List of sunbirds

Nectariniidaeis afamilyofpasserine birdsin the superfamilyPasseroidea,comprising the sunbirds and spiderhunters.[1]Members of Nectariniidae are also known as nectariniids.[2]Their range extends from theAfrotropicsnorth to theLevantand southernArabian Peninsula,and east throughSouthandSoutheast Asiaup toNew Guineaand northern Australia.[3]They inhabit a wide variety of habitats, from aridsavannahto tropicalrainforests,and can be found fromsea levelto an altitude of 4,900 m (16,100 ft). Sunbirds are generally small birds with long, thin, down-curved bills and brightly coloured,iridescentplumages.[2]They display markedsexual dimorphism,and males are much more visually striking than females, who are usually dull green, brown, or grey. Thespiderhunters(Arachnothera) are larger than other sunbirds and show less sexual dimorphism.[3]
The primary threat facing sunbirds ishabitat lossanddegradationcaused by deforestation due to agriculture.[2]Most species of sunbird are considered to be ofLeast Concernby theIUCN,although three species, theAmani sunbird,Loveridge's sunbird,and theelegant sunbird,areEndangered,and several others are consideredNear ThreatenedorVulnerable.
The exact delineation of sunbird species is somewhat contested and varies from authority to authority: theInternational Ornithologists' Union(IOU) recognizes 146 species of sunbirds in 16 genera,[1]while other authorities recognise 143–147 species.[4][5]The largest genera areCinnyrisandAethopyga,with 53 and 23 species, respectively.[1]Recentphylogeneticstudies indicate that several widespread species such as theolive-backedandblack sunbirdsmay represent complexes of multiplecryptic species.[6]Severalundescribed speciesof sunbird may also exist inSierra Leone,Djibouti,[3]andTanzania.[5]
Conventions
[edit]| Conservation status | |
|---|---|
| EX | Extinct(0 species) |
| EW | Extinct in the wild(0 species) |
| CR | Critically Endangered(0 species) |
| EN | Endangered(3 species) |
| VU | Vulnerable(4 species) |
| NT | Near threatened(7 species) |
| LC | Least concern(116 species) |
| Other categories | |
| DD | Data deficient(0 species) |
| NE | Not evaluated(16 species) |
Conservation status codes listed follow theInternational Union for Conservation of Nature(IUCN)Red List of Threatened Species.Range maps are provided wherever possible; if a range map is not available, a description of the sunbird's range is provided. Ranges are based on theIOC World Bird Listfor that species unless otherwise noted. Population estimates are of the number of mature individuals and are taken from the IUCN Red List.
This list follows thetaxonomic treatment(designation and order of species) and nomenclature (scientific and common names) of version 13.2 of the IOC World Bird List.[1]Where the taxonomy proposed by the IOC World Bird List conflicts with the taxonomy followed by the IUCN[a]or the 2023 edition ofThe Clements Checklist of Birds of the World,the disagreement is noted next to the species's common name (for nomenclatural disagreements) or scientific name (for taxonomic disagreements).
Classification
[edit]TheInternational Ornithologists' Union(IOU) recognizes 146 species of sunbirds in 16 genera;[1]other authorities recognise 143–147 species.[4][5]This list does not includehybrid species,extinct prehistoric species, or putative species not yet accepted by the IOU.
- GenusChalcoparia:one species
- GenusDeleornis:two species
- GenusAnthreptes:fifteen species
- GenusHedydipna:four species
- GenusAnabathmis:three species
- GenusDreptes:one species
- GenusAnthobaphes:one species
- GenusCyanomitra:seven species
- GenusChalcomitra:seven species
- GenusNectarinia:six species
- GenusDrepanorhynchus:one species
- GenusCinnyris:fifty-three species
- GenusAethopyga:twenty-two species
- GenusKurochkinegramma:one species
- GenusArachnothera:thirteen species
Nectariniids
[edit]| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ruby-cheeked sunbird | C. singalensis (Gmelin, J. F.,1789) Eleven subspecies
|
South Asia,Indochina,Java,andBorneo[7] | LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fraser's sunbird | D. fraseri (Jardine&Selby,1843) Three subspecies
|
WestandCentral Africa | LC
|
| Grey-headed sunbird | D. axillaris (Reichenow,1893) |
Central Africa | LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plain-backed sunbird | A. reichenowi Gunning,1909 Two subspecies
|
Disjunctly in coastalEast Africaand westernSouthern Africa | NT
|
| Anchieta's sunbird | A. anchietae (Barboza du Bocage,1878) |
