Meppen
Meppen
Möppen(Northern Low Saxon) | |
|---|---|
 Town hall | |
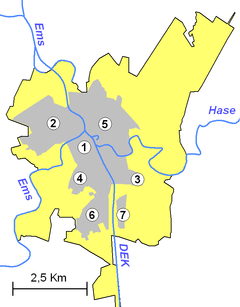
Location of Meppen within Emsland district  | |
| Coordinates:52°41′37″N7°17′34″E/ 52.69361°N 7.29278°E | |
| Country | Germany |
| State | Lower Saxony |
| District | Emsland |
| Subdivisions | 7Stadtteileand 13 villages |
| Government | |
| •Mayor(2021–26) | Helmut Knurbein[1](Ind.) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 188.48 km2(72.77 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 14 m (46 ft) |
| Population (2022-12-31)[2] | |
| • Total | 36,117 |
| • Density | 190/km2(500/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00(CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00(CEST) |
| Postal codes | 49716 |
| Dialling codes | 05931 |
| Vehicle registration | EL |
| Website | www.meppen.de |
Meppen(German pronunciation:[ˈmɛpm̩];Northern Low Saxon:Möppen) is a town in and the seat of theEmslanddistrict ofLower Saxony,Germany,at the confluence of theEms,Hase,andNordradderivers and theDortmund–Ems Canal(DEK). The name stems from the wordMappe,meaning "delta".
Geography
[edit]The town lying on the mouth of the Hase into the Ems in the central part of the Emsland between the cities ofLingenandPapenburg.
Lying about 20 kilometres (12 mi) from theDutchborder, the town has an area of 188.45 km2and is 15 mabove sea level.The population was 34,196 as of 30 June 2005.
Quarters of Meppen:
|
1stAltstadt |
Following villages are situated in Meppen:
In 1974, 13 independent municipalities in the close vicinity of the town were integrated into Meppen.
|
History
[edit]
Meppen, formerly a fortified town, boasts 12 centuries of history. The first documented mention of Meppen dates from 834, in a deed of donation byFrankishemperorLouis the Pious,transferring a missionary establishment of that name to the abbey ofCorvey.
945 --Emperor Otto the Greatgrants the town the rights tomintcoinsand collecttolls,followed in 946 by market rights.
1252—CountessJutta von Vechta-Ravensbergsells her possessions to theBishop of Münster.Meppen becomes part of theNiederstift Münster(i.e. LowerPrince-Bishopric of Münster).
1360—Meppen is granted the right to build cityfortificationsby Bishop Adolf ofMünster,and thereby, town rights. Over the next three centuries until 1660, Meppen is built up as a fortified town.
1762—at the end of theSeven Years' War,the fortifications are demolished. Some walls remain standing today, however.
1803—Resolutions of theReichsdeputationshauptschlussassign Meppen toLouis Engelbert, 6th Duke of Arenberg,to compensate for the loss of his possessions on the west bank of theRhine.Meppen becomes thecapitalof the dukedom ofArenberg.
1811—Meppen is incorporated into theFirst French Empireas acantonalseat.
1813–1814—Occupation byPrussia.
1814–1815—Resolutions of theCongress of Viennaassign Meppen and theDuchy of Arenbergto theKingdom of Hanover.
1855—Meppen connected to theHannoverschen Westbahnrailway line upon its opening.
1866—Hanover becomes a province of Prussia.
1871—Part of theGerman Empire.
1938—Kristallnacht:the German police andSAbroke down intoJewishhouses and carried out mass arrests, beatings and tortures of Jews. Germans burned down the synagogue and destroyed Jewish homes and enterprises. Some Jews were deported to theOranienburg concentration camp.[3]
1939—Germanprisoner-of-war campStalag VI-B established in Meppen-Versen, in which initially around 5,000Polishprisoners of warwere held after the Germaninvasion of Poland,which startedWorld War II,and then from 1940 to 1942French,Belgian,Polish,Sovietand other POWs were held there.[4]
1943—Italianprisoners of war brought by the Germans to the Stalag VI-B.[4]
1944—Stalag VI-B converted into asubcampof theNeuengamme concentration camp.[4][5]Over 1,700 men were imprisoned there and used asforced labour,[5]and over 20% of them died.[6]
1945—Prisoners of the subcamp were evacuated by the Germans toBremen,most in adeath march,in which at least 50 prisoners died, sick ones by train, and then they were mostly transported to the Neuengamme concentration camp.[5][6]
1946—The state of Prussia is abolished after theWorld War II.Meppen becomes part of the newly createdLandofLower Saxony.
