Second Geneva Convention

TheSecond Geneva Conventionfor theAmeliorationof the Condition of Wounded, Sick and Shipwrecked Members of Armed Forces at Sea is one of the fourtreatiesof theGeneva Conventions.[1]The Geneva Convention for the Amelioration of the Condition of Wounded, Sick and Shipwrecked Members of Armed Forces at Sea was first adopted in 1949, replacing theHague Convention(X) of 1907.[2]It adapts the main protective regime of theFirst Geneva Conventionto combat at sea.[3]
Summary of provisions[edit]
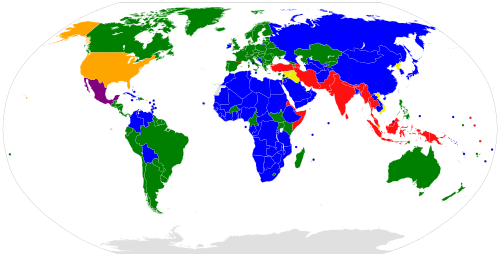
Parties to GC I–IV and P I–III | Parties to GC I–IV and P I–II |
Parties to GC I–IV and P I and III | Parties to GC I–IV and P I |
Parties to GC I–IV and P III | Parties to GC I–IV and no P |
Thetreatyis a lengthy document consisting of 63 articles. The most essential provisions of the treaty are:
- Articles 12 and 18 requires all parties to protect and care for the wounded, sick, andshipwrecked.
- Article 14 clarifies that although a warship cannot capture a hospital ship's medical staff, it can hold the wounded, sick, and shipwrecked asprisoners of war.
- Article 21 allows appeals to be made to neutral vessels to help collect and care for the wounded, sick, and shipwrecked. The neutral vessels cannot be captured.
- Articles 36 and 37 protect religious and medical personnel serving on a combat ship.
- Article 22 states thathospital shipscannot be used for any military purpose, and owing to their humanitarian mission, they cannot be attacked or captured.
For a detailed discussion of each article of the treaty, see the original text[4]and the commentary.[5]There are currently 196 countries party to the 1949Geneva Conventions,including this second treaty but also including the other three.[6]
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^"Treaties, States parties, and Commentaries - Geneva Convention (II) on Wounded, Sick and Shipwrecked of Armed Forces at Sea, 1949 - -".ihl-databases.icrc.org.Retrieved13 April2022.
- ^ICRC."Convention (II) for the Amelioration of the Condition of Wounded, Sick and Shipwrecked Members of Armed Forces at Sea. Geneva, 12 August 1949".Retrieved5 March2017.
The undersigned Plenipotentiaries of the Governments represented at the Diplomatic Conference held at Geneva from April 21 to August 12, 1949, for the purpose of revising the Xth Hague Convention of October 18, 1907 for the Adaptation to Maritime Warfare of the Principles of the Geneva Convention of 1906 [...]
- ^Fleck, Dietrich (2013).The Handbook of International Humanitarian Law.Oxford: Oxford University Press. p. 322.ISBN978-0-19-872928-0.
- ^"Convention (II) for the Amelioration of the Condition of Wounded, Sick and Shipwrecked Members of Armed Forces at Sea. Geneva, 12 August 1949".The American National Red Cross.Retrieved20 November2009.
- ^Pictet, Jean (1958).Geneva Conventions of 12 August 1949: Commentary.International Committee of the Red Cross.Retrieved20 November2009.
- ^"States party to the main treaties".The American National Red Cross.Retrieved5 December2009.
