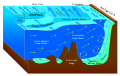
Seiche
Aseiche(/seɪʃ/SAYSH) is astanding wavein an enclosed or partially enclosedbody of water.Seiches and seiche-related phenomena have been observed onlakes,reservoirs,swimming pools,bays,harbors,caves,andseas.The key requirement for formation of a seiche is that the body of water be at least partially bounded, allowing the formation of the standing wave.
The term was promoted by the SwisshydrologistFrançois-Alphonse Forelin 1890, who was the first to make scientific observations of the effect inLake Geneva.[1]The word had apparently long been used in the region to describe oscillations in alpine lakes. According to Wilson (1972),[2][3]thisSwiss Frenchdialect word comes from the Latin wordsiccusmeaning "dry", i.e., as the water recedes, the beach dries. The French wordsecorsèche(dry) descends from the Latin.
Seiches in harbours can be caused bylong-periodorinfragravity waves,which are due to subharmonic nonlinear wave interaction with thewind waves,having periods longer than the accompanying wind-generated waves.[4]
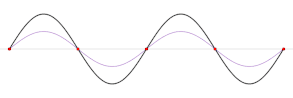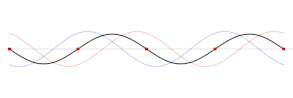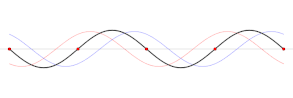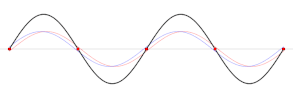
Causes and nature
[edit]Seiches are often imperceptible to the naked eye, and observers in boats on the surface may not notice that a seiche is occurring due to the extremely long periods.
The effect is caused by resonances in a body of water that has been disturbed by one or more factors, most often meteorological effects (wind and atmospheric pressure variations), seismic activity, ortsunamis.[5]Gravityalways seeks to restore the horizontal surface of a body of liquid water, as this represents the configuration in which the water is inhydrostatic equilibrium.
Vertical harmonic motion results, producing an impulse that travels the length of the basin at a velocity that depends on the depth of the water. The impulse is reflected back from the end of the basin, generating interference. Repeated reflections produce standing waves with one or more nodes, or points, that experience no vertical motion. The frequency of the oscillation is determined by the size of the basin, its depth and contours, and the water temperature.
The longest naturalperiodof a seiche is the period associated with the fundamental resonance for the body of water—corresponding to the longest standing wave. For a surface seiche in an enclosed rectangular body of water this can be estimated using Merian's formula:[6][7]
whereTis the longest natural period,Landhare the length and average depth of the body of water, andgtheacceleration of gravity.[8]
Higher-order harmonics are also observed. The period of the second harmonic will be half the natural period, the period of the third harmonic will be a third of the natural period, and so forth.
Occurrence
[edit]Seiches have been observed on both lakes and seas. The key requirement is that the body of water be partially constrained to allow formation of standing waves. Regularity of geometry is not required; even harbours with exceedingly irregular shapes are routinely observed to oscillate with very stable frequencies.
Lake seiches
[edit]Low rhythmic seiches are almost always present on larger lakes. They are usually unnoticeable among the common wave patterns, except during periods of unusual calm.Harbours,bays, andestuariesare often prone to small seiches with amplitudes of a few centimetres and periods of a few minutes.
The original studies inLake GenevabyFrançois-Alphonse Forelfound the longitudinal period to have a 73-minute cycle, and the transversal seiche to have a period of around 10 minutes.[9]Another lake well known for its regular seiches is New Zealand'sLake Wakatipu,which varies its surface height atQueenstownby 20 centimetres in a 27-minute cycle. Seiches can also form in semi-enclosed seas; theNorth Seaoften experiences a lengthwise seiche with a period of about 36 hours.

