October 2015 Hindu Kush earthquake
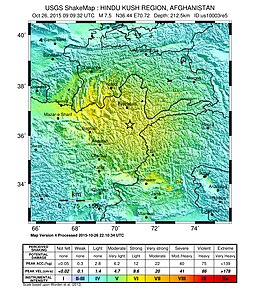 | |
| UTCtime | 2015-10-26 09:09:42 |
|---|---|
| ISCevent | 612180979 |
| USGS-ANSS | ComCat |
| Local date | 26 October 2015 |
| Local time | 13:39AFT,14:09PKT,14:39IST[1][2] |
| Magnitude | 7.5Mw[1][2] |
| Depth | 231.0 km (143.5 mi)[1] |
| Epicenter | 36°31′26″N70°22′05″E/ 36.524°N 70.368°E[1] |
| Type | Reverse[1] |
| Areas affected | |
| Max.intensity | MMI VII (Very strong) |
| Casualties | 399 deaths and 2,536 injured |
TheOctober 2015 Hindu Kush earthquakewas amagnitude7.5earthquake[1][2]that struck South Asia on 26 October 2015, at 13:39AFT(14:09PKT;14:39IST;09:09UTC)[1][2][3]with theepicenter45 km north ofKuran wa Munjan,Afghanistan,[4][5]at a depth of 231.0 km.[6]
By 5 November, it was estimated that at least 399 people were killed, mostly inPakistan.[7][8][9][10]Tremors were felt in Pakistan,Uzbekistan,Turkmenistan,[11]TajikistanandKyrgyzstan.[12][13][14]According to theUnited States Geological Survey(USGS), Pakistan is located in one of the most earthquake active zones in the world.[15]The earthquake was also felt inNew Delhi,in both Pakistan'sAzad Kashmirterritory, and the Indian state ofJammu and Kashmirand as far asLucknowand in the prefectures ofKashgar,Aksu,Hotan,andKizilsuinXinjiang,Chinawhile damage was also reported in Afghan capitalKabul.[8][16]The earthquake was also felt in the Nepalese capital ofKathmandu.
Background[edit]
TheHimalayanmountains, pushed up by the collision of tectonic plates, are prone to devastating quakes.An earthquake in April 2015,Nepal's worst in 80 years, killed over 8,600 people.[17]
The lastmajor earthquake in the same regionof similar magnitude (7.6Mw) was almost exactly ten years prior in October 2005, which resulted in 87,351 deaths, 75,266 injured, 2.8 million people being displaced, and 250,000 farm animals dying. The notable difference between this earthquake and the2005 earthquakeis the focal depth and its location with respect to the densely populated areas.[18]The 2005 earthquake was 15 km deep and centered close to some densely populated areas while this earthquake was 212.5 km deep and centered farther from populated areas, reducing its damaging effects.[19]
In recent studies, geologists claim thatglobal warmingis one of the reasons forincreased seismic activity.According to these studies melting glaciers and rising sea levels disturb the balance of pressure on Earth's tectonic plates thus causing an increase in the frequency and intensity of earthquakes. This could be one of the reasons why theHimalayasare getting more prone to earthquakes in recent years.[20][better source needed]
Earthquake[edit]
The main earthquake occurred on 26 October 2015 at 13:39AFT(14:09PKT,14:39IST,09:09UTC)[1][2]at a depth of approximately 231.0 km, with its epicenter approximately 82 km southeast ofFeyzabad,Afghanistan. The USGS initially measured the quake's magnitude at 7.7, then revised it down to 7.6 and later to 7.5. ThePakistan Meteorological Department,however, said the magnitude of the earthquake was 8.1.[21]According to USGS, the epicentre was 67 km fromChitral.[22][23][24]
Damage and casualties[edit]
Afghanistan[edit]
| Province | Deaths | Injuries |
|---|---|---|
| Badakhshan | 9 | 21 |
| Baghlan | 0 | 8 |
| Kabul | 0 | 21 |
| Kunar | 22 | 64 |
| Laghman | 4 | 0 |
| Nangarhar | 8 | 82 |
| Nuristan | 4 | 0 |
| Parwan | 0 | 30 |
| Takhar | 12 | 39 |
| Unspecified | 56 | 273 |
At least 115 people were killed and 538 others were injured inAfghanistan.[8][9]Among the fatalities were five inJalalabad,and 12 schoolgirls aged 10 to 15 who died in acrowd crushwhile trying to exit a school building inTakhar.[9][non-primary source needed][26][27][25]
Pakistan[edit]
