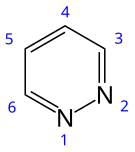
Pyridazine
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Pyridazine[1] | |||
| Systematic IUPAC name
1,2-Diazabenzene | |||
| Other names
1,2-Diazine
Orthodiazine Oizine | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| 103906 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.478 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| 49310 | |||
PubChemCID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard(EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C4H4N2 | |||
| Molar mass | 80.090g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless liquid | ||
| Density | 1.107 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | −8 °C (18 °F; 265 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 208 °C (406 °F; 481 K) | ||
| miscible | |||
| Solubility | miscible indioxane,ethanol soluble inbenzene,diethyl ether negligible incyclohexane,ligroin | ||
Refractive index(nD)
|
1.52311 (23.5 °C) | ||
| Thermochemistry | |||
Std enthalpy of
formation(ΔfH⦵298) |
224.9 kJ/mol | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHSlabelling:[2] | |||

| |||
| Warning | |||
| H302,H315,H319,H335 | |||
| P261,P264,P264+P265,P270,P271,P280,P301+P317,P302+P352,P304+P340,P305+P351+P338,P319,P321,P330,P332+P317,P337+P317,P362+P364,P403+P233,P405,P501 | |||
| Flash point | 85 °C (185 °F; 358 K) | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds
|
|||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in theirstandard state(at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Pyridazineis anaromatic,heterocyclic,organic compoundwith the molecular formulaC4H4N2.It contains a six-memberedringwith two adjacentnitrogenatoms.[3]It is a colorless liquid with aboiling pointof 208 °C. It isisomericwith two otherdiazine(C4H4N2) rings,pyrimidineandpyrazine.
Occurrence
[edit]Pyridazines are rare in nature, possibly reflecting the scarcity of naturally occurringhydrazines,common building blocks for the synthesis of these heterocycles. The pyridazine structure is a popularpharmacophorewhich is found within a number of herbicides such ascredazine,pyridafolandpyridate.It is also found within the structure of several drugs such ascefozopran,cadralazine,minaprine,pipofezine,andhydralazine.
Synthesis
[edit]In the course of his classic investigation on theFischer indole synthesis,Emil Fischer prepared the first pyridazine via the condensation ofphenylhydrazineandlevulinic acid.[4]The parent heterocycle was first prepared by oxidation ofbenzocinnolineto the pyridazinetetracarboxylic acid followed bydecarboxylation.A better route to this otherwise esoteric compound starts with themaleic hydrazide.These heterocycles are often prepared via condensation of 1,4-diketonesor 4-ketoacids withhydrazines.[5]
References
[edit]- ^"Front Matter".Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book).Cambridge:The Royal Society of Chemistry.2014. p. 141.doi:10.1039/9781849733069-FP001.ISBN978-0-85404-182-4.
- ^"Pyridazine".pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.
- ^Gumus, S. (2011)."A computational study on substituted diazabenzenes"(PDF).Turk J Chem.35:803–808. Archived fromthe original(PDF)on 2016-03-03.Retrieved2014-04-10.
- ^Fischer, E. (1886)."Indole aus Phenylhydrazin".Justus Liebigs Annalen der Chemie.236(1–2): 126–151.doi:10.1002/jlac.18862360107.
- ^Tišler, M.; Stanovnik, B. (1968). "Pyridazines".Advances in Heterocyclic Chemistry Volume 9.Vol. 9. pp. 211–320.doi:10.1016/S0065-2725(08)60374-8.ISBN9780120206094.