Angola east toTanzaniaandMozambique | LC
|
| Plain sunbird | A. simplex (Müller, S.,1843) |
Malay Peninsula,Borneo,andSumatra | LC
|
| Brown-throated sunbird | A. malacensis (Scopoli,1786) Sixteen subspecies
|
Southeast Asia | LC
|
| Grey-throated sunbird | A. griseigularis Tweeddale,1878 Two subspecies
|
Philippines | LC
|
| Red-throated sunbird | A. rhodolaemus Shelley,1878 |
Malay Peninsula,Borneo,andSumatra | NT
|
| Mangrove sunbird[b] | A. gabonicus (Hartlaub,1861) |
WestandCentral Africa | LC
|
| Western violet-backed sunbird | A. longuemarei (Lesson, R. P.,1831) Three subspecies
|
Sub-Saharan Africa | LC
|
| Eastern violet-backed sunbird | A. orientalis Hartlaub,1880 |
Horn of Africasouth toTanzania | LC
|
| Uluguru violet-backed sunbird
|
A. neglectus Neumann,1922 |
East Africa | LC
|
| Violet-tailed sunbird | A. aurantius Verreaux, J.&Verreaux, É.,1851 |
Central Africa | LC
|
| Little green sunbird | A. seimundi (Ogilvie-Grant,1908) Three subspecies
|
West Africa,Central Africa,and westernEast Africa | LC
|
| Yellow-chinned sunbird[c] | A. rectirostris[d] (Shaw,1812) |
West Africa | LC
|
| Grey-chinned sunbird[e] | A. tephrolaemus[d] (Jardine&Fraser,1852) |
Central Africa | LC
|
| Banded green sunbird[f]
|
A. rubritorques Reichenow,1905 |
Tanzania | VU
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|
| Collared sunbird | H. collaris (Vieillot,1819) Nine subspecies
|
Sub-Saharan Africa | LC
|
| Pygmy sunbird | H. platura (Vieillot,1819) |
WestandCentral Africa | LC
|
| Nile Valley sunbird | H. metallica (Lichtenstein, M. H. C.,1823) |
Egypt south toSudanand northernHorn of Africa,southwestern Arabian peninsula | LC
|
| Amani sunbird
|
H. pallidigaster (Sclater, W. L.&Moreau,1935) |
Tanzaniaand southeastern Kenya | EN
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reichenbach's sunbird | A. reichenbachii (Hartlaub,1857) |
Extreme southernWest Africaeast toCentral Africa | LC
|
| Príncipe sunbird | A. hartlaubii (Hartlaub,1857) |
Príncipe
|
LC
|
| Newton's sunbird | A. newtonii (Barboza du Bocage,1887) |
São Tomé Island
|
LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|
| Giant sunbird[g] | D. thomensis (Barboza du Bocage,1889) |
São Tomé Island
|
VU
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|
| Orange-breasted sunbird | A. violacea (Linnaeus,1766) |
Southwestern South Africa | LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|
| Green-headed sunbird | C. verticalis (Latham,1790) Four subspecies
|
West,Central,andEast Africa | LC
|
| Bannerman's sunbird
|
C. bannermani Grant, C. H. B.&Mackworth-Praed,1943 |
Central Africa | LC
|
| Blue-throated brown sunbird | C. cyanolaema (Jardine&Fraser,1852) Three subspecies
|
WestandCentral Africa | LC
|
| Cameroon sunbird | C. oritis (Reichenow,1892) Three subspecies
|
WesternCameroon,southeasternNigeria,andBioko | LC
|
| Blue-headed sunbird | C. alinae Jackson, F. J.,1904 Five subspecies
|
Eastern Rift Mountains | LC
|
| Olive sunbird | C. olivacea (Smith, A.,1840) Eleven subspecies
|
Sub-Saharan Africasouth of theSahel | LC
|
| Grey sunbird[h] | C. veroxii (Smith, A.,1832) Three subspecies
|
Coasts ofEastandSouthern Africa | LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|
| Buff-throated sunbird | C. adelberti (Gervais,1834) Two subspecies
|
West Africa | LC
|
| Carmelite sunbird | C. fuliginosa (Bechstein,1811) Two subspecies
|
WestandCentral Africa | LC
|
| Green-throated sunbird | C. rubescens (Vieillot,1819) Three subspecies
|
Central Africa | LC
|
| Amethyst sunbird | C. amethystina (Shaw,1812) Four subspecies
|
Central,East,andSouthern Africa | LC
|
| Scarlet-chested sunbird | C. senegalensis (Linnaeus,1766) Six subspecies
|
Sub-Saharan Africa | LC
|
| Hunter's sunbird | C. hunteri (Shelley,1889) |
Horn of AfricaandEast Africa | LC
|
| Socotra sunbird | C. balfouri (Sclater, P. L.&Hartlaub,1881) |
Socotra | LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purple-rumped sunbird | L. zeylonica (Linnaeus,1766) Two subspecies
|
Indian subcontinent | LC
|
| Crimson-backed sunbird | L. minima (Sykes,1832) |
Southwestern India | LC
|
| Purple-throated sunbird | L. sperata[i] (Linnaeus,1766) Four subspecies
|
Philippines | NE
|
| Van Hasselt's sunbird | L. brasiliana (Gmelin, J. F.,1788) Five subspecies
|
EasternIndian subcontinentandSoutheast Asia | LC
|
| Black sunbird | L. aspasia (Lesson, R. P.andGarnot,1828) Twenty-one subspecies
|
Eastern Indonesia andPapua New Guinea | LC
|
| Copper-throated sunbird | L. calcostetha (Jardine,1842) |
