieved10 March2019.
- ^Schroter, Sara; Tite, Leanne (2006)."Open access publishing and author-pays business models: a survey of authors' knowledge and perceptions".Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine.99(3): 141–148.doi:10.1177/014107680609900316.PMC1383760.PMID16508053.
- ^Eve, Martin Paul (3 December 2023). "Introduction, or why open access?".Open Access and the Humanities.Cambridge Core. pp. 1–42.doi:10.1017/CBO9781316161012.003.ISBN9781107097896.Retrieved30 December2020.
- ^abGadd, Elizabeth; Troll Covey, Denise (1 March 2019)."What does 'green' open access mean? Tracking twelve years of changes to journal publisher self-archiving policies".Journal of Librarianship and Information Science.51(1): 106–122.doi:10.1177/0961000616657406.ISSN0961-0006.S2CID34955879.Archivedfrom the original on 31 August 2020.Retrieved28 August2019.
- ^Weaver, Roger."Subject Guides: Copyright: Keeping Control of Your Copyright".libguides.mst.edu.Retrieved22 April2024.
- ^Bolick, Josh (2018)."Leveraging Elsevier's Creative Commons License Requirement to Undermine Embargoes"(PDF).digitalcommons.unl.edu.Archivedfrom the original on 22 April 2024.Retrieved22 April2024– viaUniversity of Nebraska–Lincoln.
- ^Laakso, Mikael; Björk, Bo-Christer (2016)."Hybrid open access—A longitudinal study".Journal of Informetrics.10(4): 919–932.doi:10.1016/j.joi.2016.08.002.
- ^Suber 2012,pp. 140–141
- ^Suber 2012,p. 140
- ^abTrust, Wellcome (23 March 2016)."Wellcome Trust and COAF Open Access Spend, 2014-15".Wellcome Trust Blog.Archived fromthe originalon 27 October 2019.Retrieved27 October2019.
- ^ab"Open access double dipping policy".Cambridge Core.Archivedfrom the original on 31 August 2020.Retrieved12 March2018.
- ^Björk, B. C. (2017)."Growth of hybrid open access, 2009–2016".PeerJ.5:e3878.doi:10.7717/peerj.3878.PMC5624290.PMID28975059.
- ^Liuta, Ioana (26 July 2020)."Open choice vs open access: Why don't" hybrid "journals qualify for the open access fund?".Radical Access.SFU Library.Archivedfrom the original on 31 August 2023.
- ^Piwowar, Heather; Priem, Jason; Larivière, Vincent; Alperin, Juan Pablo; Matthias, Lisa; Norlander, Bree; Farley, Ashley; West, Jevin; Haustein, Stefanie (13 February 2018)."The state of OA: a large-scale analysis of the prevalence and impact of Open Access articles".PeerJ.6:e4375.doi:10.7717/peerj.4375.PMC5815332.PMID29456894.
- ^abcdFuchs, Christian; Sandoval, Marisol (2013)."The diamond model of open access publishing: Why policy makers, scholars, universities, libraries, labour unions and the publishing world need to take non-commercial, non-profit open access serious".TripleC.13(2): 428–443.doi:10.31269/triplec.v11i2.502.
- ^abcGajović, S (31 August 2017)."Diamond Open Access in the quest for interdisciplinarity and excellence".Croatian Medical Journal.58(4): 261–262.doi:10.3325/cmj.2017.58.261.PMC5577648.PMID28857518.
- ^abBosman, Jeroen; Frantsvåg, Jan Erik; Kramer, Bianca; Langlais, Pierre-Carl; Proudman, Vanessa (9 March 2021).OA Diamond Journals Study. Part 1: Findings(Report).doi:10.5281/zenodo.4558704.
- ^Machovec, George (2013). "An Interview with Jeffrey Beall on Open Access Publishing".The Charleston Advisor.15(1): 50.doi:10.5260/chara.15.1.50.
- ^Öchsner, A. (2013). "Publishing Companies, Publishing Fees, and Open Access Journals".Introduction to Scientific Publishing.SpringerBriefs in Applied Sciences and Technology. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer. pp. 23–29.doi:10.1007/978-3-642-38646-6_4.ISBN978-3-642-38645-9.
- ^Normand, Stephanie (4 April 2018)."Is Diamond Open Access the Future of Open Access?".The IJournal: Graduate Student Journal of the Faculty of Information.3(2).ISSN2561-7397.Archivedfrom the original on 29 May 2020.Retrieved25 June2019.
- ^Rosenblum, Brian; Greenberg, Marc; Bolick, Josh; Emmett, Ada; Peterson, A. Townsend (17 June 2016). "Subsidizing truly open access".Science.352(6292): 1405.Bibcode:2016Sci...352.1405P.doi:10.1126/science.aag0946.hdl:1808/20978.ISSN0036-8075.PMID27313033.S2CID206650745.
- ^By (1 June 2017)."Diamond Open Access, Societies and Mission".The Scholarly Kitchen.Archivedfrom the original on 24 June 2019.Retrieved25 June2019.
- ^Pearce, Joshua M. (2022)."The Rise of Platinum Open Access Journals with Both Impact Factors and Zero Article Processing Charges".Knowledge.2(2): 209–224.doi:10.3390/knowledge2020013.ISSN2673-9585.
- ^Himmelstein, Daniel S; Romero, Ariel Rodriguez; Levernier, Jacob G; Munro, Thomas Anthony; McLaughlin, Stephen Reid; Greshake Tzovaras, Bastian; Greene, Casey S (1 March 2018)."Sci-Hub provides access to nearly all scholarly literature".eLife.7.doi:10.7554/eLife.32822.ISSN2050-084X.PMC5832410.PMID29424689.Archivedfrom the original on 21 May 2019.Retrieved21 May2019.
- ^abBjörk, Bo-Christer (2017)."Gold, green, and black open access".Learned Publishing.30(2): 173–175.doi:10.1002/leap.1096.ISSN1741-4857.
- ^Green, Toby (2017)."We've failed: Pirate black open access is trumping green and gold and we must change our approach".Learned Publishing.30(4): 325–329.doi:10.1002/leap.1116.ISSN1741-4857.
- ^Bohannon, John (28 April 2016)."Who's downloading pirated papers? Everyone".Science.352(6285): 508–12.doi:10.1126/science.352.6285.508.ISSN0036-8075.PMID27126020.Archivedfrom the original on 13 May 2019.Retrieved17 May2019.
- ^Greshake, Bastian (21 April 2017)."Looking into Pandora's Box: The Content of Sci-Hub and its Usage".F1000Research.6:541.doi:10.12688/f1000research.11366.1.ISSN2046-1402.PMC5428489.PMID28529712.
- ^Jamali, Hamid R. (1 July 2017). "Copyright compliance and infringement in ResearchGate full-text journal articles".Scientometrics.112(1): 241–254.doi:10.1007/s11192-017-2291-4.ISSN1588-2861.S2CID189875585.
- ^Swab, Michelle; Romme, Kristen (1 April 2016)."Scholarly Sharing via Twitter: #icanhazpdf Requests for Health Sciences Literature".Journal of the Canadian Health Libraries Association.37(1).doi:10.5596/c16-009.ISSN1708-6892.
- ^McKenzie, Lindsay (27 July 2017)."Sci-Hub's cache of pirated papers is so big, subscription journals are doomed, data analyst suggests".Science.doi:10.1126/science.aan7164.ISSN0036-8075.Archivedfrom the original on 17 May 2019.Retrieved17 May2019.
- ^abcdSuber, Peter (2008)."Gratis and Libre Open Access".Archived fromthe originalon 10 March 2017.Retrieved3 December2011.
- ^Suber 2012,pp. 68–69
- ^Suber 2012,pp. 7–8
- ^Balaji, B.; Dhanamjaya, M. (2019)."Preprints in Scholarly Communication: Re-Imagining Metrics and Infrastructures".Publications.7(1): 6.doi:10.3390/publications7010006.>
- ^Wilkinson, Mark D.; Dumontier, Michel; Aalbersberg, IJsbrand Jan; Appleton, Gabrielle; et al. (15 March 2016)."The FAIR Guiding Principles for scientific data management and stewardship".Scientific Data.3(1): 160018.Bibcode:2016NatSD...360018W.doi:10.1038/sdata.2016.18.OCLC961158301.PMC4792175.PMID26978244.
- ^Wilkinson, Mark D.; da Silva Santos, Luiz Olavo Bonino; Dumontier, Michel; Velterop, Jan; Neylon, Cameron; Mons, Barend (1 January 2017)."Cloudy, increasingly FAIR; revisiting the FAIR Data guiding principles for the European Open Science Cloud".Information Services & Use.37(1): 49–56.doi:10.3233/ISU-170824.hdl:20.500.11937/53669.ISSN0167-5265.
- ^"European Commission embraces the FAIR principles".Dutch Techcentre for Life Sciences.20 April 2016.Archivedfrom the original on 20 July 2018.Retrieved31 July2019.
- ^"G20 Leaders' Communique Hangzhou Summit".europa.eu.Archivedfrom the original on 31 July 2019.Retrieved31 July2019.