External links[edit]
- Final Act of the Second Peace Conference, The Hague,18 October 1907
- Geneva Conventions
- Treaties concluded in 1906
- Treaties concluded in 1949
- Treaties entered into force in 1950
- Treaties of the Kingdom of Afghanistan
- Treaties of the People's Socialist Republic of Albania
- Treaties of Algeria
- Treaties of Andorra
- Treaties of the People's Republic of Angola
- Treaties of Antigua and Barbuda
- Treaties of Argentina
- Treaties of Armenia
- Treaties of Australia
- Treaties of Austria
- Treaties of Azerbaijan
- Treaties of the Bahamas
- Treaties of Bahrain
- Treaties of Bangladesh
- Treaties of Barbados
- Treaties of the Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic
- Treaties of Belgium
- Treaties of Belize
- Treaties of the Republic of Dahomey
- Treaties of Bhutan
- Treaties of Bolivia
- Treaties of Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Treaties of Botswana
- Treaties of the Second Brazilian Republic
- Treaties of Brunei
- Treaties of the People's Republic of Bulgaria
- Treaties of Burkina Faso
- Treaties of Myanmar
- Treaties of Burundi
- Treaties of the Kingdom of Cambodia (1953–1970)
- Treaties of Cameroon
- Treaties of Canada
- Treaties of Cape Verde
- Treaties of the Central African Republic
- Treaties of Chad
- Treaties of Chile
- Treaties of the People's Republic of China
- Treaties of Colombia
- Treaties of the Comoros
- Treaties of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (1964–1971)
- Treaties of the Republic of the Congo
- Treaties of the Cook Islands
- Treaties of Costa Rica
- Treaties of Ivory Coast
- Treaties of Croatia
- Treaties of Cuba
- Treaties of Cyprus
- Treaties of the Czech Republic
- Treaties of Czechoslovakia
- Treaties of Denmark
- Treaties of Djibouti
- Treaties of Dominica
- Treaties of the Dominican Republic
- Treaties of East Timor
- Treaties of Ecuador
- Treaties of the Kingdom of Egypt
- Treaties of El Salvador
- Treaties of Equatorial Guinea
- Treaties of Eritrea
- Treaties of Estonia
- Treaties of the Ethiopian Empire
- Treaties of Fiji
- Treaties of Finland
- Treaties of the French Fourth Republic
- Treaties of Gabon
- Treaties of the Gambia
- Treaties of Georgia (country)
- Treaties of West Germany
- Treaties of East Germany
- Treaties of Ghana
- Treaties of the Kingdom of Greece
- Treaties of Grenada
- Treaties of Guatemala
- Treaties of Guinea
- Treaties of Guinea-Bissau
- Treaties of Guyana
- Treaties of Haiti
- Treaties of the Holy See
- Treaties of Honduras
- Treaties of the Hungarian People's Republic
- Treaties of Iceland
- Treaties of the Dominion of India
- Treaties of Indonesia
- Treaties of Pahlavi Iran
- Treaties of the Kingdom of Iraq
- Treaties of Ireland
- Treaties of Israel
- Treaties of Italy
- Treaties of Jamaica
- Treaties of Japan
- Treaties of Jordan
- Treaties of Kazakhstan
- Treaties of Kenya
- Treaties of Kiribati
- Treaties of North Korea
- Treaties of South Korea
- Treaties of Kuwait
- Treaties of Kyrgyzstan
- Treaties of the Kingdom of Laos
- Treaties of Latvia
- Treaties of Lebanon
- Treaties of Lesotho
- Treaties of Liberia
- Treaties of the Kingdom of Libya
- Treaties of Liechtenstein
- Treaties of Lithuania
- Treaties of Luxembourg
- Treaties of North Macedonia
- Treaties of Madagascar
- Treaties of Malawi
- Treaties of the Federation of Malaya
- Treaties of the Maldives
- Treaties of Mali
- Treaties of Malta
- Treaties of the Marshall Islands
- Treaties of Mauritania
- Treaties of Mauritius
- Treaties of Mexico
- Treaties of the Federated States of Micronesia
- Treaties of Moldova
- Treaties of Monaco
- Treaties of the Mongolian People's Republic
- Treaties of Montenegro
- Treaties of Morocco
- Treaties of the People's Republic of Mozambique
- Treaties of Namibia
- Treaties of Nauru
- Treaties of Nepal
- Treaties of the Netherlands