Southeast Asia | LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bocage's sunbird | N. bocagii Shelley,1879 |
Democratic Republic of the CongoandAngola | LC
|
| Purple-breasted sunbird | N. purpureiventris (Reichenow,1893) |
Albertine Rift Mountains | LC
|
| Tacazze sunbird | N. tacazze (Stanley,1814) Two subspecies
|
Horn of AfricaandEast Africa | LC
|
| Bronzy sunbird[j] | N. kilimensis Shelley,1885 Three subspecies
|
CentralandEast Africa | LC
|
| Malachite sunbird | N. famosa (Linnaeus,1766) Two subspecies
|
East AfricaandSouthern Africa | LC
|
| Scarlet-tufted sunbird[k] | N. johnstoni Shelley,1885 Four subspecies
|
East Africa | LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|
| Golden-winged sunbird | D. reichenowi Fischer, G. A.,1884 Three subspecies
|
East Africa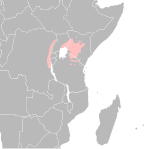
|
LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|
| Olive-bellied sunbird | C. chloropygius (Jardine,1842) Three subspecies
|
WestandCentral Africa | LC
|
| Tiny sunbird | C. minullus Reichenow,1899 |
WestandCentral Africa | LC
|
| Eastern miombo sunbird | C. manoensis Reichenow,1907 Two subspecies
|
East Africa | LC
|
| Western miombo sunbird
|
C. gertrudis Grote,1926 |
CentralandEast Africa | LC
|
| Southern double-collared sunbird | C. chalybeus (Linnaeus,1766) Two subspecies
|
Southern Africa | LC
|
| Neergaard's sunbird | C. neergaardi Grant, C. H. B.,1908 |
Southern Africa | NT
|
| Rwenzori double-collared sunbird[l] | C. stuhlmanni Reichenow,1893 Four subspecies
|
Eastern Rift Mountains | LC
|
| Whyte's double-collared sunbird
|
C. whytei[m] Benson,1948 Two subspecies
|
East Africa | NE
|
| Prigogine's double-collared sunbird
|
C. prigoginei MacDonald,1958 |
SoutheasternDemocratic Republic of the Congo | NT
|
| Ludwig's double-collared sunbird | C. ludovicensis[m] (Barboza du Bocage,1868) |
Angola | NE
|
| Northern double-collared sunbird | C. reichenowi Sharpe,1891 Two subspecies
|
WesternCentral AfricaandEast Africa | LC
|
| Greater double-collared sunbird | C. afer (Linnaeus,1766) |
Southern Africa | LC
|
| Regal sunbird | C. regius Reichenow,1893 Two subspecies
|
Albertine Rift Valley | LC
|
| Rockefeller's sunbird
|
C. rockefelleri Chapin,1932 |
EasternDemocratic Republic of the Congo | VU
|
| Eastern double-collared sunbird | C. mediocris Shelley,1885 |
Kenya andTanzania | LC
|
| Usambara double-collared sunbird
|
C. usambaricus Grote,1922 |
Southeast Kenya and northeastTanzania | NT
|
| Forest double-collared sunbird | C. fuelleborni Reichenow,1899 Two subspecies
|
East Africa | LC
|
| Moreau's sunbird
|
C. moreaui Sclater, W. L.,1933 |
CentralTanzania | NT
|
| Loveridge's sunbird | C. loveridgei Hartert, E. J. O.,1922 |
Eastern centralTanzania | EN
|
| Beautiful sunbird | C. pulchellus[n] (Linnaeus,1766) Two subspecies
|
West,Central,andEast Africa | NE
|
| Marico sunbird | C. mariquensis Smith, A.,1836 Three subspecies
|
EastandSouthern Africa | LC
|
| Shelley's sunbird | C. shelleyi[o] Alexander,1899 |
East Africa | NE
|
| Hofmann's sunbird
|
C. hofmanni[o] Reichenow,1915 |
EasternTanzania | NE
|
| Congo sunbird
|
C. congensis (van Oort,1910) |
Congo Basin | LC
|
| Red-chested sunbird | C. erythrocercus (Hartlaub,1857) |
Extreme southernSudanto centralTanzania | LC
|
| Black-bellied sunbird | C. nectarinioides Richmond,1897 Two subspecies
|
East Africa | LC
|
| Purple-banded sunbird | C. bifasciatus (Shaw,1812) Two subspecies
|
East,Central,andSouthern Africa | LC
|
| Tsavo sunbird | C. tsavoensis van Someren,1922 |
Kenya and northeasternTanzania | LC
|
| Violet-breasted sunbird
|
C. chalcomelas Reichenow,1905 |
Somaliaand Kenya | LC
|
| Pemba sunbird | C. pembae Reichenow,1905 |
Pemba Island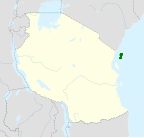
|
LC
|
| Orange-tufted sunbird | C. bouvieri Shelley,1877 |
Central Africa | LC
|
| Palestine sunbird | C. osea Bonaparte,1856 Two subspecies
|
Arabian Peninsula andCentral Africa | LC
|
| Arabian sunbird | C. hellmayri[p] Neumann,1904 Two subspecies
|
Arabian Peninsula | NE
|
| Shining sunbird | C. habessinicus[p] (Hemprich&Ehrenberg,1828) Three subspecies
|
East Africa | NE
|
| Splendid sunbird | C. coccinigastrus (Latham,1801) |
WestandCentral Africa | LC
|
| Johanna's sunbird | C. johannae Verreaux, J.&Verreaux, É.,1851 Two subspecies
|
WestandCentral Africa | LC
|
| Superb sunbird | C. superbus (Shaw,1812) Four subspecies
|
WestandCentral Africa | LC
|
| Rufous-winged sunbird
|
C. rufipennis (Jensen,1983) |
CentralTanzania | VU
|
| Oustalet's sunbird | C. oustaleti (Barboza du Bocage,1878) Two subspecies
|
Disjunctly, inAngola,and inTanzaniaandZambia | LC
