Messier object
 All Messier objects | |
| Alternative names | Messier Catalogue |
|---|---|
| Survey type | Astronomical catalogue |
| Named after | Charles Messier |
| Published | 1774 (preliminary version) |
TheMessier objectsare a set of 110astronomical objectscatalogued by the French astronomerCharles Messierin hisCatalogue des Nébuleuses et des Amas d'Étoiles(Catalogue of Nebulae and Star Clusters). Because Messier was interested only in findingcomets,he created a list of those non-comet objects that frustrated his hunt for them. This list, which Messier created in collaboration with his assistantPierre Méchain,is now known as theMessier catalogue.The Messier catalogue is one of the most famous lists of astronomical objects, and many objects on the list are still referenced by their Messier numbers.[1] The catalogue includes most of the astronomicaldeep-sky objectsthat can be easily observed from Earth'sNorthern Hemisphere;many Messier objects are popular targets for amateur astronomers.[2]
A preliminary version of the catalogue first appeared in 1774 in theMemoirsof theFrench Academy of Sciencesfor the year 1771.[3][4][5] The first version of Messier's catalogue contained 45 objects, which were not numbered. Eighteen of the objects were discovered by Messier; the rest had been previously observed by other astronomers.[6] By 1780 the catalogue had increased to 70 objects.[7]The final version of the catalogue containing 103 objects was published in 1781 in theConnaissance des Tempsfor the year 1784.[8][4] However, due to what was thought for a long time to be the incorrect addition ofMessier 102,the total number remained 102. Other astronomers, using side notes in Messier's texts, eventually filled out the list up to 110 objects.[9]
The catalogue consists of a diverse range of astronomical objects, fromstar clustersandnebulaetogalaxies.For example, Messier 1 is asupernova remnant,known as theCrab Nebula,and the greatspiralAndromeda Galaxyis M31. Further inclusions followed; the first addition came fromNicolas Camille Flammarionin 1921, who addedMessier 104after finding Messier's side note in his 1781 edition exemplar of the catalogue.M105toM107were added byHelen Sawyer Hoggin 1947,M108andM109byOwen Gingerichin 1960, andM110by Kenneth Glyn Jones in 1967.[10]
Lists and editions[edit]

The first edition of 1774 covered 45 objects (M1toM45). The total list published by Messier in 1781 contained 103 objects, but the list was expanded through successive additions by other astronomers, motivated by notes in Messier's and Méchain's texts indicating that at least one of them knew of the additional objects. The first such addition came fromNicolas Camille Flammarionin 1921, who addedMessier 104after finding a note Messier made in a copy of the 1781 edition of the catalogue.M105toM107were added byHelen Sawyer Hoggin 1947,M108andM109byOwen Gingerichin 1960, andM110by Kenneth Glyn Jones in 1967.[11]M102was observed by Méchain, who communicated his notes to Messier. Méchain later concluded that this object was simply a re-observation of M101, though some sources suggest that the object Méchain observed was the galaxyNGC 5866and identify that as M102.[12]