- ^"Hecho En Latinoamérica. Acceso Abierto, Revistas Académicas e Innovaciones Regionales".Archivedfrom the original on 6 August 2020.Retrieved31 August2020.
- ^Vuong, Quan-Hoang (2018)."The (ir)rational consideration of the cost of science in transition economies".Nature Human Behaviour.2(1): 5.doi:10.1038/s41562-017-0281-4.PMID30980055.S2CID256707733.
- ^Ross-Hellauer, Tony; Schmidt, Birgit; Kramer, Bianca (2018)."Are Funder Open Access Platforms a Good Idea?".SAGE Open.8(4).doi:10.1177/2158244018816717.
- ^Vincent-Lamarre, Philippe; Boivin, Jade; Gargouri, Yassine; Larivière, Vincent; Harnad, Stevan (2016)."Estimating Open Access Mandate Effectiveness: The MELIBEA Score"(PDF).Journal of the Association for Information Science and Technology.67(11): 2815–2828.arXiv:1410.2926.doi:10.1002/asi.23601.S2CID8144721.Archived(PDF)from the original on 23 September 2016.Retrieved28 August2019.
- ^Future of Scholarly Publishing and Scholarly Communication: Report of the Expert Group to the European Commission.Publications Office of the European Union. 30 January 2019.ISBN9789279972386.Archivedfrom the original on 3 June 2019.Retrieved28 August2019.
- ^Aguado-López, Eduardo; Becerril-Garcia, Arianna (8 August 2019)."AmeliCA before Plan S – The Latin American Initiative to develop a cooperative, non-commercial, academic led, system of scholarly communication".Impact of Social Sciences.Archived fromthe originalon 1 November 2019.Retrieved26 November2022.
- ^Johnson, Rob (2019)."From Coalition to Commons: Plan S and the Future of Scholarly Communication".Insights: The UKSG Journal.32.doi:10.1629/uksg.453.
- ^Pourret, Olivier; Irawan, Dasapta Erwin; Tennant, Jonathan P.; Hursthouse, Andrew; Van Hullebusch, Eric D. (1 September 2020)."The growth of open access publishing in geochemistry".Results in Geochemistry.1:100001.Bibcode:2020ResGc...100001P.doi:10.1016/j.ringeo.2020.100001.ISSN2666-2779.S2CID219903509.
- ^abcDOAJ."Journal metadata".doaj.org.Archivedfrom the original on 27 August 2016.Retrieved18 May2019.
- ^Matushek, Kurt J. (2017)."Take Another Look at the Instructions for Authors".Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association.250(3): 258–259.doi:10.2460/javma.250.3.258.PMID28117640.
- ^Bachrach, S.; Berry, R. S.; Blume, M.; von Foerster, T.; Fowler, A.; Ginsparg, P.; Heller, S.; Kestner, N.; Odlyzko, A.; Okerson, A.; Wigington, R.; Moffat, A. (1998). "Who Should Own Scientific Papers?".Science.281(5382): 1459–60.Bibcode:1998Sci...281.1459B.doi:10.1126/science.281.5382.1459.PMID9750115.S2CID36290551.
- ^Gadd, Elizabeth; Oppenheim, Charles; Probets, Steve (2003)."RoMEO Studies 4: An Analysis of Journal Publishers" Copyright Agreements "(PDF).Learned Publishing.16(4): 293–308.doi:10.1087/095315103322422053.hdl:10150/105141.S2CID40861778.Archived(PDF)from the original on 28 July 2020.Retrieved9 September2019.
- ^Willinsky, John (2002)."Copyright Contradictions in Scholarly Publishing".First Monday.7(11).doi:10.5210/fm.v7i11.1006.S2CID39334346.
- ^Carroll, Michael W. (2011)."Why Full Open Access Matters".PLOS Biology.9(11): e1001210.doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1001210.PMC3226455.PMID22140361.
- ^Davies, Mark (2015)."Academic Freedom: A Lawyer's Perspective"(PDF).Higher Education.70(6): 987–1002.doi:10.1007/s10734-015-9884-8.S2CID144222460.Archived(PDF)from the original on 23 December 2019.Retrieved28 August2019.
- ^abFrosio, Giancarlo F. (2014). "Open Access Publishing: A Literature Review".SSRN2697412.
- ^Peters, Diane; Margoni, Thomas (10 March 2016). "Creative Commons Licenses: Empowering Open Access".SSRN2746044.
- ^Dodds, Francis (2018)."The Changing Copyright Landscape in Academic Publishing".Learned Publishing.31(3): 270–275.doi:10.1002/leap.1157.Archivedfrom the original on 4 February 2020.Retrieved4 February2020.
- ^Morrison, Heather (2017). "From the Field: Elsevier as an Open Access Publisher".The Charleston Advisor.18(3): 53–59.doi:10.5260/chara.18.3.53.hdl:10393/35779.
- ^abPablo Alperin, Juan; Rozemblum, Cecilia (2017)."The Reinterpretation of the Visibility and Quality of New Policies to Assess Scientific Publications".Revista Interamericana de Bibliotecología.40(3): 231–241.doi:10.17533/udea.rib.v40n3a04.
- ^W. Frass; J. Cross; V. Gardner (2013).Open Access Survey: Exploring the Views of Taylor & Francis and Routledge Authors(PDF).Taylor & Francis/Routledge.
- ^"OA journal business models".Open Access Directory.2009–2012.Archivedfrom the original on 18 October 2015.Retrieved20 October2015.
- ^"Jisc supports Subscribe to Open model".Jisc.11 March 2020.Retrieved6 October2020.
- ^Markin, Pablo (25 April 2017)."The Sustainability of Open Access Publishing Models Past a Tipping Point".OpenScience.Retrieved26 April2017.
- ^Socha, Beata (20 April 2017)."How Much Do Top Publishers Charge for Open Access?".openscience.com.Archivedfrom the original on 19 February 2019.Retrieved26 April2017.
- ^Peter, Suber (2012).Open access.Cambridge, Massachusetts: MIT Press.ISBN9780262301732.OCLC795846161.
- ^abcWalt Crawford (2019).Gold Open Access 2013-2018: Articles in Journals (GOA4)(PDF).Cites & Insights Books.ISBN978-1-329-54713-1.Archived(PDF)from the original on 6 May 2019.Retrieved30 August2019.
- ^Kim, Sang-Jun; Park, Kay Sook (2021)."Influence of open access journals on the research community in Journal Citation Reports".Science Editing.8(1): 32–38.doi:10.6087/kcse.227.S2CID233380569.
- ^"An efficient journal".The Occasional Pamphlet.6 March 2012.Archivedfrom the original on 18 November 2019.Retrieved27 October2019.
- ^"Article processing charges".Nature Communications.Archivedfrom the original on 27 October 2019.Retrieved27 October2019.
- ^"Publishing options".Nature.
- ^Kozak, Marcin; Hartley, James (December 2013). "Publication fees for open access journals: Different disciplines-different methods".Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology.64(12): 2591–2594.doi:10.1002/asi.22972.
- ^Björk, Bo-Christer; Solomon, David (2015). "Article Processing Charges in OA Journals: Relationship between Price and Quality".Scientometrics.103(2): 373–385.doi:10.1007/s11192-015-1556-z.S2CID15966412.
- ^Lawson, Stuart (2014),APC Pricing,Figshare,doi:10.6084/m9.figshare.1056280.v3
- ^"Developing an Effective Market for Open Access Article Processing Charges"(PDF).Archived(PDF)from the original on 3 October 2018.Retrieved28 August2019.
- ^Schönfelder, Nina (2018)."APCs—Mirroring the Impact Factor or Legacy of the Subscription-Based Model?".Archivedfrom the original on 22 December 2019.Retrieved28 August2019.
- ^"Setting a fee for publication".eLife.29 September 2016.Archivedfrom the original on 7 November 2017.Retrieved27 October2019.
- ^"Ubiquity Press".www.ubiquitypress.com.Archivedfrom the original on 21 October 2019.Retrieved27 October2019.
- ^Schimmer, Ralf; Geschuhn, Kai Karin; Vogler, Andreas (2015). "Disrupting the Subscription Journals" Business Model for the Necessary Large-Scale Transformation to Open Access ".MPG.PuRe Repository.doi:10.17617/1.3.
- ^abcdefghVanholsbeeck, Marc; Thacker, Paul; Sattler, Susanne; Ross-Hellauer, Tony; Rivera-López, Bárbara S.; Rice, Curt; Nobes, Andy; Masuzzo, Paola; Martin, Ryan; Kramer, Bianca; Havemann, Johanna; Enkhbayar, Asura; Davila, Jacinto; Crick, Tom; Crane, Harry; Tennant, Jonathan P. (11 March 2019)."Ten Hot Topics around Scholarly Publishing".Publications.7(2): 34.doi:10.3390/publications7020034.
- ^Björk, B. C. (2017)."Growth of Hybrid Open Access".PeerJ.5:e3878.doi:10.7717/peerj.3878.PMC5624290.PMID28975059.
