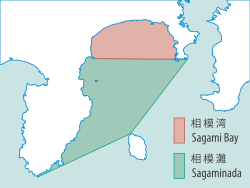
Sagami Bay

Sagami Bay(Tương mô loan,Sagami-wan,also known as theSagami GulforSagami Sea)lies south ofKanagawa PrefectureinHonshu,centralJapan,contained within the scope of theMiura Peninsula,in Kanagawa, to the east, theIzu Peninsula,inShizuoka Prefecture,to the west, and theShōnancoastline to the north, while the island ofIzu Ōshimamarks the southern extent of the bay. It lies approximately 40 kilometres (25 mi) southwest of the capital,Tokyo.Cities on the bay includeOdawara,Chigasaki,Fujisawa,Hiratsuka,Itō,andKamakura.
History
[edit]The center of theGreat Kantō earthquakein 1923 was deep beneathIzu ŌshimaIsland in Sagami Bay. It devastated Tokyo, the port city ofYokohama,and the surrounding prefectures ofChiba,Kanagawa,andShizuoka,and caused widespread damage throughout theKantō region.[1]The shallow nature of the seabed on the north of the bay, and the funnelling effect oftsunamiandtyphoonwave energy, contributed to certain parts of the Shonan coast having suffered considerable damage, including the destruction of theKōtoku-intemple housing the Great Buddha, orDaibutsuduring themassive tsunami of 1498.[2]
Natural environment
[edit]A branch of the warmKuroshio Currentwarms the bay, allowing it to host marine organisms typical of more southerly regions and giving a mild climate to the land bordering it. The maximum depth of Sagami Bay is about 1500 meters.
Organisms from sub-arctic regions are advected into the bay by intrusions of the Oyashio Current resulting in very highbiodiversity.[3]It is the major study site for research programs at the University of Tokyo (ORI) and the Japan Agency for Marine-Earth Science and Technology (JAMSTEC).
In 2004, soil samples from Sagami Bay were found to containradioactive contaminationfrom theBikini Atollnuclear teststhat took place from 1946 to 1958.[4]
TheHikiji River,Sagami RiverandSakai Riverflow into the bay.
References
[edit]- ^Hammer, Joshua (2006).Yokohama Burning: the Deadly 1923 Earthquake and Fire that Helped Forge the Path to World War II.Free Press. p. 278.ISBN978-0743264655.
- ^Kamio, Kenji; Willson, Heather (2008).An English Guide to Kamakura's Temples and Shrines.Lục phong xuất bản. pp. 143, 144.ISBN978-4-8461-0811-3.
- ^CJO – Abstract – Biodiversity in midwater cnidarians and ctenophores: submersible-based results from deep-water bays in the Japan Sea and north-western Pacific
- ^SEPAArchived2004-08-05 at theWayback Machine
External links
[edit] Media related toSagami Bayat Wikimedia Commons}
Media related toSagami Bayat Wikimedia Commons}