Henipavirus
| Henipavirus | |
|---|---|
| |
| Coloredtransmission electron micrographof aHendra henipavirusvirion (ca. 300 nm length) | |
| Virus classification | |
| (unranked): | Virus |
| Realm: | Riboviria |
| Kingdom: | Orthornavirae |
| Phylum: | Negarnaviricota |
| Class: | Monjiviricetes |
| Order: | Mononegavirales |
| Family: | Paramyxoviridae |
| Subfamily: | Orthoparamyxovirinae |
| Genus: | Henipavirus |
| Species | |
Henipavirusis agenusofnegative-strand RNA virusesin the familyParamyxoviridae,orderMononegaviralescontaining six established species,[1][2]and numerous others still under study.[3]Henipaviruses are naturally harboured by several species of small mammals, notablypteropidfruit bats(flying foxes),microbatsof several species,[4]andshrews.[5][6]Henipaviruses are characterised by longgenomesand a wide host range. Their recent emergence aszoonoticpathogens capable of causing illness and death indomestic animalsand humans is a cause of concern.[7][8]
In 2009, RNA sequences of three novel viruses in phylogenetic relationship to known henipaviruses were detected in African straw-colored fruit bats (Eidolon helvum) inGhana.The finding of these novel henipaviruses outside Australia and Asia indicates that the region of potential endemicity of henipaviruses may be worldwide.[9]These African henipaviruses are slowly being characterised.[10]
NipahandHendrahenipavirusesare both considered category C (USDA-HHS overlap)select agents.[11]
Structure
[edit]
Henipavirions arepleomorphic(variably shaped), ranging in size from 40 to 600 nm in diameter.[12]They possess alipidmembrane overlying a shell of viralmatrix protein.At the core is a single helical strand of genomicRNAtightly bound to N (nucleocapsid) protein and associated with the L (large) and P (phosphoprotein) proteins, which provideRNA polymeraseactivity during replication.
Embedded within the lipid membrane are spikes of F (fusion) protein trimers and G (attachment) protein tetramers. The function of the G protein (except in the case of MojV-G) is to attach the virus to the surface of a host cell viaEphrin B1, B2, or B3,a family of highlyconservedmammalian proteins.[13][14][15]The structure of the attachment glycoprotein has been determined by X-ray crystallography.[16]The F protein fuses the viral membrane with the host cell membrane, releasing the virion contents into the cell. It also causes infected cells to fuse with neighbouring cells to form large, multinucleatedsyncytia.
Genome
[edit]
As all mononegaviral genomes, Hendra virus and Nipah virus genomes are non-segmented, single-strandednegative-senseRNA. Both genomes are 18.2 kb in length and contain sixgenescorresponding to six structural proteins.[17]
In common with other members of theParamyxoviridaefamily, the number ofnucleotidesin the henipavirus genome is a multiple of six, consistent with what is known as the 'rule of six'.[18][19]Deviation from the rule of six, through mutation or incomplete genome synthesis, leads to inefficient viral replication, probably due to structural constraints imposed by the binding between the RNA and the N protein.
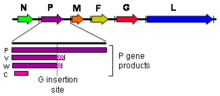
Three additional protein products are produced from the henipavirus P gene: V, W, and C. The V and W proteins are generated through an unusual process calledRNA editing.This specific process in henipaviruses involves the insertion of extraguanosineresidues into the P genemRNAprior totranslation.The addition of a single guanosine results in production of V, and the addition of two guanosines residues produces W.[20]The C protein is not produced through RNA editing but instead byleaky scanningof the host cell ribosome during translation of viral mRNA. P, V, and W possess an alternateopen reading framewhich results in production of C. P, V, W, and C are known to disrupt the host innate antiviral immune response through several different mechanisms.[21]P, V, and W containSTAT1binding domains, and act asinterferonantagonists by sequestering STAT1 in the nucleus and cytoplasm.[22]The C protein controls the early pro-inflammatory response and is also known to promote the viral budding process via aESCRT-dependent pathway.[23][24]
Life cycle
[edit]Cell receptor ephrin-B2, which is located on epithelial cells around smaller arteries, neurons, and smooth muscle cells, is targeted by the viral protein G.[25]Once the protein G binds to ephrin-B2, the viral protein F facilitates fusion with the host cell membrane and releases viral RNA into the host cell cytoplasm.[26]Upon entry, transcription of viral mRNA takes place using the viral RNA as a template. This process is started and stopped by the polymerase complex. Viral proteins are gathering in the cell as transcription occurs until the polymerase complex stops transcription and starts genome replication. Transcription of the viral RNA makes positive sense strands of RNA, which are then used as templates to make more negative sense viral RNA. Genome replication is halted before the viral particles can assemble to make a virion. Once the cell membrane is ready, new virions exit the host cell through budding.[27]
