Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub
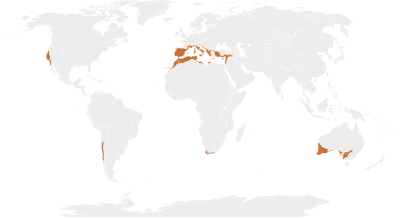
Mediterranean forests, woodlands and scrubis abiomedefined by theWorld Wide Fund for Nature.[1]The biome is generally characterized by dry summers and rainy winters, although in some areas rainfall may be uniform. Summers are typically hot in low-lying inland locations but can be cool near colder seas. Winters are typically mild to cool in low-lying locations but can be cold in inland and higher locations. All these ecoregions are highly distinctive, collectively harboring 10% of the Earth's plant species.[2]

Distribution
[edit]
The Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub biome mostly occurs in, but not limited to, theMediterranean climatezones, in the mid-latitudes:[1]
- theMediterranean Basin
- theChilean Matorral
- theCalifornia chaparral and woodlandsecoregion ofCaliforniaand theBaja California Peninsula
- theWestern CapeofSouth Africa
- thesouthwestandsouthern Australia.
The biome is not limited to the Mediterranean climate zone. It can also be present in other climate zones (which typically border the Mediterranean climate zone), such as the drier regions of theoceanicandhumid subtropical climates,and as well as the lusher areas of thesemi-arid climatezone. Non-Mediterranean climate regions that would feature Mediterranean vegetation include theNile River ValleyinEgypt(extending upstream along the riverbanks), parts of theEastern Capein South Africa, southeastern Australia, southeasternAzerbaijan,southeastern Turkey, far northernIraq,theMazandaran ProvinceinIran,Central Italy,parts of theBalkans(includingNorthern Greece), as well as Northern and WesternJordan.[citation needed]
Vegetation
[edit]
Vegetation types range fromforeststowoodlands,savannas,shrublands,andgrasslands;"mosaic habitat"landscapes are common, where differing vegetation types are interleaved with one another in complex patterns created by variations in soil, topography, exposure to wind and sun, and fire history. Much of the woody vegetation in Mediterranean-climate regions is sclerophyll, which means 'hard-leaved' in Greek.Sclerophyllous vegetationgenerally has small, dark leaves covered with a waxy outer layer to retain moisture in the dry summer months.[citation needed]
Phytogeographersconsider thefynbos(South Africa) as a separate floral kingdom because 68% of the 8,600 vascular plant species crowded into its 90,000 square kilometers (35,000 sq mi) are endemic and highly distinctive at several taxonomic levels.[1][3]This is equivalent to about 40% of the plant species of the United States andCanadacombined, found within an area the size of the state ofMaine.The fynbos and Southwest Australia shrublands have flora that are significantly more diverse than the other ecoregions, although any Mediterranean shrubland is still rich in species and endemics relative to other non-forest ecoregions.[1][3]
Biome plant groups
[edit]This sectionneeds additional citations forverification.(December 2017) |

Major plant communities in this biome include:
- Forest:Mediterranean forests are generally composed ofbroadleaf trees,such as theoakand mixedsclerophyllforests of California and the Mediterranean region, theEucalyptusforests ofSouthwest Australia,and theNothofagusforests of central Chile. Forests are often found inriparianareas, where they receive more summer water.Coniferousforests also occur, especially around the Mediterranean.Pineanddeciduousoak forest are widespread across California.Pinus halepensis,lentisk (Pistacia lentiscus), kermes oak (Quercus coccifera) andChamaeropsare found across Spanish Mediterranean forest.
- Woodland:Oak woodlandsare characteristic of the Mediterranean Basin and in California.Pinewoodlands are also present in the Mediterranean Basin. California additionally haswalnutwoodlands.
- Savannaandgrassland:TheCalifornia Central Valley grasslandsare the largest Mediterranean grassland eco-region, although these grasslands have mostly been converted to agriculture. The remaining woodlands feature mainly oak, walnut and pine. The cork oak savanna in Portugal, known asmontado,is a good example of a mediterranean savanna.
- Shrubland:Shrublands are dense thickets of evergreen sclerophyllshrubsand small trees. They are most common near the seacoast, and are often adapted to wind and salt air from the ocean. They are calledchaparral(California andsouthern Portugal),matorralin Chile and southern Spain,garrigueormaquisin France,macchiaorgarigain Italy,phryganain Greece,tomillaresin Spain,fynbos,renosterveld,Succulent Karoo,andstrandveldin South Africa,kwonganin Southwest Australia andbathain Israel.Northern coastal scrubandcoastal sage scrub,also known as soft chaparral, occur near the California coast. In some places shrublands are of the mature vegetation type, and in other places are the result of degradation of former forest or woodland by logging orovergrazing,or disturbance by major fires.
Fire as a medium of change
[edit]
Fire, both natural and human-caused, has played a large role in shaping the ecology of Mediterraneanecoregions.[4]The hot, dry summers make much of the region prone to fires, and lightning-caused fires occur with some frequency. Many of the plants arepyrophytes,or fire-loving, adapted or even depending on fire for reproduction, recycling of nutrients, and the removal of dead or senescent vegetation. In both the Australian and Californian Mediterranean-climate eco-regions, native peoples used fire extensively to clear brush and trees, making way for the grasses and herbaceous vegetation that supported game animals and useful plants.[citation needed]
The plant communities in these areas adapted to the frequent human-caused fires, and pyrophyte species grew more common and more fire-loving, while plants that were poorly adapted to fire retreated. After European colonization of these regions, fires were suppressed, which has caused someunintended consequencesin these ecoregions; fuel builds up, so that when fires do come they are much more devastating, and some species dependent on fire for their reproduction are now threatened. The European shrublands have also been shaped by anthropogenic fire,[5]historically associated withtranshumanceherding of sheep and goats.
Though adapted to infrequent fires, chaparral plant communities can be eliminated by frequent fires. A high frequency of fire (less than ten years) will result in the loss of obligate seeding shrub species such asManzanitaspp. This high frequency disallows seeder plants to reach their reproductive size before the next fire and the community shifts to a sprouter-dominance. If high frequency fires continue over time, obligate resprouting shrub species can also be eliminated by exhausting their energy reserves below-ground. Today, frequent accidental ignitions can convert chaparral from a native shrubland to non-native annual grassland and drastically reduce species diversity, especially under drought brought about by climate change.[6][7]
On 25 July 2023, devastating wildfires were burning in at least nine countries across the Mediterranean, includingCroatia,Italy,andPortugal,with thousands of firefighters inEuropeandNorth Africaworking to contain flames stoked by high temperatures, dry conditions, and strong winds. The wildfires led to casualties, evacuations of thousands of people, and widespread destruction of homes and forests.[8]
Degradation
[edit]