- ^Pinfield, Stephen; Salter, Jennifer; Bath, Peter A. (2016)."The 'Total Cost of Publication" in a Hybrid Open-Access Environment: Institutional Approaches to Funding Journal Article-Processing Charges in Combination with Subscriptions "(PDF).Journal of the Association for Information Science and Technology.67(7): 1751–1766.doi:10.1002/asi.23446.S2CID17356533.Archived(PDF)from the original on 5 June 2019.Retrieved9 September2019.
- ^Green, Toby (2019). "Is Open Access Affordable? Why Current Models Do Not Work and Why We Need Internet-Era Transformation of Scholarly Communications".Learned Publishing.32(1): 13–25.doi:10.1002/leap.1219.S2CID67869151.
- ^Pourret, Olivier; Hedding, David William; Ibarra, Daniel Enrique; Irawan, Dasapta Erwin; Liu, Haiyan; Tennant, Jonathan Peter (10 June 2021)."International disparities in open access practices in the Earth Sciences".European Science Editing.47:e63663.doi:10.3897/ese.2021.e63663.ISSN2518-3354.S2CID236300530.
- ^Koroso, Nesru H. (18 November 2015)."Diamond Open Access – UA Magazine".UA Magazine.Archivedfrom the original on 18 November 2018.Retrieved11 May2018.
- ^abcSuber, Peter (2 November 2006)."No-fee open-access journals".SPARC open access Newsletter.Archivedfrom the original on 8 December 2008.Retrieved14 December2008.
- ^Montgomery, Lucy (2014). "Knowledge Unlatched:A Global Library Consortium Model for Funding Open Access Scholarly Books".Cultural Science.7(2).hdl:20.500.11937/12680.
- ^"DOAJ search".Archivedfrom the original on 31 August 2020.Retrieved30 June2019.
- ^Wilson, Mark (20 June 2018)."Introducing the Free Journal Network – community-controlled open access publishing".Impact of Social Sciences.Archivedfrom the original on 24 April 2019.Retrieved17 May2019.
- ^"Is the EU's open access plan a tremor or an earthquake?".Science|Business.Archivedfrom the original on 17 May 2019.Retrieved17 May2019.
- ^abBastian, Hilda (2 April 2018)."A Reality Check on Author Access to Open Access Publishing".Absolutely Maybe.Archivedfrom the original on 22 December 2019.Retrieved27 October2019.
- ^Crotty, David (26 August 2015)."Is it True that Most Open Access Journals Do Not Charge an APC? Sort of. It Depends".The Scholarly Kitchen.Archivedfrom the original on 12 December 2019.Retrieved27 October2019.
- ^Ginsparg, P. (2016)."Preprint Déjà Vu".The EMBO Journal.35(24): 2620–2625.doi:10.15252/embj.201695531.PMC5167339.PMID27760783.
- ^Tennant, Jonathan; Bauin, Serge; James, Sarah; Kant, Juliane (2018). "The Evolving Preprint Landscape: Introductory Report for the Knowledge Exchange Working Group on Preprints".doi:10.17605/OSF.IO/796TU.
{{cite journal}}:Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^Neylon, Cameron; Pattinson, Damian; Bilder, Geoffrey; Lin, Jennifer (2017)."On the Origin of Nonequivalent States: How We Can Talk about Preprints".F1000Research.6:608.doi:10.12688/f1000research.11408.1.PMC5461893.PMID28620459.
- ^Balaji, B.; Dhanamjaya, M. (2019)."Preprints in Scholarly Communication: Re-Imagining Metrics and Infrastructures".Publications.7(1): 6.doi:10.3390/publications7010006.
- ^Bourne, Philip E.; Polka, Jessica K.; Vale, Ronald D.; Kiley, Robert (2017)."Ten simple rules to consider regarding preprint submission".PLOS Computational Biology.13(5): e1005473.Bibcode:2017PLSCB..13E5473B.doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005473.PMC5417409.PMID28472041.
- ^abSarabipour, Sarvenaz; Debat, Humberto J.; Emmott, Edward; Burgess, Steven J.; Schwessinger, Benjamin; Hensel, Zach (2019)."On the Value of Preprints: An Early Career Researcher Perspective".PLOS Biology.17(2): e3000151.doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.3000151.PMC6400415.PMID30789895.
- ^Powell, Kendall (2016)."Does It Take Too Long to Publish Research?".Nature.530(7589): 148–151.Bibcode:2016Natur.530..148P.doi:10.1038/530148a.PMID26863966.S2CID1013588.
- ^Crick, Tom; Hall, Benjamin A.; Ishtiaq, Samin (2017)."Reproducibility in Research: Systems, Infrastructure, Culture".Journal of Open Research Software.5(1): 32.arXiv:1503.02388.doi:10.5334/jors.73.
- ^Gadd, Elizabeth; Troll Covey, Denise (2019)."What Does" Green "Open Access Mean? Tracking Twelve Years of Changes to Journal Publisher Self-Archiving Policies".Journal of Librarianship and Information Science.51(1): 106–122.doi:10.1177/0961000616657406.S2CID34955879.Archivedfrom the original on 31 August 2020.Retrieved28 August2019.
- ^"Journal embargo finder".www.elsevier.com.Archivedfrom the original on 18 May 2019.Retrieved17 May2019.
- ^Laakso, Mikael (1 May 2014). "Green open access policies of scholarly journal publishers: a study of what, when, and where self-archiving is allowed".Scientometrics.99(2): 475–494.doi:10.1007/s11192-013-1205-3.hdl:10138/157660.ISSN1588-2861.S2CID8225450.
- ^Harnad, Stevan (2015), Holbrook, J. Britt; Mitcham, Carl (eds.),"Open access: what, where, when, how and why",Ethics, Science, Technology, and Engineering: An International Resource,Stevan Harnad, J. Britt Holbrook, Carl Mitcham, Macmillan Reference,archivedfrom the original on 5 August 2020,retrieved6 January2020
- ^Laakso, Mikael; Björk, Bo-Christer (2013). "Delayed open access: An overlooked high-impact category of openly available scientific literature".Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology.64(7): 1323–1329.doi:10.1002/asi.22856.hdl:10138/157658.
- ^Bjork, Bo-Christer; Roos, Annikki; Lauri, Mari (2009)."Scientific Journal Publishing: Yearly Volume and Open Access Availability".Information Research: An International Electronic Journal.14(1).ISSN1368-1613.Archivedfrom the original on 5 August 2020.Retrieved6 January2020.
- ^Swan, Alma; Brown, Sheridan (May 2005)."Open Access Self-Archiving: An Author Study".Departmental Technical Report. UK FE and HE Funding Councils.Archivedfrom the original on 31 August 2020.Retrieved28 August2019.
- ^Ottaviani, Jim (22 August 2016). Bornmann, Lutz (ed.)."The Post-Embargo Open Access Citation Advantage: It Exists (Probably), It's Modest (Usually), and the Rich Get Richer (of Course)".PLOS ONE.11(8): e0159614.Bibcode:2016PLoSO..1159614O.doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0159614.ISSN1932-6203.PMC4993511.PMID27548723.
- ^Suber, Peter (2014)."The evidence fails to justify publishers' demand for longer embargo periods on publicly-funded research".LSA impact blog.Archivedfrom the original on 4 March 2020.Retrieved6 January2020.
- ^"Global scientific community commits to sharing data on Zika".wellcome.ac.uk.Wellcome. 10 February 2016.Archivedfrom the original on 21 December 2019.Retrieved6 January2020.
- ^"About".Medical Journal of Australia.Australasian Medical Publishing Company.Archivedfrom the original on 5 April 2019.Retrieved12 June2019.
- ^abcSuber 2012,pp. 29–43
- ^"The Life and Death of an Open Access Journal: Q&A with Librarian Marcus Banks".31 March 2015.Archivedfrom the original on 24 May 2018.Retrieved23 May2018.,"As the BOAI text expressed it, 'the overall costs of providing open access to this literature are far lower than the costs of traditional forms of dissemination.'"
- ^"Gold open access in practice: How will universities respond to the rising total cost of publication?".Impact of Social Sciences.25 March 2015.Archivedfrom the original on 1 January 2016.Retrieved23 May2018.
- ^"Reasoning and Interest: Clustering Open Access - LePublikateur".LePublikateur.4 June 2018.Archivedfrom the original on 18 October 2018.Retrieved5 June2018.
- ^Tennant, Jonathan P.; Waldner, François; Jacques, Damien C.; Masuzzo, Paola; Collister, Lauren B.; Hartgerink, Chris. H. J. (21 September 2016)."The academic, economic and societal impacts of Open Access: an evidence-based review".F1000Research.5:632.doi:10.12688/f1000research.8460.3.PMC4837983.PMID27158456.
- ^Van Orsdel, Lee C. & Born, Kathleen. 2005."Periodicals Price Survey 2005: Choosing Sides".Library Journal.15 April 2005.Archivedfrom the original on 30 June 2017.Retrieved18 October2017.
- ^Hardisty, David J.; Haaga, David A.F. (2008)."Diffusion of Treatment Research: Does Open Access Matter?"(PDF).Journal of Clinical Psychology.64(7): 821–839.CiteSeerX10.1.1.487.5198.doi:10.1002/jclp.20492.PMID18425790.Archived fromthe original(PDF)on 28 May 2008.Retrieved22 April2008.