TheNational Weather Serviceissues low water advisories for portions of the Great Lakes when seiches of 2 feet or greater are likely to occur.[10]Lake Erieis particularly prone to wind-caused seiches because of its shallowness and its elongation on a northeast–southwest axis, which frequently matches the direction of prevailing winds and therefore maximises thefetchof those winds. These can lead to extreme seiches of up to 5 metres (16 ft) between the ends of the lake.
The effect is similar to astorm surgelike that caused by hurricanes along ocean coasts, but the seiche effect can cause oscillation back and forth across the lake for some time. In 1954, the remnants ofHurricane Hazelpiled up water along the northwesternLake Ontarioshoreline nearToronto,causing extensive flooding, and established a seiche that subsequently caused flooding along the south shore.
Lake seiches can occur very quickly: on July 13, 1995, a large seiche onLake Superiorcaused the water level to fall and then rise again by three feet (one metre) within fifteen minutes, leaving some boats hanging from the docks on their mooring lines when the water retreated.[11]The same storm system that caused the 1995 seiche on Lake Superior produced a similar effect inLake Huron,in which the water level atPort Huronchanged by 6 feet (1.8 m) over two hours.[12]OnLake Michigan,eight fishermen were swept away from piers at Montrose and North Avenue Beaches and drowned when a 10-foot (3.0 m) seiche hit theChicagowaterfront on June 26, 1954.[13]
Lakes in seismically active areas, such asLake TahoeinCalifornia/Nevada,are significantly at risk from seiches. Geological evidence indicates that the shores of Lake Tahoe may have been hit by seiches and tsunamis as much as 10 metres (33 ft) high in prehistoric times, and local researchers have called for the risk to be factored into emergency plans for the region.[14]
Earthquake-generated seiches can be observed thousands of miles away from the epicentre of a quake.Swimming poolsare especially prone to seiches caused by earthquakes, as the ground tremors often match the resonant frequencies of small bodies of water. The 1994Northridge earthquakeinCaliforniacaused swimming pools to overflow across southern California. The massiveGood Friday earthquakethat hitAlaskain 1964 caused seiches in swimming pools as far away asPuerto Rico.[15]Theearthquake that hit Lisbon, Portugalin 1755 also caused seiches 1,300 miles (2,100 km) farther north in Loch Lomond, Loch Long, Loch Katrine and Loch Ness inScotland,[16]and incanalsinSweden.The2004 Indian Ocean earthquakecaused seiches in standing water bodies in many Indian states as well as inBangladesh,Nepal,and northernThailand.[17]Seiches were again observed inUttar Pradesh,Tamil NaduandWest BengalinIndiaas well as in many locations inBangladeshduring the2005 Kashmir earthquake.[18]
The1950 Assam–Tibet earthquakeis known to have generated seiches as far away asNorwayand southernEngland.Other earthquakes in the Indian sub-continent known to have generated seiches include the 1803 Kumaon-Barahat,1819 Allah Bund,1842 Central Bengal, 1905 Kangra, 1930 Dhubri, 1934 Nepal-Bihar, 2001 Bhuj, 2005 Nias, 2005 Teresa Island earthquakes. TheFebruary 27, 2010 Chile earthquakeproduced a seiche onLake Pontchartrain,Louisiana,with a height of around 0.5 feet. The2010 Sierra El Mayor earthquakeproduced large seiches that quickly became an internet phenomenon.[19]
Seiches up to at least 1.8 m (6 feet) were observed inSognefjorden,Norway,during the2011 Tōhoku earthquakein Japan.[20][21]
Sea and bay seiches
[edit]Seiches have been observed in seas such as theAdriatic Seaand theBaltic Sea.This results in the flooding ofVeniceandSaint Petersburg,respectively, as both cities are constructed on former marshland. In St. Petersburg, seiche-induced flooding is common along theNeva Riverin the autumn. The seiche is driven by a low-pressure region in theNorth Atlanticmoving onshore, giving rise tocycloniclows on theBaltic Sea.The low pressure of the cyclone draws greater-than-normal quantities of water into the virtually landlocked Baltic. As the cyclone continues inland, long, low-frequency seiche waves with wavelengths up to several hundred kilometres are established in the Baltic. When the waves reach the narrow and shallow Neva Bay, they become much higher—ultimately flooding the Neva embankments.[22]Similar phenomena are observed at Venice, resulting in theMOSE Project,a system of 79 mobile barriers designed to protect the three entrances to theVenetian Lagoon.