Messier's final catalogue was included in theConnaissance des Tempspour l'Année 1784[Knowledge of the Times for the Year 1784], the French official yearly publication of astronomicalephemerides.[8][4]
Messier lived and did his astronomical work at the Hôtel de Cluny (now theMusée national du Moyen Âge), inParis,France. The list he compiled contains only objects found in the sky area he could observe: from the northcelestial poleto a celestial latitude of about −35.7°. He did not observe or list objects visible only from farther south, such as theLargeandSmall Magellanic Clouds.[13]
Observations[edit]
The Messier catalogue comprises nearly all of the most spectacular examples of the five types ofdeep-sky object–diffuse nebulae,planetary nebulae,open clusters,globular clusters,andgalaxies– visible from European latitudes. Furthermore, almost all of the Messier objects are among the closest to Earth in their respective classes, which makes them heavily studied with professional class instruments that today can resolve very small and visually significant details in them. A summary of the astrophysics of each Messier object can be found in theConcise Catalog of Deep-sky Objects.[14]
Since these objects could be observed visually with the relatively small-aperturerefracting telescope(approximately 100 mm ≈ 4 inches) used by Messier to study the sky, they are among the brightest and thus most attractiveastronomical objects(popularly calleddeep-sky objects) observable from Earth, and are popular targets for visual study andastrophotographyavailable to modernamateur astronomersusing larger aperture equipment. In early spring, astronomers sometimes gather for "Messier marathons",when all of the objects can be viewed over a single night.[15][16]
Messier objects[edit]
| Messier number | NGC/ICnumber | Common name | Image | Object type | Distance (kly) | Constellation | Apparent magnitude | Apparent dimensions | Right ascension | Declination |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1[17] | NGC 1952 | Crab Nebula | 
|
Supernova remnant | 4.9–8.1 | Taurus | 8.4 | 420″ × 290″ | 05h34m31.94s | +22° 00′ 52.2″ |
| M2[18] | NGC 7089 | – | 
|
Globular cluster | 33 | Aquarius | 6.5 | 16' | 21h33m27.02s | −00° 49′ 23.7″ |
| M3[19] | NGC 5272 | – | 
|
Globular cluster | 33.9 | Canes Venatici | 6.2 | 18' | 13h42m11.62s | +28° 22′ 38.2″ |
| M4[20] | NGC 6121 | Spider Globular | 
|
Globular cluster | 7.2 | Scorpius | 5.6 | 26' | 16h23m35.22s | −26° 31′ 32.7″ |
| M5[21] | NGC 5904 | Rose Cluster | 
|
Globular cluster | 24.5 | Serpens | 5.6 | 23' | 15h18m33.22s | +02° 04′ 51.7″ |
| M6[22] | NGC 6405 | Butterfly Cluster | 
|
Open cluster | 1.6 | Scorpius | 4.2 | 25' | 17h40.1m | −32° 13′ |
| M7[23] | NGC 6475 | Ptolemy's Cluster | 
|
Open cluster | 0.65–1.31 | Scorpius | 3.3 | 80' | 17h53m51.2s | −34° 47′ 34″ |
| M8[24] | NGC 6523 | Lagoon Nebula | Nebulawith cluster | 4.1 | Sagittarius | 4.6 | 90′ × 40′ | 18h03m37s | −24° 23′ 12″ | |
| M9[25] | NGC 6333 | – | 
|
Globular cluster | 25.8 | Ophiuchus | 7.7 | 9.3' | 17h19m11.78s | −18° 30′ 58.5″ |
| M10[26] | NGC 6254 | – | 
|
Globular cluster | 14.3 | Ophiuchus | 6.6 | 20' | 16h57m8.92s | −04° 05′ 58.07″ |