Vaccine
[edit]Henipaviruses have high mortality rates in mammalian hosts, both human and animal. Because of this, there is a need for immunization against HeV and NiV. TheWorld Health Organizationhas classified henipaviral agents as R&D Blueprint Priority Pathogens, indicating that they pose a significant risk due to their epidemic potential.[28]The broad species tropism of NiV and HeV have resulted in mortality in livestock species in addition to humans, and as a result veterinary vaccines are in various stages of development or licensure. EquiVac HeV, a veterinary vaccine for horses was licensed in Australia in 2012.[29][30]A number of experimental vaccines designed for humans are in preclinical development, but none have yet been licensed. A soluble HeV attachment glycoprotein vaccine designed to protect against NiV completed aphase I clinical trialin November 2022, but results have not yet been published.[31]
The primary mechanism of protection against NiV and HeV induced by vaccination is thought to be neutralizing antibodies.[32]However, a number of preclinical vaccine studies in animal models of disease have identified that the cell-mediated immune response including CD8+ and CD4+ T-cells may play a role in protection.[33]
Causes of emergence
[edit]The emergence of henipaviruses parallels the emergence of otherzoonoticviruses in recent decades.SARS coronavirus,Australian bat lyssavirus,Menangle virus,Marburg virus,COVID 19 and possiblyEbolaviruses are also harboured by bats, and are capable of infecting a variety of other species. The emergence of each of these viruses has been linked to an increase in contact between bats and humans, sometimes involving an intermediate domestic animal host. The increased contact is driven both by human encroachment into the bats' territory (in the case of Nipah, specifically pigpens in said territory) and by movement of bats towards human populations due to changes in food distribution and loss of habitat.
There is evidence that habitat loss for flying foxes, both in South Asia and Australia (particularly along the east coast) as well as encroachment of human dwellings and agriculture into the remaining habitats, is creating greater overlap of human and flying fox distributions.[34]
Taxonomy
[edit]| Genus | Species | Virus (Abbreviation) |
| Henipavirus | Cedar henipavirus | Cedar virus(CedV) |
| Ghanaian bat henipavirus | Kumasi virus(KV) | |
| Hendra henipavirus | Hendra virus(HeV) | |
| Mojiang henipavirus | Mòjiāng virus(MojV)[3] | |
| Nipah henipavirus | Nipah virus(NiV) | |
| Langya henipavirus | Langya virus(LayV)[6][36] |
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^Rima, B; Balkema-Buschmann, A; Dundon, WG;Duprex, WP;Easton, A; Fouchier, R; Kurath, G; Lamb, R; Lee, B; Rota, P; Wang, L; ICTV Report Consortium (December 2019)."ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile:Paramyxoviridae".The Journal of General Virology.100(12): 1593–1594.doi:10.1099/jgv.0.001328.PMC7273325.PMID31609197.
- ^"ICTV Report Paramyxoviridae".
- ^abWu, Zhiqiang; et al. (2014)."Novel Henipa-like Virus, Mojiang Paramyxovirus, in Rats, China, 2012".Emerging Infectious Diseases.20(6): 1064–1066.doi:10.3201/eid2006.131022.PMC4036791.PMID24865545.
- ^Li, Y; Wang, J; Hickey, AC; Zhang, Y; Li, Y; Wu, Y; Zhang, Huajun; et al. (December 2008)."Antibodies to Nipah or Nipah-like viruses in bats, China [letter]".Emerging Infectious Diseases.14(12): 1974–6.doi:10.3201/eid1412.080359.PMC2634619.PMID19046545.
- ^Cheng, Amy (10 August 2022)."New Langya virus that may have spilled over from animals infects dozens".The Washington Post.
- ^abZhang, Xiao-Ai; et al. (2022)."A Zoonotic Henipavirus in Febrile Patients in China".The New England Journal of Medicine.387(5): 470–472.doi:10.1056/NEJMc2202705.PMID35921459.S2CID251315935.
- ^Sawatsky (2008)."Hendra and Nipah Virus".Animal Viruses: Molecular Biology.Caister Academic Press.ISBN978-1-904455-22-6.
- ^"Nipah yet to be confirmed, 86 under observation: Shailaja".OnManorama.Retrieved4 June2019.
- ^Drexler JF, Corman VM, Gloza-Rausch F, Seebens A, Annan A (2009). Markotter W (ed.)."Henipavirus RNA in African Bats".PLOS ONE.4(7): e6367.Bibcode:2009PLoSO...4.6367D.doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0006367.PMC2712088.PMID19636378.
- ^Drexler JF, Corman VM; et al. (2012)."Bats host major mammalian paramyxoviruses".Nat Commun.3:796.Bibcode:2012NatCo...3..796D.doi:10.1038/ncomms1796.PMC3343228.PMID22531181.