In Japan, seiches have been observed inNagasaki Bay,most often in the spring. During a seiche event on 31 March 1979, a water-level displacement of 2.78 metres (9.1 ft) was recorded at Nagasaki tide station; the maximum displacement in the whole bay is thought to have reached as much as 4.70 metres (15.4 ft). Seiches in WesternKyushu—including Nagasaki Bay—are often induced by a low in the atmospheric pressure passing South of Kyushu island.[23]Seiches in Nagasaki Bay have aperiodof about 30 to 40 minutes. Locally, seiches have caused floods, destroyed port facilities and damaged the fishery: hence the local word for seiche, あびき(abiki),from võng dẫn き(amibiki),meaning 'the dragging-away of a fishing net'.
On occasion,tsunamiscan produce seiches as a result of local geographic peculiarities. For instance, the tsunami that hitHawaiiin 1946 had a fifteen-minute interval between wave fronts. The natural resonant period ofHilo Bayis about thirty minutes. That meant that every second wave was in phase with the bay, creating a seiche. As a result, Hilo suffered worse damage than any other place in Hawaii, with the combined tsunami and seiche reaching a height of 26 feet (7.9 m) along the Bayfront, killing 96 people in the city alone. Seiche waves may continue for several days after a tsunami.
Tide-generated internal solitary waves (solitons) can excite coastal seiches at the following locations:Magueyes Islandin Puerto Rico,[24][25][26] Puerto Princesain Palawan Island,[27] Trincomalee Bayin Sri Lanka,[28][29] and in theBay of Fundyin eastern Canada, where seiches cause some of the highest recorded tidal fluctuations in the world.[30] A dynamical mechanism exists for the generation of coastal seiches by deep-sea internal waves. These waves can generate a sufficient current at the shelf break to excite coastal seiches.[31]

Underwater (internal) waves
[edit]Seiches are also observed beneath the surface of constrained bodies of water, acting along thethermocline.[32]
In analogy with theMerian formula,the expected period of the internal wave can be expressed as:[33]
- with
whereTis the naturalperiod,Lis the length of the water body,the average thicknesses of the two layers separated bystratification(e.g.epilimnionandhypolimnion),thedensitiesof these two same layers andgtheacceleration of gravity.
As thethermoclinemoves up and down a sloping lake bed, it creates a 'swash zone', where temperatures can vary rapidly,[34]potentially affecting fish habitat. As the thermocline rises up a sloping lake bed, it can also causebenthicturbulence by convective overturning, whereas the falling thermocline experiences greater stratification and low turbulence at the lake bed.[35][36]Internal waves can also degenerate into non-linear internal waves on sloping lake-beds.[37]When such non-linear waves break on the lake bed, they can be an important source of turbulence and have the potential for sediment resuspension[38]
Cave seiches
[edit]On September 19, 2022, a seiche reaching 4 feet (1.2 metres) occurred atDevils HoleatDeath Valley National Parkin the U.S. after a7.6-magnitude earthquakehit westernMexico,about 1,500 miles (2,400 kilometres) away. Seiches were also observed in the cave after powerful earthquakes in 2012, 2018 and 2019.[39]
Engineering for seiche protection
[edit]This sectionneeds expansion.You can help byadding to it.(June 2008) |
Engineers consider seiche phenomena in the design of flood protection works (e.g.,Saint Petersburg Dam),reservoirsand dams (e.g.,Grand Coulee Dam), potable water storage basins, harbours, and even spent nuclear fuel storage basins.