| M11[27] | NGC 6705 | Wild Duck Cluster | 
|
Open cluster | 6.2 | Scutum | 5.8 | 22.8' | 18h51.1m | −06° 16′ |
| M12[28] | NGC 6218 | – | 
|
Globular cluster | 15.7 | Ophiuchus | 6.7 | 16' | 16h47m14.18s | −01° 56′ 54.7″ |
| M13[29] | NGC 6205 | Great Hercules Cluster | 
|
Globular cluster | 22.2 | Hercules | 5.8 | 20' | 16h41m41.24s | +36° 27′ 35.5″ |
| M14[30] | NGC 6402 | – | 
|
Globular cluster | 30.3 | Ophiuchus | 7.6 | 11' | 17h37m36.15s | −03° 14′ 45.3″ |
| M15[31] | NGC 7078 | Great Pegasus Cluster | 
|
Globular cluster | 33 | Pegasus | 6.2 | 18' | 21h29m58.33s | +12° 10′ 01.2″ |
| M16[32] | NGC 6611 | Eagle Nebula | 
|
H II regionnebula with cluster | 7 | Serpens | 6.4 | 70' x 50' | 18h18m48s | −13° 49′ |
| M17[33] | NGC 6618 | Omega,Swan,Horseshoe,Lobster,orCheckmark Nebula | 
|
H II regionnebula with cluster | 5–6 | Sagittarius | 6.0 | 11' | 18h20m26s | −16° 10′ 36″ |
| M18[34] | NGC 6613 | Black Swan Cluster | 
|
Open cluster | 4.9 | Sagittarius | 7.5 | 9.8' | 18h19.9m | −17° 08′ |
| M19[35] | NGC 6273 | – | 
|
Globular cluster | 28.7 | Ophiuchus | 6.8 | 17' | 17h02m37.69s | −26° 16′ 04.6″ |
| M20[36] | NGC 6514 | Trifid Nebula | 
|
H II regionnebulawith cluster | 5.2 | Sagittarius | 6.3 | 28' | 18h02m23s | −23° 01′ 48″ |
| M21[37] | NGC 6531 | Webb's Cross Cluster | 
|
Open cluster | 4.25 | Sagittarius | 6.5 | 14' | 18h04.6m | −22° 30′ |
| M22[38] | NGC 6656 | Great Sagittarius Cluster | 
|
Globular cluster | 9.6–11.6 | Sagittarius | 5.1 | 32' | 18h36m23.94s | −23° 54′ 17.1″ |
| M23[39] | NGC 6494 | – | 
|
Open cluster | 2.15 | Sagittarius | 5.5 | 35' | 17h56.8m | −19° 01′ |
| M24[40] | IC 4715 | Small Sagittarius Star Cloud | 
|
Milky Waystar cloud | ~10 | Sagittarius | 2.5 | 2°x1° | 18h17m | −18° 33′ |
| M25[41] | IC 4725 | – | 
|
Open cluster | 2.0 | Sagittarius | 4.6 | 36' | 18h31.6m | −19° 15′ |
| M26[42] | NGC 6694 | – | 
|
Open cluster | 5.0 | Scutum | 8.0 | 14' | 18h45.2m | −09° 24′ |
| M27[43] | NGC 6853 | Dumbbell Nebula | 
|
Planetary nebula | 1.148–1.52 | Vulpecula | 7.4 | 8.0' × 5.6' | 19h59m36.340s | +22° 43′ 16.09″ |
| M28[44] | NGC 6626 | – | 
|
Globular cluster | 17.9 | Sagittarius | 6.8 | 11.2' | 18h24m32.89s | −24° 52′ 11.4″ |
| M29[45] | NGC 6913 | Cooling Tower | 
|
Open cluster | 7.2 | Cygnus | 7.1 | 7' | 20h23m56s | +38° 31′ 24″ |
| M30[46] | NGC 7099 | Jellyfish Cluster | 
|
Globular cluster | 27.8–31 | Capricornus | 7.2 | 12' | 21h40m22.12s | −23° 10′ 47.5″ |
| M31[47] | NGC 224 | Andromeda Galaxy | Spiral galaxy | 2,430–2,650 | Andromeda | 3.4 | 3.167° × 1° | 00h42m44.3s | +41° 16′ 09″ | |
| M32[48] | NGC 221 | Andromeda Satellite #1 | 
|
Dwarf elliptical galaxy | 2,410–2,570 | Andromeda | 8.1 | 8.7' × 6.5' | 00h42m41.8s | +40° 51′ 55″ |
| M33[49] | NGC 598 | Triangulum/Pinwheel Galaxy | 
|
Spiral galaxy | 2,380–3,070 | Triangulum | 5.7 | 70.8' x 41.7' | 01h33m50.02s | +30° 39′ 36.7″ |
| M34[50] | NGC 1039 | Spiral Cluster | 
|
Open cluster | 1.5 | Perseus | 5.5 | 35' | 02h42.1m | +42° 46′ |
| M35[51] | NGC 2168 | Shoe-Buckle Cluster | 
|
Open cluster | 2.8 | Gemini | 5.3 | 28' | 06h09.1m | +24° 21′ |
| M36[52] | NGC 1960 | Pinwheel Cluster | 
|
Open cluster | 4.1 | Auriga | 6.3 | 12' | 05h36m12s | +34° 08′ 04″ |