This sectionneeds additional citations forverification.(December 2017) |

Mediterranean ecoregions are some of the most endangered and vulnerable on the planet. Many have suffered tremendous degradation and habitat loss through logging, overgrazing, conversion to agriculture, urbanization,fire suppression,and introduction of exotic andinvasive species.The ecoregions around the Mediterranean basin and in California have been particularly affected by degradation due to human activity, suffering extensive loss of forests and soil erosion, and many native plants and animals have become extinct or endangered.
See also
[edit]- Aegean and Western Turkey sclerophyllous and mixed forests
- Forest Sciences Centre of Catalonia(CTFC)
- Food and Agriculture Organization(Silva mediterranea workgroup)
References
[edit]- ^abcd
 This article incorporates text available under theCC BY-SA 3.0license.World Wide Fund for Nature."Mediterranean Forests, Woodlands, and Scrub Ecoregions".Archived fromthe originalon 1 April 2011.Retrieved27 May2010.
This article incorporates text available under theCC BY-SA 3.0license.World Wide Fund for Nature."Mediterranean Forests, Woodlands, and Scrub Ecoregions".Archived fromthe originalon 1 April 2011.Retrieved27 May2010.
- ^Cody, M.L. (1986). "Diversity, rarity, and conservation in Mediterranean-climate regions". In Soulé, M.E. (ed.).Conservation biology.Massachusetts, US. pp. 122–152.
{{cite book}}:CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^abCowling, R.M.; MacDonald, I.A.W.; Simmons, M.T. (1996)."The Cape Peninsula, South Africa: Physiographical, biological and historical background to an extraordinary hot-spot of biodiversity".Biodiversity and Conservation.5(5): 527–550.Bibcode:1996BiCon...5..527C.doi:10.1007/bf00137608.S2CID23314811.
- ^Gil-Tena, Assu; Aquilue, Nuria; Duane, Andrea; de Caceres, Miquel; Brotons, Lluis (2016). "Mediterranean fire regime effects on pine-oak forest landscape mosaics under global change in NE Spain".European Journal of Forest Research.135(2): 403–416.doi:10.1007/s10342-016-0943-1.S2CID15011913.
- ^Casals, Pere; Valor, Teresa; Besalú, Arnau; Molina-Terren, Domingo (2016)."Understory fuel load and structure eight to nine years after prescribed burning in Mediterranean pine forests"(PDF).Forest Ecology and Management.362:156–168.Bibcode:2016ForEM.362..156C.doi:10.1016/j.foreco.2015.11.050.Archived(PDF)from the original on 24 February 2021.Retrieved25 July2016.
- ^Syphard, Alexandra D.; Radeloff, Volker C.; Keeley, Jon E.; Hawbaker, Todd J.; Clayton, Murray K.; Stewart, Susan I.; Hammer, Roger B. (1 July 2007). "Human Influence on California Fire Regimes".Ecological Applications.17(5): 1388–1402.Bibcode:2007EcoAp..17.1388S.doi:10.1890/06-1128.1.ISSN1939-5582.PMID17708216.
- ^Pratt, R. Brandon; Jacobsen, Anna L.; Ramirez, Aaron R.; Helms, Anjel M.; Traugh, Courtney A.; Tobin, Michael F.; Heffner, Marcus S.; Davis, Stephen D. (1 March 2014). "Mortality of resprouting chaparral shrubs after a fire and during a record drought: physiological mechanisms and demographic consequences".Global Change Biology.20(3): 893–907.Bibcode:2014GCBio..20..893P.doi:10.1111/gcb.12477.ISSN1365-2486.PMID24375846.S2CID19688559.
- ^Sullivan, Helen; Tondo, Lorenzo (26 July 2023)."'Like a blowtorch': Mediterranean on fire as blazes spread across nine countries ".The Guardian.Archivedfrom the original on 31 July 2023.Retrieved31 July2023.
External links
[edit] Media related toMediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrubat Wikimedia Commons
Media related toMediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrubat Wikimedia Commons
