Redoubt
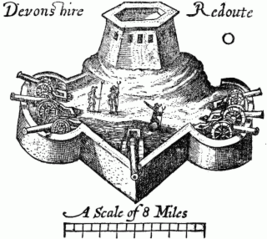
Aredoubt(historicallyredout)[1][2]is afort or fort systemusually consisting of an enclosed defensive emplacement outside a larger fort, usually relying onearthworks,although some are constructed of stone or brick.[3]It is meant to protect soldiers outside the main defensive line and can be a permanent structure or a hastily constructed temporary fortification. The word means "a place of retreat".[2]Redoubts were a component of the military strategies of most European empires during the colonial era, especially in the outer works ofVauban-style fortresses made popular during the 17th century, although the concept of redoubts has existed sincemedieval times.A redoubt differs from aredanin that the redan is open in the rear, whereas the redoubt was considered an enclosed work.[4]
Historically important redoubts[edit]
English Civil War[edit]
During theEnglish Civil War,redoubts were frequently built to protect older fortifications from the more effective artillery of the period. Often close to ancient fortifications, there were small hills that overlooked the defences, but in previous centuries, they had been too far from the fortifications to be a threat. A small hill close to Worcester was used as an artillery platform by theParliamentarianswhen they successfullybesieged Worcester in 1646.In 1651 before theBattle of Worcesterthe hill was turned into a redoubt by theRoyalists,(the remains of which can be seen today inFort Royal Hill Park).
During the battle, the Parliamentarians captured the redoubt and turned its guns on Worcester. In so doing they made the defence of the city untenable. That action effectively ended the battle, the last of theEnglish Civil War.
Malta[edit]

From 1715 onwards, theOrder of Saint Johnbuilt a number of redoubts inMalta,as part of an effort to improve thecoastal fortificationsof the islands. They were built in the middle of bays to prevent enemy forces from disembarking and outflanking thecoastal batteries.[5]
The design of the redoubts was influenced by ones built in the French colonies. In all, eleven pentagonal redoubts and a few semi-circular or rectangular ones were built. Most redoubts have been demolished over the years, but a few still survive, such asBriconet Redoubt,Saint George RedoubtandXimenes Redoubt.[6]
Fourtour-reduitswere also built. These were redoubts built in the form of a tower, with rows of musketry loopholes. Three were aroundMarsaxlokkBay, and one was located inMarsalforn,Gozo.The only one still in existence isVendôme Towerin Marsaxlokk.[7]
During thesiege of Malta of 1798–1800,Maltese insurgents builta number of fortificationsto bombard French positions and repel a possible counterattack. Most of the fortifications were batteries, but at least two redoubts,Windmill RedoubtandŻabbar Redoubt,were also built. In 1799, British forces also builtSan Rocco RedoubtandSan Lucian Redoubtin Malta. No redoubts from the French blockade survive today.[8]
In the late 19th century, the British built a redoubt nearFomm ir-Riħas part of theVictoria Lines.[9]
Other important redoubts[edit]

The American Revolution defenses atWest Point,New York included several redoubts, forts, and theGreat Chainwith links weighing more than 100 pounds each that Continental Army military engineers stretched across the Hudson River. The purpose behind the West Point defensive system was to prevent the British Army and Royal Navy from gaining control of the Hudson and splitting New England off from the mid-Atlantic and southern states. The chain blocked the river, the forts were positioned to fire on ships attempting to approach the chain, and outlying redoubts were well placed to defend land routes into West Point.[10]
Examples where redoubts played a crucial role in military history:
- Battle of Poltava(1709)
- Battle of Bunker Hill(1775)
- Battle of Saratoga(1777)
- Battle of Yorktown(1781) in whichAlexander Hamiltonled his only infantry command's assault against a British redoubt
- Lines of Torres Vedrasof thePeninsular War(1809–1810)
- Harwich Redoubt(1809–1810)
- Battle of Borodino(1812)
- Charge of the Light Brigade(1854)
- Railroad Redoubtof theBattle of Vicksburg(1863)
- Battle of Plevna(1877–1878)
- Battle of Rorke's Drift(1879)
- DuringWorld War I:National Redoubt of Antwerp(1914), GermanHohenzollern Redoubt,andHawthorn Ridge Redoubt(1916)
- DuringWorld War II:Vercors Plateauredoubt used by theFree French Forces
National redoubt[edit]
A national redoubt is an area to which the remnant forces of a nation can be withdrawn if the main battle has been lost, or beforehand if defeat is considered inevitable. Typically a region is chosen with a geography favouring defence, such as a mountainous area or a peninsula, in order to function as a final hold-out to preserve national independence for the duration of the conflict.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^"Browse 1828 => Word REDOUT:: Search the 1828 Noah Webster's Dictionary of the English Language".1828.mshaffer.com. 3 June 2012.Retrieved3 June2012.
- ^ab"Online Etymology Dictionary: redoubt".Etymonline.com.Retrieved6 September2012.
- ^"Dictionary of Fortifications: Redoubt".Civil War Field Fortifications flair Website.September 2005. Archived fromthe originalon 19 January 2010.
- ^"Field Fortification: On The Trace Of Field Fortifications".Civil War Field Fortifications Website.March 2003. Archived fromthe originalon 9 January 2010.
- ^Debono, Charles."Coastal Redoubts".Mellieha.com.Archived fromthe originalon 23 September 2018.Retrieved23 April2015.
- ^Spiteri, Stephen C. (10 April 2010)."18th Century Hospitaller Coastal Batteries".MilitaryArchitecture.com.Archived fromthe originalon 8 November 2015.Retrieved23 April2015.
- ^"Vendôme Tower"(PDF).Mare Nostrum.Archived fromthe original(PDF)on 31 May 2015.Retrieved23 April2015.
- ^Spiteri, Stephen C. (May 2008)."Maltese 'siege' batteries of the blockade 1798–1800"(PDF).Arx – Online Journal of Military Architecture and Fortification(6): 30–46. Archived fromthe original(PDF)on 26 November 2016.Retrieved23 April2015.
- ^Spiteri, Stephen C."Naxxar and its fortifications".MilitaryArchitecture.com.Archived fromthe originalon 16 January 2016.Retrieved29 January2016.
- ^Ruppert, Bob (11 January 2016)."Redoubt No. 4: Lynchpin of Fortress West Point".Journal of the American Revolution.Retrieved8 February2016.