| M37[53] | NGC 2099 | Salt and Pepper Cluster | 
|
Open cluster | 4.511 | Auriga | 6.2 | 24' | 05h52m18s | +32° 33′ 02″ |
| M38[54] | NGC 1912 | Starfish Cluster | 
|
Open cluster | 4.2 | Auriga | 7.4 | 21' | 05h28m42s | +35° 51′ 18″ |
| M39[55] | NGC 7092 | – | 
|
Open cluster | 0.8244 | Cygnus | 4.6 | 29' | 21h31m42s | +48° 26′ 00″ |
| M40[56] | – | Winnecke 4 | 
|
Optical Double | 0.51 | Ursa Major | 8.4 | 51.7″ | 12h22m12.5s | +58° 04′ 59″ |
| M41[57] | NGC 2287 | Little Beehive Cluster | 
|
Open cluster | 2.3 | Canis Major | 4.5 | 38' | 06h46.0m | −20° 46′ |
| M42[58] | NGC 1976 | Great Orion Nebula | 
|
H II regionnebula | 1.324–1.364 | Orion | 4.0 | 65' x 60' | 05h35m17.3s | −05° 23′ 28″ |
| M43[59] | NGC 1982 | De Mairan's Nebula | 
|
H II regionnebula (part of the Orion Nebula) |
1.6 | Orion | 9.0 | 20' x 15' | 05h35.6m | −05° 16′ |
| M44[60] | NGC 2632 | Beehive ClusterorPraesepe | 
|
Open cluster | 0.577 | Cancer | 3.7 | 95' | 08h40.4m | +19° 59′ |
| M45[61] | – | Pleiades,Seven SistersorSubaru | Open cluster | 0.39–0.46 | Taurus | 1.6 | 2° | 03h47m24s | +24° 07′ 00″ | |
| M46[62] | NGC 2437 | – | 
|
Open cluster | 5.4 | Puppis | 6.0 | 22.8' | 07h41.8m | −14° 49′ |
| M47[63] | NGC 2422 | – | 
|
Open cluster | 1.6 | Puppis | 4.4 | 30' | 07h36.6m | −14° 30′ |
| M48[64] | NGC 2548 | – | 
|
Open cluster | 1.5 | Hydra | 5.5 | 30' | 08h13.7m | −05° 45′ |
| M49[65] | NGC 4472 | – | 
|
Elliptical galaxy | 53,600–58,200 | Virgo | 8.4 | 10.2' × 8.3' | 12h29m46.7s | +08° 00′ 02″ |
| M50[66] | NGC 2323 | Heart-Shaped Cluster | 
|
Open cluster | 3.2 | Monoceros | 5.9 | 16' | 07h03.2m | −08° 20′ |
| M51[67] | NGC 5194,NGC 5195 | Whirlpool Galaxy | Spiral galaxy | 19,000–27,000 | Canes Venatici | 8.4 | 11.2′ × 6.9′ | 13h29m52.7s | +47° 11′ 43″ | |
| M52[68] | NGC 7654 | Scorpion Cluster | 
|
Open cluster | 5.0 | Cassiopeia | 7.3 | 13' | 23h24.2m | +61° 35′ |
| M53[69] | NGC 5024 | – | 
|
Globular cluster | 58 | Coma Berenices | 7.6 | 13' | 13h12m55.25s | +18° 10′ 05.4″ |
| M54[70] | NGC 6715 | – | 
|
Globular cluster | 87.4 | Sagittarius | 7.6 | 12' | 18h55m03.33s | −30° 28′ 47.5″ |
| M55[71] | NGC 6809 | Specter Cluster | 
|
Globular cluster | 17.6 | Sagittarius | 6.3 | 19' | 19h39m59.71s | −30° 57′ 53.1″ |
| M56[72] | NGC 6779 | – | 
|
Globular cluster | 32.9 | Lyra | 8.3 | 8.8' | 19h16m35.57s | +30° 11′ 00.5″ |
| M57[73] | NGC 6720 | Ring Nebula | 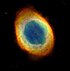
|
Planetary nebula | 1.6–3.8 | Lyra | 8.8 | 230 "× 230" | 18h53m35.079s | +33° 01′ 45.03″ |
| M58[74] | NGC 4579 | – | 
|
Barred Spiral galaxy | ~63,000 | Virgo | 9.7 | 5.9' × 4.7' | 12h37m43.5s | +11° 49′ 05″ |
| M59[75] | NGC 4621 | – | 
|
Elliptical galaxy | 55,000–65,000 | Virgo | 9.6 | 5.4' × 3.7' | 12h42m02.3s | +11° 38′ 49″ |
| M60[76] | NGC 4649 | – | 
|
Elliptical galaxy | 51,000–59,000 | Virgo | 8.8 | 7.4' × 6.0' | 12h43m39.6s | +11° 33′ 09″ |
| M61[77] | NGC 4303 | Swelling Spiral | 
|
Spiral galaxy | 50,200–54,800 | Virgo | 9.7 | 6.5' × 5.8' | 12h21m54.9s | +04° 28′ 25″ |
| M62[78] | NGC 6266 | Flickering Globular | 
|
Globular cluster | 22.2 | Ophiuchus | 6.5 | 15' | 17h01m12.60s | −30° 06′ 44.5″ |