|
| White-bellied sunbird | C. talatala Smith, A.,1836 |
Southern Africa | LC
|
| Variable sunbird | C. venustus (Shaw,1799) Five subspecies
|
West,Central,andEast Africa | LC
|
| Dusky sunbird | C. fuscus Vieillot,1819 Two subspecies
|
Southwestern Africa | LC
|
| Ursula's sunbird | C. ursulae (Alexander,1903) |
Cameroon | LC
|
| Bates's sunbird | C. batesi Ogilvie-Grant,1908 |
WestandCentral Africa | LC
|
| Copper sunbird | C. cupreus (Shaw,1812) Two subspecies
|
West,Central,andEast Africa | LC
|
| Purple sunbird | C. asiaticus (Latham,1790) Thre subspecies
|
Eastern Arabian Peninsula east toSouth AsiaandIndochina | LC
|
| Olive-backed sunbird | C. jugularis[q] (Linnaeus,1766) Twenty-one subspecies
|
Southeast AsiatoPapua New Guineaand northern Australia | NE
|
| Apricot-breasted sunbird | C. buettikoferi Hartert, E. J. O.,1896 |
Sumba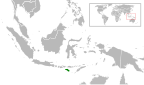
|
LC
|
| Flame-breasted sunbird | C. solaris (Temminck,1825) Two subspecies
|
Lesser Sunda IslandsandWetar | LC
|
| Souimanga sunbird | C. sovimanga (Gmelin, J. F.,1788) Five subspecies
|
Madagascar andSeychelles | LC
|
| Malagasy green sunbird[r] | C. notatus[s] (Müller, P. L. S.,1776) Three subspecies
|
Madagascar andComoros | NE
|
| Seychelles sunbird | C. dussumieri (Hartlaub,1861) |
Seychelles | LC
|
| Humblot's sunbird | C. humbloti Milne-Edwards, A.&Oustalet,1885 Two subspecies
|
Grande ComoreandMohéli | LC
|
| Anjouan sunbird | C. comorensis Peters, W.,1864 |
Anjouan | LC
|
| Mayotte sunbird | C. coquerellii (Hartlaub,1860) |
Mayotte
|
LC
|
| Loten's sunbird | C. lotenius (Linnaeus,1766) Two subspecies
|
India andSri Lanka | LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grey-hooded sunbird | A. primigenia (Hachisuka,1941) Two subspecies
|
Mindanao | LC
|
| Apo sunbird | A. boltoni[t] Mearns,1905 Three subspecies
|
Mindanao | LC
|
| Lina's sunbird | A. linaraborae Kennedy, R. S.,Gonzales&Miranda,1997 |
Mindanao | NT
|
| Flaming sunbird | A. flagrans Oustalet,1876 |
LuzonandCatanduanes | LC
|
| Maroon-naped sunbird | A. guimarasensis (Steere,1890) Two subspecies
|
Negros,Panay,andGuimaras | LC
|
| Metallic-winged sunbird | A. pulcherrima[u] Sharpe,1876 |
Central and southernPhilippines | NE
|
| Luzon sunbird | A. jefferyi[u] (Ogilvie-Grant,1894) |
Luzon | NE
|
| Bohol sunbird | A. decorosa[u] (McGregor, 1907) |
Bohol | NE
|
| Elegant sunbird | A. duyvenbodei (Schlegel,1871) |
Sangihe Islands | EN
|
| Lovely sunbird | A. shelleyi Sharpe,1876 |
Palawan archipelago | LC
|
| Handsome sunbird | A. bella Tweeddale,1877 Six subspecies
|
Philippines | LC
|
| Mrs. Gould's sunbird | A. gouldiae (Vigors,1831) Four subspecies
|
Indochina,southern China, andHimalayan foothills | LC
|
| Green-tailed sunbird | A. nipalensis (Hodgson,1836) Nine subspecies
|
Indochina,southern China, andHimalayan foothills | LC
|
| White-flanked sunbird | A. eximia (Horsfield,1821) |
Java | LC
|
| Fork-tailed sunbird | A. christinae[v] Swinhoe,1869 Three subspecies
|
China,Vietnam,andLaos | NE
|
| Black-throated sunbird | A. saturata (Hodgson,1836) Ten subspecies
|
Indochina,southern China, andHimalayan foothills | LC
|
| Crimson sunbird | A. siparaja (Raffles,1822) Fourteen subspecies
|
South Asia,Southeast Asia,and southern China | LC
|
| Magnificent sunbird | A. magnifica Sharpe,1876 |
WesternandCentral Visayas | LC
|
| Vigors's sunbird | A. vigorsii (Sykes,1832) |
Western India | LC
|
| Javan sunbird | A. mystacalis (Temminck,1822) |
Java | LC
|
| Temminck's sunbird | A. temminckii (Müller, S.,1843) |
Malay Peninsula,Sumatra,andBorneo | LC
|
| Fire-tailed sunbird | A. ignicauda (Hodgson,1836) Two subspecies
|
Himalayas | LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purple-naped sunbird | K. hypogrammicum (Müller, S.,1843) Five subspecies
|
Indochina,Borneo,andSumatra | LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|
| Little spiderhunter | A. longirostra (Latham,1790) Ten subspecies
|
SouthandSoutheast Asia | LC
|
| Orange-tufted spiderhunter | A. flammifera Tweeddale,1878 Two subspecies
|
Philippines | LC
|
| Pale spiderhunter | A. dilutior Sharpe,1876 |
Palawan | LC
|
| Thick-billed spiderhunter | A. crassirostris (Reichenbach,1853) |
Malay Peninsula,Sumatra,andBorneo | LC
|
| Long-billed spiderhunter | A. robusta Müller, S.&Schlegel,1844 Two subspecies
|
Malay Peninsula,Sumatra,Java,andBorneo | LC
|
| Spectacled spiderhunter | A. flavigaster (Eyton,1839) |
Malay Peninsula,Sumatra,andBorneo | LC
|
| Yellow-eared spiderhunter | A. chrysogenys (Temminck,1826) Two subspecies
|