- ^"Federal Select Agent Program".www.selectagents.gov.8 January 2021.Retrieved15 January2021.
- ^Hyatt AD, Zaki SR, Goldsmith CS, Wise TG, Hengstberger SG (2001). "Ultrastructure of Hendra virus and Nipah virus within cultured cells and host animals".Microbes and Infection.3(4): 297–306.doi:10.1016/S1286-4579(01)01383-1.PMID11334747.
- ^Bonaparte, M; Dimitrov, A; Bossart, K (2005)."Ephrin-B2 ligand is a functional receptor for Hendra virus and Nipah virus".Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.102(30): 10652–7.Bibcode:2005PNAS..10210652B.doi:10.1073/pnas.0504887102.PMC1169237.PMID15998730.
- ^Negrete OA, Levroney EL, Aguilar HC (2005)."EphrinB2 is the entry receptor for Nipah virus, an emergent deadly paramyxovirus".Nature.436(7049): 401–5.Bibcode:2005Natur.436..401N.doi:10.1038/nature03838.PMID16007075.S2CID4367038.
- ^Bowden, Thomas A.; Crispin, Max; Jones, E. Yvonne; Stuart, David I. (1 October 2010)."Shared paramyxoviral glycoprotein architecture is adapted for diverse attachment strategies".Biochemical Society Transactions.38(5): 1349–1355.doi:10.1042/BST0381349.PMC3433257.PMID20863312.
- ^Bowden, Thomas A.; Crispin, Max; Harvey, David J.; Aricescu, A. Radu; Grimes, Jonathan M.; Jones, E. Yvonne; Stuart, David I. (1 December 2008)."Crystal Structure and Carbohydrate Analysis of Nipah Virus Attachment Glycoprotein: a Template for Antiviral and Vaccine Design".Journal of Virology.82(23): 11628–11636.doi:10.1128/JVI.01344-08.PMC2583688.PMID18815311.
- ^Wang L, Harcourt BH, Yu M (2001). "Molecular biology of Hendra and Nipah viruses".Microbes and Infection.3(4): 279–87.doi:10.1016/S1286-4579(01)01381-8.PMID11334745.
- ^Halpin, Kim; Bankamp, Bettina; Harcourt, Brian H.; Bellini, William J.; Rota, Paul A. (2004)."Nipah virus conforms to the rule of six in a minigenome replication assay".Journal of General Virology.85(3): 701–707.doi:10.1099/vir.0.19685-0.ISSN1465-2099.PMID14993656.
- ^Kolakofsky, D; Pelet, T; Garcin, D; Hausmann, S; Curran, J; Roux, L (February 1998)."Paramyxovirus RNA synthesis and the requirement for hexamer genome length: the rule of six revisited".Journal of Virology.72(2): 891–9.doi:10.1128/JVI.72.2.891-899.1998.PMC124558.PMID9444980.
- ^Shaw, Megan L. (December 2009)."Henipaviruses Employ a Multifaceted Approach to Evade the Antiviral Interferon Response".Viruses.1(3): 1190–1203.doi:10.3390/v1031190.ISSN1999-4915.PMC3185527.PMID21994589.
- ^Lawrence, Philip; Escudero-Pérez, Beatriz (29 April 2022)."Henipavirus Immune Evasion and Pathogenesis Mechanisms: Lessons Learnt from Natural Infection and Animal Models".Viruses.14(5): 936.doi:10.3390/v14050936.ISSN1999-4915.PMC9146692.PMID35632678.
- ^Shaw, Megan L.; García-Sastre, Adolfo; Palese, Peter; Basler, Christopher F. (June 2004)."Nipah virus V and W proteins have a common STAT1-binding domain yet inhibit STAT1 activation from the cytoplasmic and nuclear compartments, respectively".Journal of Virology.78(11): 5633–5641.doi:10.1128/JVI.78.11.5633-5641.2004.ISSN0022-538X.PMC415790.PMID15140960.
- ^Lo, Michael K.; Peeples, Mark E.; Bellini, William J.; Nichol, Stuart T.; Rota, Paul A.; Spiropoulou, Christina F. (19 October 2012)."Distinct and Overlapping Roles of Nipah Virus P Gene Products in Modulating the Human Endothelial Cell Antiviral Response".PLOS ONE.7(10): e47790.Bibcode:2012PLoSO...747790L.doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0047790.ISSN1932-6203.PMC3477106.PMID23094089.
- ^Park, Arnold; Yun, Tatyana; Vigant, Frederic; Pernet, Olivier; Won, Sohui T.; Dawes, Brian E.; Bartkowski, Wojciech; Freiberg, Alexander N.; Lee, Benhur (20 May 2016)."Nipah Virus C Protein Recruits Tsg101 to Promote the Efficient Release of Virus in an ESCRT-Dependent Pathway".PLOS Pathogens.12(5): e1005659.doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1005659.ISSN1553-7374.PMC4874542.PMID27203423.