| M63[79] | NGC 5055 | Sunflower Galaxy | Spiral galaxy | 37,000 | Canes Venatici | 8.6 | 12.6' × 7.2' | 13h15m49.3s | +42° 01′ 45″ | |
| M64[80] | NGC 4826 | Black Eye Galaxy | 
|
Spiral galaxy | 22,000–26,000 | Coma Berenices | 8.5 | 10.7' × 5.1' | 12h56m43.7s | +21° 40′ 58″ |
| M65[81] | NGC 3623 | Leo Triplet | Barred Spiral galaxy | 41,000–42,000 | Leo | 9.3 | 8.7' × 2.5' | 11h18m55.9s | +13° 05′ 32″ | |
| M66[82] | NGC 3627 | Leo Triplet | 
|
Barred Spiral galaxy | 31,000–41,000 | Leo | 8.9 | 9.1' × 4.2' | 11h20m15.0s | +12° 59′ 30″ |
| M67[83] | NGC 2682 | King CobraorGolden Eye Cluster | 
|
Open cluster | 2.61–2.93 | Cancer | 6.1 | 30' | 08h51.3m | +11° 49′ |
| M68[84] | NGC 4590 | – | 
|
Globular cluster | 33.6 | Hydra | 7.8 | 11' | 12h39m27.98s | −26° 44′ 38.6″ |
| M69[85] | NGC 6637 | – | 
|
Globular cluster | 29.7 | Sagittarius | 7.6 | 10.8' | 18h31m23.10s | −32° 20′ 53.1″ |
| M70[86] | NGC 6681 | – | 
|
Globular cluster | 29.4 | Sagittarius | 7.9 | 8' | 18h43m12.76s | −32° 17′ 31.6″ |
| M71[87] | NGC 6838 | Angelfish Cluster | 
|
Globular cluster | 13.0 | Sagitta | 8.2 | 7.2' | 19h53m46.49s | +18° 46′ 45.1″ |
| M72[88] | NGC 6981 | – | 
|
Globular cluster | 53.40–55.74 | Aquarius | 9.3 | 6.6' | 20h53m27.70s | −12° 32′ 14.3″ |
| M73[89] | NGC 6994 | – | 
|
Asterism | ~2.5 | Aquarius | 9.0 | 2.8' | 20h58m54s | −12° 38′ |
| M74[90] | NGC 628 | Phantom Galaxy[91] | 
|
Spiral galaxy | 24,000–36,000 | Pisces | 9.4 | 10.5' x 9.5' | 01h36m41.8s | +15° 47′ 01″ |
| M75[92] | NGC 6864 | – | 
|
Globular cluster | 67.5 | Sagittarius | 8.5 | 6.8' | 20h06m04.75s | −21° 55′ 16.2″ |
| M76[93] | NGC 650, NGC 651 | Little Dumbbell Nebula | 
|
Planetary nebula | 2.5 | Perseus | 10.1 | 2.7' × 1.8' | 01h42.4m | +51° 34′ 31″ |
| M77[94] | NGC 1068 | Cetus AorSquid Galaxy | 
|
Spiral galaxy | 47,000 | Cetus | 8.9 | 7.1' × 6.0' | 02h42m40.7s | −00° 00′ 48″ |
| M78[95] | NGC 2068 | – | 
|
Diffuse nebula | 1.6 | Orion | 8.3 | 8' × 6' | 05h46m46.7s | +00° 00′ 50″ |
| M79[96] | NGC 1904 | – | 
|
Globular cluster | 41 | Lepus | 7.7 | 8.7' | 05h24m10.59s | −24° 31′ 27.3″ |
| M80[97] | NGC 6093 | – | 
|
Globular cluster | 32.6 | Scorpius | 7.3 | 10' | 16h17m02.41s | −22° 58′ 33.9″ |
| M81[98] | NGC 3031 | Bode's Galaxy | 
|
Spiral galaxy | 11,400–12,200 | Ursa Major | 6.9 | 26.9' × 14.1' | 09h55m33.2s | +69° 03′ 55″ |
| M82[99] | NGC 3034 | Cigar Galaxy | 
|
Starburst galaxy | 10,700–12,300 | Ursa Major | 8.4 | 11.2' × 4.3' | 09h55m52.2s | +69° 40′ 47″ |
| M83[100] | NGC 5236 | Southern Pinwheel Galaxy | 
|
Barred Spiral galaxy | 14,700 | Hydra | 7.6 | 12.9' × 11.5' | 13h37m00.9s | −29° 51′ 57″ |
| M84[101] | NGC 4374 | – | 
|
Lenticular galaxy | 57,000–63,000 | Virgo | 9.1 | 6.5' × 5.6' | 12h25m03.7s | +12° 53′ 13″ |
| M85[102] | NGC 4382 | – | 
|
Lenticular galaxy | 56,000–64,000 | Coma Berenices | 9.1 | 7.1' × 5.5' | 12h25m24.0s | +18° 11′ 28″ |
| M86[103] | NGC 4406 | – | 
|
Lenticular galaxy | 49,000–55,000 | Virgo | 8.9 | 8.9' × 5.8' | 12h26m11.7s | +12° 56′ 46″ |
| M87[104] | NGC 4486 | Virgo AorSmoking Gun Galaxy | 
|
Elliptical galaxy | 51,870–55,130 | Virgo | 8.6 | 7.2' × 6.8' | 12h30m49.42338s | +12° 23′ 28.0439″ |
| M88[105] | NGC 4501 | – | 
|
Spiral galaxy | 39,000–56,000 | Coma Berenices | 9.6 | 6.9' × 3.7' | 12h31m59.2s | +14° 25′ 14″ |