Malay Peninsula,Sumatra,Java,andBorneo | LC
|
| Naked-faced spiderhunter | A. clarae Blasius, W.,1890 Four subspecies
|
Philippines | LC
|
| Gray-breasted spiderhunter | A. modesta (Eyton,1839) Three subspecies
|
Malay Peninsula,Sumatra,andBorneo | LC
|
| Streaky-breasted spiderhunter | A. affinis (Horsfield,1821) |
JavaandBali | LC
|
| Bornean spiderhunter | A. everetti[w] (Sharpe,1893) |
Borneo | NE
|
| Streaked spiderhunter | A. magna[w] (Hodgson,1836) Five subspecies
|
EasternIndian subcontinentandIndochina | NE
|
| Whitehead's spiderhunter | A. juliae Sharpe,1887 |
Borneo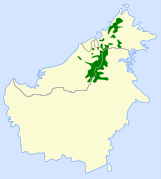
|
LC
|
Notes
[edit]- ^The IUCN follows the taxonomy proposed by theHBW and BirdLife Taxonomic Checklist.[4]
- ^Called mouse-brown sunbird byThe Clements Checklist.[5]
- ^Called yellow-throated sunbird byThe Clements Checklist.[5]
- ^abThe yellow-chinned and grey-chinned sunbirds are treated as a single species, the green sunbird, by the Clements Checklist.[5]
- ^Called gray-throated sunbird byThe Clements Checklist.[5]
- ^Called banded sunbird byThe Clements Checklist.[5]
- ^Called São Tomé sunbird byThe Clements Checklist.[5]
- ^Called mouse-colored sunbird byThe Clements Checklist.[5]
- ^The IUCN splits the purple-throated sunbirdsensu latointo two species, the purple-throated sunbirdsensu stricto(L. sperata) and the orange-lined sunbird (L. juliae).[4]
- ^Called bronze sunbird byThe Clements Checklistand theIUCN.[5]
- ^Called red-tufted sunbird byThe Clements Checklistand theIUCN.[5]
- ^Called Stuhlmann's sunbird byThe Clements Checklistand the Ruwenzori sunbird by theIUCN.[5]
- ^abWhyte's double-collared sunbird and Ludwig's double-collared sunbird are treated as a single species, the montane double-collared sunbird, by the IUCN and Clements.[4][5]
- ^The IUCN splits the beautiful sunbirdsensu latointo two species, the gorgeous sunbird (C. melanogastrus) and beautiful sunbirdsensu stricto(C. pulchellus).[4]
- ^abHofmann's sunbird is considered a subspecies of Shelley's sunbird by the IUCN and Clements.[4][5]
- ^abThe Arabian sunbird is treated as a subspecies of the shining sunbird by the Clement's Checklist.[5]
- ^The IUCN splits the olive-backed sunbirdsensu latointo two species, Rand's sunbird (C. idenburgi) and olive-backed sunbirdsensu stricto(C. jugularis),[4]while The Clements Checklist splits it into eight different species.[5]
- ^Called Malagasy sunbird byThe Clements Checklist.[5]
- ^The IUCN splits the Malagasy green sunbird into three species, the long-billed sunbird (C. notatus), Grand Comoro sunbird (C. moebii), and Moheli sunbird (C. voeltzkowi).[4]
- ^The Clement's Checklist splits the Apo sunbirdsensu latointo two species, Tboli sunbird (A. tibolii) and Apo sunbirdsensu stricto(A. malindangensis).[5]
- ^abcThe Bohol and Luzon sunbirds are treated as a subspecies of the metallic-winged sunbird by the IUCN and Clements.[4][5]
- ^The IUCN splits the fork-tailed sunbirdsensu latointo two species, the Hainan sunbird (A. christinae) and fork-tailed sunbirdsensu stricto(A. latouchii).[4]
- ^abThe Bornean spiderhunter is treated as a subspecies of the streaked spiderhunter by the IUCN.[4]
References
[edit]- ^abcdeGill, F.; Donsker, D.; Rasmussen, P., eds. (July 2023)."Dippers, leafbirds, flowerpeckers, sunbirds".IOC World Bird List.v 13.2.Archivedfrom the original on October 23, 2021.RetrievedOctober 3,2023.
- ^abcWinkler, David W.; Billerman, Shawn M.; Lovette, Irby J. (March 4, 2020). Billerman, Shawn M.; Keeney, Brooke K.; Rodewald, Paul G.; Schulenberg, Thomas S. (eds.)."Sunbirds and Spiderhunters (Nectariniidae)".Birds of the World.Cornell Lab of Ornithology.doi:10.2173/bow.nectar1.01.S2CID216264284.RetrievedMay 25,2023.
- ^abcCheke, Robert A.; Mann, Clive F. (2010).Sunbirds: A Guide to the Sunbirds, Flowerpeckers, Spiderhunters and Sugarbirds of the World.London:Christopher Helm.ISBN978-1-4081-3567-9.Archivedfrom the original on October 7, 2023.RetrievedJuly 10,2023.
- ^abcdefghijkl"Handbook of the Birds of the World and BirdLife International digital checklist of the birds of the world. Version 7".HBW and BirdLife International. 2022.Archivedfrom the original on December 8, 2023.RetrievedJune 9,2023.
- ^abcdefghijklmnopqrstClements, James F.;Rasmussen, P. C.; Schulenberg, T. S.; Iliff, M. J.; Fredericks, T. A.; Gerbracht, J. A.; Lepage, Denis; Billerman, S. M.; Sullivan, B. L.; Wood, C. L. (2023)."The eBird/Clements checklist of Birds of the World: v2023".Clements Checklist.Archivedfrom the original on January 1, 2020.RetrievedOctober 30,2023.