See also
[edit]- Clapotis– Non-breaking standing wave pattern
- Earthquake engineering– Study of earthquake-resistant structures
- Severe weather terminology (United States)– Terminology used by the National Weather Service to describe severe weather in the US
- Severe weather terminology (Canada)– Severe weather-related terminology used by the Meteorological Service of Canada
- Tsunamis in lakes
- Villa Epecuén– Tourist village in Argentina
- Vajont Dam,Disused gravity arch dam in Italy, destroyed by a seiche in 1963
Notes
[edit]- ^Darwin, G. H.(1898).The Tides and Kindred Phenomena in the Solar System.London: John Murray. pp. 21–31.
- ^Rabinovich, Alexander B. (2018). "Seiches and Harbor Oscillations".Handbook of Coastal and Ocean Engineering.World Scientific. pp. 243–286.doi:10.1142/9789813204027_0011.ISBN978-981-320-401-0.
- ^Wilson, Basil W. (1972).Seiches.Advances in Hydroscience. Vol. 8. Elsevier. pp. 1–94.doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-021808-0.50006-1.ISBN978-0-12-021808-0.
- ^Munk, Walter H.(1950).Origin and generation of waves.1st International Conference on Coastal Engineering, Long Beach, California. Council on Wave Research,American Society of Civil Engineers.doi:10.9753/icce.v1.1.ISSN2156-1028.Archivedfrom the original on 2017-01-11.Retrieved2017-04-19.
- ^Tsunamis are normally associated with earthquakes, but landslides, volcanic eruptions and meteorite impacts all have the potential to generate a tsunami.
- ^Proudman, J.(1953).Dynamical oceanography.London: Methuen. §117 (p. 225).OCLC223124129.
- ^Merian, J. R. (1828).Ueber die Bewegung tropfbarer Flüssigkeiten in Gefässen[On the motion of drippable liquids in containers] (thesis) (in German). Basel: Schweighauser.OCLC46229431.
- ^As an example, the period for a seiche wave in a body of water 10 meters deep and 5 kilometers long would be 1000 seconds or about 17 minutes, while a body about 300 km long (such as theGulf of Finland) and somewhat deeper has a period closer to 12 hours.
- ^Lemmin, Ulrich (2012), "Surface Seiches", in Bengtsson, Lars; Herschy, Reginald W.; Fairbridge, Rhodes W. (eds.),Encyclopedia of Lakes and Reservoirs,Encyclopedia of Earth Sciences Series, Springer Netherlands, pp. 751–753,doi:10.1007/978-1-4020-4410-6_226,ISBN978-1-4020-4410-6
- ^Pierce, T. (July 5, 2006)."Marine and Coastal Services Abbreviations and Definitions"(PDF).National Weather Service,Office of Climate, Water, and Weather Services. Archived fromthe original(PDF)on May 17, 2008.RetrievedApril 19,2017.
- ^Korgen, Ben (February 2000)."Bonanza for Lake Superior: Seiches Do More Than Move Water".seagrant.umn.edu.University of Minnesota Duluth.Archived fromthe originalon 2007-12-27.
- ^"Lake Huron Storm Surge July 13, 1995".NOAA. Archived fromthe originalon 2008-09-16.Retrieved2009-03-13.
- ^"Huge Lake Wave Hits Chicago; Four Drowned, Ten Are Missing".The New York Times.Vol. 103, no. 35218. 27 June 1954.Archivedfrom the original on 2 October 2021.Retrieved2 October2021.
- ^Brown, Kathryn (10 June 2000)."Tsunami! At Lake Tahoe?".Science News.157(24): 378–380.doi:10.2307/4012358.JSTOR4012358.
- ^"Seiche".www.soest.hawaii.edu.Archivedfrom the original on 2019-01-26.Retrieved2019-03-12.