| M89[106] | NGC 4552 | – | 
|
Elliptical galaxy | 47,000–53,000 | Virgo | 9.8 | 5.1' × 4.7' | 12h35m39.8s | +12° 33′ 23″ |
| M90[107] | NGC 4569 | – | 
|
Spiral galaxy | 55,900–61,500 | Virgo | 9.5 | 9.5' × 4.4' | 12h36m49.8s | +13° 09′ 46″ |
| M91[108] | NGC 4548 | – | 
|
Barred Spiral galaxy | 47,000–79,000 | Coma Berenices | 10.2 | 5.4' × 4.3' | 12h35m26.4s | +14° 29′ 47″ |
| M92[109] | NGC 6341 | – | Globular cluster | 26.7 | Hercules | 6.4 | 14' | 17h17m07.39s | +43° 08′ 09.4″ | |
| M93[110] | NGC 2447 | Critter Cluster | 
|
Open cluster | 3.6 | Puppis | 6.0 | 10' | 07h44.6m | −23° 52′ |
| M94[111] | NGC 4736 | Crocodile EyeorCat's Eye Galaxy | 
|
Spiral galaxy | 14,700–17,300 | Canes Venatici | 8.2 | 11.2' × 9.1' | 12h50m53.1s | +41° 07′ 14″ |
| M95[112] | NGC 3351 | – | 
|
Barred Spiral galaxy | 31,200–34,000 | Leo | 9.7 | 3.1' × 2.9' | 10h43m57.7s | +11° 42′ 14″ |
| M96[113] | NGC 3368 | – | 
|
Spiral galaxy | 28,000–34,000 | Leo | 9.2 | 7.6' × 5.2' | 10h46m45.7s | +11° 49′ 12″ |
| M97[114] | NGC 3587 | Owl Nebula | 
|
Planetary nebula | 2.03 | Ursa Major | 9.9 | 3.4' × 3.3' | 11h14m47.734s | +55° 01′ 08.50″ |
| M98[115] | NGC 4192 | – | Spiral galaxy | 44,400 | Coma Berenices | 10.1 | 9.8' × 2.8' | 12h13m48.292s | +14° 54′ 01.69″ | |
| M99[116] | NGC 4254 | St. Catherine's Wheel | 
|
Spiral galaxy | 44,700–55,700 | Coma Berenices | 9.9 | 5.4' × 4.7' | 12h18m49.6s | +14° 24′ 59″ |
| M100[117] | NGC 4321 | Mirror Galaxy | 
|
Spiral galaxy | 55,000 | Coma Berenices | 9.3 | 7.4' × 6.3' | 12h22m54.9s | +15° 49′ 21″ |
| M101[118] | NGC 5457 | Pinwheel Galaxy | 
|
Spiral galaxy | 19,100–22,400 | Ursa Major | 7.9 | 28.8' × 26.9' | 14h03m12.6s | +54° 20′ 57″ |
| M102[119] | NGC 5866 | Spindle Galaxy | 
|
Lenticular galaxy | 50,000 | Draco | 9.9 | 4.7' x 1.9' | 15h06m29.5s | +55° 45′ 48″ |
| M103[120] | NGC 581 | – | 
|
Open cluster | 10 | Cassiopeia | 7.4 | 6' | 01h33.2m | +60° 42′ |
| M104[121] | NGC 4594 | Sombrero Galaxy | Spiral galaxy | 28,700–30,900 | Virgo | 8.0 | 9' x 4' | 12h39m59.4s | −11° 37′ 23″ | |
| M105[122] | NGC 3379 | – | 
|
Elliptical galaxy | 30,400–33,600 | Leo | 9.3 | 5.4' × 4.8' | 10h47m49.6s | +12° 34′ 54″ |
| M106[123] | NGC 4258 | – | 
|
Spiral galaxy | 22,200–25,200 | Canes Venatici | 8.4 | 18.6' × 7.2' | 12h18m57.5s | +47° 18′ 14″ |
| M107[124] | NGC 6171 | Crucifix Cluster | 
|
Globular cluster | 20.9 | Ophiuchus | 7.9 | 10' | 16h32m31.86s | −13° 03′ 13.6″ |
| M108[125] | NGC 3556 | Surfboard Galaxy | Barred Spiral galaxy | 46,000 | Ursa Major | 10.0 | 8.7' × 2.2' | 11h11m31.0s | +55° 40′ 27″ | |
| M109[126] | NGC 3992 | Vacuum Cleaner Galaxy | Barred Spiral galaxy | 59,500–107,500 | Ursa Major | 9.8 | 7.6' × 4.7' | 11h57m36.0s | +53° 22′ 28″ | |
| M110[127] | NGC 205 | – | 
|
Dwarf elliptical galaxy | 2,600–2,780 | Andromeda | 8.5 | 21.9' × 11.0' | 00h40m22.1s | +41° 41′ 07″ |
Star chart of Messier objects[edit]

See also[edit]
- Lists of astronomical objects
- Caldwell catalogue
- Deep-sky object
- Herschel 400 Catalogue
- New General Catalogue
References[edit]
- ^ "Original Messier Catalog of 1781".Students for the Exploration and Development of Space.10 November 2007.