- ^Ó Marcaigh, Fionn; Kelly, David J; O’Connell, Darren P; Analuddin, Kangkuso; Karya, Adi; McCloughan, Jennifer; Tolan, Ellen; Lawless, Naomi; Marples, Nicola M (May 5, 2023)."Small islands and large biogeographic barriers have driven contrasting speciation patterns in Indo-Pacific sunbirds (Aves: Nectariniidae)".Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society.198(1): 72–92.doi:10.1093/zoolinnean/zlac081.hdl:2262/101492.ISSN0024-4082.Archivedfrom the original on June 12, 2023.RetrievedJune 14,2023.
- ^Karuthedathu, Dipu; Das, Vinay; J., Praveen; Ramachandran, Vijay; Shurpali, Sachin; Nair, Manoj V. (January 17, 2014)."Some significant avian records from Odisha"(PDF).Indian Birds.9(1): 16.Archived(PDF)from the original on May 25, 2023.RetrievedJune 14,2023.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Chalcoparia singalensis".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22717626A94542835.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22717626A94542835.en.RetrievedOctober 3,2023.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Deleornis fraseri".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T103792577A94541369.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T103792577A94541369.en.RetrievedOctober 3,2023.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Deleornis axillaris".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T103792599A104232364.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T103792599A104232364.en.RetrievedOctober 3,2023.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Anthreptes reichenowi".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22717602A94541610.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22717602A94541610.en.RetrievedOctober 3,2023.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Anthreptes anchietae".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22717606A94541876.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22717606A94541876.en.RetrievedOctober 3,2023.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Anthreptes simplex".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22717611A94542063.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22717611A94542063.en.RetrievedOctober 3,2023.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Anthreptes malacensis".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T103792612A94542270.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T103792612A94542270.en.RetrievedOctober 3,2023.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Anthreptes griseigularis".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T103792631A104295009.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T103792631A104295009.en.RetrievedOctober 3,2023.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Anthreptes rhodolaemus".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22717618A94542527.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22717618A94542527.en.RetrievedOctober 3,2023.
- ^BirdLife International (2018)."Anthreptes gabonicus".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2018:e.T22717629A131977277.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T22717629A131977277.en.RetrievedOctober 3,2023.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Anthreptes longuemarei".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22717635A94543374.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22717635A94543374.en.RetrievedOctober 3,2023.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Anthreptes orientalis".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22717640A94543716.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22717640A94543716.en.RetrievedOctober 3,2023.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Anthreptes neglectus".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22717645A94543945.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22717645A94543945.en.RetrievedOctober 3,2023.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Anthreptes aurantius".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22717649A94544121.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22717649A94544121.en.RetrievedOctober 3,2023.
- ^BirdLife International (2018)."Anthreptes seimundi".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2018:e.T22717683A131977855.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T22717683A131977855.en.RetrievedOctober 3,2023.
- ^BirdLife International (2022)."Anthreptes rectirostris".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2022:e.T103792746A210661407.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2022-1.RLTS.T103792746A210661407.en.RetrievedOctober 3,2023.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Anthreptes tephrolaemus".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T103792796A104295279.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T103792796A104295279.en.RetrievedOctober 3,2023.
- ^BirdLife International (2017)."Anthreptes rubritorques".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2017:e.T22717663A118905827.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-3.RLTS.T22717663A118905827.en.RetrievedOctober 3,2023.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Hedydipna collaris".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22717668A94545190.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22717668A94545190.en.RetrievedNovember 11,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2018)."Hedydipna platura".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2018:e.T22717672A131977543.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T22717672A131977543.en.RetrievedNovember 13,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Hedydipna metallica".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22717676A94545911.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22717676A94545911.en.RetrievedNovember 13,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2021)."Hedydipna pallidigaster".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2021:e.T22717653A180120536.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2021-3.RLTS.T22717653A180120536.en.RetrievedOctober 3,2023.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Anabathmis reichenbachii".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22717705A94547607.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22717705A94547607.en.RetrievedNovember 17,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2018)."Anabathmis hartlaubii".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2018:e.T22717709A131458593.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T22717709A131458593.en.RetrievedNovember 16,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2018)."Anabathmis newtonii".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2018:e.T22717714A131458327.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T22717714A131458327.en.RetrievedNovember 17,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2018)."Dreptes thomensis".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2018:e.T22717719A132236453.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T22717719A132236453.en.RetrievedNovember 17,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Anthobaphes violacea".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22717695A94547235.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22717695A94547235.en.RetrievedNovember 12,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Cyanomitra verticalis".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22717738A94548805.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22717738A94548805.en.RetrievedNovember 17,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2018)."Cyanomitra cyanolaema".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2018:e.T22717746A131978715.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T22717746A131978715.en.RetrievedNovember 12,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Cyanomitra oritis".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22717728A94548457.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22717728A94548457.en.RetrievedNovember 12,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2018)."Cyanomitra alinae".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2018:e.T22717733A131978531.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T22717733A131978531.en.RetrievedNovember 13,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2018)."Cyanomitra olivacea".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2018:e.T22717691A131978137.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T22717691A131978137.en.RetrievedNovember 13,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Cyanomitra verreauxii".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22717699A94547409.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22717699A94547409.en.RetrievedNovember 12,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Chalcomitra adelberti".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22717778A94551393.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22717778A94551393.en.RetrievedNovember 13,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2018)."Chalcomitra fuliginosa".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2018:e.T22717758A131979010.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T22717758A131979010.en.RetrievedNovember 12,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Chalcomitra rubescens".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22717766A94550517.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22717766A94550517.en.RetrievedNovember 12,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Chalcomitra amethystina".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22717762A94550241.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22717762A94550241.en.RetrievedNovember 17,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2018)."Chalcomitra senegalensis".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2018:e.T22717770A131979279.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T22717770A131979279.en.RetrievedNovember 11,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Chalcomitra hunteri".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22717774A94551180.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22717774A94551180.en.RetrievedNovember 12,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Chalcomitra balfouri".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22717750A94549624.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22717750A94549624.en.RetrievedFebruary 19,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Leptocoma zeylonica".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22717782A94551632.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22717782A94551632.en.RetrievedNovember 12,2021.