- Treaties of New Zealand
- Treaties of Nicaragua
- Treaties of Niger
- Treaties of Nigeria
- Treaties of Norway
- Treaties of Oman
- Treaties of the Dominion of Pakistan
- Treaties of Palau
- Treaties of the State of Palestine
- Treaties of Panama
- Treaties of Papua New Guinea
- Treaties of Paraguay
- Treaties of Peru
- Treaties of the Philippines
- Treaties of the Polish People's Republic
- Treaties of the Estado Novo (Portugal)
- Treaties of Qatar
- Treaties of the Socialist Republic of Romania
- Treaties of Rwanda
- Treaties of Saint Kitts and Nevis
- Treaties of Saint Lucia
- Treaties of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
- Treaties of Samoa
- Treaties of San Marino
- Treaties of São Tomé and Príncipe
- Treaties of Saudi Arabia
- Treaties of Senegal
- Treaties of Serbia and Montenegro
- Treaties of Seychelles
- Treaties of Sierra Leone
- Treaties of Singapore
- Treaties of Slovakia
- Treaties of Slovenia
- Treaties of the Solomon Islands
- Treaties of the Somali Republic
- Treaties of the Union of South Africa
- Treaties of South Sudan
- Treaties of the Soviet Union
- Treaties of Francoist Spain
- Treaties of the Dominion of Ceylon
- Treaties of the Republic of the Sudan (1956–1969)
- Treaties of Suriname
- Treaties of Eswatini
- Treaties of Sweden
- Treaties of Switzerland
- Treaties of the Syrian Republic (1930–1963)
- Treaties of Tajikistan
- Treaties of Tanganyika
- Treaties of Thailand
- Treaties of Togo
- Treaties of Tonga
- Treaties of Trinidad and Tobago
- Treaties of Tunisia
- Treaties of Turkey
- Treaties of Turkmenistan
- Treaties of Tuvalu
- Treaties of Uganda
- Treaties of the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic
- Treaties of the United Arab Emirates
- Treaties of the United Kingdom
- Treaties of the United States
- Treaties of Uruguay
- Treaties of Uzbekistan
- Treaties of Vanuatu
- Treaties of Venezuela
- Treaties of North Vietnam
- Treaties of the Yemen Arab Republic
- Treaties of Yugoslavia
- Treaties of Zambia
- Treaties of Zimbabwe
- Treaties of South Yemen
- Treaties of South Vietnam
- Treaties of the Sultanate of Zanzibar
- Treaties extended to Greenland
- Treaties extended to the Faroe Islands
- Treaties extended to Niue
- Treaties extended to Aruba
- Treaties extended to the Netherlands Antilles
- Treaties extended to the Territory of Papua and New Guinea
- Treaties extended to the Belgian Congo
- Treaties extended to Ruanda-Urundi
- Treaties extended to French Somaliland
- Treaties extended to Surinam (Dutch colony)
- Treaties extended to Portuguese Macau
- Treaties extended to the West Indies Federation
- Treaties extended to the Colony of the Bahamas
- Treaties extended to Bahrain (protectorate)
- Treaties extended to Bermuda
- Treaties extended to the British Antarctic Territory
- Treaties extended to the Falkland Islands
- Treaties extended to the Colony of Fiji
- Treaties extended to the Gambia Colony and Protectorate
- Treaties extended to Gibraltar
- Treaties extended to British Guiana
- Treaties extended to British Hong Kong
- Treaties extended to the Gilbert and Ellice Islands
- Treaties extended to the Sheikhdom of Kuwait
- Treaties extended to Basutoland
- Treaties extended to the Crown Colony of Malta
- Treaties extended to British Mauritius
- Treaties extended to the Colony and Protectorate of Nigeria
- Treaties extended to Qatar (protectorate)
- Treaties extended to Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha
- Treaties extended to the Colony of Sierra Leone
- Treaties extended to the British Solomon Islands
- Treaties extended to South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands
- Treaties extended to Tanganyika (territory)
- Treaties extended to the Kingdom of Tonga (1900–1970)
- Treaties extended to the Trucial States
- Treaties extended to West Berlin