The earthquake resulted in 280 fatalities, 1,770 injuries, and damage to 109,123 buildings.[7][28]There were 202 deaths and 1,486 injuries inKhyber Pakhtunkhwa;30 deaths and 59 injured in theFederally Administered Tribal Areas;nine deaths and 30 injuries inGilgit-Baltistan;five deaths and 78 injuries inPunjaband two deaths and 12 injuries inAzad Kashmir.[25]The most affected areas from Khyber Pakhtunkhwa includeShangla,Lower Dir,Upper Dir,SwatandChitral,which were in close proximity of the epicenter.[29][28]As a result of land sliding, theKarakoram Highwaywas closed.[30]The observed damage was mostly concentrated in rural and old urban masonry buildings, both being built with no or minimal consideration for earthquake loading and having been constructed employing poor construction practices.[31]
India[edit]
Four people were killed and 20 others were injured inJammu and Kashmir.[10]ADelhi Metrospokesman told AFP "All of around 190 trains plying on the tracks were stopped at the time of the earthquake." Mobile phone services were choked for several hours because of the high voice traffic.[32]
Tajikistan[edit]
InTajikistan,14 children suffered injuries inYovon Districtwhen stairs at a local school collapsed.[33]
Rescue and relief[edit]
 Pakistan
Pakistan- Pakistani Prime MinisterNawaz Sharifdirected all federal, civil, military and provincial agencies to declare an immediate alert and mobilise all resources to ensure the security of citizens of Pakistan. According toInter-Services Public Relations,Chief of Army Staff GeneralRaheel Sharifhas directed army personnel to reach out where required to help affected people without waiting for orders.[22][23]
 Afghanistan
Afghanistan- Chief executive officer of AfghanistanAbdullah Abdullahcalled an emergency meeting of senior officials to respond to the disaster.[34]
 India
India- The Indian Prime Minister,Narendra Modi,contacted Afghan PresidentAshraf Ghaniand Pakistani Prime MinisterNawaz Sharifand offered help.[35]
 United Nations
United Nations- According to UN Secretary-GeneralBan Ki-moon,UN agencies are mobilizing to assist Pakistani and Afghan relief operations.[36]
See also[edit]
- List of earthquakes in 2015
- List of earthquakes in Afghanistan
- List of earthquakes in Pakistan
- Thrust tectonics
References[edit]
- ^abcdefgh"M7.5 – 45 km N of 'Alaqahdari-ye Kiran wa Munjan, Afghanistan".United States Geological Survey.26 October 2015.
- ^abcdeNational Geophysical Research Institute (26 October 2015)."afg.doc"(PDF).Archived fromthe original(PDF)on 3 March 2016.Retrieved28 October2015.
- ^"M 7.7 Earthquake 45 km SSW of Jarm, Afghanistan".26 October 2015.
- ^"Map of the earthquake M7.5 – 45 km N of 'Alaqahdari-ye Kiran wa Munjan, Afghanistan".26 October 2015.
- ^"M7.5 – 45 km N of 'Alaqahdari-ye Kiran wa Munjan, Afghanistan".United States Geological Survey.26 October 2015.Retrieved26 October2015.
- ^"Pakistan and Afghanistan rocked by Earthquake".The Guardian.26 October 2015.Retrieved26 October2015.
- ^ab"Live Updates".ndma.gov.pk.Archived fromthe originalon 21 November 2015.Retrieved5 January2015.
- ^abc"The Latest: UN Mobilizing to Aid Quake Victims".ABC News.Associated Press.26 October 2015.Retrieved26 October2015.
- ^abc"115 killed & 538 injured; 7,630 homes,12 schools, 17 mosques, 20 office buildings have been damaged in 9 provinces by #AfghanistanEarthquake".president.gov.af. 27 October 2015.
- ^ab"Earthquake claims four lives in Jammu and Kashmir, 20 others injured".Firstpost. 27 October 2015.Retrieved27 October2015.
- ^"PRI.org: It's your world. Jump in. | Public Radio International".worldnews.org.Retrieved29 October2015.
- ^Jon Boone (26 October 2015)."Strong earthquake in Afghanistan causes tremors across region Powerful quake felt in Pakistan, Afghanistan and India but full extent of impact not yet known".The Guardian.
- ^"7.5 magnitude earthquake hits Hindu Kush in Afghanistan".The Times of India.26 October 2015.
- ^"Deaths, damage reported in powerful Afghanistan quake".CNN.26 October 2015.Retrieved26 October2015.
- ^"Pakistan in the most active quake zone, says US Geological Survey".Dawn.Pakistan. 27 October 2015.Retrieved28 October2015.