- ^BirdLife International(2020)."Leptocoma minima".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2020:e.T22717785A94551846.RetrievedNovember 6,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Leptocoma brasiliana".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T103795247A104297009.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T103795247A104297009.en.RetrievedNovember 18,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2018)."Leptocoma aspasia".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2018:e.T22717791A132114755.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T22717791A132114755.en.RetrievedNovember 18,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Leptocoma calcostetha".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22717794A94552451.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22717794A94552451.en.RetrievedNovember 12,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Nectarinia bocagii".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22717966A94560196.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22717966A94560196.en.RetrievedNovember 11,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Nectarinia purpureiventris".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22717962A94560024.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22717962A94560024.en.RetrievedNovember 12,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Nectarinia tacazze".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22717958A94559801.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22717958A94559801.en.RetrievedNovember 12,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Nectarinia kilimensis".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22717970A94560374.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22717970A94560374.en.RetrievedNovember 13,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2018)."Nectarinia famosa".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2018:e.T22717979A132114939.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T22717979A132114939.en.RetrievedNovember 12,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2018)."Nectarinia johnstoni".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2018:e.T22717984A132115208.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T22717984A132115208.en.RetrievedNovember 12,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2018)."Drepanorhynchus reichenowi".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2018:e.T22717975A131981080.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T22717975A131981080.en.RetrievedNovember 13,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Cinnyris chloropygius".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22717919A94557353.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22717919A94557353.en.RetrievedNovember 12,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2018)."Cinnyris minullus".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2018:e.T22717923A131980390.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T22717923A131980390.en.RetrievedNovember 11,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Cinnyris manoensis".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T103797506A94556226.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T103797506A94556226.en.RetrievedNovember 13,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Cinnyris gertrudis".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T103797518A104294788.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T103797518A104294788.en.RetrievedNovember 12,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2018)."Cinnyris chalybeus".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2018:e.T22717869A131979925.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T22717869A131979925.en.RetrievedNovember 20,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2018)."Cinnyris neergaardi".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2018:e.T22717903A131980130.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T22717903A131980130.en.RetrievedNovember 12,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Cinnyris stuhlmanni".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T103798409A104275812.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T103798409A104275812.en.RetrievedNovember 18,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Cinnyris prigoginei".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T103798427A104275573.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T103798427A104275573.en.RetrievedNovember 18,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Cinnyris reichenowi".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22717887A94556635.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22717887A94556635.en.RetrievedNovember 11,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Cinnyris afer".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T103798399A94556884.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T103798399A94556884.en.RetrievedNovember 11,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Cinnyris regius".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22717927A94557969.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22717927A94557969.en.RetrievedNovember 11,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Cinnyris rockefelleri".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22717941A94558639.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22717941A94558639.en.RetrievedNovember 12,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Cinnyris mediocris".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T103799498A95119695.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T103799498A95119695.en.RetrievedNovember 17,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Cinnyris usambaricus".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T103799620A104276065.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T103799620A104276065.en.RetrievedNovember 13,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Cinnyris fuelleborni".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22735340A95108399.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22735340A95108399.en.RetrievedNovember 12,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Cinnyris moreaui".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22717936A94558420.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22717936A94558420.en.RetrievedNovember 12,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2021)."Cinnyris loveridgei".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2021:e.T22717931A179267691.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2021-3.RLTS.T22717931A179267691.en.RetrievedNovember 11,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2018)."Cinnyris mariquensis".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2018:e.T22718003A131882840.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T22718003A131882840.en.RetrievedNovember 11,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Cinnyris congensis".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22717998A94561701.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22717998A94561701.en.RetrievedNovember 15,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2018)."Cinnyris erythrocercus".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2018:e.T22717994A131981463.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T22717994A131981463.en.RetrievedNovember 12,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Cinnyris nectarinioides".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22718043A94564210.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22718043A94564210.en.RetrievedNovember 13,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Cinnyris bifasciatus".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T103801419A94562143.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T103801419A94562143.en.RetrievedNovember 11,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Cinnyris tsavoensis".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T103801517A104297631.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T103801517A104297631.en.RetrievedNovember 11,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Cinnyris chalcomelas".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22718012A94562467.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22718012A94562467.en.RetrievedNovember 16,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Cinnyris pembae".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22718017A94562636.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22718017A94562636.en.RetrievedNovember 12,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2018)."Cinnyris bouvieri".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2018:e.T22717846A131979675.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T22717846A131979675.en.RetrievedNovember 15,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Cinnyris osea".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22717850A94555242.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22717850A94555242.en.RetrievedFebruary 20,2022.
