Province of Lleida
Province of Lleida
| |
|---|---|
 Map of Spain with the Province of Lleida highlighted | |
| Coordinates:42°00′N1°10′E/ 42.000°N 1.167°E | |
| Country | Spain |
| Autonomous community | |
| Capital | Lleida |
| Government | |
| • President | Joan Talarn i Gilabert[2](ERC) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 12,150 km2(4,690 sq mi) |
| • Rank | Ranked 18th |
| 2.41% of Spain | |
| Population (2013) | |
| • Total | 440,915[1] |
| • Rank | Ranked 33rd |
| Official languages | |
| Parliament | Cortes Generales |
| Website | www |


TheProvince of Lleida(Western Calatan:[ˈʎejða];Spanish:Lérida[ˈleɾiða];Aranese:Lhèida[ˈʎɛjda]) is one of the fourprovincesofCatalonia.It lies in northeasternSpain,in the western part of theautonomous communityofCatalonia,and is bordered by the provinces ofGirona,Barcelona,Tarragona,ZaragozaandHuescaand the country ofFranceand the principality ofAndorra.It is often popularly referred to asPonent(i.e. the West).
Of the population of 414,015 (2007), about 30% live in the capital,Lleida.Some other towns in the province of Lleida areLa Seu d'Urgell(thearchbishopof which is also the co-prince ofAndorra),Mollerussa,Cervera,Tàrrega,andBalaguer.There are 231 municipalities in Lleida.
Located in thePyrenees,theAran Valleyis a specialcomarcawith greater autonomy and withAranese,a variety ofOccitan,as its official language.
TheAigüestortes i Estany de Sant Maurici National Parkis located in this province.
The province enjoys a thriving fruit-growing industry, including pears and peaches.
According to the 2006Statute of Autonomy of Catalonia,the provinces of Catalonia are due to be superseded by territorial units (unitats territorials) orvegueriesbased on a more historical political division, and the province of Lleida would become two territorial units:Ponentor Terres de Lleida Vegueria (the entire southern area) andAlt Pirineu i AranVegueria (the entire northern part plus thecomarcaofCerdanya,part of which is currently in theProvince of Girona), the county of Solsona going to theComarques Centrals(Central Counties) Vegueria. The plan is currently on hold as of 2015.
Language[edit]
The province of Lleida has a characteristicCatalandialect popularly known aslleidatà,withlo/losused as the masculinedefinite articleinstead ofel/elsas well as its pronunciation in a large number of words. One example of the pronunciation is theaat the end of the word that is pronounced like ane.The local dialect, properly known asNorth-Western Catalan,is part of theWestern Catalanblock, and as such, shares some features withValencian(whose dialects are also part of that group).
Lleida is the only province in Catalonia to have a second native language:Occitan,in theAran Valley.
| Largest groups of foreign residents | |
| Nationality | Population (2022) |
|---|---|
| 20,469 | |
| 18,783 | |
| 5,400 | |
| 3,456 | |
| 3,127 | |
| 2,638 | |
Tourism[edit]
Lleida is located in the western part ofCataloniaand in the northeast of theIberian Peninsula,betweenBarcelonaandMadrid,and not far fromZaragoza.It borders France andAndorrato the north. This is a popular destination for mountain activities such as skiing andadventure sports.
Nature[edit]
Lleida has a wide variety of landscapes. This includes the mountain area of thePyrenees.TheAigüestortes i Estany de Sant Maurici National Park,the only National Park in Catalonia, and theAlt Pirineu(High Pyrenees) andCadí-Moixerónatural parks are all in the Pyrenees region. The Collegats-Terradets Territorial Park, the Boumort Natural Hunting Reserve and the Congost de Mont-rebei gorge are in thePre-Pyrenees.