- ^"DFID Research: DFID's Policy Opens up a World of Global Research".dfid.gov.uk.Archivedfrom the original on 3 January 2013.
- ^How To Integrate University and Funder Open Access MandatesArchived16 March 2008 at theWayback Machine.Openaccess.eprints.org (2 March 2008). Retrieved on 3 December 2011.
- ^Libbenga, Jan. (11 May 2005)Dutch academics declare research free-for-allArchived15 July 2017 at theWayback Machine.Theregister.co.uk. Retrieved on 3 December 2011.
- ^Portal NARCISArchived5 November 2010 at theWayback Machine.Narcis.info. Retrieved on 3 December 2011.
- ^"Open and closed access scholarly publications in NARCIS per year of publication".NARCIS.Archivedfrom the original on 26 April 2019.Retrieved26 February2019.
- ^"Coalition of Open Access Policy Institutions (COAPI) – SPARC".arl.org.Archivedfrom the original on 18 October 2015.Retrieved20 October2015.
- ^"Good practices for university open-access policies".Harvard.Archivedfrom the original on 5 October 2016.Retrieved4 October2016.
- ^"About the AOASG".Australian Open Access Support Group.5 February 2013.Archivedfrom the original on 20 December 2014.
- ^"Australian Open Access Support Group expands to become Australasian Open Access Support Group".17 August 2015.Archivedfrom the original on 17 November 2015.
- ^"Creative Commons Australia partners with Australasian Open Access Strategy Group".Creative Commons Australia.31 August 2016.
- ^Suber, Peter (2003)."Removing the Barriers to Research: An Introduction to Open Access for Librarians".College & Research Libraries News.62(2): 92–94, 113.doi:10.5860/crln.64.2.92.Archivedfrom the original on 20 June 2018.Retrieved20 June2018.
- ^Baich, Tina (2015)."Capturing the Benefits of Open Access in Interlibrary Loan".doi:10.7912/C2KW2F.
{{cite journal}}:Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^"IFLA Statement on Open Access (2011)".IFLA.6 March 2019.Archivedfrom the original on 31 August 2020.
- ^Scholarly Publishing and Academic Resources CoalitionArchived15 August 2013 at theWayback Machine.Arl.org. Retrieved on 3 December 2011.
- ^Open Access for Scholarly PublishingArchived19 May 2014 at theWayback Machine.Southern Cross University Library. Retrieved on 14 March 2014.
- ^ALAScholarly Communication ToolkitArchived8 September 2005 at theWayback Machine
- ^CARL – Institutional Repositories ProgramArchived7 June 2013 at theWayback Machine.Carl-abrc.ca. Retrieved on 12 June 2013.
- ^Lippincott, Sarah (5 July 2016)."The Library Publishing Coalition: organizing libraries to enhance scholarly publishing".Insights.29(2): 186–191.doi:10.1629/uksg.296.ISSN2048-7754.Archivedfrom the original on 21 July 2018.Retrieved2 September2019.
- ^Kopfstein, Janus (13 March 2013)."Aaron Swartz to receive posthumous 'Freedom of Information' award for open access advocacy".The Verge.Archivedfrom the original on 15 March 2013.Retrieved24 March2013.
- ^"James Madison Award".Ala.org. 17 January 2013.Archivedfrom the original on 22 March 2013.Retrieved24 March2013.
- ^Brandom, Russell (26 March 2013)."Entire library journal editorial board resigns, citing 'crisis of conscience' after death of Aaron Swartz".The Verge.Archivedfrom the original on 31 December 2013.Retrieved1 January2014.
- ^New, Jake (27 March 2013)."Journal's Editorial Board Resigns in Protest of Publisher's Policy Toward Authors".The Chronicle of Higher Education.Archivedfrom the original on 8 January 2014.
- ^Bourg, Chris (23 March 2013)."My short stint on the JLA Editorial Board".Feral Librarian.Archivedfrom the original on 24 August 2014.
It was just days after Aaron Swartz' death, and I was having a crisis of conscience about publishing in a journal that was not open access
- ^ATA | The Alliance for Taxpayer AccessArchived27 September 2007 at theWayback Machine.Taxpayeraccess.org (29 October 2011). Retrieved on 3 December 2011.
- ^Open Access: Basics and Benefits.Eprints.rclis.org. Retrieved on 3 December 2011.
- ^Eysenbach, Gunther (2006)."The Open Access Advantage".J Med Internet Res.8(2): e8.doi:10.2196/jmir.8.2.e8.PMC1550699.PMID16867971.
- ^Scientific Electronic Library OnlineArchived31 August 2005 at theWayback Machine.SciELO. Retrieved on 3 December 2011.
- ^Pearce, J. M. (2012)."The case for open source appropriate technology".Environment, Development and Sustainability.14(3): 425–431.Bibcode:2012EDSus..14..425P.doi:10.1007/s10668-012-9337-9.
- ^A. J. Buitenhuis, et al., "Open Design-Based Strategies to Enhance Appropriate Technology Development",Proceedings of the 14th Annual National Collegiate Inventors and Innovators Alliance Conference: Open,25–27 March 2010, pp.1–12.
- ^abPiwowar, Heather; Priem, Jason; Larivière, Vincent; Alperin, Juan Pablo; Matthias, Lisa; Norlander, Bree; Farley, Ashley; West, Jevin; Haustein, Stefanie (13 February 2018)."The state of OA: a large-scale analysis of the prevalence and impact of Open Access articles".PeerJ.6:e4375.doi:10.7717/peerj.4375.ISSN2167-8359.PMC5815332.PMID29456894.
- ^abBjörk, B. C.; Welling, P.; Laakso, M.; Majlender, P.; Hedlund, T.; Guðnason, G. N. (2010). Scalas, Enrico (ed.)."Open Access to the Scientific Journal Literature: Situation 2009".PLOS ONE.5(6): e11273.Bibcode:2010PLoSO...511273B.doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0011273.PMC2890572.PMID20585653.
- ^Cummings, J. (2013). "Open access journal content found in commercial full-text aggregation databases and journal citation reports".New Library World.114(3/4): 166–178.doi:10.1108/03074801311304078.hdl:2376/4903.
- ^"Open access to research publications reaching 'tipping point'".Press Releases.europa.eu.Archivedfrom the original on 24 August 2013.Retrieved25 August2013.
- ^"Proportion of Open Access Peer-Reviewed Papers at the European and World Levels—2004–2011"(PDF).Science-Metrix. August 2013.Archived(PDF)from the original on 3 September 2013.Retrieved25 August2013.
- ^Van Noorden, Richard (2013)."Half of 2011 papers now free to read".Nature.500(7463): 386–7.Bibcode:2013Natur.500..386V.doi:10.1038/500386a.PMID23969438.
- ^"Area-wide transition to open access is possible: A new study calculates a redeployment of funds in Open Access".www.mpg.de/en.Max Planck Gesellschaft. 27 April 2015.Archivedfrom the original on 16 June 2017.Retrieved12 May2017.
- ^Björk, Bo-Christer (2011)."A Study of Innovative Features in Scholarly Open Access Journals".Journal of Medical Internet Research.13(4): e115.doi:10.2196/jmir.1802.PMC3278101.PMID22173122.
- ^ab"Directory of Open Access Journals".Directory of Open Access Journals.Archivedfrom the original on 27 August 2016.Retrieved26 February2019.
- ^Chun-Kai (Karl) Huang;Cameron Neylon;Richard Hosking; Lucy Montgomery; Katie S Wilson; Alkim Ozaygen; Chloe Brookes-Kenworthy (14 September 2020)."Meta-Research: Evaluating the impact of open access policies on research institutions".eLife.9.doi:10.7554/ELIFE.57067.ISSN2050-084X.PMC7536542.PMID32924933.WikidataQ99410785.
- ^"Institutions' open access over time: Evolution of green and gold OA".storage.googleapis.com.Curtin Open Knowledge Initiative.Retrieved13 October2021.
- ^Piwowar, H.; Priem, J.; Larivière, V.; Alperin, J. P.; Matthias, L.; Norlander, B.; Farley, A.; West, J.; Haustein, S. (2018)."The state of OA: A large-scale analysis of the prevalence and impact of Open Access articles".PeerJ.6:e4375.doi:10.7717/peerj.4375.PMC5815332.PMID29456894.
- ^https://www.scopus.com/results/results.uri?sort=plf-f&src=s&sid=7c069198c393343d11b72b903c0e4a02&sot=a&sdt=a&sl=14&s=PUBYEAR+%3D+2023&origin=searchadvanced&editSaveSearch=&txGid=45ccd8149540fa063d893d60c4e835dc&sessionSearchId=7c069198c393343d11b72b903c0e4a02&limit=10[bare URL]
- ^ab"Registry of Open Access Repositories (ROAR)"Archived30 October 2012 at theWayback Machine.Roar.eprints.org. Retrieved on 3 December 2011.
- ^"Browse by Repository Type".Registry of Open Access Repositories.Archivedfrom the original on 31 August 2020.Retrieved26 February2019.