1977—District reforms in Lower Saxony unite the former districts ofLingen,MeppenandAschendorf-Hümmlingin the district of Emsland, with Meppen as administrative seat.
Culture and sights
[edit]






Theatre
[edit]Between September and April the Meppen Theatre Group (Theatergemeinde Meppen) offers a comprehensive programme. Productions take place in the Meppen Theatre and Concert Hall, which was designed byEberhard Kulenkampffand completed in 1959. It also acts as a school hall for the Windthorst Gymnasium. The programme includes both touring theatre productions as well as musical events of various genres.
From May to September, the Emsland Open Air Stage at Meppen (Emsländische Freilichtbühne Meppen) offers visitors afamily musicaland an evening event, mostly based on musical productions. More than 30,000 visitors come each year to the open air theatre in Esterfeld Forest to see large musical performances involving casts of up to 100.
Museums
[edit]- Town Museum in the ArenbergRenteiinObergerichtsstraße,built byAugust Reinking
- Exhibition Centre for the Archaeology of theEmslandonKoppelschleusestreet
- Art exhibitions in the arts centre onKoppelschleusestreet
Buildings
[edit]- Around 1461–62 the Priory Church of St. Vitus was built as a three-aisledlate Gothichall church.Whilst there were only wooden churches in the surrounding area, at this sport there was already a simple stone building as early as the 9th century. This was expanded in the 11th century; the heart of the present tower being one of the additions. Further expansion in the 13th century resulting in the Bridle and North Portals being built.
- TheResidenz,which today houses the council and the headmaster's office of the Windthorst Gymnasium, was built between 1726 and 1729. Later, in 1743–46, the Gymnasium Church was built onto the Residenz under the Pater Superior,Karl Immendorf.
- Thetown hall(Rathaus), today the symbol of the town, was constructed in 1408 fromglacial erratics.From 1601 to 1605 it was considerably expanded and an additional brick storey added. In order to increase the floor area for the upper storey, an open arched hall was erected in front of the building. Thestepped gablewith its semi-circular elements was heavily based on Münster prototypes at (Rothenburg 44,built 1583, and theKrameramtshausof 1589). At the start of the 19th century the building appears to have fallen considerably into disrepair, because the Arenberg architect,Josef Niehaus,was invited by the town submit an assessment for its renovation. He recommended that the ruined tower was demolished and the ornamentation of the gable removed, but initially that came to nought. In 1885 the ornamentation was finally removed and the gable end furnished with a plain triangular gable. In addition the turret of the staircase tower at the side, added in 1611 was demolished due to its poor condition. In 1909 it was decided to rebuild the tower and gable in their present form. Inside the building is a 1605 sandstone fireplace.
- The armoury (Zeughaus) was built in 1752 on the site of the former castle, thePaulsburg(residence of theseneschalorDrost,built in 1374) by order ofPrince-Elector Clemens August.It was to act as a store room for weapons, munitions, uniforms and battle equipment for soldiers studying at Meppen Fortress. In the 19th century the building was used for commercial purposes and survives today as a private residence, albeit with a number of structural alterations.
- The history of theHerrenmühle,awater millon theNordraddestream, goes back to the 16th century. It is used today for cultural events.
- Residential housesBy contrast withLingen,just a few kilometres away, the centre of Meppen has hardly any historic buildings. The town houses mainly consist of new buildings with a few 19th century brick houses. Of national significance is the Arenberg Rentei (Arenbergische Rentei) at No. 7,Obergerichtsstraße.The two-storeyclassicalbuilding withpilastersand amansard roofwas built as a residence in 1805 byAugust Reinkingfor the merchant, Ferdindand Frye, and his wife, Josefine Mulert. From 1835, it was used as a finance office (Rentei), it now serves as a town museum. Four years later, based on plans by the same architect, the so-calledHeyl'sche Hauswas built at No. 3,Emsstraße.The owner was the Duchy ofArenberg's privy councillor (Kammerrat), Anton Heyl. While the house itself was demolished in 1977 in favour of a bank, the adjoining hall, with its remarkable ornamentation, was kept and restored. Next to the huge bank, it looks rather lost. The town community centre, built in 1816 by physician, Nicholas Vagedes, not far from the town hall, has housed the town council since 1936. Amongst the few remaining timber-framed buildings are the single-storey houses No. 24,Kuhstraßeand No. 12,Im Sack.The former dates essentially to the 16th century and is one of the oldest buildings in the town. It has been expanded and extended several times. No. 12Im Sack,by contrast, was built in 1797 and still has a gateway to the hall or threshing floor (Dielentor). Today, it houses the offices of the newspaper and the senior citizens' volunteer agency.