In contrast, the Lleida Plain has more peaceful landscapes. In some cases, these are rather sober, while in others there is fertile land with century-old olive trees, fruit trees, meadows and crop fields. In this area, it is particularly relevant to highlight such spectacular settings as the Estany d'Ivars i Vila-sana pool and the Aiguabarreig (confluence) of the rivers Segre, Cinca and Ebro. On 6 January 2021, inTuc de la Llança,Spain's absolute minimum temperature of −34.1 °C (−29.4 °F) was registered.[3]
Sports[edit]
The comarques (local districts) of Lleida are also market leaders within Spain in the provision of adventure sports, with more than 170 companies organising around fifty different activities on land and water and in the air. This area is also Spain's leading ski destination.[citation needed]
Lleida has 11 different ski resorts which are marketed under the brand "Neu de Lleida" (Lleida Snow) and offer over 450 km (280 mi) of ski slopes. Their 81 ski lifts have the capacity to carry 115,000 skiers per hour, while the area immediately surrounding these winter sports complexes can also accommodate more than 30,000 visitors.[citation needed]
Culture[edit]
Lleida has a rich architectural heritage. The churches of theVall de Boihave been declared part of aUNESCO World Heritage Site.Recently Lleida has started many new initiatives for tourists. These include: the Centre d'Observació de l'Univers (Centre for Observing the Universe), or PAM, of Montsec, which is an ambitious project that combines research, education and diffusion within the field of cultural and scientific tourism; the establishment of the Tren dels Llacs (Lakes Train), a touristic railway that connects the provincial capital to the Pre-Pyrenees; the creation of new exhibition spaces (including theMuseum of Lleida,the Paper Dresses Museum of Mollerussa and the Skiing Museum of the Val d'Aran); the organisation of routes to help discover the natural, cultural and monumental treasures of Lleida (with the Castles of Sió Route, the Pyrenean Counties and Nostalgic Pallars Route, the Wine Route of Les Garrigues, and the Literary Routes of Pallars, etc.); and also projects to promote excellence in the field of tourism, such as the Network of Villages with Charm.
The city of Lleida[edit]

Lleida,the capital of the province, is notable for its historical-architectural legacy, which includes buildings such as theSeu Vella(old cathedral) and theKnights TemplarCastle of Gardeny. These buildings coexist with modern constructions such asLa Llotja,a congress and conference centre. Other city landmarks include the diocese and county museum (which has a collection of Roman, Islamic, Romanesque, Gothic, Renaissance and Baroque artefacts and paintings), the Jaume Morera Museum of Modern Art, and the "Roda Roda" Automobile Museum.
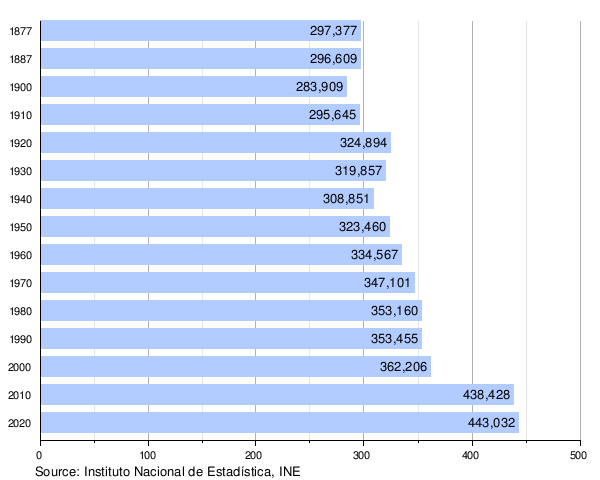
Population development[edit]
The historical population is given in the following chart:
Notes and references[edit]
- ^Population Figures referring to Municipal Register 1 January 2013Archived6 October 2014 at theWayback Machine– Instituto Nacional de Estadística. (National Statistics Institute)
- ^"Biografia – Joan Talarn i Gilabert".Retrieved6 March2021.
- ^"Meteo Valls d'àneu"(in Spanish). Meteo Valls d'Àneu.Retrieved6 January2021.