- ^abMcKiernan, Erin C; Bourne, Philip E; Brown, C Titus; Buck, Stuart; Kenall, Amye; Lin, Jennifer; McDougall, Damon; Nosek, Brian A; Ram, Karthik; Soderberg, Courtney K; Spies, Jeffrey R (7 July 2016). Rodgers, Peter (ed.)."How open science helps researchers succeed".eLife.5:e16800.doi:10.7554/eLife.16800.ISSN2050-084X.PMC4973366.PMID27387362.
- ^abcdWang, Xianwen; Liu, Chen; Mao, Wenli; Fang, Zhichao (1 May 2015). "The open access advantage considering citation, article usage and social media attention".Scientometrics.103(2): 555–564.arXiv:1503.05702.Bibcode:2015arXiv150305702W.doi:10.1007/s11192-015-1547-0.ISSN1588-2861.S2CID14827780.
- ^abDavis, Philip M. (30 March 2011)."Open access, readership, citations: a randomized controlled trial of scientific journal publishing".The FASEB Journal.25(7): 2129–2134.doi:10.1096/fj.11-183988.ISSN0892-6638.PMID21450907.S2CID205367842.
- ^abDavis, Philip M. (2010). "Does open access lead to increased readership and citations? A randomized controlled trial of articles published in APS journals".The Physiologist.53(6): 197, 200–201.ISSN0031-9376.PMID21473414.
- ^abDavis, Philip M.; Lewenstein, Bruce V.; Simon, Daniel H.; Booth, James G.; Connolly, Mathew J. L. (31 July 2008)."Open access publishing, article downloads, and citations: randomised controlled trial".BMJ.337(jul31 1): a568.doi:10.1136/bmj.a568.ISSN0959-8138.PMC2492576.PMID18669565.
- ^abcAdie, Euan (24 October 2014)."Attention! A study of open access vs non-open access articles".Figshare.doi:10.6084/m9.figshare.1213690.v1.S2CID155854134.Archivedfrom the original on 3 January 2020.Retrieved3 January2020.
- ^abcTeplitskiy, M.; Lu, G.; Duede, E. (2016). "Amplifying the impact of open access: Wikipedia and the diffusion of science".Journal of the Association for Information Science and Technology.68(9): 2116.arXiv:1506.07608.doi:10.1002/asi.23687.S2CID10220883.
- ^Maximising the Return on the UK's Public Investment in Research – Open Access ArchivangelismArchived2 July 2017 at theWayback Machine.Openaccess.eprints.org (14 September 2005). Retrieved on 3 December 2011.
- ^Garfield, E. (1988)Can Researchers Bank on Citation Analysis?Archived25 October 2005 at theWayback MachineCurrent Comments,No. 44, 31 October 1988
- ^Committee on Electronic Information and Communication (CEIC) of theInternational Mathematical Union(15 May 2001)."Call to All Mathematicians".Archivedfrom the original on 7 June 2011.
- ^abDavis, P. M. (2011)."Open access, readership, citations: a randomized controlled trial of scientific journal publishing".The FASEB Journal.25(7): 2129–34.doi:10.1096/fj.11-183988.PMID21450907.S2CID205367842.
- ^abElSabry, ElHassan (1 August 2017)."Who needs access to research? Exploring the societal impact of open access".Revue française des sciences de l'information et de la communication(11).doi:10.4000/rfsic.3271.ISSN2263-0856.Archivedfrom the original on 31 August 2020.Retrieved3 January2020.
- ^Gentil-Beccot, Anne; Mele, Salvatore; Brooks, Travis (2009). "Citing and Reading Behaviours in High-Energy Physics. How a Community Stopped Worrying about Journals and Learned to Love Repositories".arXiv:0906.5418[cs.DL].
- ^Swan, Alma (2006)The culture of Open Access: researchers' views and responsesArchived22 May 2012 at theWayback Machine.In: Neil Jacobs (Ed.)Open access: key strategic, technical and economic aspects,Chandos.
- ^Piwowar, Heather; Priem, Jason; Larivière, Vincent; Alperin, Juan Pablo; Matthias, Lisa; Norlander, Bree; Farley, Ashley; West, Jevin; Haustein, Stefanie (13 February 2018)."The state of OA: a large-scale analysis of the prevalence and impact of Open Access articles".PeerJ.6:e4375.doi:10.7717/peerj.4375.ISSN2167-8359.PMC5815332.PMID29456894.
- ^Swan, Alma (2010)."The Open Access citation advantage: Studies and results to date".eprints.soton.ac.uk.Alma Swan.Archivedfrom the original on 3 January 2020.Retrieved3 January2020.
- ^abTennant, Jonathan P.; Waldner, François; Jacques, Damien C.; Masuzzo, Paola; Collister, Lauren B.; Hartgerink, Chris. H. J. (21 September 2016)."The academic, economic and societal impacts of Open Access: an evidence-based review".F1000Research.5:632.doi:10.12688/f1000research.8460.3.ISSN2046-1402.PMC4837983.PMID27158456.
- ^abcdClayson, Peter E.; Baldwin, Scott A.; Larson, Michael J. (1 June 2021)."The open access advantage for studies of human electrophysiology: Impact on citations and Altmetrics".International Journal of Psychophysiology.164:103–111.doi:10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2021.03.006.ISSN0167-8760.PMID33774077.S2CID232409668.
- ^Online or Invisible? Steve Lawrence; NEC Research InstituteArchived16 March 2007 at theWayback Machine.Citeseer.ist.psu.edu. Retrieved on 3 December 2011.
- ^Davis, P. M; Lewenstein, B. V; Simon, D. H; Booth, J. G; Connolly, M. J L (2008)."Open access publishing, article downloads, and citations: randomised controlled trial".BMJ.337(jul31 1): a568.doi:10.1136/bmj.a568.PMC2492576.PMID18669565.
- ^Effect of OA on citation impact: a bibliography of studiesArchived2 November 2017 at theWayback Machine.Opcit.eprints.org. Retrieved on 3 December 2011.
- ^Swan, Alma (2010)."The Open Access citation advantage: Studies and results to date".eprints.soton.ac.uk.Alma Swan.Archivedfrom the original on 3 January 2020.
- ^abcClayson, Peter E.; Baldwin, Scott A.; Larson, Michael J. (1 June 2021)."The open access advantage for studies of human electrophysiology: Impact on citations and Altmetrics".International Journal of Psychophysiology.164:103–111.doi:10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2021.03.006.ISSN0167-8760.PMID33774077.S2CID232409668.
- ^Eysenbach, Gunther (16 May 2006). Tenopir, Carol (ed.)."Citation Advantage of Open Access Articles".PLOS Biology.4(5): e157.doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0040157.ISSN1545-7885.PMC1459247.PMID16683865.
- ^Björk, Bo-Christer; Solomon, David (17 July 2012)."Open access versus subscription journals: a comparison of scientific impact".BMC Medicine.10(1): 73.doi:10.1186/1741-7015-10-73.ISSN1741-7015.PMC3398850.PMID22805105.
- ^Shema, Hadas; Bar-Ilan, Judit; Thelwall, Mike (15 January 2014). "Do blog citations correlate with a higher number of future citations? Research blogs as a potential source for alternative metrics".Journal of the Association for Information Science and Technology.65(5): 1018–1027.doi:10.1002/asi.23037.ISSN2330-1635.S2CID31571840.
- ^Alhoori, Hamed; Ray Choudhury, Sagnik; Kanan, Tarek; Fox, Edward; Furuta, Richard; Giles, C. Lee (15 March 2015)."On the Relationship between Open Access and Altmetrics".IConference 2015 Proceedings.Archivedfrom the original on 3 January 2020.Retrieved3 January2020.
- ^Gargouri, Yassine; Hajjem, Chawki; Lariviere, Vincent; Gingras, Yves; Carr, Les; Brody, Tim; Harnad, Stevan (2018). "The Journal Impact Factor: A Brief History, Critique, and Discussion of Adverse Effects".arXiv:1801.08992.Bibcode:2018arXiv180108992L.
{{cite journal}}:Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^Curry, Stephen (2018)."Let's Move beyond the Rhetoric: It's Time to Change How We Judge Research".Nature.554(7691): 147.Bibcode:2018Natur.554..147C.doi:10.1038/d41586-018-01642-w.PMID29420505.
- ^Chua, SK; Qureshi, Ahmad M; Krishnan, Vijay; Pai, Dinker R; Kamal, Laila B; Gunasegaran, Sharmilla; Afzal, MZ; Ambawatta, Lahiru; Gan, JY; Kew, PY; Winn, Than (2 March 2017)."The impact factor of an open access journal does not contribute to an article's citations".F1000Research.6:208.doi:10.12688/f1000research.10892.1.ISSN2046-1402.PMC5464220.PMID28649365.
- ^Csiszar, Alex (2016)."Peer Review: Troubled from the Start".Nature.532(7599): 306–308.Bibcode:2016Natur.532..306C.doi:10.1038/532306a.PMID27111616.