- TheKoppelschleuselocks, built between 1826 and 1830, have survived in its original state as part of the old Ems–Hase Canal.
- TheHölting Mill(Höltingmühle), asmock mill,was probably built in 1639 nearBockhornin the county ofFriesland.The mill was bought by the Hölting Citizens Preservation Society and re-erected during the town's 600th anniversary celebrations in 1959–60 on the tongue of land between theDortmund–Ems Canaland theRiver Hase.Inside the mill today is a café, which is open during summer weekends. Civil ceremonies also take place in the mill.
- On the 131-metre-highcooling towerof the now closedMeppen-Hüntel Peak Load Gasworksis, according to theGuinness Book of Records,is the largest map of the world in the world. It was painted by the Swiss artist,Christoph Rihs.
- TheMeppener Högerhaus,a former administrative building for the county ofMeppen,(built 1936–1937) was designed by architect,Fritz Höger.Today a police station is housed in the double-winged, brick building onBahnhofstraße,with itshipped roof.The entrance staircase on the southwest side is dominated by anarchway.
Parks
[edit]- The former counterscarp of MeppenFortresshas survived and forms part of a park area with trees.
Natural monuments
[edit]- In the parish of Borken is theBorkener ParadiesNature Reserve, a historicwood pasture.
Population statistics
[edit](*including the villages belonging to the town of Meppen)
| Year | Inhabitants | Year | Inhabitants | Year | Inhabitants | Year | Inhabitants | Year | Inhabitants |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1821* | 4,815 | 1848* | 5,130 | 1905* | 7,687 | 1939* | 15,045 | 1950* | 19,141 |
| 1971* | 27,305 | 1990 | 30,508 | 2005 | 34,196 | 2010 | 34.944 | 2015 | 34.918 |
Notable people
[edit]
- Levin Schücking(1814-1883), a German novelist.[7]
- Karl Brandi(1868–1946), a German historian.
- Gerd Zacher(1929–2014), composer, organist and writer on music.
- Hermann Lause(1939-2005), film actor; appeared in more than seventy films
- Hermann Korte(1949-2020), academic specialising in German literature, language and linguistics.
- Richard Wiese(born 1953), German linguist who studies thephonologyandmorphologyof German
Sport
[edit]- Maurits van Löben Sels(1876–1944), a Dutch épée, foil and sabre fencer; team bronze medallist at the1906 Intercalated Games
- Alwin Schockemöhle(born 1937), former show-jumper, gold medallist at the1976 Summer Olympicsand team medallist at several other Olympics
- Thomas Bröker(born 1985), a retired footballer who played 349 games
- Jana Franziska Poll(born 1988), volleyball player, 87 caps with theGermany women's national volleyball team
- Nils Zumbeel(born 1990), footballer who played over 275 games
Sport clubs
[edit]- SV Meppen(football)
- SV Union Meppen (football, tennis, gymnastics, volleyball, table tennis, athletics)
Twin towns – sister cities
[edit] Ostrołęka,Poland
Ostrołęka,Poland
Gallery
[edit]-
Town hall
-
Gymnasium
-
A street in the town centre
-
Buildings in the town centre
-
Museum
-
Pedestrian zone onBahnhofstraße
-
Meppen's old harbour
-
Vormeppen railway station
-
Ems River in Meppen
-
Installing the new lifting bridge in 2007
References
[edit]- ^"Direktwahlen in Niedersachsen vom 12. September 2021"(PDF).Landesamt für Statistik Niedersachsen.13 October 2021.
- ^"LSN-Online Regionaldatenbank, Tabelle A100001G: Fortschreibung des Bevölkerungsstandes, Stand 31. Dezember 2022"(in German).Landesamt für Statistik Niedersachsen.
- ^"Meppen"(in German).Retrieved11 September2020.
- ^abc"Meppen-Versen"(in German).Retrieved11 September2020.
- ^abc"Meppen-Versen".KZ-Gedenkstätte Neuengamme.Retrieved11 September2020.
- ^ab"Meppen-Versen"(in German).Retrieved11 September2020.
- ^.Encyclopædia Britannica.Vol. 24 (11th ed.). 1911. p. 382.
- ^"Städtepartnerschaft Meppen - Ostroleka".meppen.de(in German). Meppen.Retrieved2021-02-25.
External links
[edit]- Official website
 (in German)
(in German) - Webcam(German)