- ^Bonaparte, Matthew I.; Dimitrov, Antony S.; Bossart, Katharine N.; Crameri, Gary; Mungall, Bruce A.; Bishop, Kimberly A.; Choudhry, Vidita; Dimitrov, Dimiter S.; Wang, Lin-Fa; Eaton, Bryan T.; Broder, Christopher C. (5 July 2005)."Ephrin-B2 ligand is a functional receptor for Hendra virus and Nipah virus".Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.102(30): 10652–10657.Bibcode:2005PNAS..10210652B.doi:10.1073/pnas.0504887102.ISSN0027-8424.PMC1169237.PMID15998730.
- ^Zuckerman, Arie J. (10 June 1996)."Fields virology, 3rd edn. (two vol. set): Edited by B.N. Fields, D.M. Knipe, P.M. Howley, R.M. Chanock, J.L. Melnick, T.P. Monath, B. Roizman and S.E. Straus, Lippincott-Raven, Philadelphia, PA. 1996. 3216 pp. $339.50 (hc). ISBN 0 7817 0253 4".FEBS Letters.388(1): 88.Bibcode:1996FEBSL.388...88Z.doi:10.1016/0014-5793(96)88179-8.
- ^Rota, Paul A.; Lo, Michael K. (2012), Lee, Benhur; Rota, Paul A. (eds.), "Molecular Virology of the Henipaviruses",Henipavirus,vol. 359, Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, pp. 41–58,doi:10.1007/82_2012_211,ISBN978-3-642-29818-9,PMID22552699
- ^"Prioritizing diseases for research and development in emergency contexts".www.who.int.Retrieved29 March2023.
- ^"Equivac® HeV".www.zoetis.com.au.Retrieved29 March2023.
- ^Halpin, Kim; Graham, Kerryne; Durr, Peter A. (2 July 2021)."Sero-Monitoring of Horses Demonstrates the Equivac® HeV Hendra Virus Vaccine to Be Highly Effective in Inducing Neutralising Antibody Titres".Vaccines.9(7): 731.doi:10.3390/vaccines9070731.ISSN2076-393X.PMC8310234.PMID34358146.
- ^Auro Vaccines LLC (16 November 2022)."A Phase 1 Randomized, Placebo-controlled, Observer-blind Trial to Assess the Safety and Immunogenicity of a Nipah Vaccine, HeV-sG-V (Hendra Virus Soluble Glycoprotein Vaccine), in Healthy Adults".ClinicalTrials.gov.PATH, Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations, Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center (CCHMC).
- ^Amaya, Moushimi; Broder, Christopher C. (29 September 2020)."Vaccines to Emerging Viruses: Nipah and Hendra".Annual Review of Virology.7(1): 447–473.doi:10.1146/annurev-virology-021920-113833.ISSN2327-056X.PMC8782152.PMID32991264.
- ^Liew, Yvonne Jing Mei; Ibrahim, Puteri Ainaa S.; Ong, Hui Ming; Chong, Chee Ning; Tan, Chong Tin; Schee, Jie Ping; Gómez Román, Raúl; Cherian, Neil George; Wong, Won Fen; Chang, Li-Yen (June 2022)."The Immunobiology of Nipah Virus".Microorganisms.10(6): 1162.doi:10.3390/microorganisms10061162.ISSN2076-2607.PMC9228579.PMID35744680.
- ^Breed, Andrew C.; Field, Hume E.; Epstein, Jonathan H.; Daszak, Peter (August 2006)."Emerging henipaviruses and flying foxes - Conservation and management perspectives".Biological Conservation.131(2): 211–220.Bibcode:2006BCons.131..211B.doi:10.1016/j.biocon.2006.04.007.ISSN0006-3207.PMC7096729.PMID32226079.
- ^Amarasinghe, Gaya K.; Bào, Yīmíng; Basler, Christopher F.; Bavari, Sina; Beer, Martin; Bejerman, Nicolás; Blasdell, Kim R.; Bochnowski, Alisa; Briese, Thomas (7 April 2017)."Taxonomy of the order Mononegavirales: update 2017".Archives of Virology.162(8): 2493–2504.doi:10.1007/s00705-017-3311-7.ISSN1432-8798.PMC5831667.PMID28389807.
- ^"Zoonotic Langya virus found in China, CDC says - Taipei Times".9 August 2022.
External links
[edit]- ICTV Report:Paramyxoviridae
- Disease card
- ViralZone: Henipavirus
- Henipavirus– Henipavirus Ecology Research Group (HERG) INFO
- Virus Pathogen Database and Analysis Resource (ViPR): Paramyxoviridae