- ^Moxham, Noah; Fyfe, Aileen (2018)."The Royal Society and the Prehistory of Peer Review, 1665–1965"(PDF).The Historical Journal.61(4): 863–889.doi:10.1017/S0018246X17000334.S2CID164984479.Archived(PDF)from the original on 31 August 2020.Retrieved28 August2019.
- ^Tennant, Jonathan P.; Dugan, Jonathan M.; Graziotin, Daniel; Jacques, Damien C.; Waldner, François; Mietchen, Daniel; Elkhatib, Yehia; B. Collister, Lauren; Pikas, Christina K.; Crick, Tom; Masuzzo, Paola (29 November 2017)."A multi-disciplinary perspective on emergent and future innovations in peer review".F1000Research.6:1151.doi:10.12688/f1000research.12037.3.ISSN2046-1402.PMC5686505.PMID29188015.
- ^Tennant, Jonathan P. (1 October 2018)."The state of the art in peer review".FEMS Microbiology Letters.365(19).doi:10.1093/femsle/fny204.ISSN0378-1097.PMC6140953.PMID30137294.Archived fromthe originalon 24 February 2020.Retrieved3 January2020.
- ^Noorden, Richard Van (4 March 2019)."Peer-review experiments tracked in online repository".Nature.doi:10.1038/d41586-019-00777-8.S2CID86845470.Archivedfrom the original on 12 December 2019.Retrieved3 January2020.
- ^Penfold, Naomi C.; Polka, Jessica K. (2020)."Technical and social issues influencing the adoption of preprints in the life sciences".PLOS Genetics.16(4): e1008565.doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1008565.PMC7170218.PMID32310942.
- ^Nosek, Brian A.; Ebersole, Charles R.; DeHaven, Alexander C.; Mellor, David T. (12 March 2018)."The preregistration revolution".Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.115(11): 2600–2606.Bibcode:2018PNAS..115.2600N.doi:10.1073/pnas.1708274114.ISSN0027-8424.PMC5856500.PMID29531091.
- ^abcRoss-Hellauer, Tony (31 August 2017)."What is open peer review? A systematic review".F1000Research.6:588.doi:10.12688/f1000research.11369.2.ISSN2046-1402.PMC5437951.PMID28580134.
- ^Munafò, Marcus R.; Nosek, Brian A.; Bishop, Dorothy V. M.; Button, Katherine S.; Chambers, Christopher D.; Percie du Sert, Nathalie; Simonsohn, Uri; Wagenmakers, Eric-Jan; Ware, Jennifer J.; Ioannidis, John P. A. (10 January 2017)."A manifesto for reproducible science".Nature Human Behaviour.1(1): 0021.doi:10.1038/s41562-016-0021.ISSN2397-3374.PMC7610724.PMID33954258.
- ^Pawlik, Mateusz; Hütter, Thomas; Kocher, Daniel; Mann, Willi; Augsten, Nikolaus (1 July 2019)."A Link is not Enough – Reproducibility of Data".Datenbank-Spektrum.19(2): 107–115.doi:10.1007/s13222-019-00317-8.ISSN1610-1995.PMC6647556.PMID31402850.
- ^Munafò, Marcus R.; Nosek, Brian A.; Bishop, Dorothy V. M.; Button, Katherine S.; Chambers, Christopher D.; Percie Du Sert, Nathalie; Simonsohn, Uri; Wagenmakers, Eric-Jan; Ware, Jennifer J.; Ioannidis, John P. A. (2017)."A Manifesto for Reproducible Science".Nature Human Behaviour.1(1): 0021.doi:10.1038/s41562-016-0021.PMC7610724.PMID33954258.Archivedfrom the original on 31 August 2020.Retrieved25 September2019.
- ^Bowman, Nicholas David; Keene, Justin Robert (2018)."A Layered Framework for Considering Open Science Practices".Communication Research Reports.35(4): 363–372.doi:10.1080/08824096.2018.1513273.
- ^McKiernan, E. C.; Bourne, P. E.; Brown, C. T.; Buck, S.; Kenall, A.; Lin, J.; McDougall, D.; Nosek, B. A.; Ram, K.; Soderberg, C. K.; Spies, J. R.; Thaney, K.; Updegrove, A.; Woo, K. H.; Yarkoni, T. (2016)."Point of View: How Open Science Helps Researchers Succeed".eLife.5.doi:10.7554/eLife.16800.PMC4973366.PMID27387362.
- ^Wicherts, Jelte M. (29 January 2016)."Peer Review Quality and Transparency of the Peer-Review Process in Open Access and Subscription Journals".PLOS ONE.11(1): e0147913.Bibcode:2016PLoSO..1147913W.doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0147913.ISSN1932-6203.PMC4732690.PMID26824759.
- ^Brembs, Björn (12 February 2019)."Reliable novelty: New should not trump true".PLOS Biology.17(2): e3000117.doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.3000117.ISSN1545-7885.PMC6372144.PMID30753184.
- ^Spezi, Valerie; Wakeling, Simon; Pinfield, Stephen; Creaser, Claire; Fry, Jenny; Willett, Peter (13 March 2017)."Open-access mega-journals".Journal of Documentation.73(2): 263–283.doi:10.1108/JD-06-2016-0082.ISSN0022-0418.
- ^Pourret, Olivier; Irawan, Dasapta Erwin; Tennant, Jonathan P.; Wien, Charlotte; Dorch, Bertil F. (15 June 2020)."Comments on" Factors affecting global flow of scientific knowledge in environmental sciences "by Sonne et al. (2020)".Science of the Total Environment.721:136454.Bibcode:2020ScTEn.72136454P.doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136454.ISSN0048-9697.PMID31924309.S2CID210150077.
- ^Grudniewicz, Agnes; Moher, David; Cobey, Kelly D.; Bryson, Gregory L.; Cukier, Samantha; Allen, Kristiann; Ardern, Clare; Balcom, Lesley; Barros, Tiago; Berger, Monica; Ciro, Jairo Buitrago (12 December 2019)."Predatory journals: no definition, no defence".Nature.576(7786): 210–212.Bibcode:2019Natur.576..210G.doi:10.1038/d41586-019-03759-y.hdl:11584/281794.ISSN0028-0836.PMID31827288.S2CID209168864.
- ^Dadkhah, Mehdi; Borchardt, Glenn (1 June 2016)."Hijacked Journals: An Emerging Challenge for Scholarly Publishing".Aesthetic Surgery Journal.36(6): 739–741.doi:10.1093/asj/sjw026.ISSN1090-820X.PMID26906349.Archivedfrom the original on 8 June 2019.Retrieved5 January2020.
- ^Dadkhah, Mehdi; Maliszewski, Tomasz; Teixeira da Silva, Jaime A. (24 June 2016). "Hijacked journals, hijacked web-sites, journal phishing, misleading metrics, and predatory publishing: actual and potential threats to academic integrity and publishing ethics".Forensic Science, Medicine, and Pathology.12(3): 353–362.doi:10.1007/s12024-016-9785-x.ISSN1547-769X.PMID27342770.S2CID38963478.
- ^Shen, Cenyu; Björk, Bo-Christer (2015)."'Predatory "Open Access: A Longitudinal Study of Article Volumes and Market Characteristics".BMC Medicine.13(1): 230.doi:10.1186/s12916-015-0469-2.PMC4589914.PMID26423063.
- ^Perlin, Marcelo S.; Imasato, Takeyoshi; Borenstein, Denis (2018). "Is Predatory Publishing a Real Threat? Evidence from a Large Database Study".Scientometrics.116(1): 255–273.doi:10.1007/s11192-018-2750-6.hdl:10183/182710.S2CID4998464.
- ^Bohannon, John (2013)."Who's Afraid of Peer Review?".Science.342(6154): 60–65.Bibcode:2013Sci...342...60B.doi:10.1126/science.342.6154.60.PMID24092725.
- ^Olivarez, Joseph; Bales, Stephen; Sare, Laura; Vanduinkerken, Wyoma (2018)."Format Aside: Applying Beall's Criteria to Assess the Predatory Nature of Both OA and Non-OA Library and Information Science Journals".College & Research Libraries.79(1).doi:10.5860/crl.79.1.52.
- ^Shamseer, Larissa; Moher, David; Maduekwe, Onyi; Turner, Lucy; Barbour, Virginia; Burch, Rebecca; Clark, Jocalyn; Galipeau, James; Roberts, Jason; Shea, Beverley J. (2017)."Potential Predatory and Legitimate Biomedical Journals: Can You Tell the Difference? A Cross-Sectional Comparison".BMC Medicine.15(1): 28.doi:10.1186/s12916-017-0785-9.PMC5353955.PMID28298236.
- ^Eisen, Michael (3 October 2013)."I confess, I wrote the Arsenic DNA paper to expose flaws in peer-review at subscription based journals".www.michaeleisen.org.Archived fromthe originalon 24 September 2018.Retrieved5 January2020.
- ^Silver, Andrew (2017). "Pay-to-View Blacklist of Predatory Journals Set to Launch".Nature.doi:10.1038/nature.2017.22090.