- ^"A phú hãn phát sinh 7.8 cấp cường chấn tân cương nam bộ đa địa chấn cảm cường liệt".Xinhua News Agency. Archived fromthe originalon 28 October 2015.Retrieved26 October2015.
- ^"Nepal earthquake death toll reaches 8,635, over 300 missing".The Indian Express.Press Trust of India.23 May 2015.Retrieved30 October2015.
- ^Ismail, Najif; Khattak, Nouman (26 December 2015)."Reconnaissance report on the Mw 7.5 Hindu Kush earthquake of 26th October 2015 and the subsequent aftershocks"(PDF).United Arab Emirates University,Al Ain /Earthquake Engineering Research Institute.Retrieved6 August2019.
- ^"Afghanistan Struck by Powerful Earthquake".The New York Times.26 October 2015.Retrieved26 October2015.
- ^"Nepal earthquake could have been manmade disaster climate change brings".Newsweek.Retrieved19 December2015.
- ^"8.1 magnitude earthquake strikes Pakistan".Daily Times.Retrieved27 October2015.
- ^ab"Over 139 dead as 7.5 magnitude earthquake jolts Pakistan".Dawn.Pakistan. 26 October 2015.Retrieved26 October2015.
- ^ab"Strong earthquake in remote northern Afghanistan felt across Asia, more than 150 dead – CTV News".CTVNews.26 October 2015.Retrieved26 October2015.
- ^"Latest earthquakes".PMDNMCC.Pakistan Meteorological Department. Archived fromthe originalon 29 October 2015.Retrieved27 October2015.
- ^abc"Afghan, Pakistan Officials Assess Quake Damage".Voice of America.27 October 2015.Retrieved2 May2023.
- ^"Nearly 280 dead as powerful earthquake jolts Afghanistan, Pakistan".The Economic Times.27 October 2015. Archived fromthe originalon 29 October 2015.Retrieved27 October2015.
- ^Schmitz, Melanie (26 October 2015)."The Afghan Schoolgirls Killed in an Earthquake Were The Victims of a Devastating Panic".Bustle.Retrieved28 October2015.
- ^abIsmail, Najif; Khattak, Nouman (25 August 2016). "Building typologies prevalent in Northern Pakistan and their performance during the 2015 Hindu Kush Earthquake".Earthquake Spectra.32(4): 2473–2493.Bibcode:2016EarSp..32.2473I.doi:10.1193/012116eqs022m.S2CID113440383.
- ^"Pakistan and Afghanistan rocked by earthquake – live updates".The Guardian.26 October 2015.Retrieved26 October2015.
- ^"LIVE: Hundreds feared dead as 7.5-magnitutude earthquake strikes Pakistan, Afghanistan".The Tribune.26 October 2015.Retrieved26 October2015.
- ^Ismail, Najif; Khattak, Nouman (14 September 2016)."Observed failure modes of unreinforced masonry buildings during the 2015 Hindu Kush earthquake".ResearchGate.in press.ISSN1671-3664.
- ^Desk, Internet (26 October 2015)."Massive earthquake kills 105 across South Asia".The Hindu.Retrieved27 October2015.
- ^"14 children suffered minor injuries".Radiofreeeurope/Radioliberty.Firstpost.Retrieved1 November2015.
- ^"Powerful Earthquake Shakes Afghanistan, Pakistan".The Wall Street Journal.26 October 2015.Retrieved26 October2015.
- ^"PM Narendra Modi calls up J&K CM Mufti, offers help to quake-hit Pakistan, Afghanistan".Daily News and Analysis.26 October 2015.Retrieved26 October2015.
- ^"Statement attributable to the Spokesman for the Secretary-General on earthquake in South Asia".United Nations. 26 October 2015.Retrieved27 October2015.
External links[edit]
- Detailed reportfrom theUnited States Geological Survey
- Technical reportfrom theNational Geophysical Research Institute
- Satellite imagery map of the region affected by the earthquakefromNASA
- TheInternational Seismological Centrehas abibliographyand/orauthoritative datafor this event.
- ReliefWeb'smain pagefor this event.
- 2015 earthquakes
- 2015 in Afghanistan
- 2015 disasters in Pakistan
- 2015 disasters in India
- Earthquakes in Afghanistan
- Earthquakes in Pakistan
- Earthquakes in Tajikistan
- Earthquakes in India
- October 2015 events in Asia
- October 2015 events in Afghanistan
- October 2015 events in India
- October 2015 events in Pakistan
- Hindu Kush