- ^BirdLife International (2018)."Cinnyris coccinigastrus".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2018:e.T22718027A131981699.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T22718027A131981699.en.RetrievedNovember 13,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2018)."Cinnyris johannae".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2018:e.T22718031A131982012.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T22718031A131982012.en.RetrievedNovember 12,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2018)."Cinnyris superbus".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2018:e.T22718035A131982280.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T22718035A131982280.en.RetrievedNovember 13,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2021)."Cinnyris rufipennis".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2021:e.T22717954A179271612.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2021-3.RLTS.T22717954A179271612.en.RetrievedNovember 13,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Cinnyris oustaleti".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22717841A94554825.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22717841A94554825.en.RetrievedNovember 15,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2018)."Cinnyris talatala".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2018:e.T22717836A132441087.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T22717836A132441087.en.RetrievedNovember 12,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2018)."Cinnyris venustus".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2018:e.T22717826A131882422.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T22717826A131882422.en.RetrievedNovember 12,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Cinnyris fuscus".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22717950A94559334.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22717950A94559334.en.RetrievedNovember 12,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2017)."Cinnyris ursulae".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2017:e.T22717831A118496874.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-3.RLTS.T22717831A118496874.en.RetrievedNovember 15,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Cinnyris batesi".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22717687A94546628.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22717687A94546628.en.RetrievedNovember 12,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2018)."Cinnyris cupreus".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2018:e.T22717945A131980663.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T22717945A131980663.en.RetrievedNovember 11,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2019)."Cinnyris asiaticus".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2019:e.T22717855A155489800.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-3.RLTS.T22717855A155489800.en.RetrievedNovember 20,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Cinnyris buettikoferi".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22717801A94552966.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22717801A94552966.en.RetrievedNovember 12,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Cinnyris solaris".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22717805A94553131.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22717805A94553131.en.RetrievedNovember 15,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Cinnyris sovimanga".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22717808A94553308.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22717808A94553308.en.RetrievedNovember 12,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Cinnyris dussumieri".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22717754A94549803.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22717754A94549803.en.RetrievedNovember 12,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Cinnyris humbloti".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22717813A94553492.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22717813A94553492.en.RetrievedNovember 12,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Cinnyris comorensis".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22717817A94553660.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22717817A94553660.en.RetrievedNovember 15,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Cinnyris coquerellii".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22717822A94553815.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22717822A94553815.en.RetrievedNovember 16,2021.
- ^BirdLife International(2016)."Cinnyris lotenius".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22717862A94556053.RetrievedNovember 6,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2020)."Aethopyga primigenia".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2020:e.T22718048A179048340.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-3.RLTS.T22718048A179048340.en.RetrievedNovember 14,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2020)."Aethopyga boltoni".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2020:e.T22718059A179061446.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-3.RLTS.T22718059A179061446.en.RetrievedNovember 14,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2020)."Aethopyga linaraborae".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2020:e.T22724518A177948824.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-3.RLTS.T22724518A177948824.en.RetrievedNovember 14,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Aethopyga flagrans".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T103805010A94564834.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T103805010A94564834.en.RetrievedNovember 12,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Aethopyga guimarasensis".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T103809131A104301389.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T103809131A104301389.en.RetrievedNovember 18,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Aethopyga duyvenbodei".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22718068A94565160.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22718068A94565160.en.RetrievedNovember 12,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2018)."Aethopyga shelleyi".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2018:e.T22734230A132035299.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T22734230A132035299.en.RetrievedNovember 13,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2018)."Aethopyga bella".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2018:e.T22732130A132034102.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T22732130A132034102.en.RetrievedNovember 13,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Aethopyga gouldiae".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22718077A94565475.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22718077A94565475.en.RetrievedNovember 15,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Aethopyga nipalensis".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22718081A94565721.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22718081A94565721.en.RetrievedNovember 12,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Aethopyga eximia".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22718084A94565956.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22718084A94565956.en.RetrievedNovember 11,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Aethopyga saturata".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22718090A94566293.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22718090A94566293.en.RetrievedNovember 12,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Aethopyga siparaja".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T103804411A94566535.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T103804411A94566535.en.RetrievedNovember 19,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2018)."Aethopyga magnifica".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2018:e.T103810377A132044827.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T103810377A132044827.en.RetrievedNovember 19,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Aethopyga vigorsii".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T103804493A104300369.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T103804493A104300369.en.RetrievedNovember 12,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Aethopyga mystacalis".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T103804351A94566823.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T103804351A94566823.en.RetrievedNovember 12,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Aethopyga temminckii".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T103804369A104300960.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T103804369A104300960.en.RetrievedNovember 12,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2018)."Aethopyga ignicauda".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2018:e.T22718100A131982762.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T22718100A131982762.en.RetrievedNovember 13,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Kurochkinegramma hypogrammicum".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22717680A94546136.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22717680A94546136.en.RetrievedNovember 13,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Arachnothera longirostra".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T103778625A94567188.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T103778625A94567188.en.RetrievedNovember 15,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2018)."Arachnothera flammifera".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2018:e.T103778923A132044412.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T103778923A132044412.en.RetrievedNovember 18,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Arachnothera dilutior".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T103778680A104295930.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T103778680A104295930.en.RetrievedNovember 18,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Arachnothera crassirostris".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22718106A94567472.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22718106A94567472.en.RetrievedNovember 11,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Arachnothera robusta".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22718109A94567652.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22718109A94567652.en.RetrievedNovember 12,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Arachnothera flavigaster".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22718112A94567832.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22718112A94567832.en.RetrievedNovember 11,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Arachnothera chrysogenys".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22718115A94568017.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22718115A94568017.en.RetrievedNovember 12,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2018)."Arachnothera clarae".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2018:e.T22718118A131982953.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T22718118A131982953.en.RetrievedNovember 13,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Arachnothera modesta".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T103792501A104296539.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T103792501A104296539.en.RetrievedNovember 16,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Arachnothera affinis".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T103792496A94568389.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T103792496A94568389.en.RetrievedNovember 12,2021.
- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Arachnothera juliae".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22718131A94569006.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22718131A94569006.en.RetrievedNovember 12,2021.




































































































