- ^Strinzel, Michaela; Severin, Anna; Milzow, Katrin; Egger, Matthias (2019)."Blacklists and Whitelists to Tackle Predatory Publishing: A Cross-Sectional Comparison and Thematic Analysis".mBio.10(3).doi:10.1128/mBio.00411-19.PMC6550518.PMID31164459.
- ^Polka, Jessica K.; Kiley, Robert; Konforti, Boyana; Stern, Bodo; Vale, Ronald D. (2018)."Publish Peer Reviews".Nature.560(7720): 545–547.Bibcode:2018Natur.560..545P.doi:10.1038/d41586-018-06032-w.PMID30158621.
- ^Hull, Duncan (15 February 2012)."The Open Access Irony Awards: Naming and shaming them".O'Really?.
- ^Duncan, Green (7 August 2013)."Whatever happened to the Academic Spring? (Or the irony of hiding papers on transparency and accountability behind a paywall)".From Poverty to Power.Archived fromthe originalon 20 October 2020.Retrieved30 October2020.
- ^abMarwick, Ben (29 October 2020)."Open Access to Publications to Expand Participation in Archaeology".Norwegian Archaeological Review.53(2): 163–169.doi:10.1080/00293652.2020.1837233.S2CID228961066.
- ^Schultz, Teresa Auch (2 March 2018)."Practicing What You Preach: Evaluating Access of Open Access Research".The Journal of Electronic Publishing.21(1).doi:10.3998/3336451.0021.103.hdl:2027/spo.3336451.0021.103.
- ^Eve, Martin Paul (21 October 2013)."How ironic are the open access irony awards?".Martin Paul Eve.
- ^"Browse by Year".roar.eprints.org.Registry of Open Access Repositories.Archivedfrom the original on 24 March 2019.Retrieved10 March2019.
- ^Peiperl, Larry (16 April 2018)."Preprints in medical research: Progress and principles".PLOS Medicine.15(4): e1002563.doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1002563.ISSN1549-1676.PMC5901682.PMID29659580.
- ^Elmore, Susan A. (2018)."Preprints: What Role do These Have in Communicating Scientific Results?".Toxicologic Pathology.46(4): 364–365.doi:10.1177/0192623318767322.PMC5999550.PMID29628000.
- ^"A List of Preprint Servers".Research Preprints.9 March 2017.Archivedfrom the original on 9 March 2019.Retrieved10 March2019.
- ^Eve, Martin (2014)..Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 9–10.ISBN9781107484016.
- ^Harnad, S.2007."The Green Road to Open Access: A Leveraged Transition"Archived12 March 2010 at theWayback Machine.In:The Culture of Periodicals from the Perspective of the Electronic Age,pp. 99–105, L'Harmattan. Retrieved 3 December 2011.
- ^Harnad, S.; Brody, T.; Vallières, F. O.; Carr, L.; Hitchcock, S.; Gingras, Y.; Oppenheim, C.; Stamerjohanns, H.; Hilf, E. R. (2004). "The Access/Impact Problem and the Green and Gold Roads to Open Access".Serials Review.30(4): 310–314.doi:10.1016/j.serrev.2004.09.013.
- ^Fortier, Rose; James, Heather G.; Jermé, Martha G.; Berge, Patricia; Del Toro, Rosemary (14 May 2015)."Demystifying Open Access Workshop".e-Publications@Marquette.Archivedfrom the original on 18 May 2015.Retrieved18 May2015.
- ^"SPARC Europe – Embargo PeriodsArchived18 November 2015 at theWayback Machine.Retrieved on 18 October 2015.
- ^Ann Shumelda Okerson and James J. O'Donnell (eds). 1995."Scholarly Journals at the Crossroads: A Subversive Proposal for Electronic Publishing"Archived12 September 2012 at theWayback Machine.Association of Research Libraries. Retrieved on 3 December 2011.
- ^Poynder, Richard. 2004."Poynder On Point: Ten Years After"Archived26 September 2011 at theWayback Machine.Information Today,21(9), October 2004. Retrieved on 3 December 2011.
- ^Harnad, S.2007."Re: when did the Open Access movement" officially "begin"Archived13 September 2016 at theWayback Machine.American Scientist Open Access Forum,27 June 2007. Retrieved on 3 December 2011.
- ^SHERPA/RoMEO – Publisher copyright policies & self-archivingArchived11 November 2007 at theWayback Machine.Sherpa.ac.uk. Retrieved on 3 December 2011.
- ^"Evaluating Institutional Repository Deployment in American Academe Since Early 2005: Repositories by the Numbers, Part 2".www.dlib.org.Archivedfrom the original on 11 August 2017.Retrieved10 March2019.
- ^Dawson, Patricia H.; Yang, Sharon Q. (1 October 2016)."Institutional Repositories, Open Access and Copyright: What Are the Practices and Implications?"(PDF).Science & Technology Libraries.35(4): 279–294.doi:10.1080/0194262X.2016.1224994.ISSN0194-262X.S2CID63819187.Archived(PDF)from the original on 19 July 2018.Retrieved11 July2019.
- ^Mongeon, Philippe; Paul-Hus, Adèle (2016). "The Journal Coverage of Web of Science and Scopus: A Comparative Analysis".Scientometrics.106(1): 213–228.arXiv:1511.08096.doi:10.1007/s11192-015-1765-5.S2CID17753803.
- ^Falagas, Matthew E.; Pitsouni, Eleni I.; Malietzis, George A.; Pappas, Georgios (2008)."Comparison of PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar: Strengths and Weaknesses".The FASEB Journal.22(2): 338–342.doi:10.1096/fj.07-9492LSF.PMID17884971.S2CID303173.
- ^Harzing, Anne-Wil; Alakangas, Satu (2016)."Google Scholar, Scopus and the Web of Science: A Longitudinal and Cross-Disciplinary Comparison"(PDF).Scientometrics.106(2): 787–804.doi:10.1007/s11192-015-1798-9.S2CID207236780.Archived fromthe original(PDF)on 23 June 2021.Retrieved27 March2021.
- ^Robinson-Garcia, Nicolas; Chavarro, Diego Andrés; Molas-Gallart, Jordi; Ràfols, Ismael (28 May 2016). "On the Dominance of Quantitative Evaluation in 'Peripheral" Countries: Auditing Research with Technologies of Distance ".SSRN2818335.
- ^England, Higher Funding Council of."Clarivate Analytics will provide citation data during REF 2021 - REF 2021".Higher Education Funding Council for England.Archivedfrom the original on 31 August 2020.Retrieved4 January2020.
- ^"World University Rankings 2019: methodology".Times Higher Education (THE).7 September 2018.Archivedfrom the original on 11 December 2019.Retrieved4 January2020.
- ^Okune, Angela; Hillyer, Rebecca; Albornoz, Denisse; Posada, Alejandro; Chan, Leslie (2018). "Whose Infrastructure? Towards Inclusive and Collaborative Knowledge Infrastructures in Open Science".22nd International Conference on Electronic Publishing.Vol. Connecting the Knowledge Commons: From Projects to Sustainable Infrastructure.doi:10.4000/proceedings.elpub.2018.31.
- ^Budapest Open Access Initiative, FAQArchived3 July 2006 at theWayback Machine.Earlham.edu (13 September 2011). Retrieved on 3 December 2011.
- ^Public Knowledge Project."Open Journal Systems"Archived1 March 2013 at theWayback Machine.Retrieved on 13 November 2012.
- ^"Welcome - ROAD".road.issn.org.Archivedfrom the original on 15 May 2017.Retrieved12 May2017.
- ^Martin, Greg."Research Guides: Open Access: Finding Open Access Content".mcphs.libguides.com.Archived fromthe originalon 8 September 2018.Retrieved12 May2017.
- ^ab"BASE - Bielefeld Academic Search Engine | What is BASE?".Archived from the original on 16 February 2016.Retrieved16 January2018.
{{cite web}}:CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ^"Search CORE".Archived from the original on 12 March 2016.Retrieved11 March2016.
{{cite web}}:CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ^Edgar, Brian D.; Willinsky, John (14 June 2010)."A survey of scholarly journals using open journal systems".Scholarly and Research Communication.1(2).doi:10.22230/src.2010v1n2a24.ISSN1923-0702.
- ^Suber 2012,pp. 77–78
- ^"RCUK Open Access Block Grant analysis - Research Councils UK".www.rcuk.ac.uk.Archivedfrom the original on 31 August 2020.Retrieved12 February2018.
- ^Harnad, Stevan."Re: Savings from Converting to On-Line-Only: 30%- or 70%+?".University of Southampton.Archivedfrom the original on 10 December 2005.
- ^"(#710) What Provosts Need to Mandate".American Scientist Open Access Forum Archives.Listserver.sigmaxi.org. Archived fromthe originalon 11 January 2007.
- ^"Recommendations For UK Open-Access Provision Policy".Ecs.soton.ac.uk. 5 November 1998. Archived fromthe originalon 7 January 2006.
- ^"Open Access".RCUK.Archivedfrom the original on 26 December 2015.Retrieved19 December2015.
- ^About the Repository – ROARMAP.Roarmap.eprints.org. Retrieved on 3 December 2011.
