Parotid duct
| Parotid duct | |
|---|---|
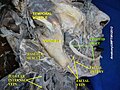
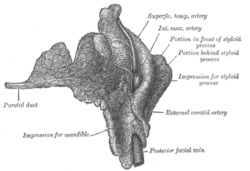 Right parotid gland. Deep and anterior aspects. (Parotid duct labeled at center left.) | |
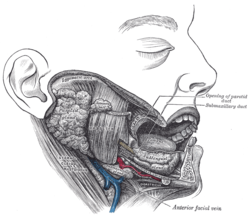 Dissection, showing salivary glands of right side. (Parotid duct visible at center.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | ductus parotideus |
| TA98 | A05.1.02.007 |
| TA2 | 2805 |
| FMA | 10420 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Theparotid ductorStensen ductis a salivary duct. It is the route thatsalivatakes from the majorsalivary gland,theparotid gland,into themouth.[1]It opens into the mouth opposite thesecond upper molar tooth.
Structure
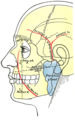
[edit]The parotid duct is formed when several interlobular ducts, the largest ducts inside theparotid gland,join. It emerges from the parotid gland. It runs forward along thelateralside of themasseter musclefor around 7 cm.[2]In this course, the duct is surrounded by thebuccal fat pad.[2][3]It takes a steep turn at the border of the masseter and passes through thebuccinator muscle,opening into thevestibule of the mouth,the region of the mouth between thecheekand thegums,at the parotid papilla, which lies across the second maxillary (upper)molar tooth.[4]The exit of the parotid ducts can be felt as small bumps (papillae) on both sides of the mouth that usually positioned next to themaxillary second molar.[citation needed]
The buccinator acts as a valve that prevents air forcing into the duct, which would causepneumoparotitis.[5]
Relations
[edit]The parotid duct lies close to thebuccal branchof thefacial nerve(VII).[2]It is also close to thetransverse facial artery.[2]
Running along with the duct superiorly is thetransverse facial artery,and the upperbuccal nerve.The lower buccal nerve runs inferiorly along the duct.[citation needed]
Clinical significance
[edit]Blockage, whether caused bysalivary duct stonesor external compression, may cause pain and swelling of theparotid gland(parotitis).
Koplik's spotswhich are pathognomonic ofmeaslesare found near the opening of the parotid duct.
The parotid duct may be cannulated by inserting a tube through the internal orifice in themouth.[2]Dye may be injected to allow for imaging of the parotid duct.[2]
History
[edit]The parotid duct is named afterNicolas Steno(1638–1686), also known asNiels Stensen,aDanishanatomist(albeit best known as ageologist) credited with its detailed description in 1660.[6]This is where the alternative name "Stensen duct" originates from.[2][6]
Additional images
[edit]-
Outline of side of face, showing chief surface markings.
-
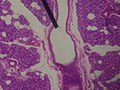
Microscopic slide of a human interlobular duct.
-
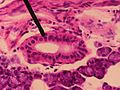
Microscopic slide of a human striated duct.
-
The left papilla (soft tissue protuberance at the exit) of the parotid duct is clearly visible on the cheek in the right of the photo.
-
Parotid duct
-
Parotid duct
-
Parotid duct
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^Nanci A (2013).Ten Cate's Oral Histology: Development, Structure, and Function.Elsevier. p. 255.ISBN978-0-323-07846-7.
- ^abcdefgSteinberg, Mark J.; Herréra, Andres F. (2005-02-01)."Management of parotid duct injuries".Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology, Oral Radiology, and Endodontology.99(2): 136–141.doi:10.1016/j.tripleo.2004.05.001.ISSN1079-2104.PMID15660081.
- ^Latarjet M, Ruiz Liard A (2005).Human Anatomy(Spanish ed.). Editorial Médica Panamericana.ISBN978-950-06-1368-2.
- ^Bath-Balogh M, Fehrenbach MJ (2011).Illustrated Dental Embryology, Histology, and Anatomy, Bath-Balogh and Fehrenbach.Elsevier. p. 135.ISBN978-1-4377-1730-3.
- ^Faizal B, Chandran MP (2012)."Pneumoparotitis"(PDF).Amrita Journal of Medicine.8(2): 1–44. Archived fromthe original(PDF)on 2015-12-11.
- ^abNatale G, Bocci G, Ribatti D (September 2017)."Scholars and scientists in the history of the lymphatic system".Journal of Anatomy.231(3): 417–429.doi:10.1111/joa.12644.PMC5554832.PMID28614587.
Further reading
[edit]- Casseri GC(1627).Tabulae anatomicae, lxxiix.Venetis.
- Stensen N(1662).Observationes anatomicae, quibus varia oris, oculorum & narium vas describuntur novique salivae, lacrymarum & muci fontes deteguntur.Lugduni Batavorum:J. Chouët.
External links
[edit]- Diagram at MSU
- ent/178ateMedicine- Parotid duct injuries
- doctor/2052atWho Named It?