- ^ Garner, Rob (18 December 2018)."Hubble's Messier catalog".Goddard SFC.NASA.Retrieved17 January2019.
- ^ Messier, Charles (16 February 1771)."Catalogue des Nébuleuses et des amas d'Étoiles, que l'on découvre parmi les Étoiles fixes, sur l'horizon de Paris. Observées à l'Observatoire de la Marine, avec differens instrumens".Histoire de l'Académie Royale des Sciences.Avec les Mémoires de Mathématique & de Physique, pour la même Année, Tirés des Registres de cette Académie. année 1774. Paris, FR: L'Imprimerie Royale: 435.Retrieved7 January2021– via Gallica (Archives de l'Académie des sciences).
- ^abc "Charles Messier's original catalog of 1771".Students for the Exploration and Development of Space(SEDS).15 June 2007.Retrieved5 November2015.
- ^ "Messier catalog".Encyclopædia Britannica.Retrieved27 May2015.
- ^ Gingerich, Owen (September 1953)."Messier and his catalogue II".Sky & Telescope.No. 142 – via archive.org.
- ^ Messier, Charles (1780)."Catalogue des Nébuleuses et des amas d'Étoiles, Observées à Paris, par M. Messier, à l'Observatoire de la Marine, hôtel de Clugni, rue des Mathurins".Connoissance des Temps.pour l'année commune 1783. Paris, FR: L'Imprimerie Royale:225–249, &408– via Gallica (Archives de l'Académie des sciences).
- ^ab Messier, Charles (1781)."Catalogue des Nébuleuses et des amas d'Étoiles, Observées à Paris, par M. Messier, à l'Observatoire de la Marine, hôtel de Clugni, rue des Mathurins".Connoissance des Temps, ou Connoissance des mouvemens célestes.pour l'année bissextile 1784. Paris, FR: L'Imprimerie Royale: 227–267.Bibcode:1781cote.rept..227M– via Gallica.
- ^ "The Messier Catalogue".SEDS Messier Database.SEDS.27 May 2015.
- ^ Moore, Patrick (1979).The Guinness Book of Astronomy.Guinness Superlatives.ISBN978-0-900424-76-2– via archive.org.
- ^ Moore, Patrick (1979).The Guinness Book of Astronomy.Guinness Superlatives.ISBN0-900424-76-1– via archive.org.
- ^ Frommert, Hartmut (10 May 1995)."Messier 102".MSFC X-Ray Astronomy (InterNetNews)(Press release).Retrieved24 February2019– viaSEDS.
- ^ English, Neil (2018).Chronicling the Golden Age of Astronomy: A history of visual observing from Harriot to Moore.Springer. p. 91.ISBN978-3319977072.Retrieved9 October2019.
- ^ Finlay, W.H. (2003).Concise Catalog of Deep-sky Objects: Astrophysical information for 500 galaxies.Springer.ISBN1-85233-691-9.
- ^ "The Messier Marathon".Students for the Exploration and Development of Space(SEDS). 19 March 2013.Retrieved17 May2014.
- ^ Stoyan, Ronald; Binnewies, Stefan; Friedrich, Susanne (2008).Atlas of the Messier Objects: Highlights of the Deep Sky.Cambridge University Press.ISBN9783319977072.
- ^"Messier 1".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved17 March2014.
- ^"Messier 2".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved17 March2014.
- ^"Messier 3".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved17 March2014.
- ^"Messier 4".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved17 March2014.
- ^"Messier 5".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved17 March2014.
- ^"Messier 6".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved17 March2014.
- ^"Messier 7".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved17 March2014.
- ^Stoyan, Ronald (2008).Atlas of the Messier Objects: Highlights of the Deep Sky.Cambridge University Press. p. 88.ISBN978-0521895545.
- ^"Messier 9".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved17 March2014.