- ^Palazzo, Alex (27 August 2007)."PRISM – a new lobby against open access".Science Blogs.Archivedfrom the original on 22 October 2013.Retrieved17 October2013.
- ^Basken, Paul (5 January 2012)."Science-Journal Publishers Take Fight Against Open-Access Policies to Congress".The Chronicle of Higher Education.Archivedfrom the original on 17 October 2013.Retrieved17 October2013.
- ^Albanese, Andrew (15 February 2013)."Publishers Blast New Open Access Bill, FASTR".Publishers Weekly.Archivedfrom the original on 17 October 2013.Retrieved17 October2013.
- ^"OSTP Issues Guidance to Make Federally Funded Research Freely Available Without Delay | OSTP".The White House.25 August 2022.Retrieved16 March2023.
- ^"White House requires immediate public access to all U.S.-funded research papers by 2025".www.science.org.Retrieved30 January2023.
- ^Sanderson, Katharine (2 June 2023)."EU council's 'no pay' publishing model draws mixed response".Nature.doi:10.1038/d41586-023-01810-7.PMID37264131.S2CID259023820.
- ^Lenharo, Mariana (4 April 2024)."Will the Gates Foundation's preprint-centric policy help open access?".Nature.Nature Publishing Group.doi:10.1038/d41586-024-00996-8.PMID38575826.Retrieved6 April2024.
- ^Singh Chawla, Dalmeet (30 May 2024). "Japan's push to make all research open access is taking shape".Nature.doi:10.1038/d41586-024-01493-8.ISSN0028-0836.PMID38822103.
- ^"Browse by Policymaker Type".ROARMAP.Archivedfrom the original on 12 March 2019.Retrieved5 March2019.
- ^Pontika, Nancy; Rozenberga, Dace (5 March 2015)."Developing strategies to ensure compliance with funders' open access policies".Insights: The UKSG Journal.28(1): 32–36.doi:10.1629/uksg.168.ISSN2048-7754.
- ^Kirkman, Noreen; Haddow, Gaby (15 June 2020)."Compliance with the first funder open access policy in Australia".informationr.net.Retrieved3 April2021.
- ^Van Noorden, Richard (31 March 2021). "Do you obey public-access mandates? Google Scholar is watching".Nature.doi:10.1038/d41586-021-00873-8.ISSN0028-0836.PMID33790439.S2CID232481789.
- ^Vranas, Kelly C.; Ouyang, David; Lin, Amber L.; Slatore, Christopher G.; Sullivan, Donald R.; Kerlin, Meeta Prasad; Liu, Kathleen D.; Baron, Rebecca M.; Calfee, Carolyn S.; Ware, Lorraine B.; Halpern, Scott D.; Matthay, Michael A.; Herridge, Margaret S.; Mehta, Sangeeta; Rogers, Angela J. (1 April 2020)."Gender Differences in Authorship of Critical Care Literature".American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine.201(7): 840–847.doi:10.1164/rccm.201910-1957OC.ISSN1073-449X.PMC7124723.PMID31968182.
- ^Gemma Derrick; Alesia Ann Zuccala; Georgiana Turculet (5 October 2021)."Open Access Publishing Probabilities Based on Gender and Authorship Structures in Vietnam".Publications.9(4): 45.doi:10.3390/publications9040045.
- ^Smith, Audrey C.; Merz, Leandra; Borden, Jesse B.; Gulick, Chris K.; Kshirsagar, Akhil R.; Bruna, Emilio M. (4 February 2022)."Assessing the effect of article processing charges on the geographic diversity of authors using Elsevier's" Mirror Journal "system".Quantitative Science Studies.2(4): 1123–1143.doi:10.1162/qss_a_00157.ISSN2641-3337.S2CID244600816.
- ^Kwon, Diana (16 February 2022)."Open-access publishing fees deter researchers in the global south".Nature.doi:10.1038/d41586-022-00342-w.PMID35177842.S2CID246943816.
Sources
[edit] This article incorporatestextby Tennant JP, Crane H, Crick T, Davila J, Enkhbayar A, Havemann J, Kramer B, Martin R, Masuzzo P, Nobes A, Rice C, Rivera-López BS, Ross-Hellauer T, Sattler S, Thacker P, Vanholsbeeck M. available under theCC BY 4.0license.
This article incorporatestextby Tennant JP, Crane H, Crick T, Davila J, Enkhbayar A, Havemann J, Kramer B, Martin R, Masuzzo P, Nobes A, Rice C, Rivera-López BS, Ross-Hellauer T, Sattler S, Thacker P, Vanholsbeeck M. available under theCC BY 4.0license. This article incorporates text from afree contentwork. Licensed under CC-BY-SA. Text taken fromPolicy guidelines for the development and promotion of open access,45-48, Swan, Alma, UNESCO. UNESCO.
This article incorporates text from afree contentwork. Licensed under CC-BY-SA. Text taken fromPolicy guidelines for the development and promotion of open access,45-48, Swan, Alma, UNESCO. UNESCO.
Further reading
[edit]- Darnton, Robert,"The Dream of a Universal Library" (review ofPeter Baldwin,Athena Unbound: Why and How Scholarly Knowledge Should Be Free for All,MIT Press,2023, 405 pp.),The New York Review of Books,vol. LXX, no. 20 (21 December 2023), pp. 73–74. ReviewerDarntonwrites: "Baldwinwarns:journalpublishers are gouging their customers, scholarlymonographsreach a tiny audience,librariesare floundering underbudgetpressures,academicsare pursuingcareersrather thantruth,and readers are not getting all theinformationthey deserve. "(p. 74.) Writes Darnton:" Most scientific research is subsidized by the federal government. "Under a 2022White Housedirective, "As of December 31, 2025, all agencies... must require immediate open access... TheG7leaders took a similar stand on May 14, 2023, as did theEuropean Councilon May 23. The tide is turning in favor of unrestricted access, but the countervailing forces are so complex that the future remains cloudy. "(p. 73.)
- Suber, Peter(2012).Open access(The MIT Press Essential Knowledge Series ed.). Cambridge, Mass.:MIT Press.ISBN978-0-262-51763-8.Retrieved20 October2015.
- Kirsop, Barbara, and Leslie Chan. (2005)Transforming access to research literature for developing countries.Serials Reviews, 31(4): 246–255.
- Laakso, Mikael; Welling, Patrik; Bukvova, Helena; Nyman, Linus; Björk, Bo-Christer; Hedlund, Turid (2011)."The Development of Open Access Journal Publishing from 1993 to 2009".PLOS ONE.6(6): e20961.Bibcode:2011PLoSO...620961L.doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0020961.PMC3113847.PMID21695139.
- Hajjem, C.;Harnad, S;Gingras, Y. (2005)."Ten-Year Cross-Disciplinary Comparison of the Growth of Open Access and How It Increases Research Citation Impact".IEEE Data Engineering Bulletin.28(4): 39–47.arXiv:cs/0606079.Bibcode:2006cs........6079H.
- Tötösy; de Zepetnek, S.; Joshua, Jia (2014)."Electronic Journals, Prestige, and the Economics of Academic Journal Publishing".CLCWeb: Comparative Literature and Culture.16(1): 2014.doi:10.7771/1481-4374.2426.
- "Open and Shut?"Blogon open access by Richard Poynder, a freelance journalist, who has done aseries of interviewswith a few of the leaders of the open access movement.
- Mietchen, Daniel (15 January 2014)."Wikimedia and Open Access — a rich history of interactions".Wikimedia Blog.Wikimedia Foundation.Retrieved10 January2015.
- Okerson, Ann; O'Donnell, James (Eds.) (June 1995).Scholarly Journals at the Crossroads: A Subversive Proposal for Electronic Publishing.Washington, DC:Association of Research Libraries.ISBN978-0-918006-26-4..
- Willinsky, John (2006).The Access Principle: The Case for Open Access to Research and Scholarship(PDF).Cambridge, MA:MIT Press.ISBN9780262512664.Archived fromthe original(PDF)on 5 November 2013.
- "Accessibility, sustainability, excellence: how to expand access to research publications"(PDF).United Kingdom: Working Group on Expanding Access to Published Research Findings. 2012. Archived fromthe original(PDF)on 19 June 2012.Retrieved15 July2012.
- In Oldenburg's Long Shadow: Librarians, Research Scientists, Publishers, and the Control of Scientific Publishing
- Glyn Moody (17 June 2016)."Open access: All human knowledge is there—so why can't everybody access it?".Ars Technica.Retrieved20 June2016.
External links
[edit]- OAD:Open Access Directory,an "open-access, wiki-based, community-updated encyclopedia of OA factual lists" (started byPeter Suberand Robin Peek).OCLC757073363.Published bySimmons School of Library and Information Sciencein US.
- OASPA: Open Access Scholarly Publishing Association,a community of organisations engaged in open scholarship with a mission to encourage and enable open access as the predominant model of communication for scholarly outputs
- OATP:Open Access Tracking Project,a crowd-sourced tagging project providing real-time alerts about new OA developments and organizing knowledge of the field (started by Peter Suber).OCLC1040261573
- GOAP:UNESCO's Global Open Access Portal, providing "status of open access to scientific information around the world"