- ^"Seismic Seiches".USGS Earthquake Hazards Program.Abridged from Earthquake Information Bulletin, January–February 1976, Volume 8, Number 1.Archivedfrom the original on 20 April 2017.Retrieved19 April2017.
- ^In fact, "one person drowned in a pond as a result of a seiche in Nadia, West Bengal"."26 December 2004, M9.1" Boxing Day "Earthquake & Tsunami/Sumatra-Andaman Earthquake/Indian Ocean Tsunami".Amateur Seismic Centre.Pune. 22 Feb 2008.Archivedfrom the original on 21 January 2007.Retrieved19 April2017.
- ^"M7.6 Kashmir-Kohistan Earthquake, 2005".Amateur Seismic Centre.Pune. 31 Oct 2008.Archivedfrom the original on 6 June 2017.Retrieved19 April2017.
- ^"Arizona Geology: Video of seiche in Devils Hole pupfish pond. (Posted: April 27, 2010)".2010-04-27.Archivedfrom the original on 2014-12-19.Retrieved17 October2014.
- ^Fjorden svinga av skjelvet(tr. "The fjord swayed from the earthquake")Archived2011-03-18 at theWayback MachineRetrieved on 2011-03-17.
- ^Johnson, Scott K. (30 June 2013)."Japanese earthquake literally made waves in Norway".Ars Technica.Archivedfrom the original on 30 July 2022.Retrieved18 April2019.
- ^This behaves in a fashion similar to atidal borewhere incoming tides are funneled into a shallow, narrowing river via a broad bay. The funnel-like shape increases the height of the tide above normal, and the flood appears as a relatively rapid increase in the water level.
- ^Hibiya, Toshiyuki; Kinjiro Kajiura (1982)."Origin of theAbikiPhenomenon (a kind of Seiche) in Nagasaki Bay "(PDF).Journal of Oceanographical Society of Japan.38(3): 172–182.doi:10.1007/BF02110288.S2CID198197231.Archived fromthe original(PDF)on 2011-05-27.Retrieved2009-02-26.
- ^ Giese, Graham S.; R. B. Hollander; J. E. Fancher; B. S. Giese (1982). "Evidence of coastal Seiche excitation by tide-generated internal solitary waves".Geophysical Research Letters.9(12): 1305–1308.Bibcode:1982GeoRL...9.1305G.doi:10.1029/GL009i012p01305.
- ^ Giese, Graham S.; David C. Chapman; Peter G. Black; John A. Fornshell (1990)."Causation of Large-Amplitude Coastal Seiches on the Caribbean Coast of Puerto Rico".J. Phys. Oceanogr.20(9): 1449–1458.Bibcode:1990JPO....20.1449G.doi:10.1175/1520-0485(1990)020<1449:COLACS>2.0.CO;2.
- ^Alfonso-Sosa, Edwin (September 2012)."Estimated Speed of Aves Ridge Solitons Packets by Analysis of Sequential Images from the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer(MODIS)"(PDF):1–11.doi:10.13140/RG.2.2.14561.45929.Archivedfrom the original on 2022-07-30.Retrieved2022-07-30.
{{cite journal}}:Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Giese, Graham S.; David C. Chapman; Margaret Goud Collins; Rolu Encarnacion; Gil Jacinto (1998)."The Coupling between Harbor Seiches at Palawan Island and Sulu Sea Internal Solitons".J. Phys. Oceanogr.28(12): 2418–2426.Bibcode:1998JPO....28.2418G.doi:10.1175/1520-0485(1998)028<2418:TCBHSA>2.0.CO;2.S2CID55974279.
- ^ Wijeratne, E. M. S.; P. L. Woodworth; D. T. Pugh (2010)."Meteorological and internal wave forcing of seiches along the Sri Lanka coast".Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans.115(C3): C03014.Bibcode:2010JGRC..115.3014W.doi:10.1029/2009JC005673.