- ^"Messier 10".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved17 March2014.
- ^O'Meara, Stephen James; Levy, David H. (1998),Deep-Sky Companions: The Messier Objects,Cambridge University Press, p. 65,ISBN978-0521553322.
- ^"Messier 12".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved17 March2014.
- ^"Messier 13".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved17 March2014.
- ^"Messier 14".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved17 March2014.
- ^"Messier 15".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved17 March2014.
- ^"Messier 16".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved17 March2014.
- ^"Messier 17".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved17 March2014.
- ^"Messier 18".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved17 March2014.
- ^"Messier 19".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved17 March2014.
- ^"Messier 20 (The Trifid Nebula)".Hubble's Messier Catalog.6 October 2017.Retrieved28 April2022.
- ^"Messier 21".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved17 March2014.
- ^"Messier 22".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved17 March2014.
- ^Thompson, Robert; Thompson, Barbara (2007),Illustrated Guide to Astronomical Wonders: From Novice to Master Observer,DIY science, O'Reilly Media, Inc., p. 408,ISBN978-0596526856
- ^French, Sue (July 2015)."Small Sagittarius star cloud: The Sagittarius Milky Way is host to dark nebulae and open clusters".Sky & Telescope.p. 56.
- ^"Messier 25".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved17 March2014.
- ^"Messier 26".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved17 March2014.
- ^"Messier 27".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved17 March2014.
- ^"Messier 28".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved17 March2014.
- ^"Messier 29".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved17 March2014.
- ^"Messier 30".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved17 March2014.
- ^"Messier 31".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved17 March2014.
- ^"Messier 32".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved17 March2014.
- ^"Messier 33".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved17 March2014.
- ^"Messier 34".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved17 March2014.
- ^"Messier 35".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved17 March2014.
- ^"Messier 36".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved17 March2014.
- ^"Messier 37".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved17 March2014.
- ^"Messier 38".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved17 March2014.
- ^"Messier 39".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved17 March2014.
- ^"Messier 40".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved17 March2014.
- ^"Messier 41".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved17 March2014.
- ^"Messier 42".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved17 March2014.
- ^"Messier 43".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved17 March2014.
- ^"Messier 44".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved17 March2014.
- ^"Messier 45".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved17 March2014.
- ^"Messier 46".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved17 March2014.
- ^Stoyan, Ronald (2008).Atlas of the Messier Objects: Highlights of the Deep Sky.Cambridge University Press. p. 195.ISBN978-0521895545.
- ^"Messier 48".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved17 March2014.
- ^"Messier 49".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved17 March2014.
- ^"Messier 50".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved17 March2014.
- ^"Messier 51".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^"Messier 52".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^"Messier 53".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^"Messier 54".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^"Messier 55".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^"Messier 56".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^"Messier 57".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^"Messier 58".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^"Messier 59".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^"Messier 60".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^"Messier 61".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^"Messier 62".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^"Messier 63".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^"Messier 64".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^"Messier 65".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^"Messier 66".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^"Messier 67".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^"Messier 68".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^"Messier 69".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^"Messier 70".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^"Messier 71".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^"Messier 72".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^"Messier 73".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^"Messier 74".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^"Messier 74 Phantom Galaxy".24 July 2015.Retrieved20 April2020.
- ^"Messier 75".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^"Messier 76".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^"Messier 77".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^"Messier 78".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^"Messier 79".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^"Messier 80".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^"Messier 81".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^"Messier 82".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^"Messier 83".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^"Messier 84".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^"Messier 85".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^"Messier 86".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^"Messier 87".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^"Messier 88".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^"Messier 89".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^"Messier 90".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^"Messier 91".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^"Messier 92".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^"Messier 93".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^"Messier 94".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^"Messier 95".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^"Messier 96".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^"Messier 97".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^"Messier 98".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^"Messier 99".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^"Messier 100".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^"Messier 101".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^"Messier 102".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved28 December2016.
- ^ "Messier 103".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^"Messier 104".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^ "Messier 105".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^ "Messier 106".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^"Messier 107".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^ "Messier 108".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^"Messier 109".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
- ^"Messier 110".SEDS Messier catalog.Retrieved18 March2014.
External links[edit]
- "SEDS Messier Database".Students for the Exploration and Development of Space(SEDS).— includes images
- "Messier gallery".Messier Objects 101.
- "Messier objects".Deep Sky Videos.
- "Messier objects".Constellation Guide.
- "Messier Objects Ranked By Viewing Difficulty".Starlust.

