Intumescent
This articleneeds additional citations forverification.(December 2022) |

Anintumescentis a substance that swells as a result ofheatexposure, leading to an increase involumeand decrease indensity.Intumescencerefers to the process of swelling.[1]Intumescent materials are typically used inpassive fire protectionand requirelisting, approval, and compliancein their installed configurations in order to comply with the national building codes andlaws.[citation needed]
The details for individual building parts are specified in technical standards which are compiled and published by national or international standardization bodies like theBritish Standards Institute(BSI), theGerman Institute for Standardization(DIN), theAmerican Society for Testing and Materials(ASTM) or theInternational Organization for Standardization(ISO).
Intumescent coatings for steel constructions must be approved in standardized fire tests.
Types
[edit]Soft char
[edit]These intumescent materials produce a lightcharwhich is a poor conductor ofheat,thus retarding heat transfer. Typically the light char consists of microporous carbonaceous foam formed by a chemical reaction of three main components:ammonium polyphosphate,pentaerythritol,andmelamine.[2]The reaction takes place in a matrix formed by the molten binder which is typically based onvinyl acetatecopolymers orstyreneacrylates.
Ablative coatings contain a significant amount ofhydrates.When the hydrates are heated, they decompose, and water vapour is released, which has a cooling effect. Once the water is spent, the insulation characteristics of the char that remains can retard heat transfer through the fire stop assembly.
Soft char products are typically used in thin film intumescent materials forfireproofingprotection ofstructural steelas well as infirestop pillows.
Hard char
[edit]Harder char is produced withsodium silicatesandgraphite.These products are suitable for use inplasticpipefirestopsin which applications it is necessary to exert expansionpressureto fill the gap left in the middle of the fire stop assembly left by the melting plastic pipe.
Intumescent coatings
[edit]Intumescent coatings may be designed for protection of metals from fire, such asstructural steel.Reviews of the technology are available.[3]They may be based on a number of resin binders includingepoxy,and silicone.[4]Melamine-formaldehyde resin systems have been used using layered double-hydroxide modified phosphate esters that improved the intumescent properties.[5]
Problems
[edit]Some intumescent materials are susceptible to environmental influences such as humidity, which can reduce or negate their ability to function.[citation needed]
Gallery
[edit]-
Low pressure intumescent resin: This product is suitable for use inpassive fire protectionin general, and infirestoppingand interior fireproofing in particular. The small, orange chunk on the bottom right is capable of growing into the large black object above and to its left.
-
Pipecovered with a thin-film intumescent spray fireproofing
-
In this picture, the flame has been removed after the thin-film intumescent spray fireproofing product has completely expanded.
-
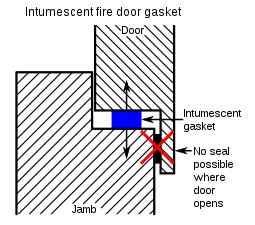
Intumescent gasketing used inpassive fire protection,forfire doorapplications.
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^Merriam-Webster Dictionary,intumescence,accessed 13 March 2023
- ^Werle, Peter; Morawietz, Marcus; Lundmark, Stefan; Sörensen, Kent; Karvinen, Esko; Lehtonen, Juha (2008). "Alcohols, Polyhydric".Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry.Weinheim: Wiley-VCH.doi:10.1002/14356007.a01_305.pub2.ISBN978-3527306732.
- ^Puri, Ravindra G.; Khanna, A. S. (2017-01-01)."Intumescent coatings: A review on recent progress".Journal of Coatings Technology and Research.14(1): 1–20.doi:10.1007/s11998-016-9815-3.ISSN1935-3804.S2CID138961125.
- ^Cardoso, de Sa, Beraldo, Hidalgo and Ferreira (November 2020)."Intumescent coatings using epoxy, alkyd, acrylic, silicone and silicone-epoxy hybrid resins for steel fire protection".Journal of Coatings Technology and Research.17(6): 1471–1488.doi:10.1007/s11998-020-00366-9.S2CID220375908.
{{cite journal}}:CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^Xu, Deng and Lang (January 2020). "Flame retardancy and smoke suppression properties of transparent intumescent fire-retardant coatings reinforced with layered double hydroxides".Journal of Coatings Technology and Research.17(1): 157–169.doi:10.1007/s11998-019-00249-8.S2CID199473315.
External links
[edit]- "The proof is in the fire" Chemical Innovation Magazine, American Chemical Society
- American Chemical Society: Fire Retardancy of Polypropylene Composites Using Intumescent Coatings
- ASTM E 2786 - 2010 Standard Test Methods for Measuring Expansion of Intumescent Materials Used in Firestop and Joint Systems