- ^Alfonso-Sosa, Edwin (April 2014)."Tide-Generated Internal Solitons in Bay of Bengal Excite Coastal Seiches in Trincomalee Bay"(PDF):1–16.doi:10.13140/RG.2.2.32105.70242.Archivedfrom the original on 2022-07-30.Retrieved2022-07-30.
{{cite journal}}:Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^Canada, Parks Canada Agency, Government of (2017-03-28)."index".www.pc.gc.ca.Archivedfrom the original on 2016-03-04.Retrieved9 April2018.
{{cite web}}:CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Chapman, David C.; Graham S. Giese (1990)."A Model for the Generation of Coastal Seiches by Deep-Sea Internal Waves".J. Phys. Oceanogr.20(9): 1459–1467.Bibcode:1990JPO....20.1459C.doi:10.1175/1520-0485(1990)020<1459:AMFTGO>2.0.CO;2.
- ^Thethermoclineis the boundary between colder lower layer (hypolimnion) and warmer upper layer (epilimnion).
- ^Mortimer, C. H. (1974). Lake hydrodynamics. Mitt. Internat. Verein. Limnol. 20, 124–197.
- ^Cossu, R.; Ridgway, M.S.; Li, J.Z.; Chowdhury, M.R.; Wells, M.G. (2017)."Wash-zone dynamics of the thermocline in Lake Simcoe, Ontario".Journal of Great Lakes Research.43(4): 689–699.Bibcode:2017JGLR...43..689C.doi:10.1016/j.jglr.2017.05.002.ISSN0380-1330.
- ^Cossu, Remo; Wells, Mathew G. (2013-03-05)."The Interaction of Large Amplitude Internal Seiches with a Shallow Sloping Lakebed: Observations of Benthic Turbulence in Lake Simcoe, Ontario, Canada".PLOS ONE.8(3): e57444.Bibcode:2013PLoSO...857444C.doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0057444.ISSN1932-6203.PMC3589419.PMID23472085.
- ^Bouffard, Damien; Wüest, Alfred (2019-01-05)."Convection in Lakes"(PDF).Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics.51(1): 189–215.Bibcode:2019AnRFM..51..189B.doi:10.1146/annurev-fluid-010518-040506.ISSN0066-4189.S2CID125132769.
- ^Boegman, L.; Ivey, G. N.; Imberger, J. (September 2005)."The degeneration of internal waves in lakes with sloping topography"(PDF).Limnology and Oceanography.50(5): 1620–1637.Bibcode:2005LimOc..50.1620B.doi:10.4319/lo.2005.50.5.1620.ISSN0024-3590.S2CID55292327.Archived(PDF)from the original on 2019-04-29.Retrieved2020-09-06.
- ^Boegman, Leon; Stastna, Marek (2019-01-05)."Sediment Resuspension and Transport by Internal Solitary Waves".Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics.51(1): 129–154.Bibcode:2019AnRFM..51..129B.doi:10.1146/annurev-fluid-122316-045049.ISSN0066-4189.S2CID126363796.
- ^"Mexico earthquake caused waves at California's Death Valley".BNO News.September 21, 2022.RetrievedSeptember 22,2022.
Further reading
[edit]- Jackson, J. R. (1833). "On the Seiches of Lakes".Journal of the Royal Geographical Society of London.3:271–275.doi:10.2307/1797612.JSTOR1797612.
External links
[edit]- .Encyclopædia Britannica.Vol. 24 (11th ed.). 1911.
General
- What is aseiche?
- Seiche. Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved January 24, 2004, from Encyclopædia Britannica Premium Service.
- Seiche calculator
- Bonanza for Lake Superior: Seiches Do More Than Move WaterArchived2011-09-28 at theWayback Machine
- Great Lakes Storms Photo Gallery Seiches, Storm Surges, and Edge WavesArchived2009-08-25 at theWayback MachinefromNOAA
- Shelf Response for an identical pair of incident KdV solitons
Relationship to aquatic "monsters"